Design optimization of a sensitivity-enhanced tilt sensor based on femtosecond fiber bragg grating
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2024-0034
-
摘要:
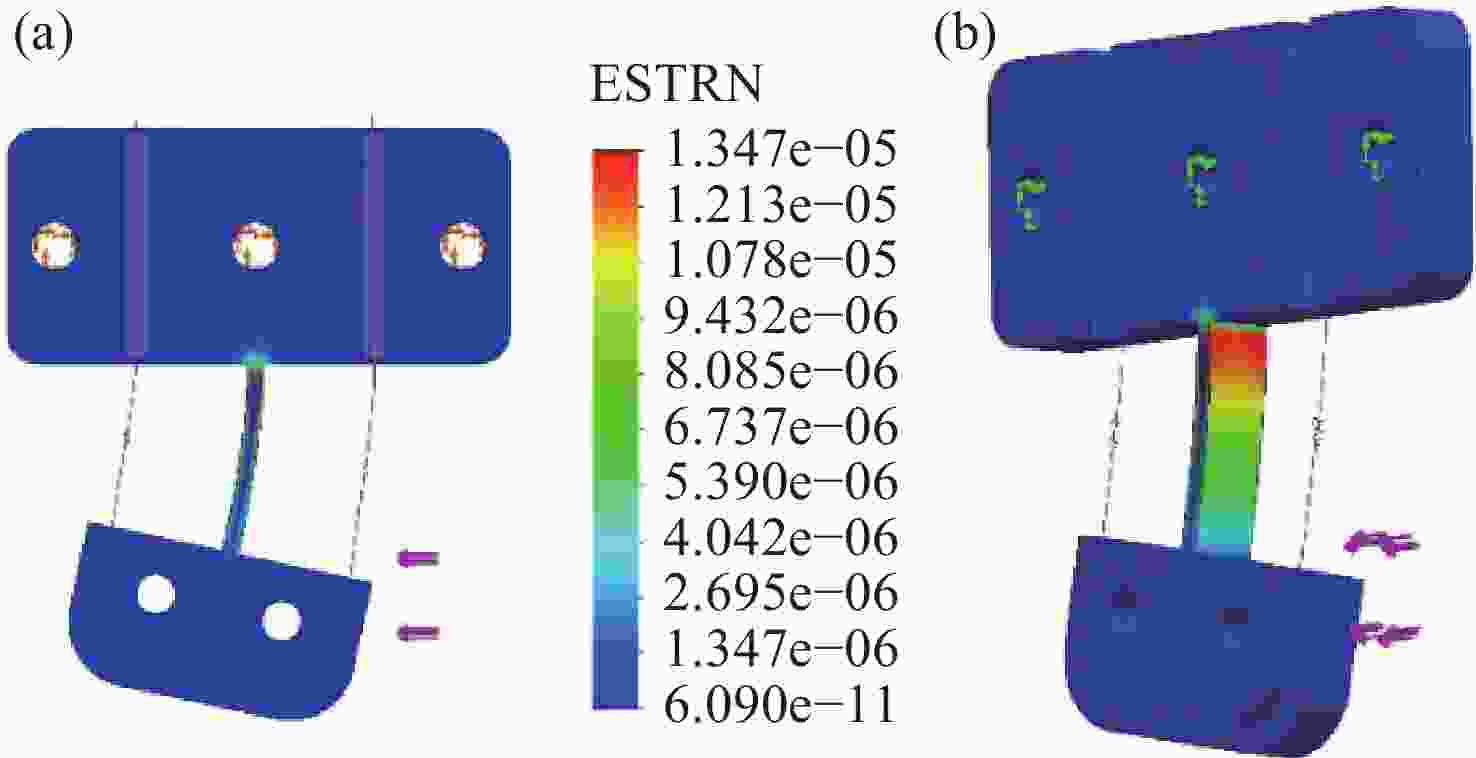
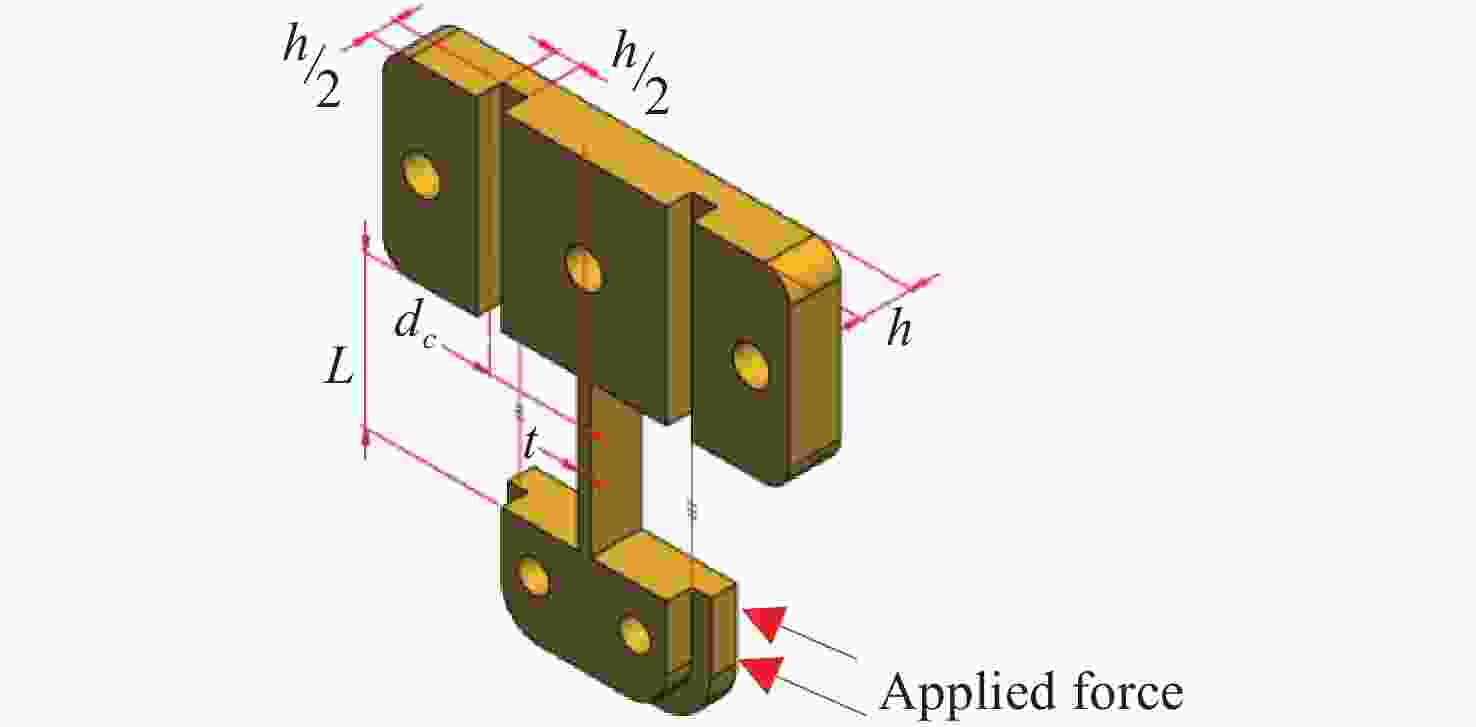
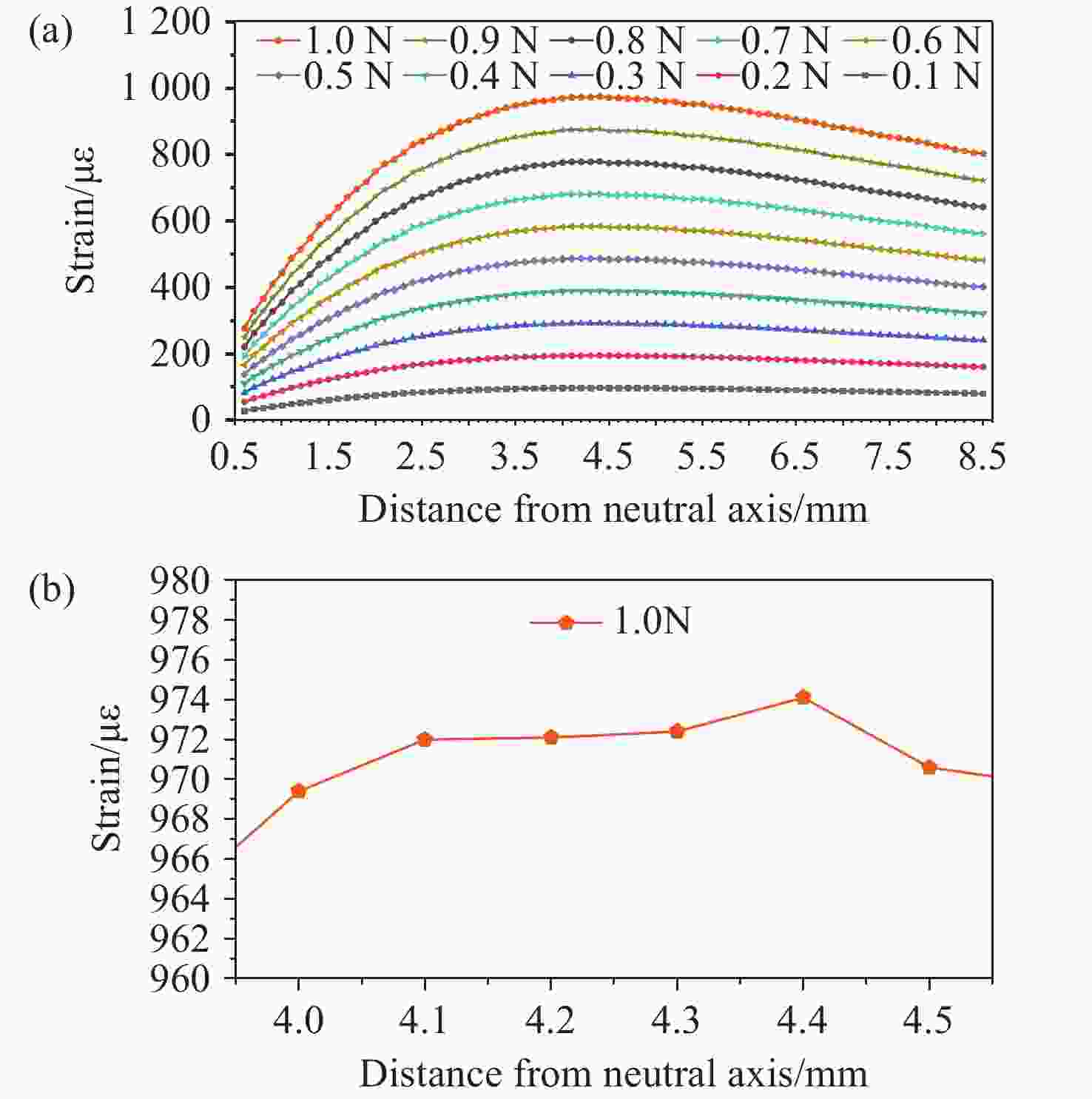
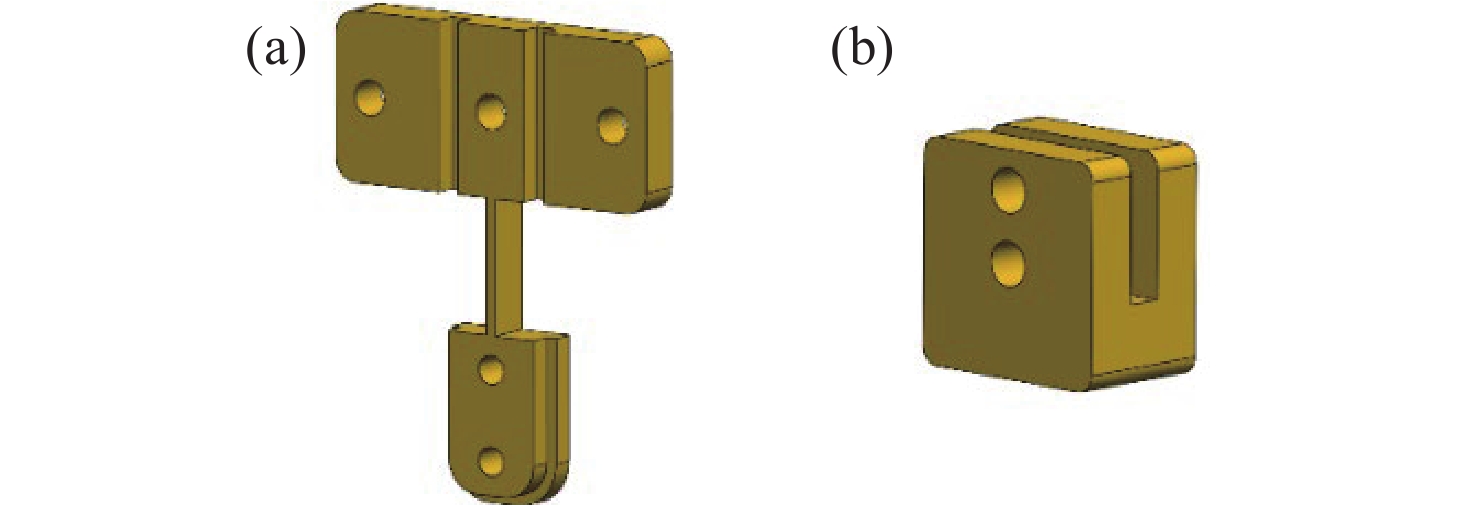
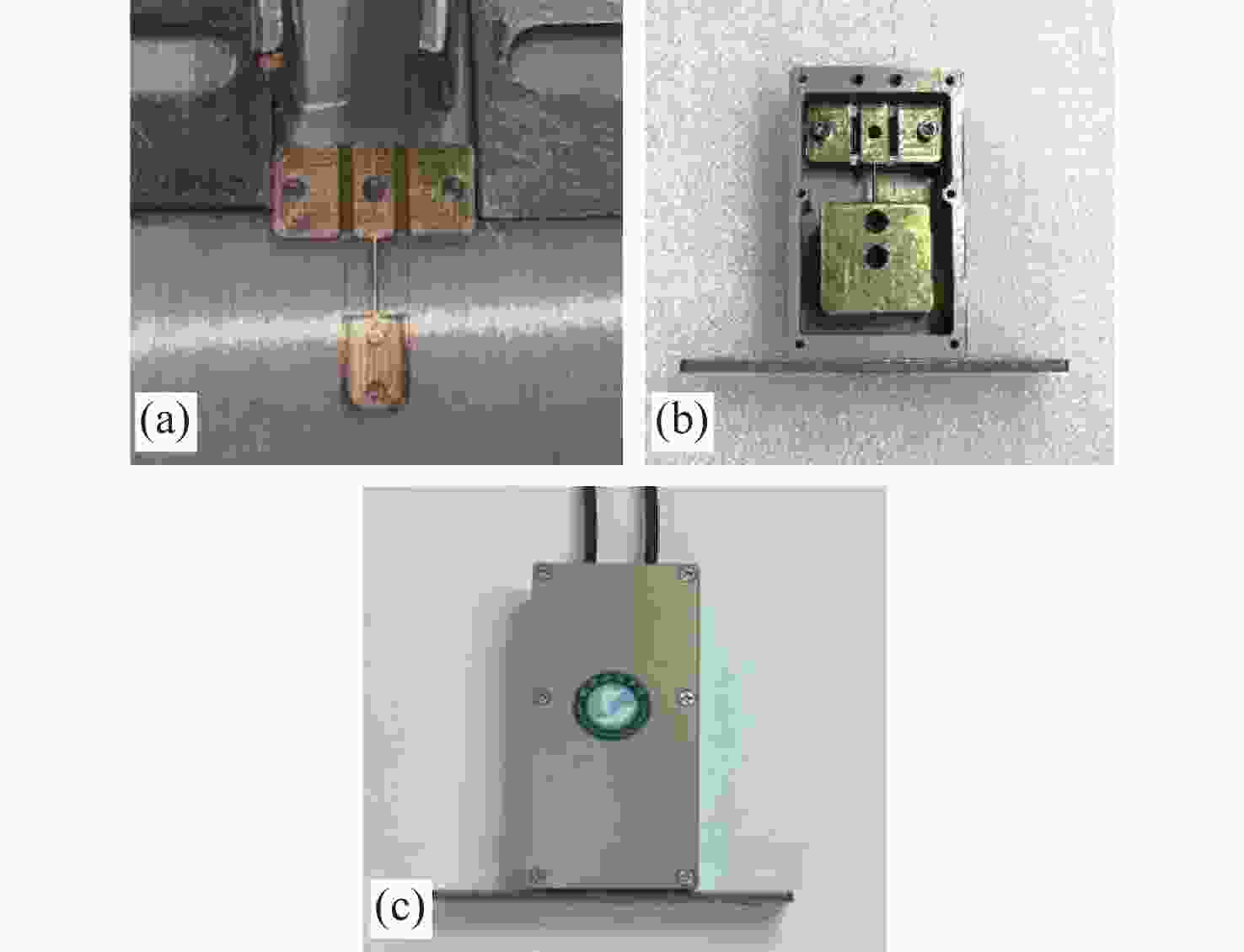
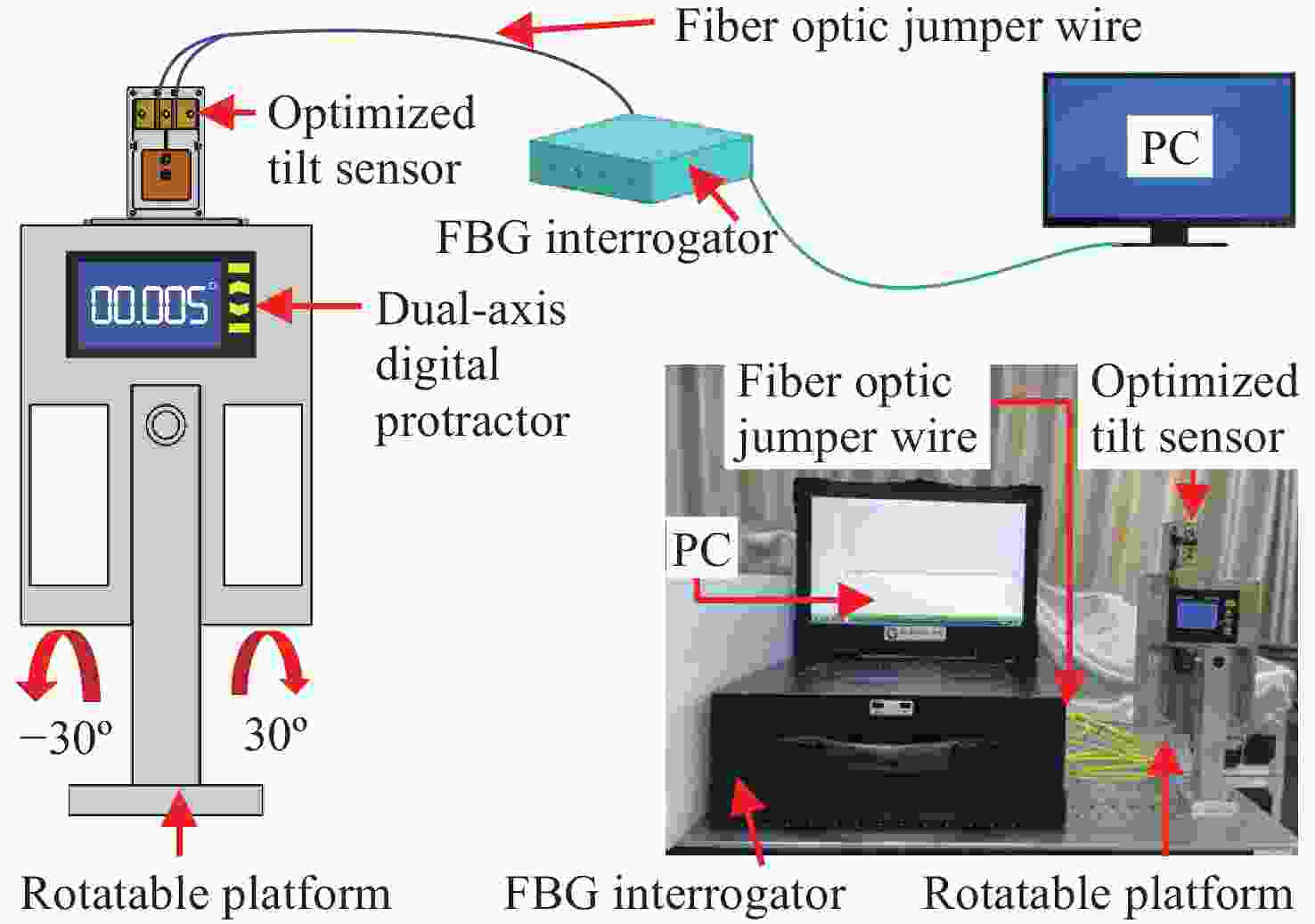
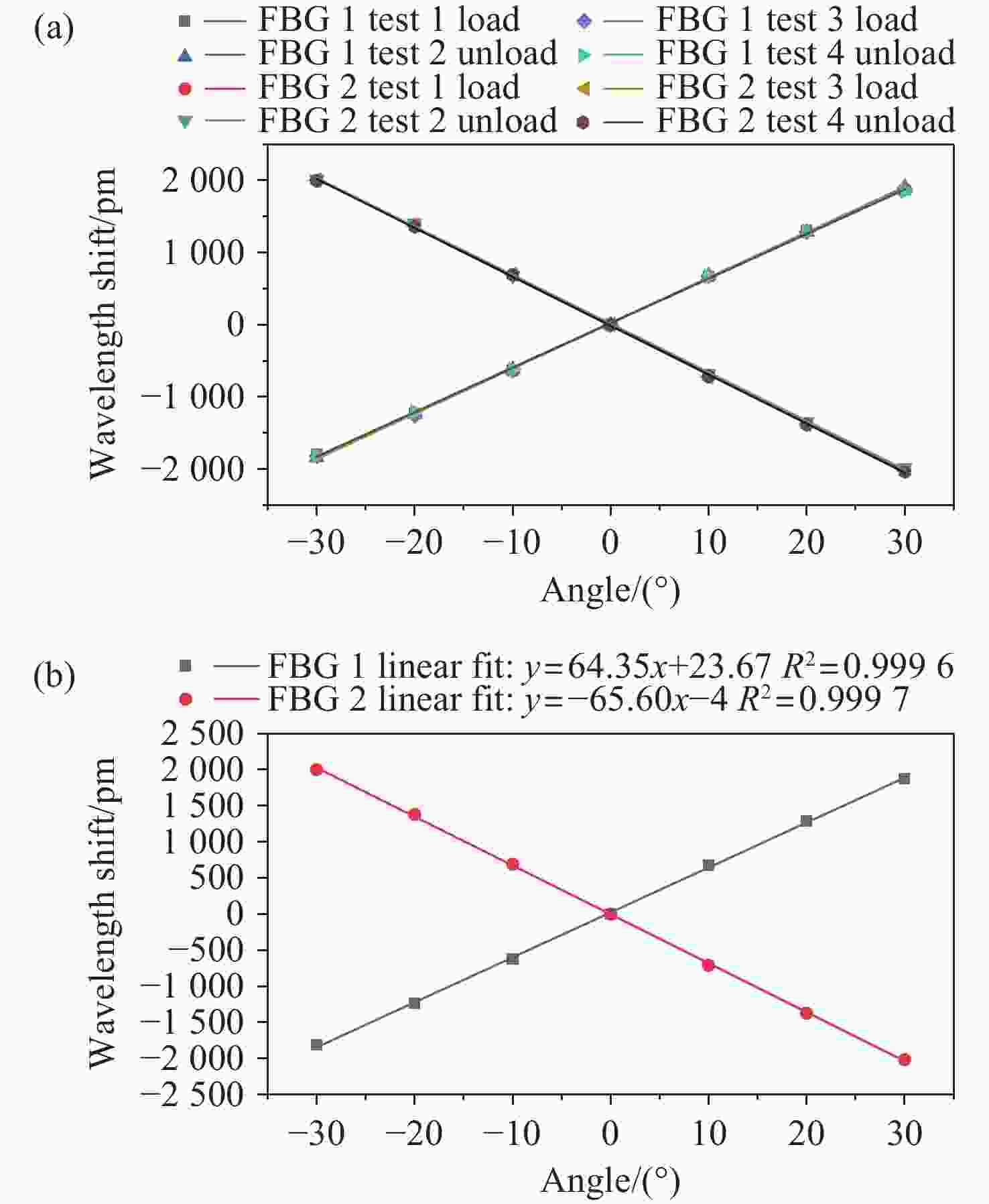
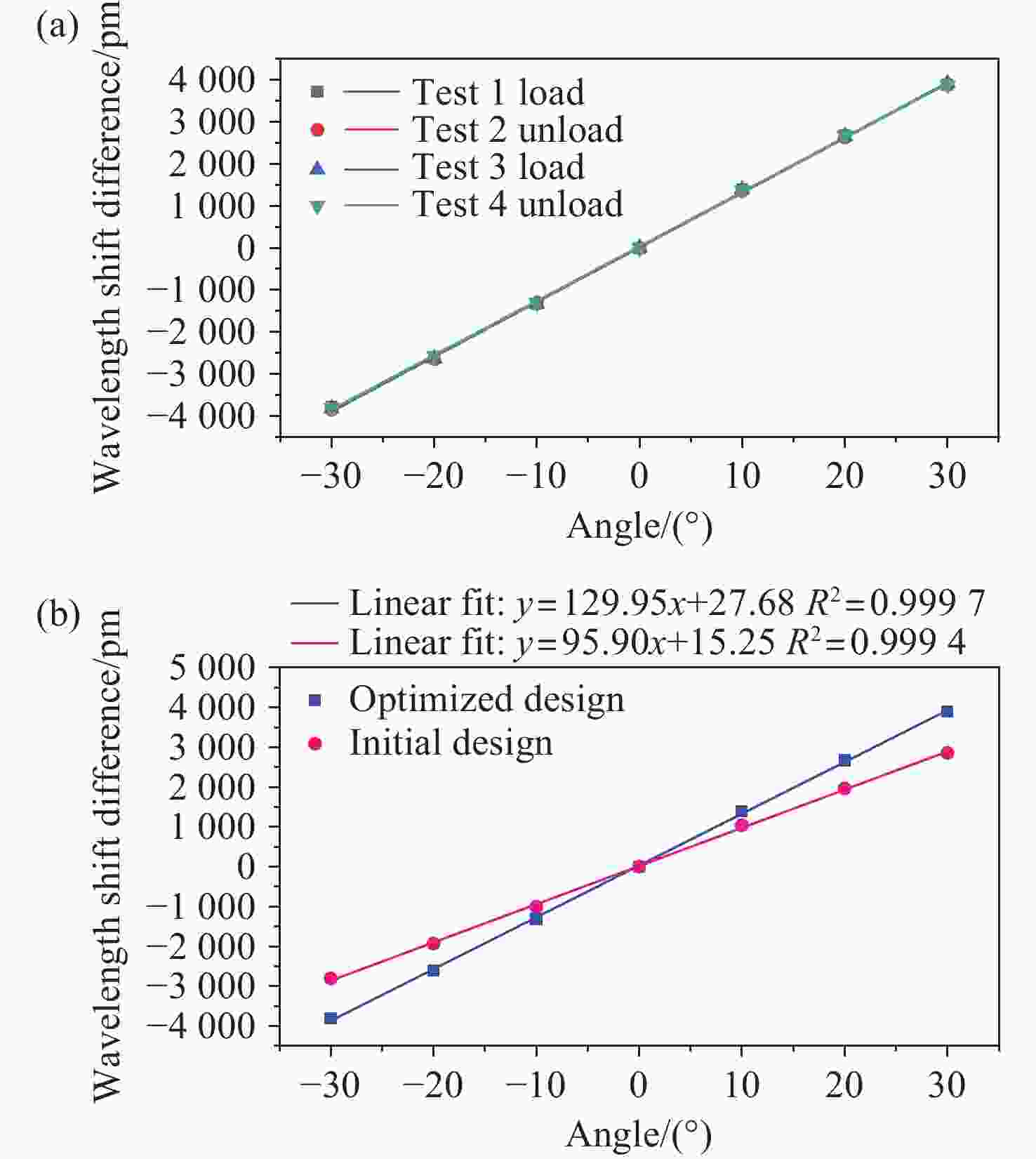
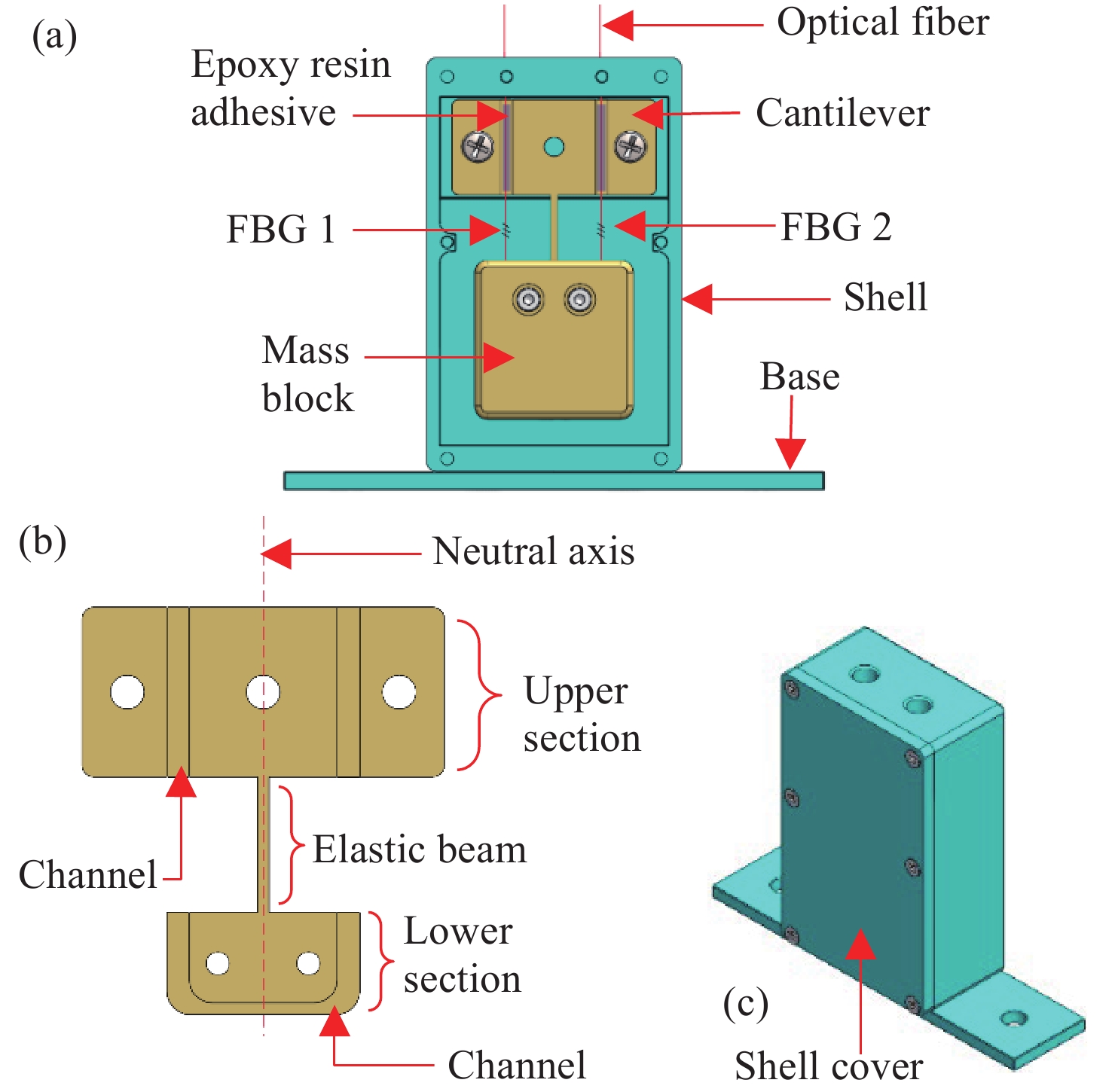
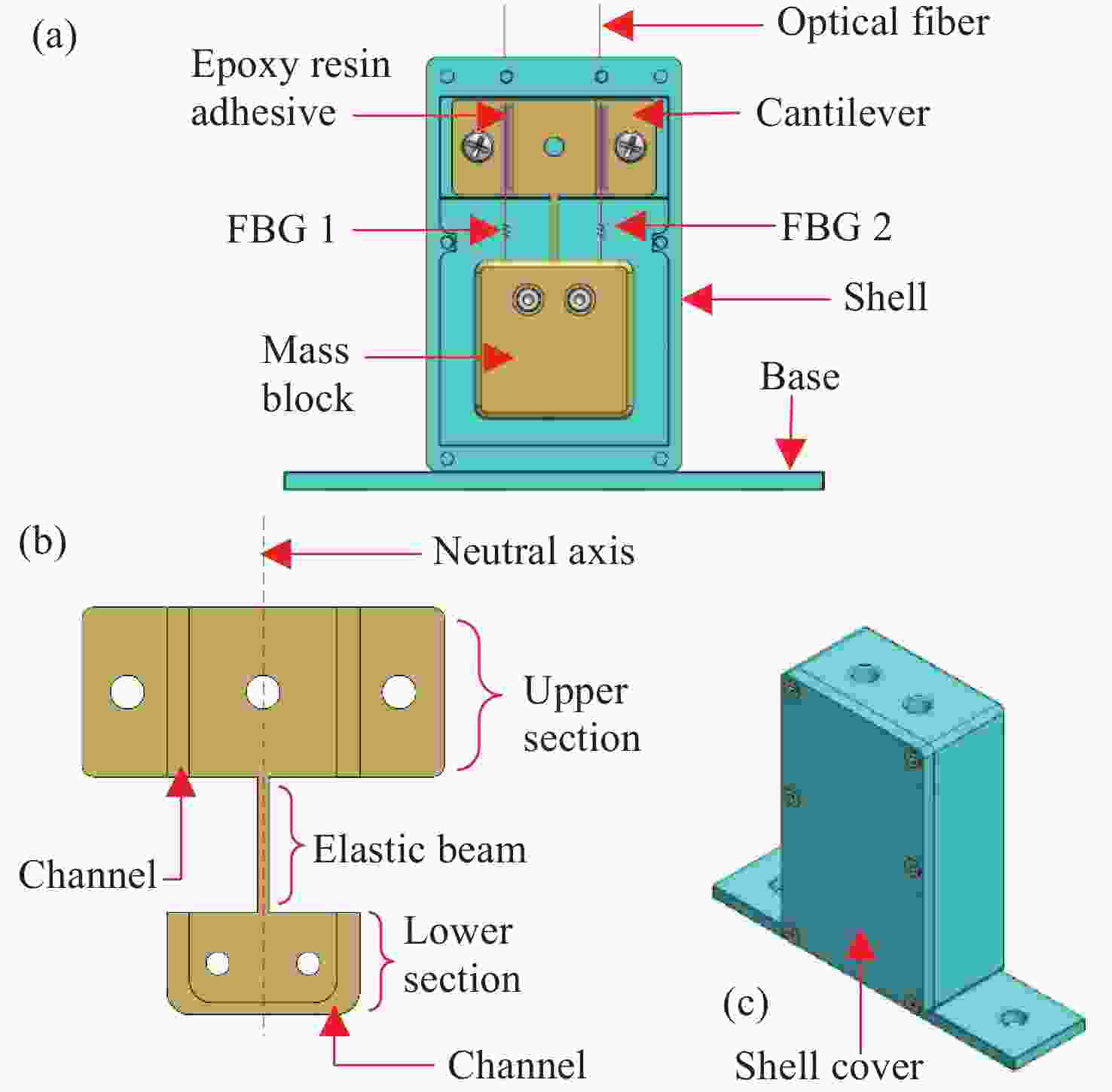
面向结构健康监测领域中的倾角信息高精度监测需求,本文提出了一种基于飞秒光纤光栅的灵敏度增强型倾角传感器。首先,运用静力学原理对倾角传感器进行结构设计,通过设置偏离梁中性轴的光纤光栅,实现光纤光栅应变线性增加,进而提高传感器的灵敏度;接着,通过建立光纤光栅应变、力和中性轴偏离距离之间的关系,确定了产生最大应变所对应的最佳距离;然后,基于此优化方案设计制造了倾角传感器的原型并进行了实验测试。结果表明,倾角传感器最大灵敏度的光纤光栅偏离距离为4.4 mm,在−30°至30°的倾角范围内灵敏度达到了129.95 pm/°,线性度提高至
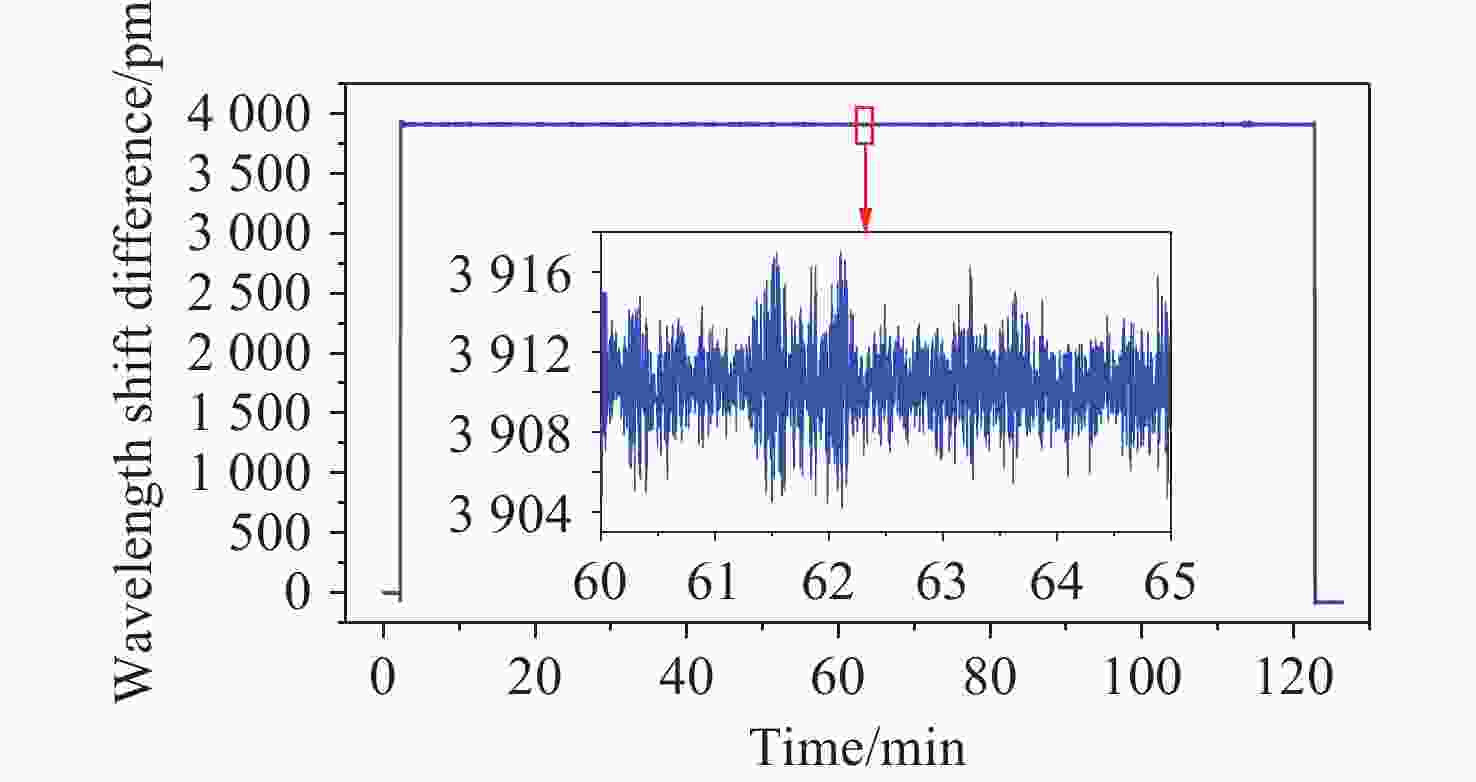
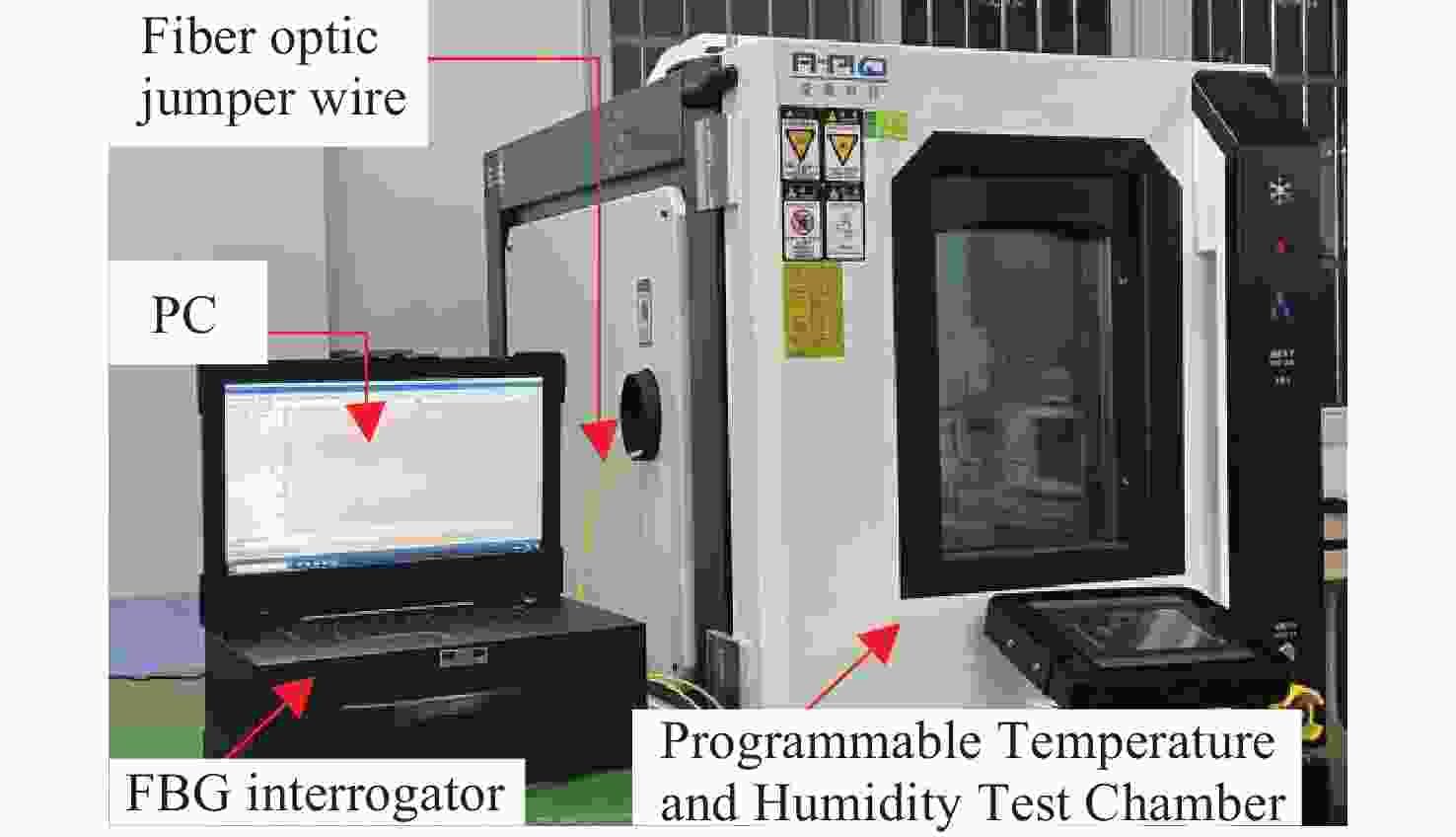
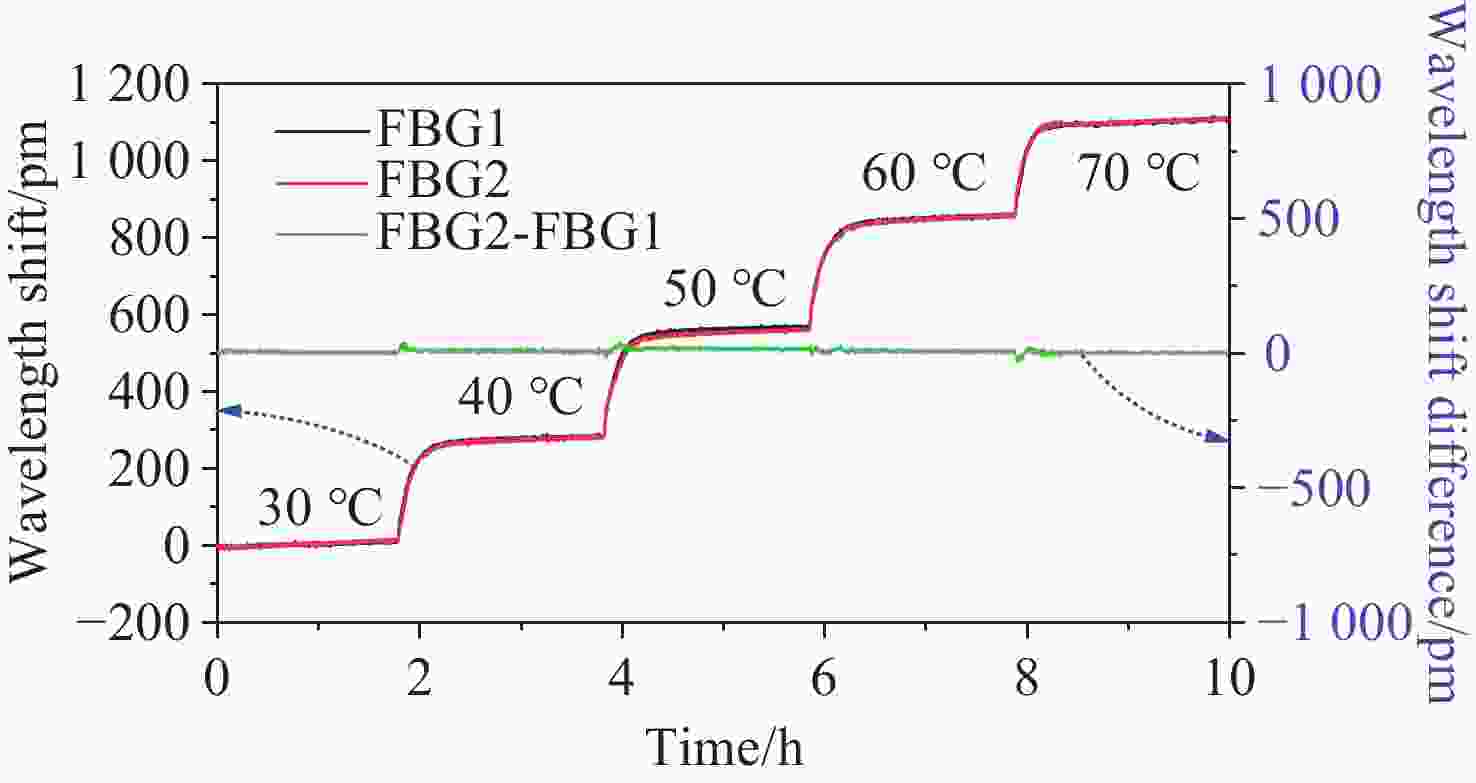
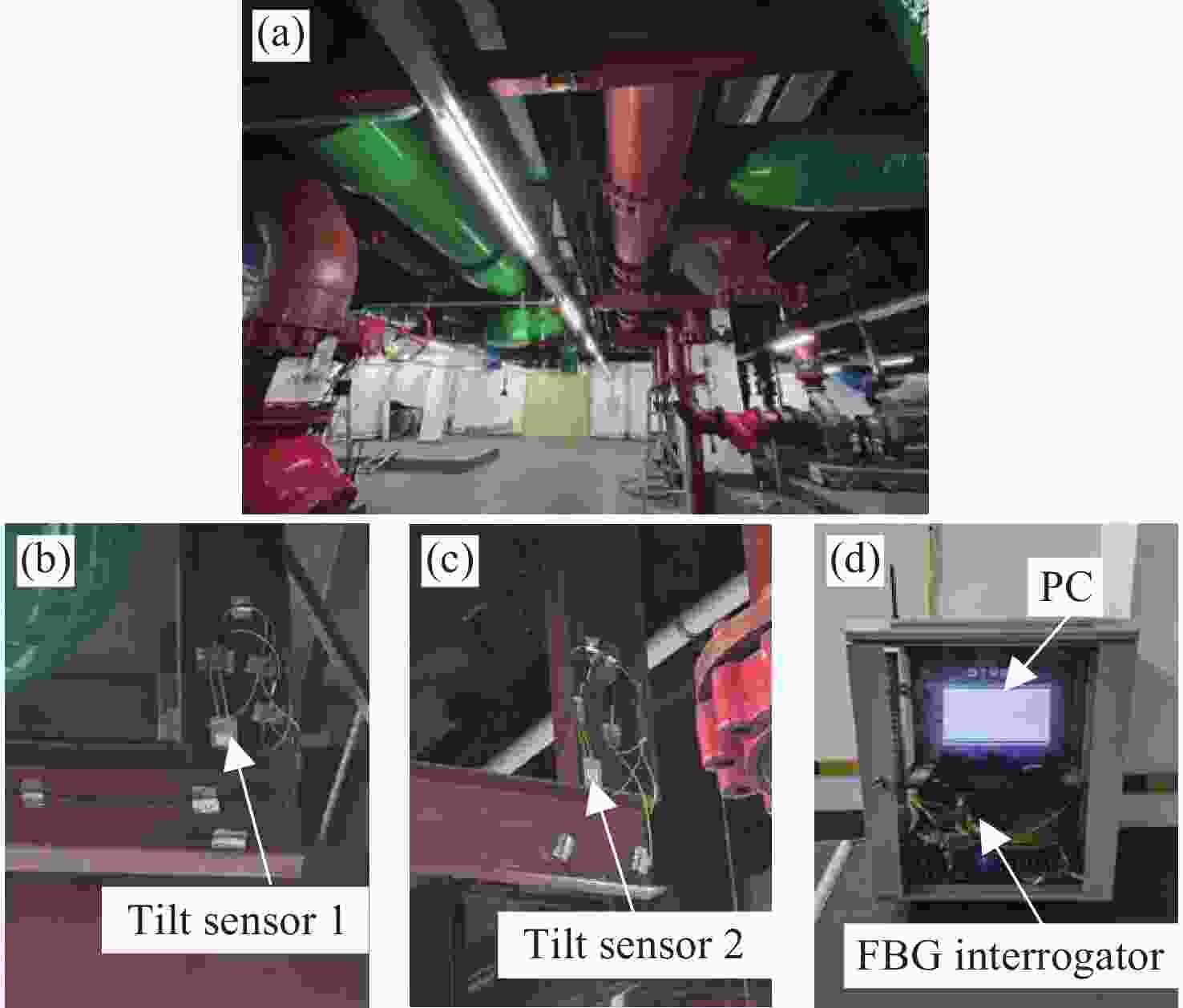
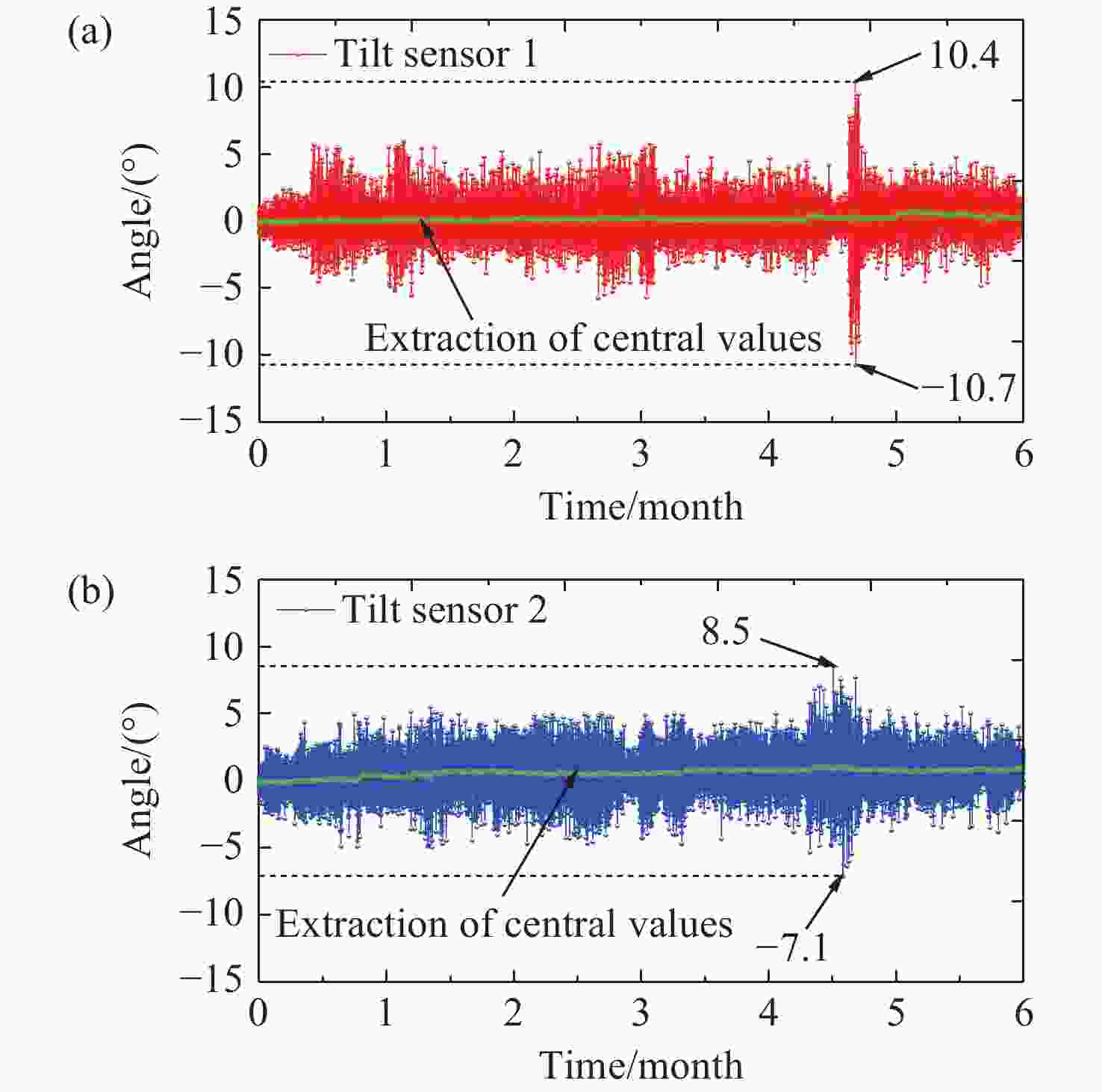
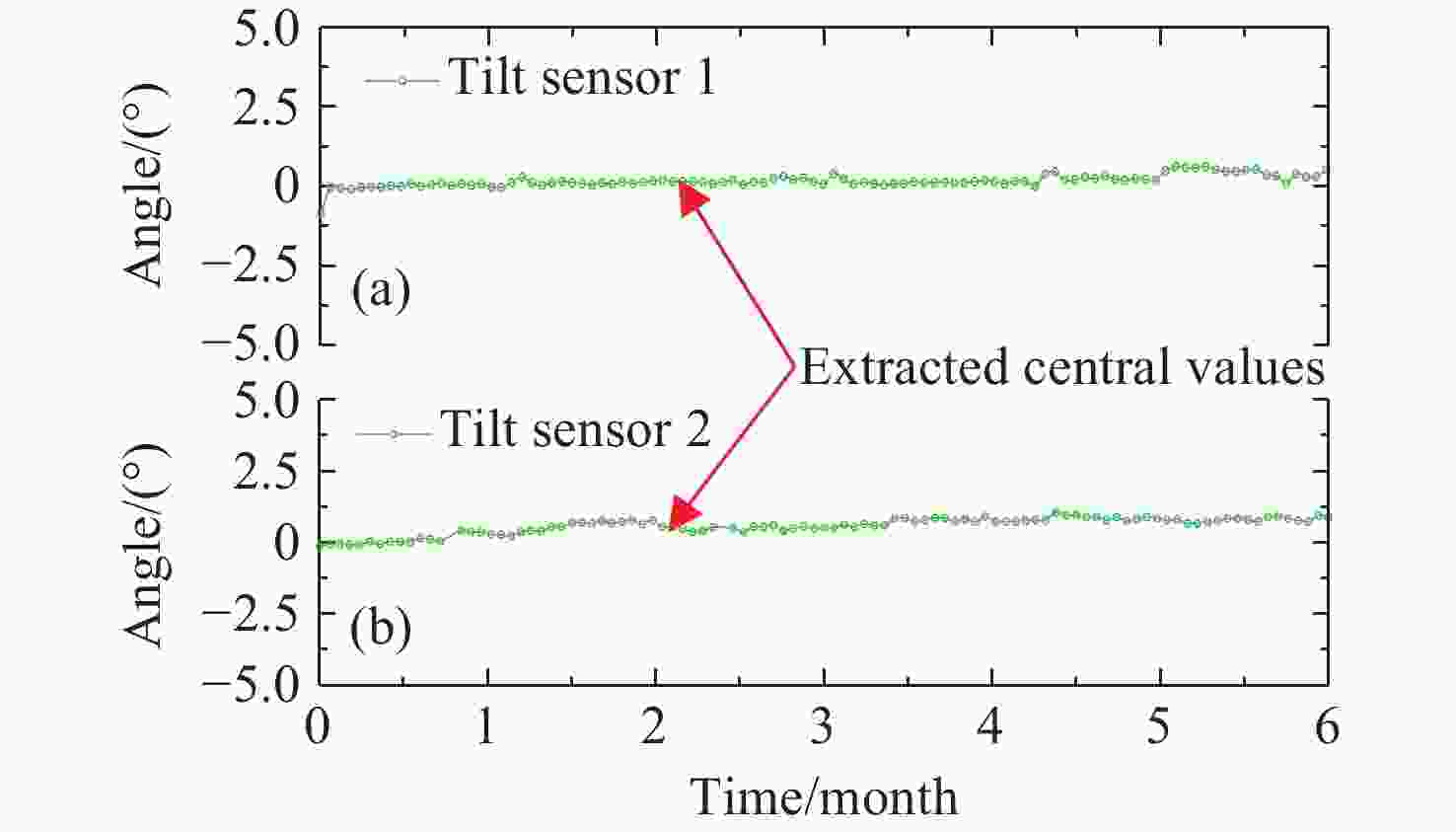
0.9997 ,相较于传统的光纤光栅倾角传感器,灵敏度和线性度均得到了显著提升,同时还表现出了良好的重复性(误差<0.94%)、蠕变抗性(误差<0.30%)和温度稳定性(误差<0.90%)。结果证明该倾角传感器在结构健康监测中拥有着优秀的应用潜力。传感器已成功应用于地下管道项目中,对项目中钢支撑结构的倾角与变形进行了长期监测,进一步证明了其工程安全监测应用价值。Abstract:Aiming at the requirement for high-precision tilt monitoring in the field of structural health monitoring (SHM), this paper proposes a sensitivity-enhanced tilt sensor based on a femtosecond fiber Bragg grating (FBG). Firstly, structural design of the tilt sensor was conducted based on static mechanics principles. By positioning the FBG away from the beam’s neutral axis, linear strain enhancement in the FBG was achieved, thereby improving sensor sensitivity. The relationship between FBG strain, applied force, and the offset distance from the neutral axis was established, determining the optimal distance corresponding to maximum strain. Based on this optimization scheme, a prototype of the tilt sensor was designed, fabricated, and experimentally tested. Experimental results show that the FBG offset distance yielding maximum sensitivity is 4.4 mm. Within a tilt angle range of −30° to 30°, the sensor achieved a sensitivity of 129.95 pm/° and a linearity of
0.9997 . Compared to conventional FBG-based tilt sensors, both sensitivity and linearity were significantly improved. Furthermore, the sensor demonstrated excellent repeatability (error < 0.94%), creep resistance (error < 0.30%), and temperature stability (error < 0.90%). These results demonstrate the sensor’s excellent potential for SHM applications. The sensor has been successfully deployed in an underground pipeline project, conducting long-term monitoring of tilt and deformation in the steel support structures, further proving its value for engineering safety monitoring.-
Key words:
- fiber Bragg grating /
- tilt sensor /
- sensitivity-enhanced /
- femtosecond FBG
-
Table 1. Material properties of brass and silica
Properties Young’s Modulus Poisson’s Ratio Brass 100 GPa 0.33 Silica 73 GPa 0.17 Table 2. Sensitivity and linearity comparison between the initial and optimized design
Property Sensitivity (pm/°) Linearity Initial design 95.90 0.9994 Optimized design 129.95 0.9997 -
[1] GHANBARI M, YAZDANPANAH M J. Delay compensation of tilt sensors based on MEMS accelerometer using data fusion technique[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2015, 15(3): 1959-1966. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2014.2366874 [2] LIN W Y, CHEN C H, LEE M Y. Design and implementation of a wearable accelerometer-based motion/tilt sensing internet of things module and its application to bed fall prevention[J]. Biosensors, 2021, 11(11): 428. doi: 10.3390/bios11110428 [3] XIAO F, CHEN G S, HULSEY J L. Monitoring bridge dynamic responses using fiber Bragg grating tiltmeters[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(10): 2390. doi: 10.3390/s17102390 [4] NORGIA M, BONIOLO I, TANELLI M, et al. Optical sensors for real-time measurement of motorcycle tilt angle[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2009, 58(5): 1640-1649. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2008.2009421 [5] ROMTRAIRAT P, VIRULSRI C, WATTANASIRI P, et al. A performance study of a wearable balance assistance device consisting of scissored-pair control moment gyroscopes and a two-axis inclination sensor[J]. Journal of Biomechanics, 2020, 109: 109957. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2020.109957 [6] DIKSHIT A, SATYAM N. Real-time term monitoring of unstable slopes of Darjeeling Himalayas, India[C]. Proceedings of the 21st EGU General Assembly, EGU, 2019: 3818. [7] HA D W, PARK H S, CHOI S W, et al. A wireless MEMS-based inclinometer sensor node for structural health monitoring[J]. Sensors, 2013, 13(12): 16090-16104. doi: 10.3390/s131216090 [8] LI K, ZHAO Y H, LI Y Q, et al. Fiber Bragg grating biaxial tilt sensor using one optical fiber[J]. Optik, 2020, 218: 164973. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164973 [9] RAO K, LIU H F, WEI X L, et al. A high-resolution area-change-based capacitive MEMS tilt sensor[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2020, 313: 112191. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2020.112191 [10] ZHAN F, LI P L, FU J H, et al. Liquid metal-based angle detection sensor[J]. ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2023, 5(7): 3571-3578. doi: 10.1021/acsaelm.3c00228 [11] YAVSAN E. A planar coil-based novel two-channel differential inductive tilt sensor with a simple pendulum mechanism[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(5): 6286-6292. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3351952 [12] ŁUCZAK S, ZAMS M, DĄBROWSKI B, et al. Tilt sensor with recalibration feature based on MEMS accelerometer[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(4): 1504. doi: 10.3390/s22041504 [13] OLARU R, COTAE C. Tilt sensor with magnetic liquid[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 1997, 59(1-3): 133-135. doi: 10.1016/S0924-4247(97)80162-8 [14] SAHOTA J K, GUPTA N, DHAWAN D. Fiber Bragg grating sensors for monitoring of physical parameters: a comprehensive review[J]. Optical Engineering, 2020, 59(6): 060901. [15] RAO Y J. In-fibre Bragg grating sensors[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 1997, 8(4): 355-375. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/8/4/002 [16] JIANG SH CH, WANG J, SUI Q M. Distinguishable circumferential inclined direction tilt sensor based on fiber Bragg grating with wide measuring range and high accuracy[J]. Optics Communications, 2015, 355: 58-63. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2015.05.055 [17] MA G M, LI CH R, QUAN J T, et al. A fiber Bragg grating tension and tilt sensor applied to icing monitoring on overhead transmission lines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2011, 26(4): 2163-2170. doi: 10.1109/TPWRD.2011.2157947 [18] LIANG M F, FANG X Q, LI SH, et al. A fiber Bragg grating tilt sensor for posture monitoring of hydraulic supports in coal mine working face[J]. Measurement, 2019, 138: 305-313. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.02.060 [19] YANG R G, BAO H L, ZHANG SH Q, et al. Simultaneous measurement of tilt angle and temperature with pendulum-based fiber Bragg grating sensor[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2015, 15(11): 6381-6384. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2458894 [20] GUO Y X, ZHANG D SH, ZHOU Z D, et al. Cantilever based FBG vibration transducer with sensitization structure[J]. Optoelectronics Letters, 2013, 9(6): 410-413. doi: 10.1007/s11801-013-3139-7 [21] NUTSUGLO T, GUO CH CH, LI Q, et al. Sensitivity-enhanced tilt sensor based on femtosecond fiber bragg grating[C]. Proceedings of 2023 International Conference on Sensing, Measurement & Data Analytics in the era of Artificial Intelligence, IEEE, 2023: 1-6. [22] GUO Y X, HU P, XIONG L, et al. Design and investigation of a fiber Bragg grating tilt sensor with vibration damping[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(3): 2193-2203. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3229397 -





 下载:
下载: