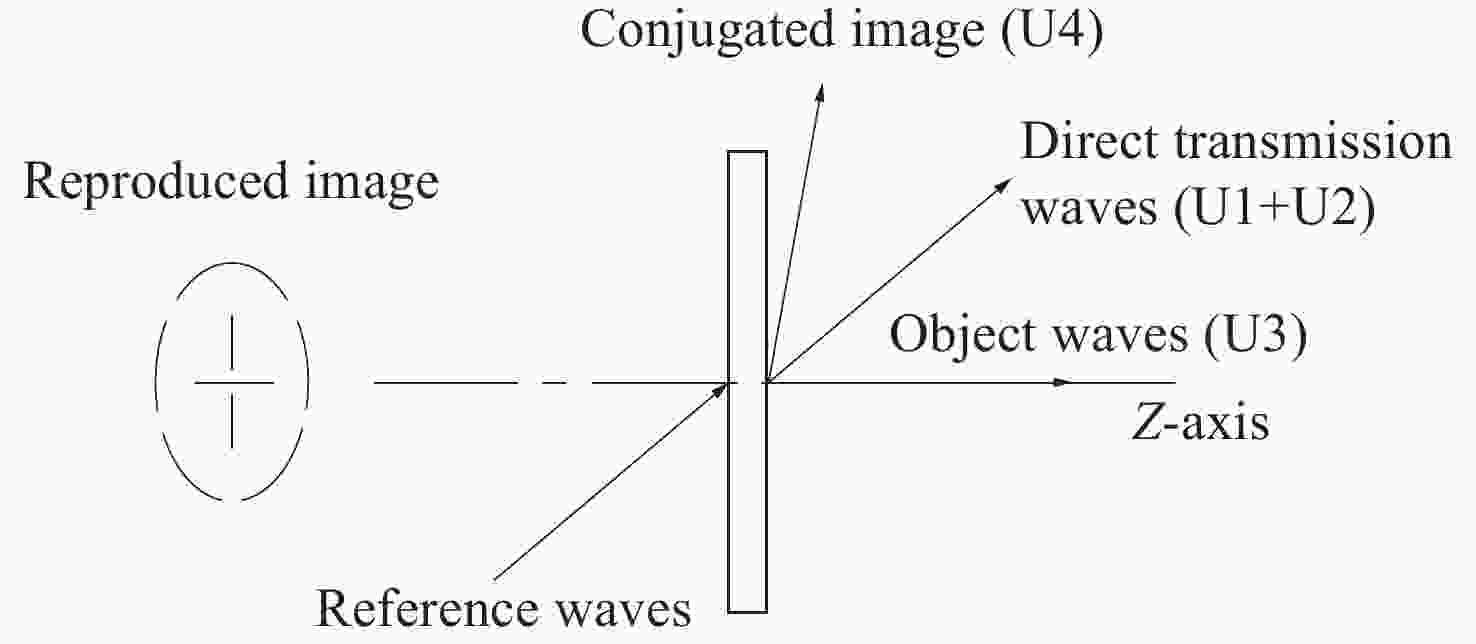
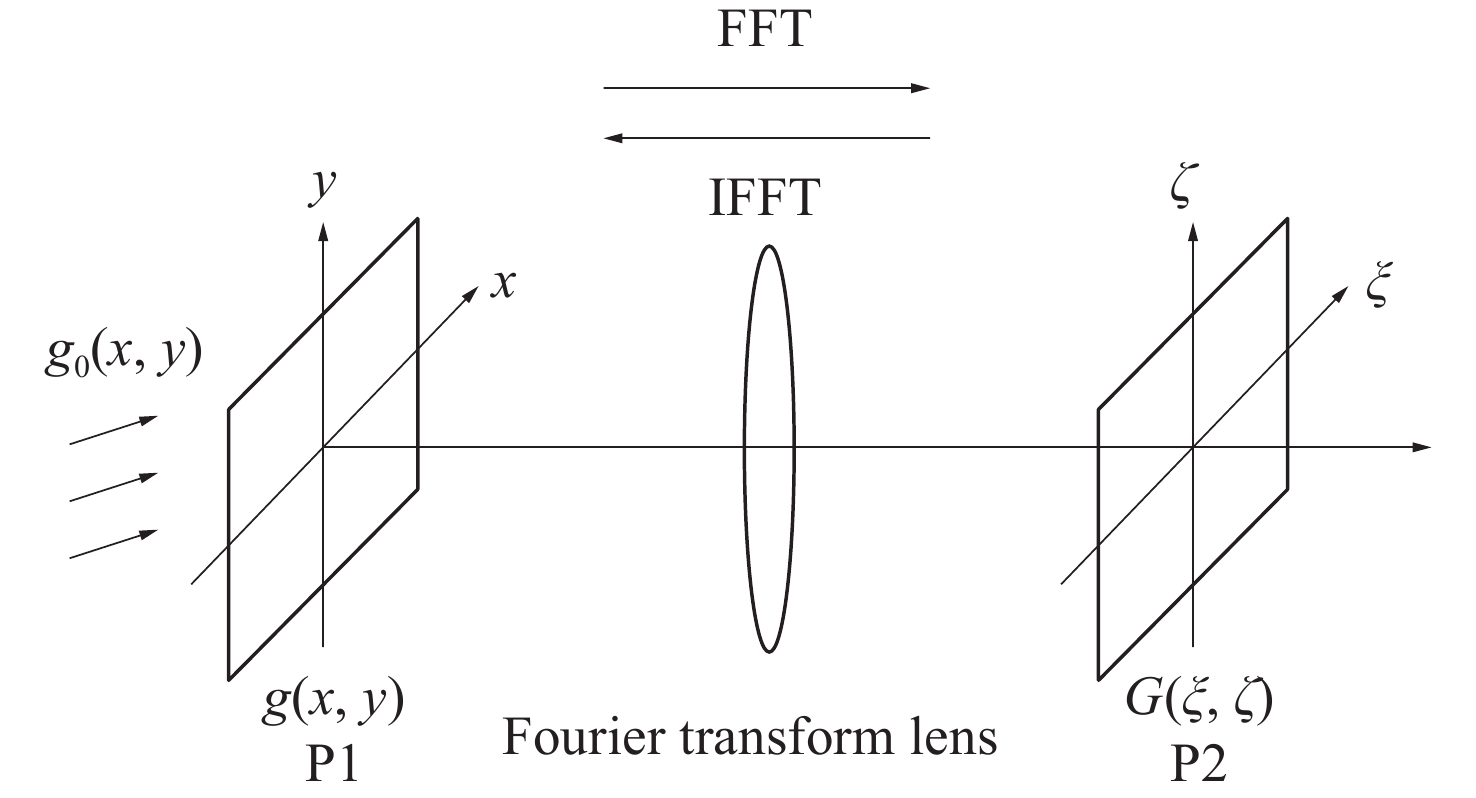
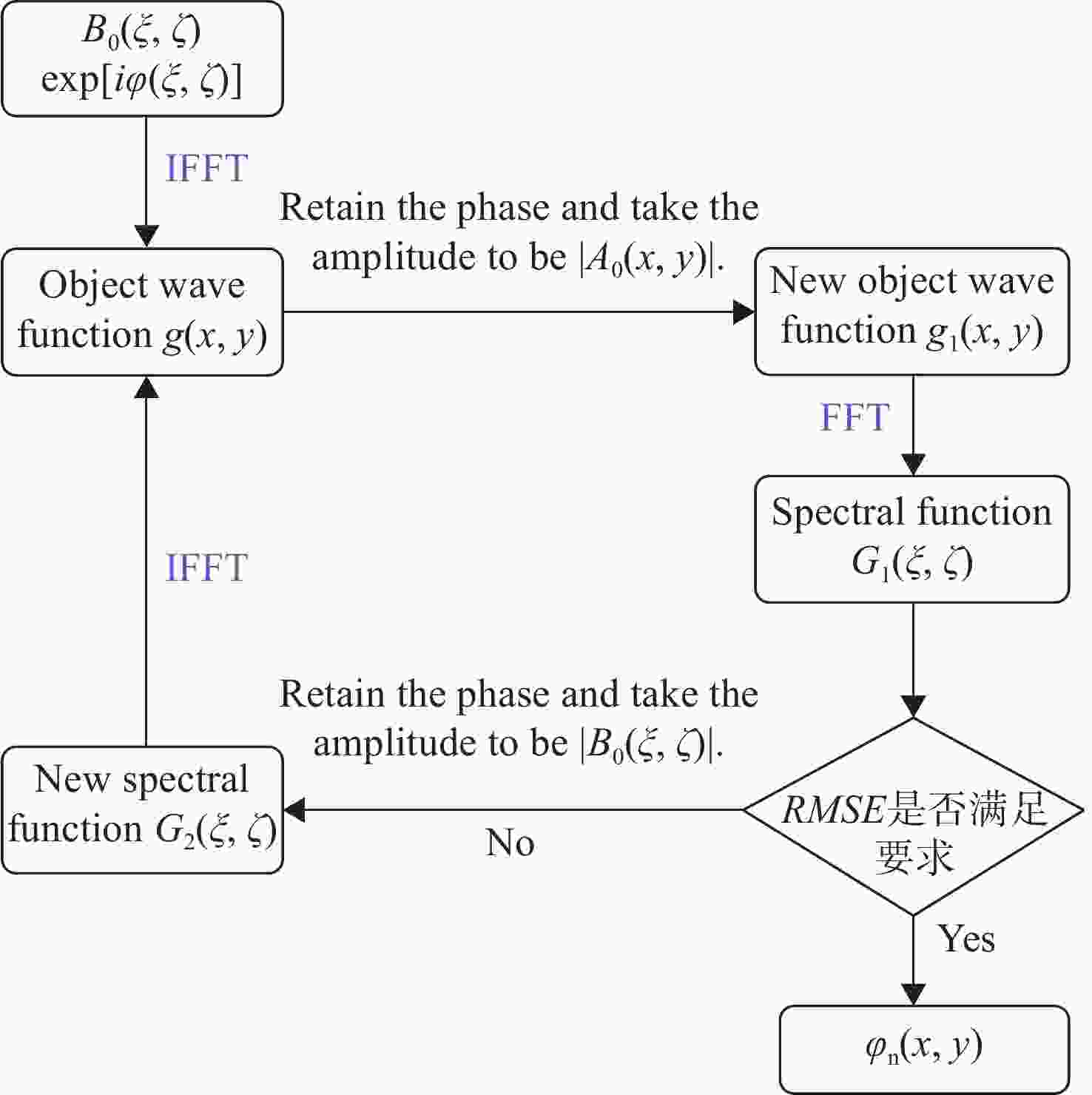
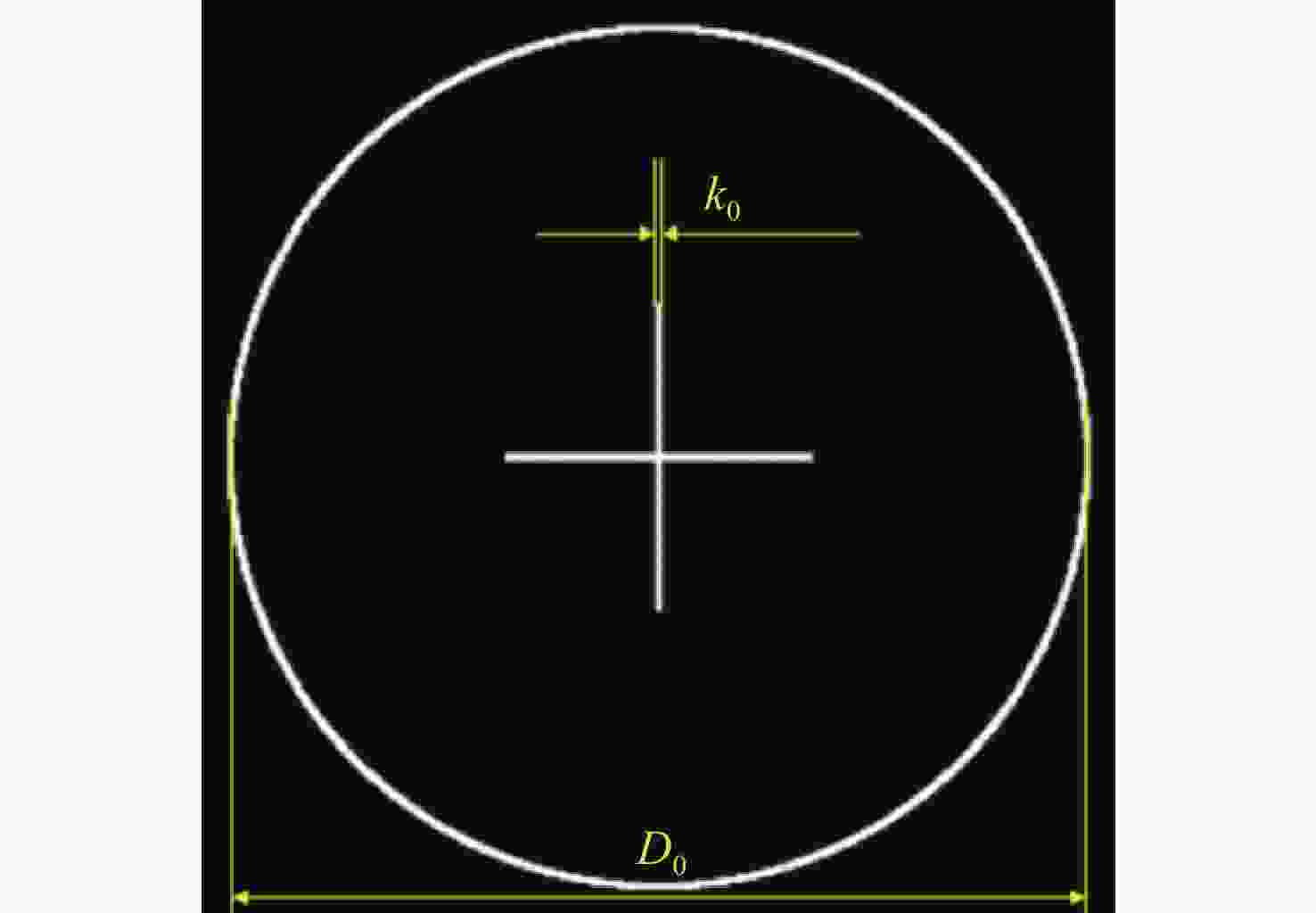
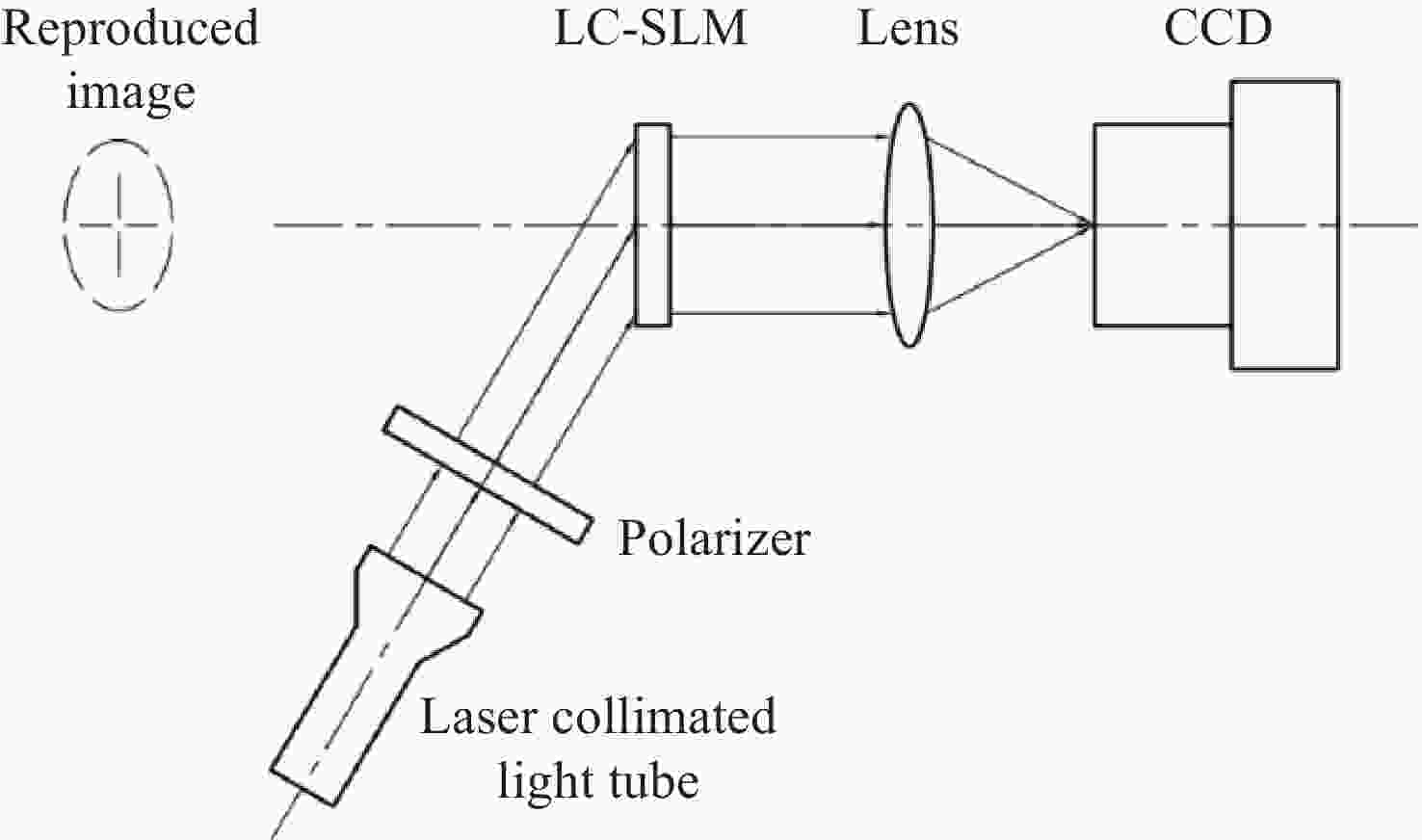
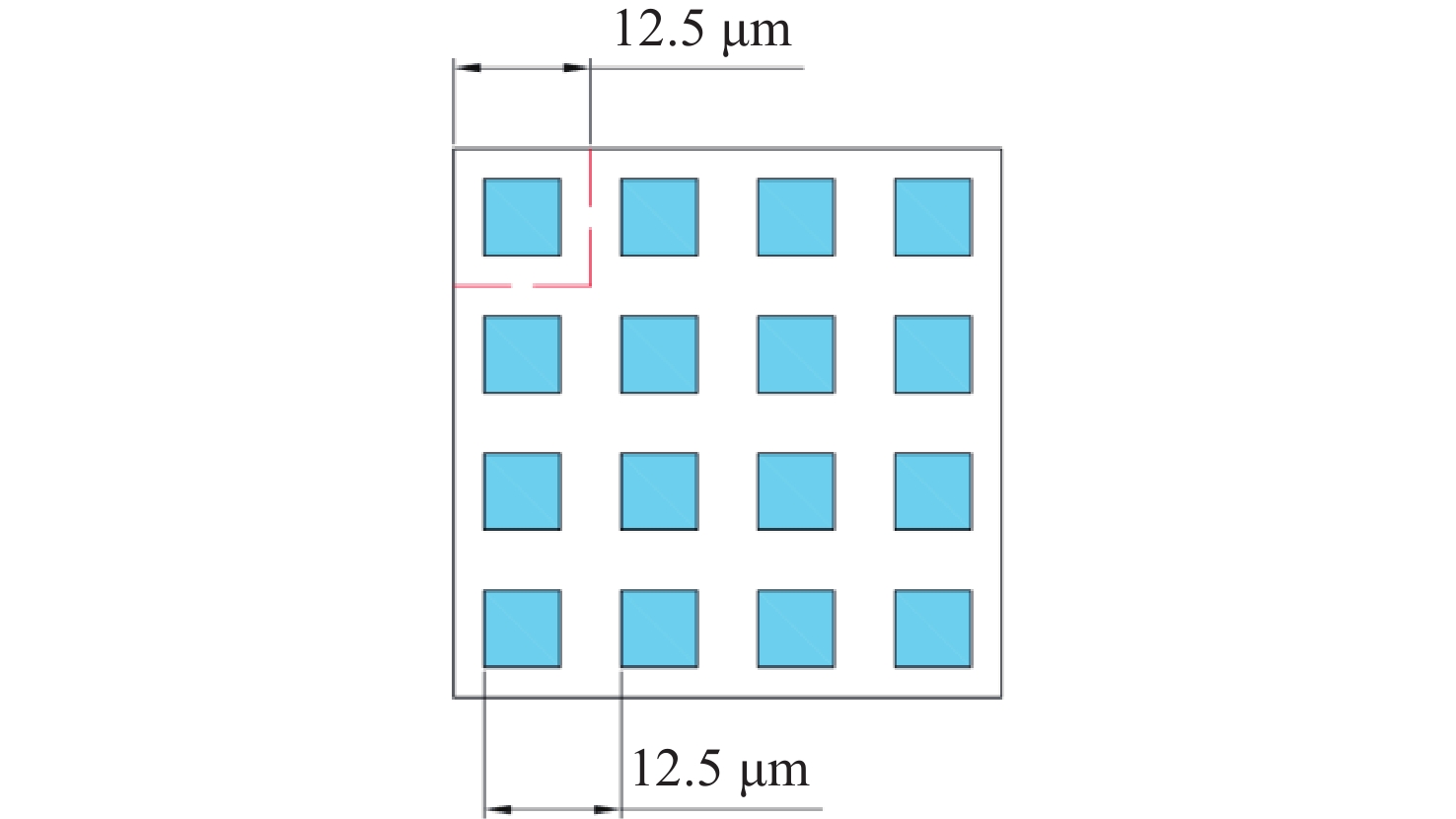
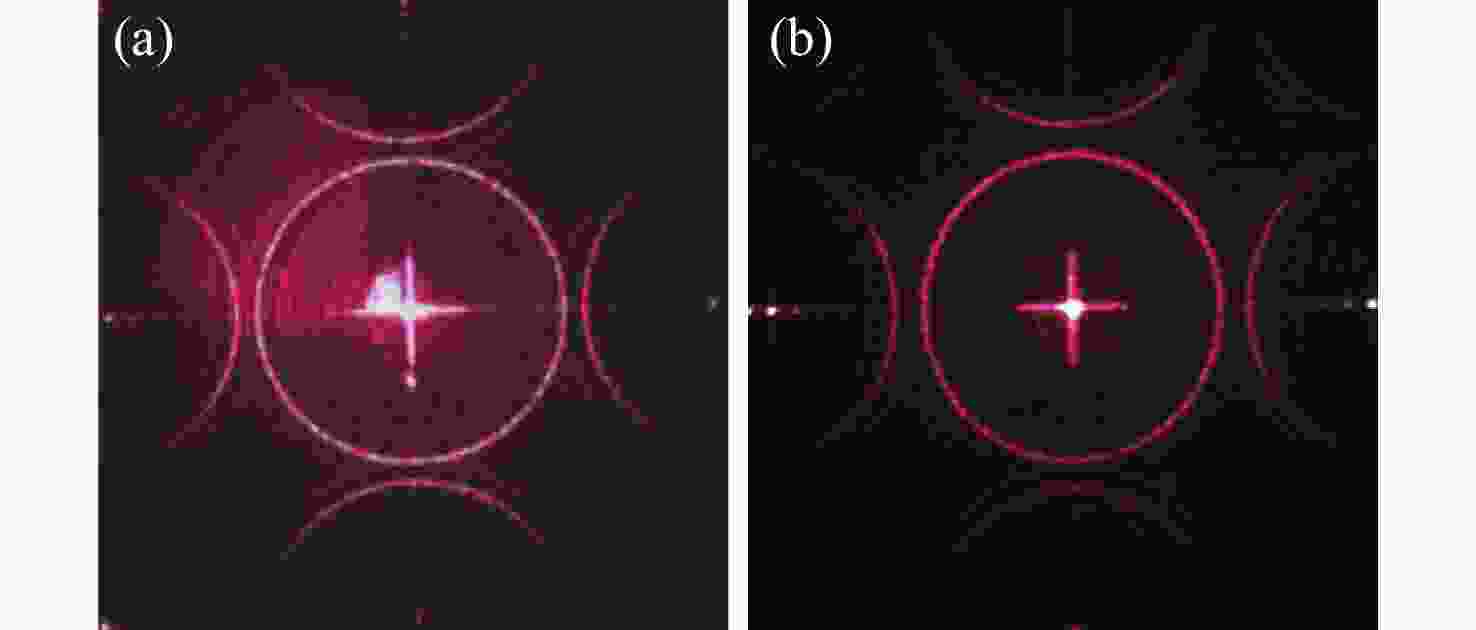
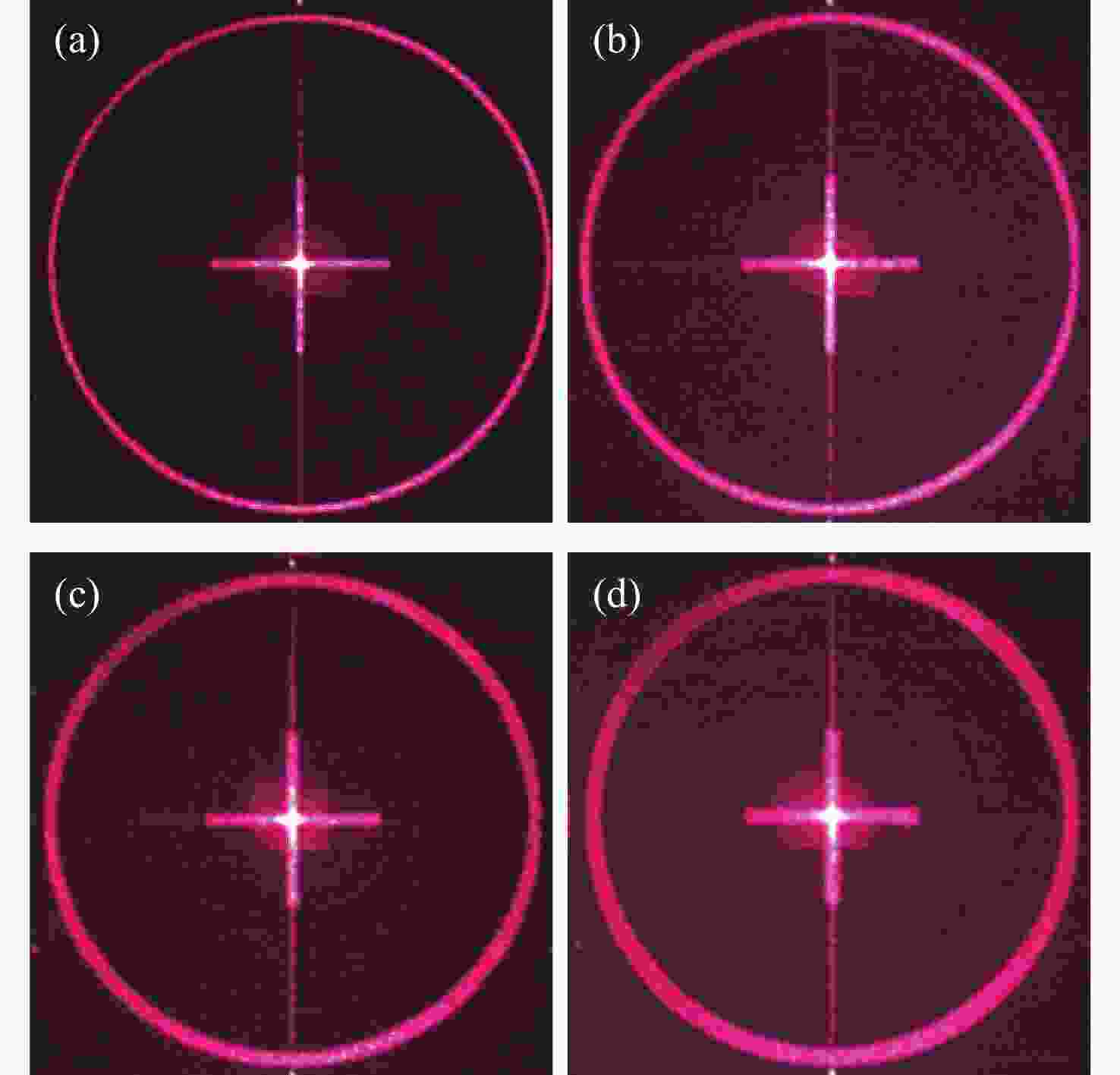
Design of holographic reproduction images based on liquid crystal spatial light modulator
-
摘要:
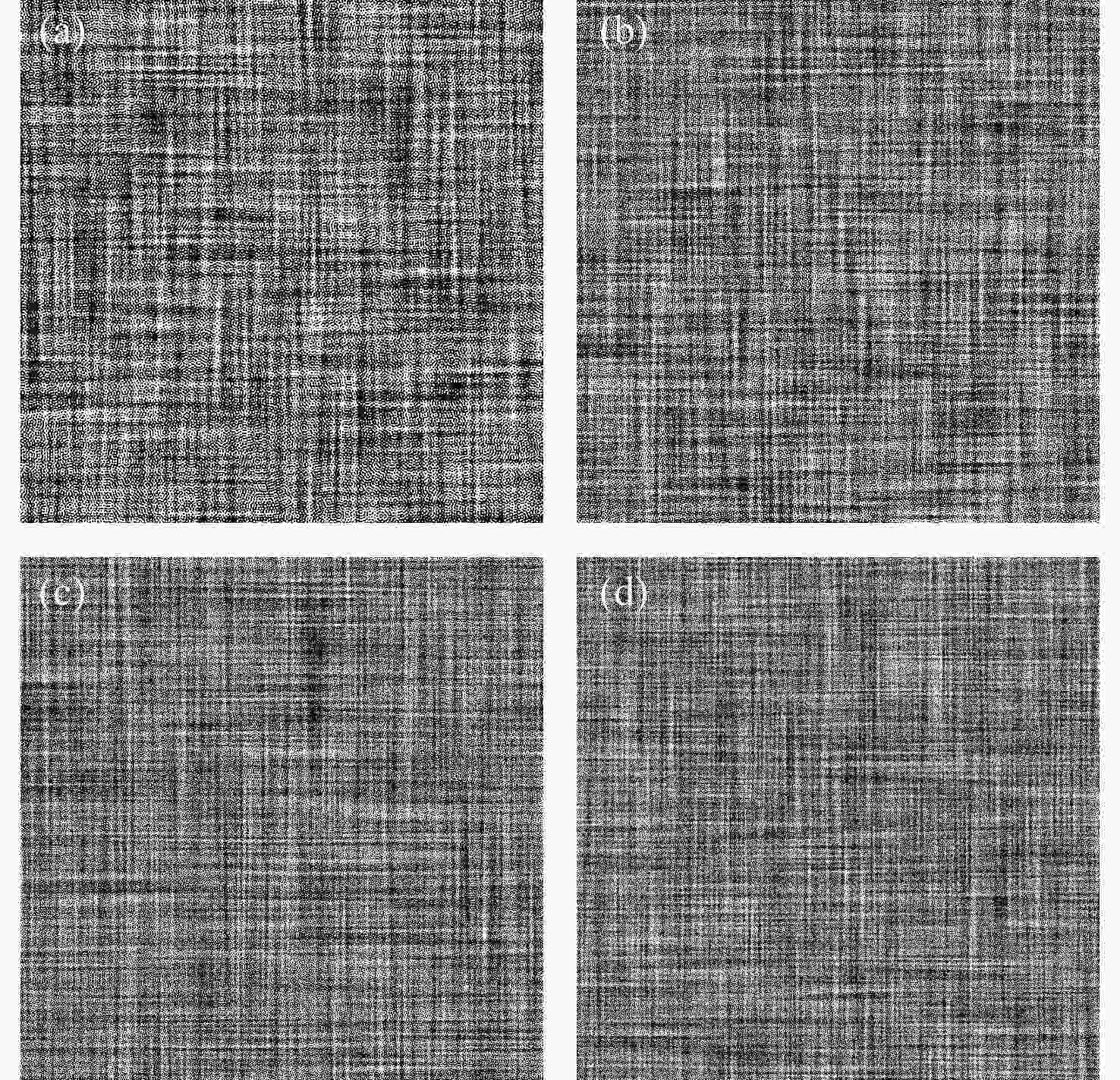
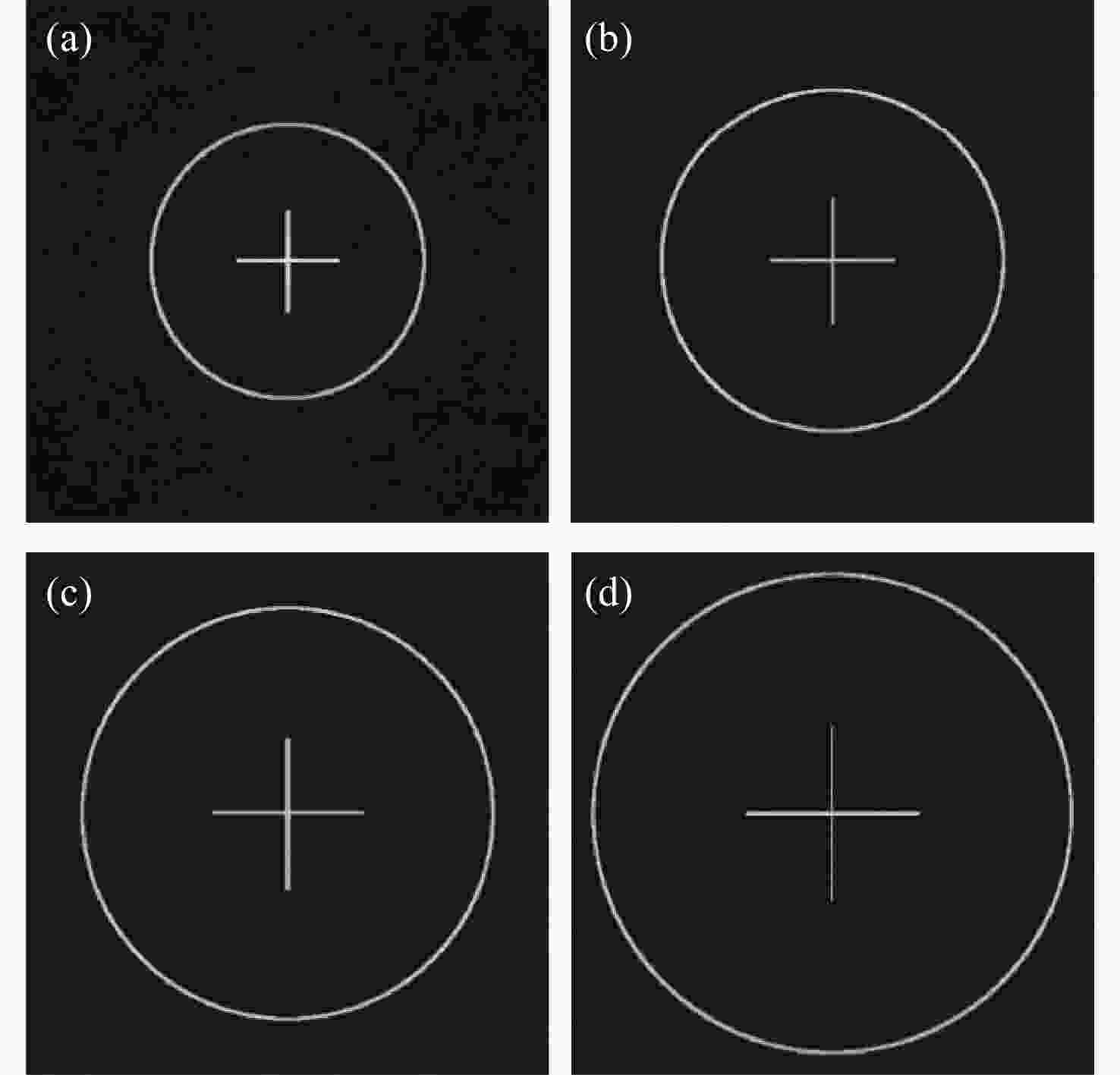
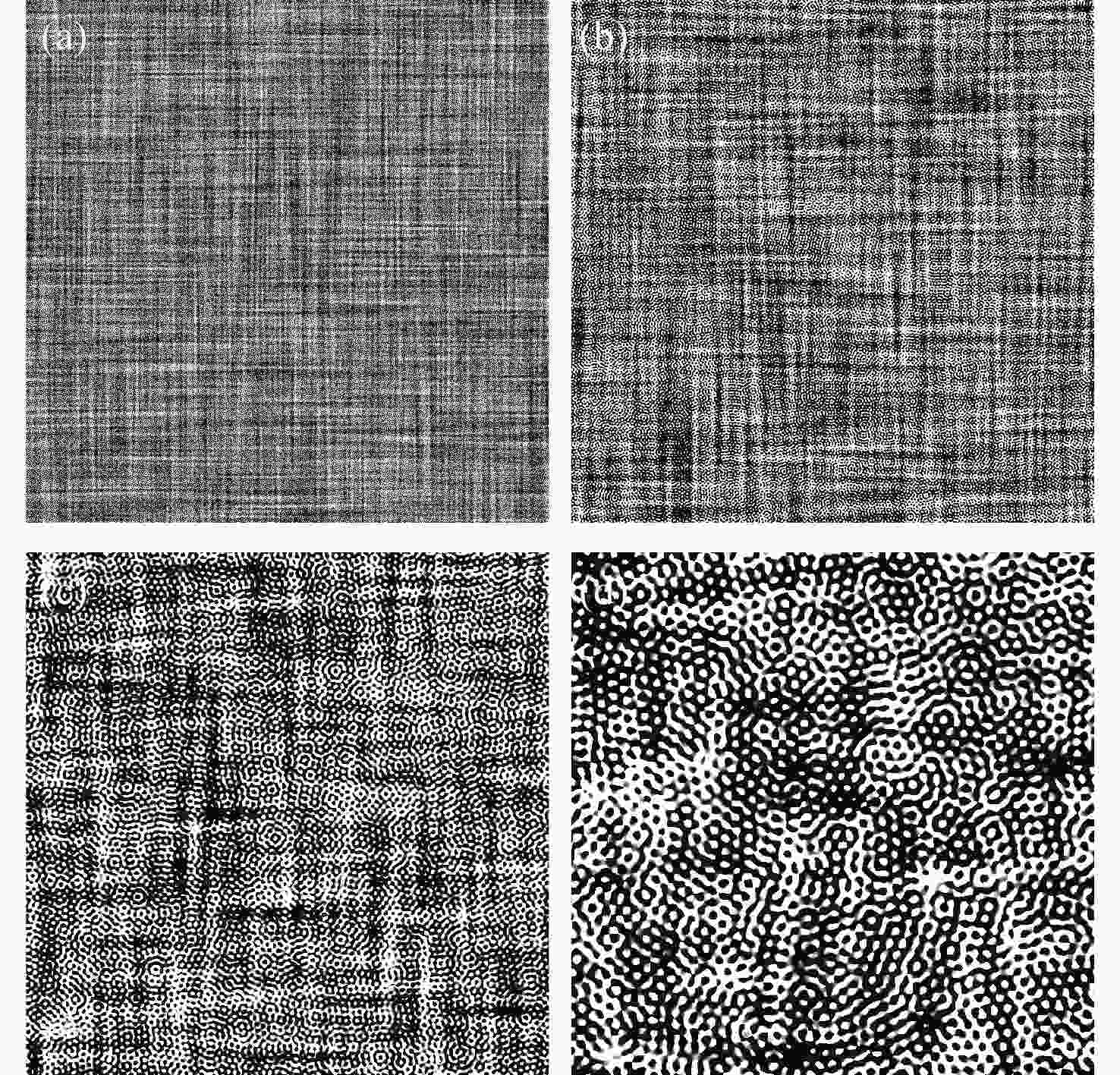
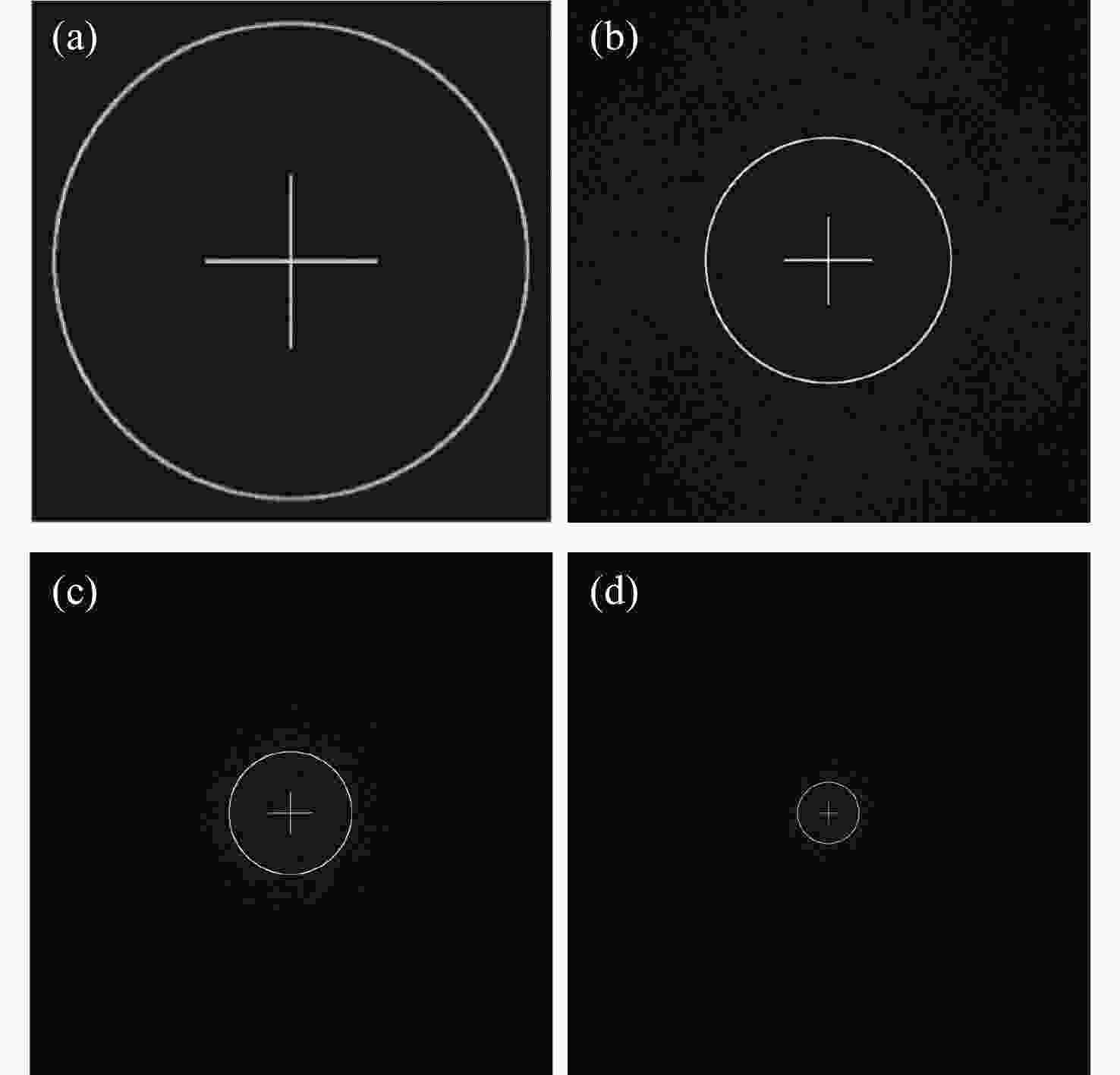
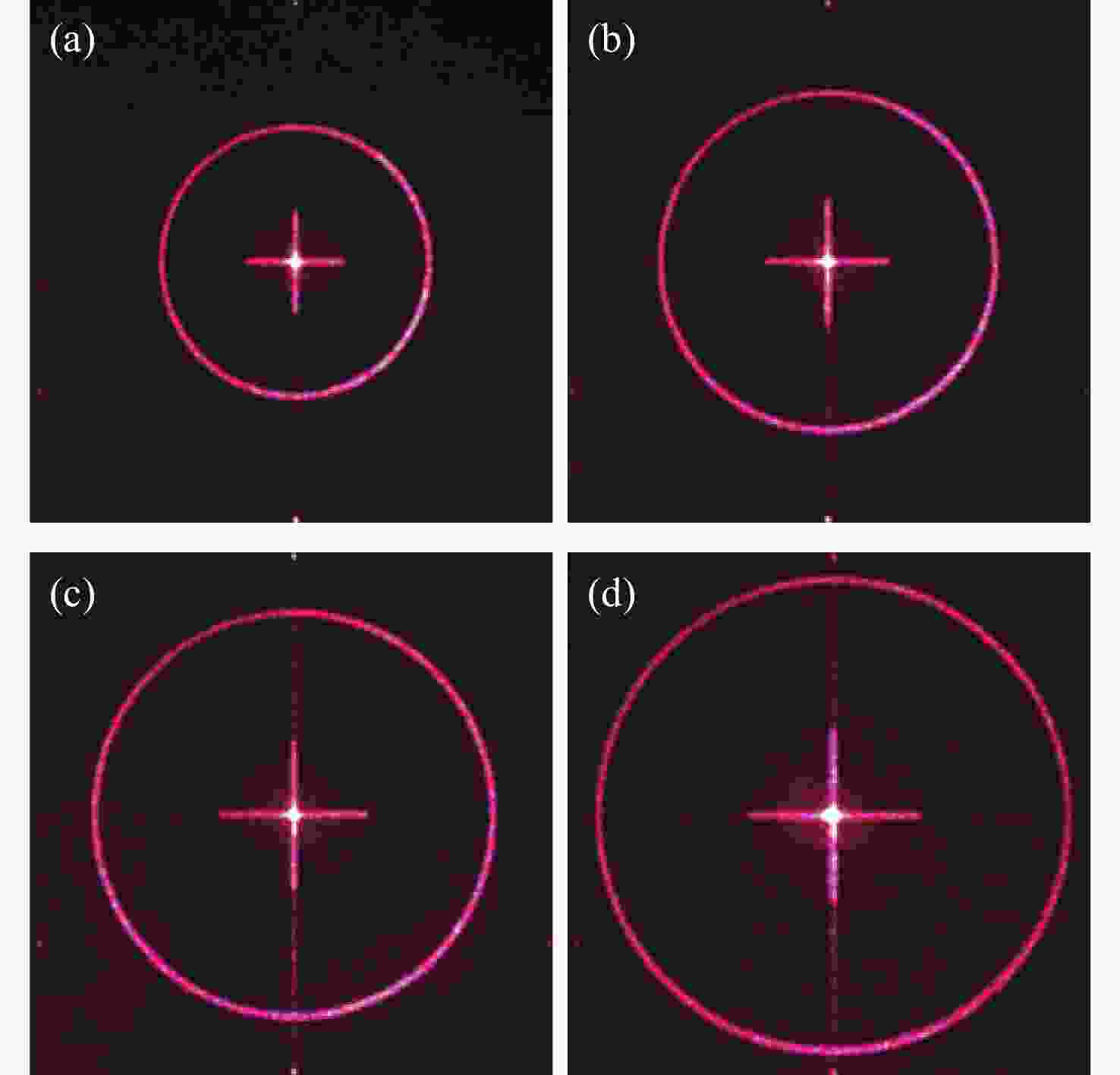
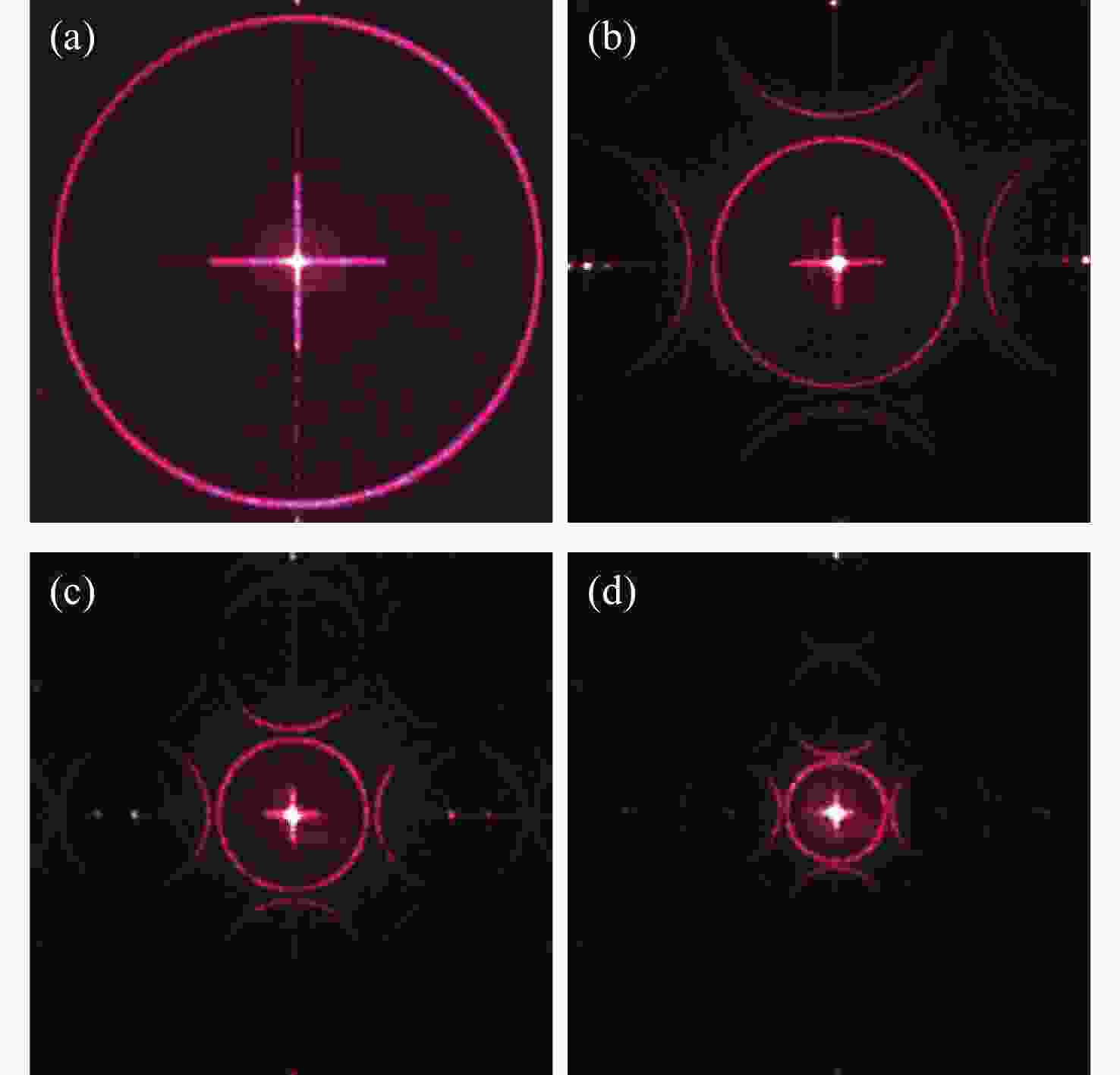
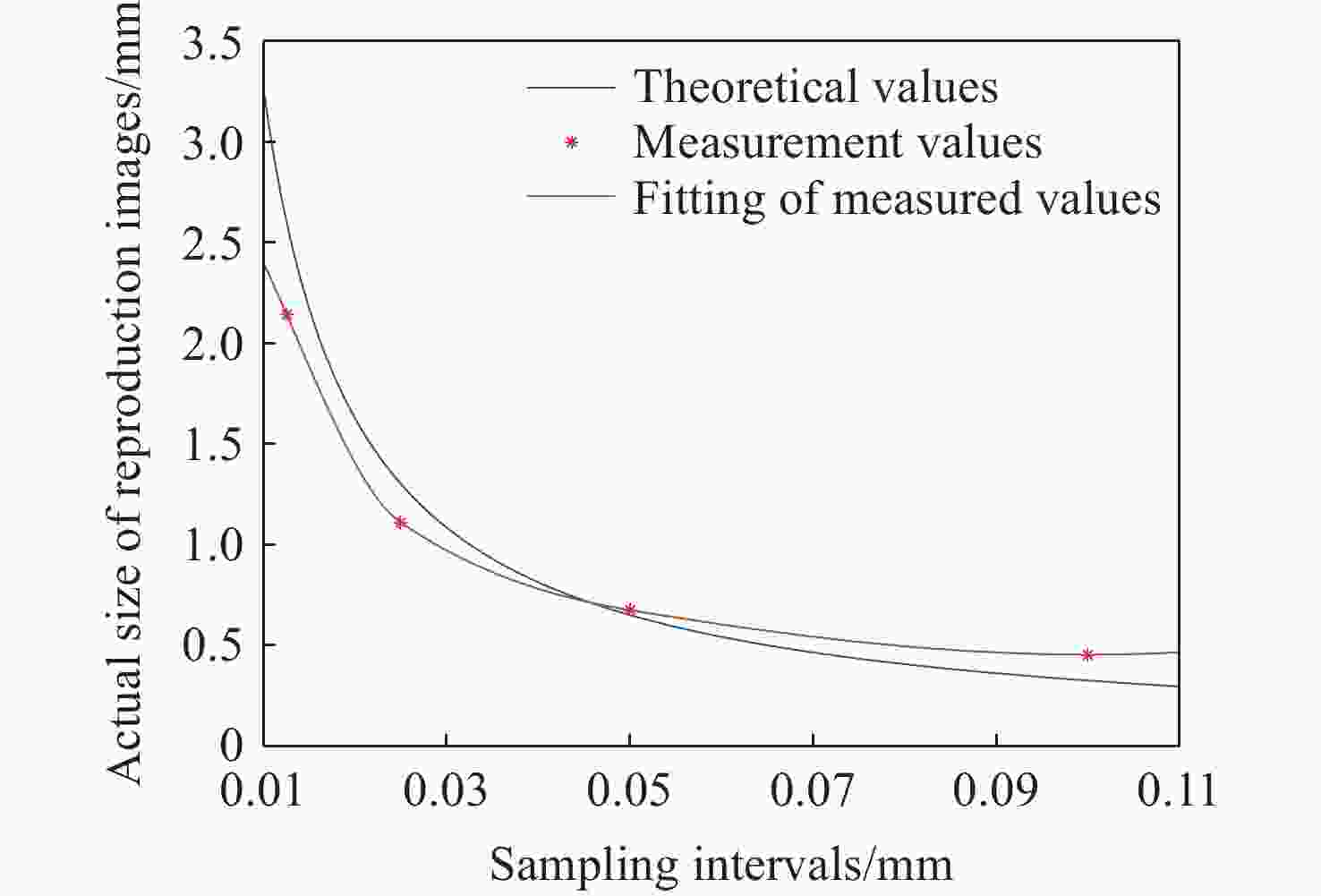
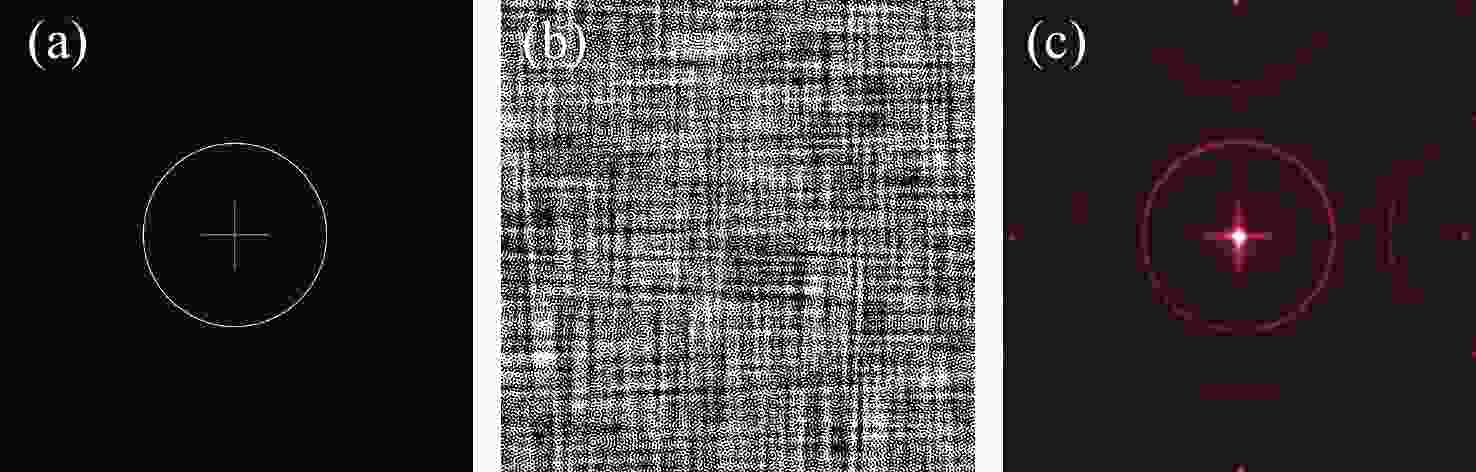
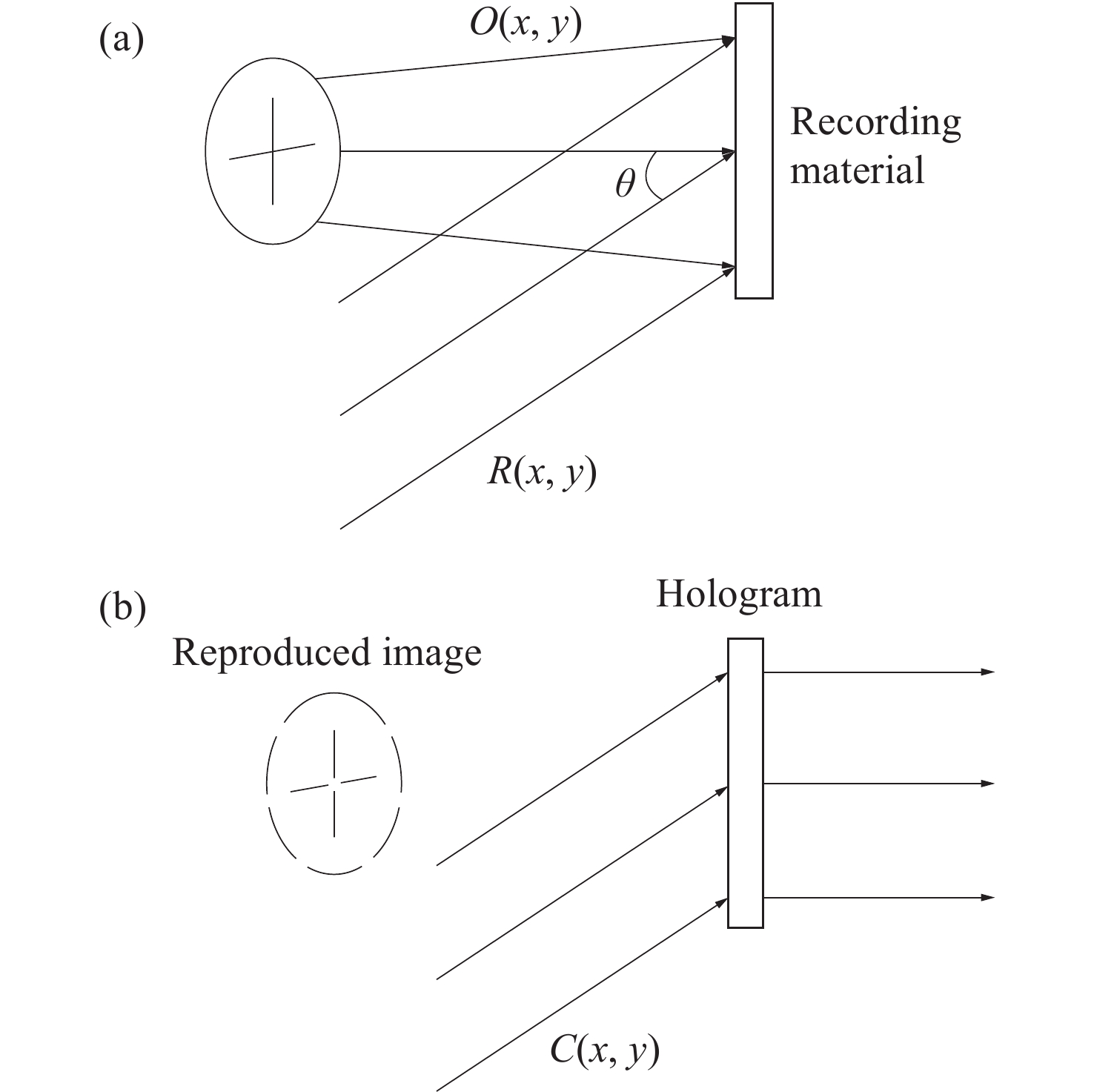
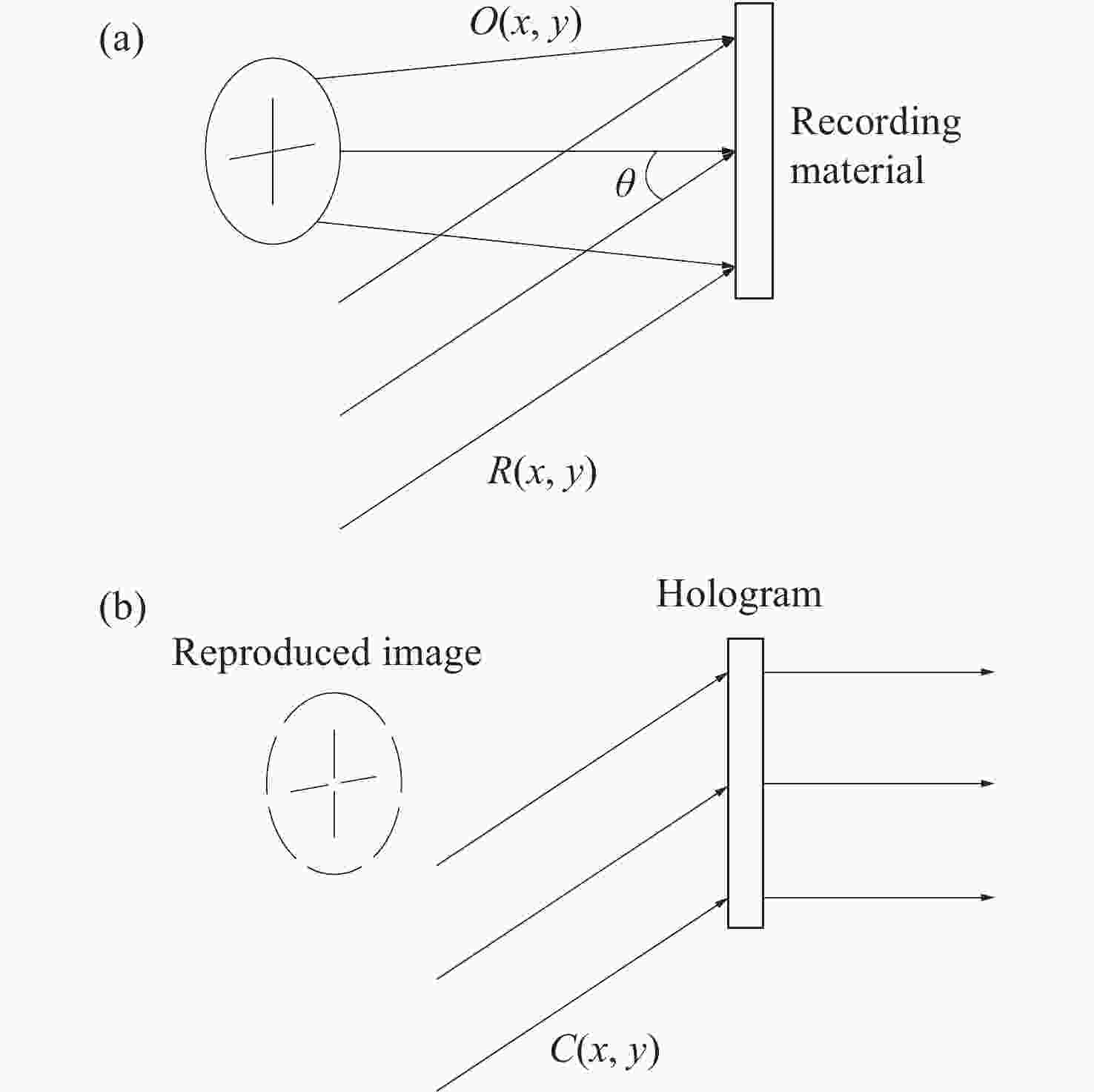
本文根据计算全息再现成像原理,采用Gerchberg-Saxton (GS) 算法对输入与输出平面光场分布进行正、逆傅立叶变换迭代求解,得到原始仿真图像在不同特征参数(线宽、圆环直径)和不同计算采样间隔下的相位分布,并仿真计算得到相应的再现图像。利用液晶空间光调制器搭建全息再现实验光路,通过加载不同原始仿真图像的相位分布图进行再现实验,采用相机拍摄得到远场衍射全息再现图像并进行图像处理得到再现图像的实际特征尺寸。实验结果表明:再现图像特征尺寸与原始仿真图像特征尺寸基本呈线性变化关系,再现图像尺寸与仿真计算采样间隔呈现非线性变化关系,且与理论推导的关系曲线一致。为了进一步验证结论的正确性,设计预期再现图像尺寸,当圆环直径为0.943 mm,中心十字线宽为0.015 mm时,仿真计算得到预期目标原始仿真图像的特征尺寸和采样间隔分别为线宽3 pixel、圆环直径594 pixel、采样间隔25 μm。通过再现实验测量得到的全息再现图像圆环直径为0.93 mm,线宽为0.017 mm,误差精度在0.02 mm以内。本文研究结果对全息显示、AR/VR显示等应用场景下提高虚拟显示图像尺寸真实性提供了有益参考。
-
关键词:
- 计算全息 /
- 傅里叶变换 /
- Gerchberg-Saxton算法 /
- 采样间隔 /
- 液晶空间光调制器
Abstract:Based on the principle of computer-generated holograms reproduction imaging, this paper used the Gerchberg-Saxton (GS) algorithm to iteratively solve the phase distribution of the original simulation images under different characteristic parameters (line width, ring diameter) and different calculated sampling intervals by performing direct and inverse Fourier transforms on the optical field distributions of the input and output planes, and the corresponding reproduced images were obtained by simulation calculation. The optical path of the holographic reproduction experiment was constructed by using the liquid crystal spatial light modulator, and the reproduction experiment was carried out by loading the phase distribution maps of different original simulation images, the holographic reproduction images of far-field diffraction were taken by the camera, and the actual feature size of the reproduced images was obtained by image processing. The experimental results show that the feature size of the reproduced images is basically linear with the characteristic size of the original simulation images. Furthermore, the reproduction image size shows a non-linear change relationship with the sampling intervals of the simulation calculation, which is consistent with the derived theoretical calculation relationship curve. In order to further verify the correctness of the conclusion, when the size of the expected reproduced image is designed as the ring diameter of 0.943 mm and the line width of the central cross of 0.015 mm. The characteristic size and sampling interval of the original simulation image of the expected target are obtained by the simulation calculation as the line width of 3 pixel, the ring diameter of 594 pixel and the sampling interval of 25 μm, respectively. The ring diameter and line width of the holographic reproduction image, as measured by the reproduction experiment, are 0.93 mm and 0.017 mm, respectively. The error accuracy is within 0.02 mm. The findings of this study provide an effective reference for application scenarios such as holographic display and AR/VR display to improve the authenticity of virtual display image size.
-
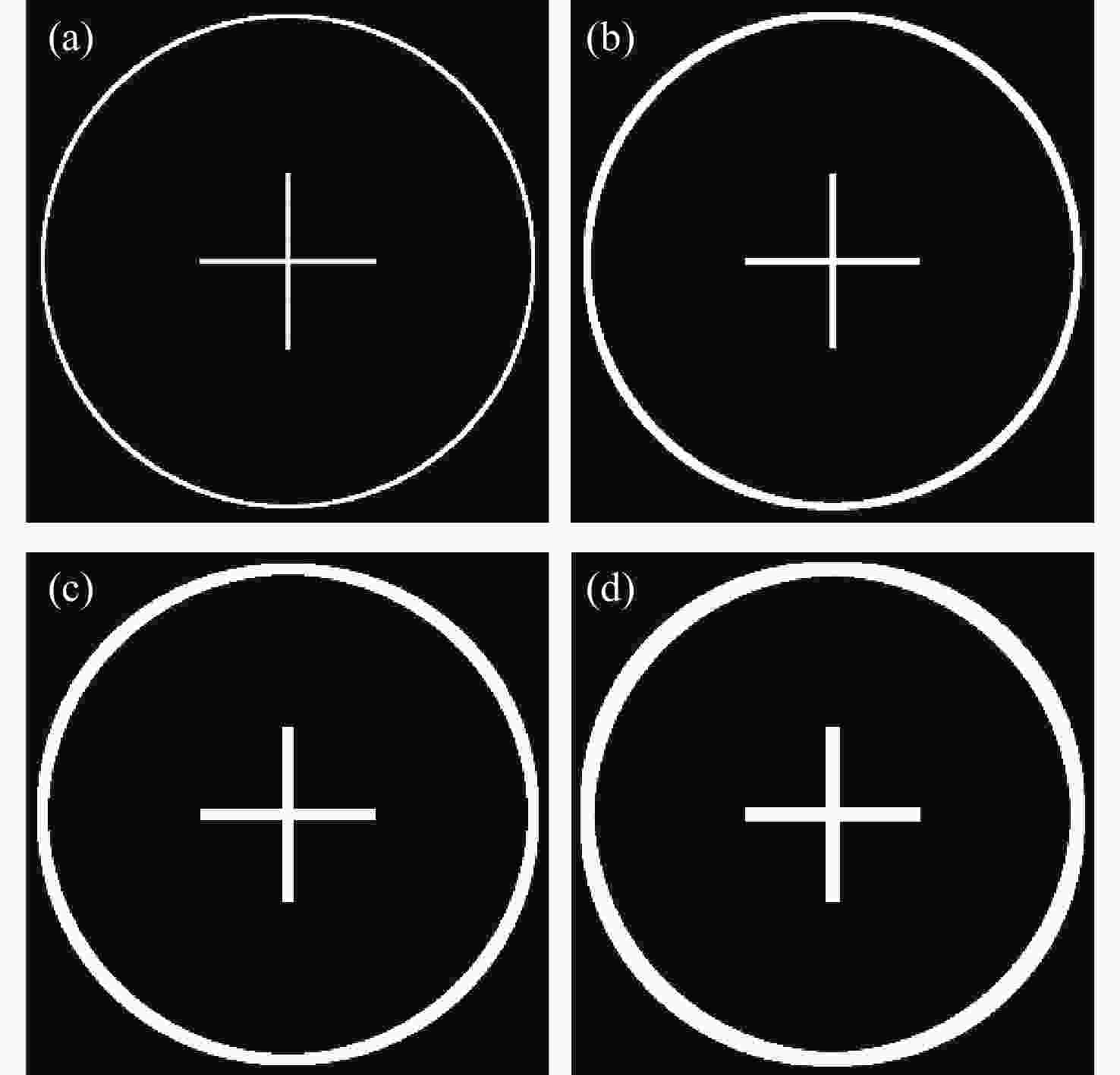
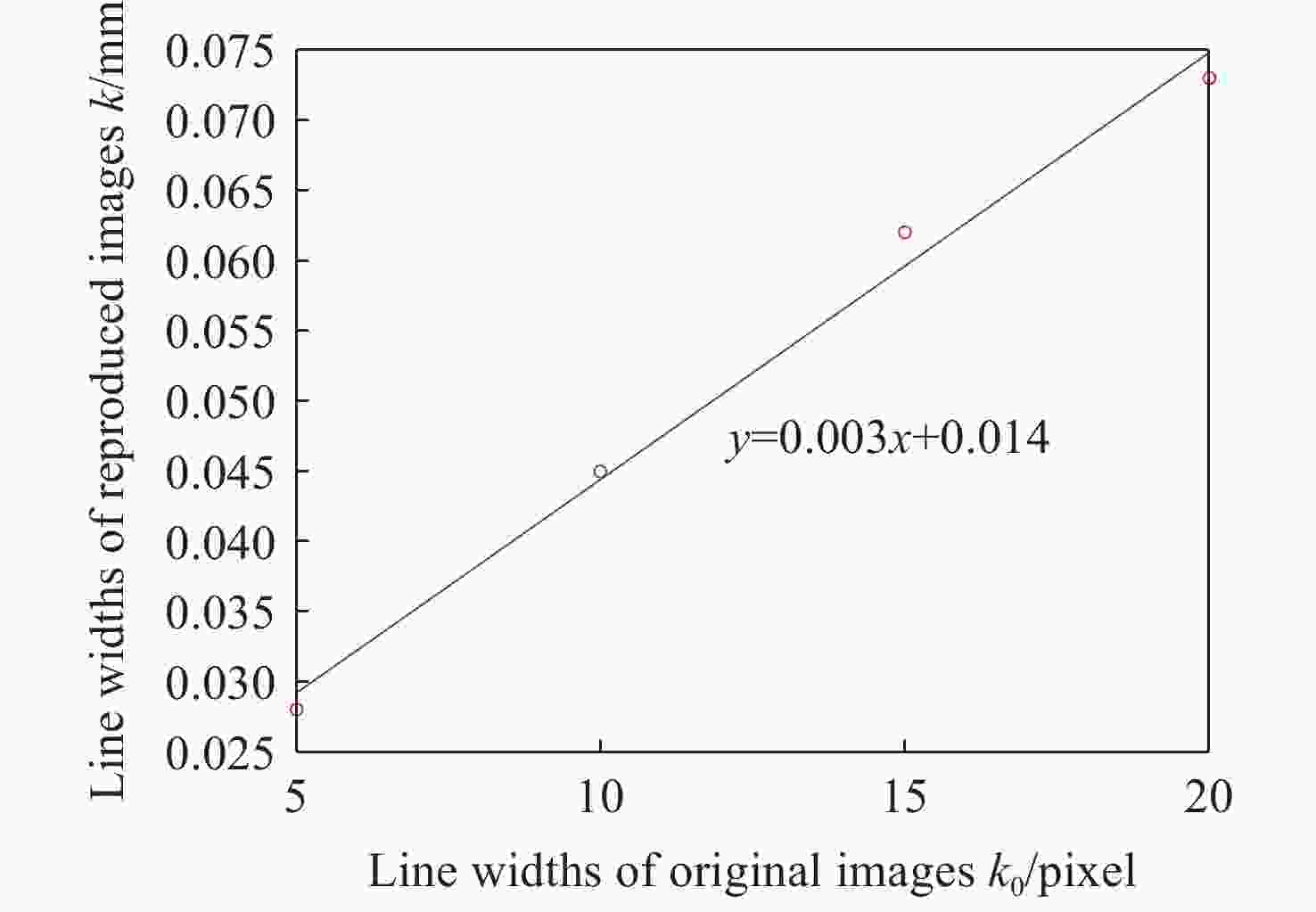
表 1 不同原始图像线宽对应的仿真再现图像线宽值
Table 1. Line widths of simulated reproduction images corresponding to line widths of different original images
Line width of the original
images k0 (pixel)Line width of the simulated
reproduction images (pixel)Fitting
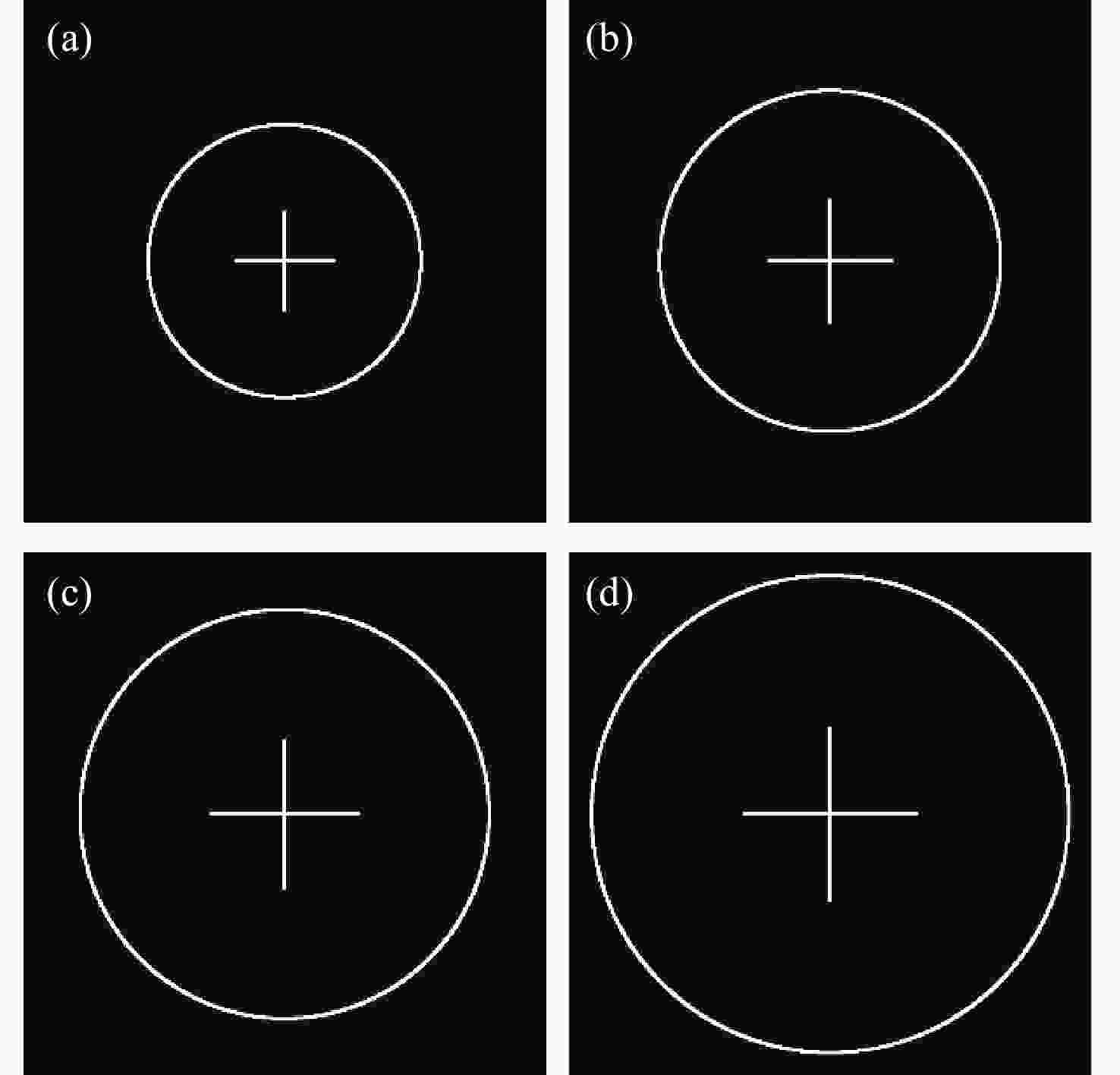
slope5 5 1 10 10 15 15 20 20 表 2 不同原始图像圆环直径对应的仿真再现图像圆环直径
Table 2. Simulated reproduction image ring diameters corresponding to different original image ring diameters
Ring diameter of the
original images D0 (pixel)Ring diameter in simulated
reproduction images (pixel)Fitting
slope400 400 1 500 500 600 600 700 700 表 3 不同采样间隔对应的仿真再现图像圆环直径值
Table 3. Simulated reproduction image ring diameters corresponding to different sampling intervals
Ring diameter
of original
imagesSampling
coefficient
NSampling
interval d
(μm)Ring diameter of
simulated reproduction
images (pixel)Fitting
slope700 1 12.5 700 1 2 25 350 1/2 4 50 175 1/4 8 100 87 1/8 表 4 LC-SLM的工作参数
Table 4. Operating parameters of LC-SLM
Parameter Parameter value Effective area size 12.8 mm×9.6 mm Number of pixels 1024×768 Pixel size 12.5 μm×12.5 μm Pixel pitch 12.5 μm Fill factor 80% Gray scale range 0~255 表 5 CCD相机及成像镜头的工作参数
Table 5. Operating parameters of CCD cameras and imaging lens
Parameter Parameter value Camera operating
parametersNumber of pixels 2048×1536 Pixel size 2.8 μm×2.8 μm Lens operating
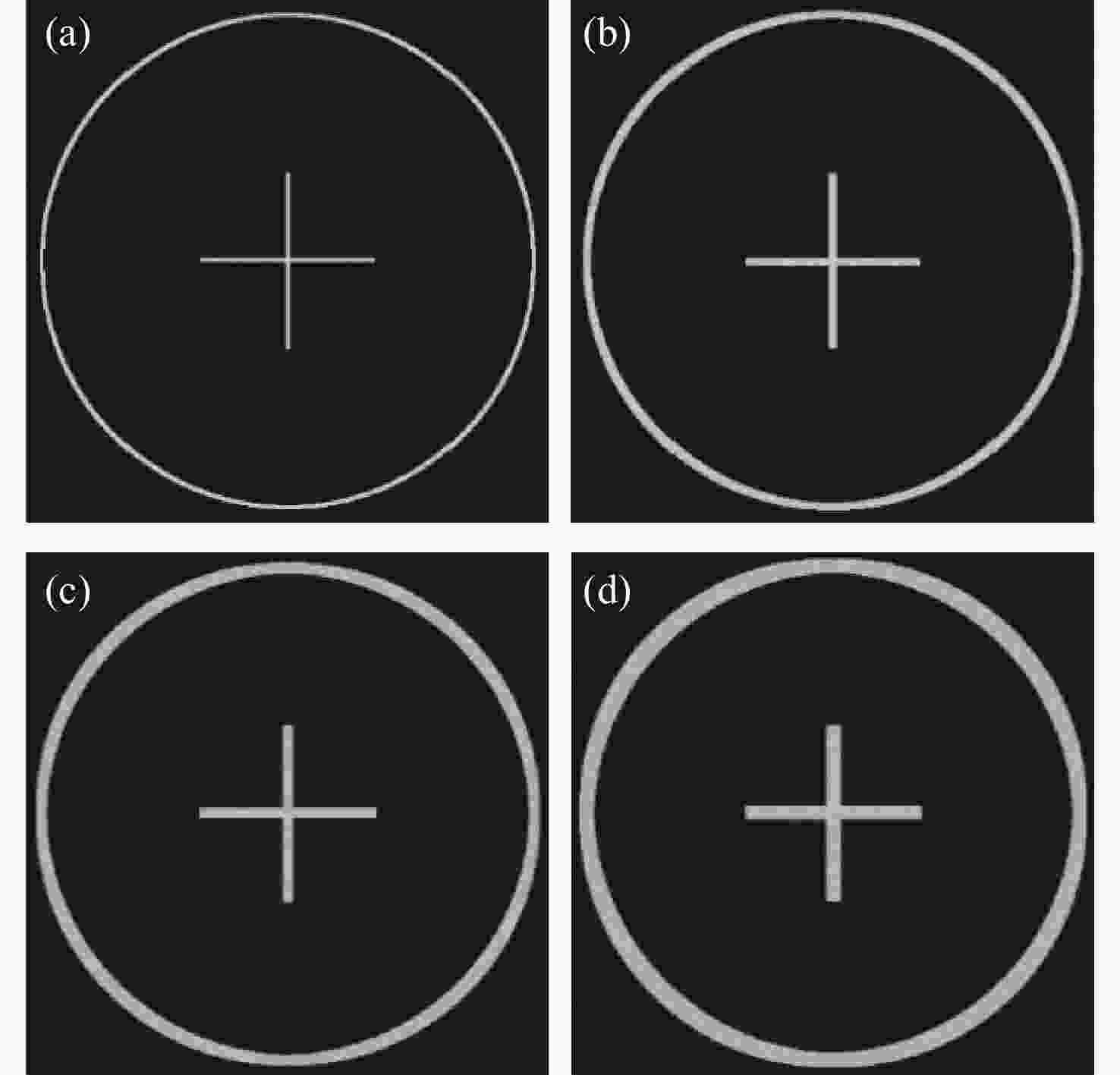
parametersFocal length 50 mm Aperture range F/1.8~F/10 表 6 实验测试的不同原始图像线宽对应的再现图像线宽值
Table 6. Reproduction image line widths corresponding to different original image line widths tested experimentally
Line width of the
original images
k0 (pixel)Line width of the
reproduction images
in pixels (pixel)Line width of the
reproduction images
k (mm)Fitting
slope
(mm/pixel)5 10 0.0280 0.0030 10 16 0.0450 15 22 0.0620 20 26 0.0730 表 7 实验测试的不同原始图像圆环直径对应的再现图像圆环直径值
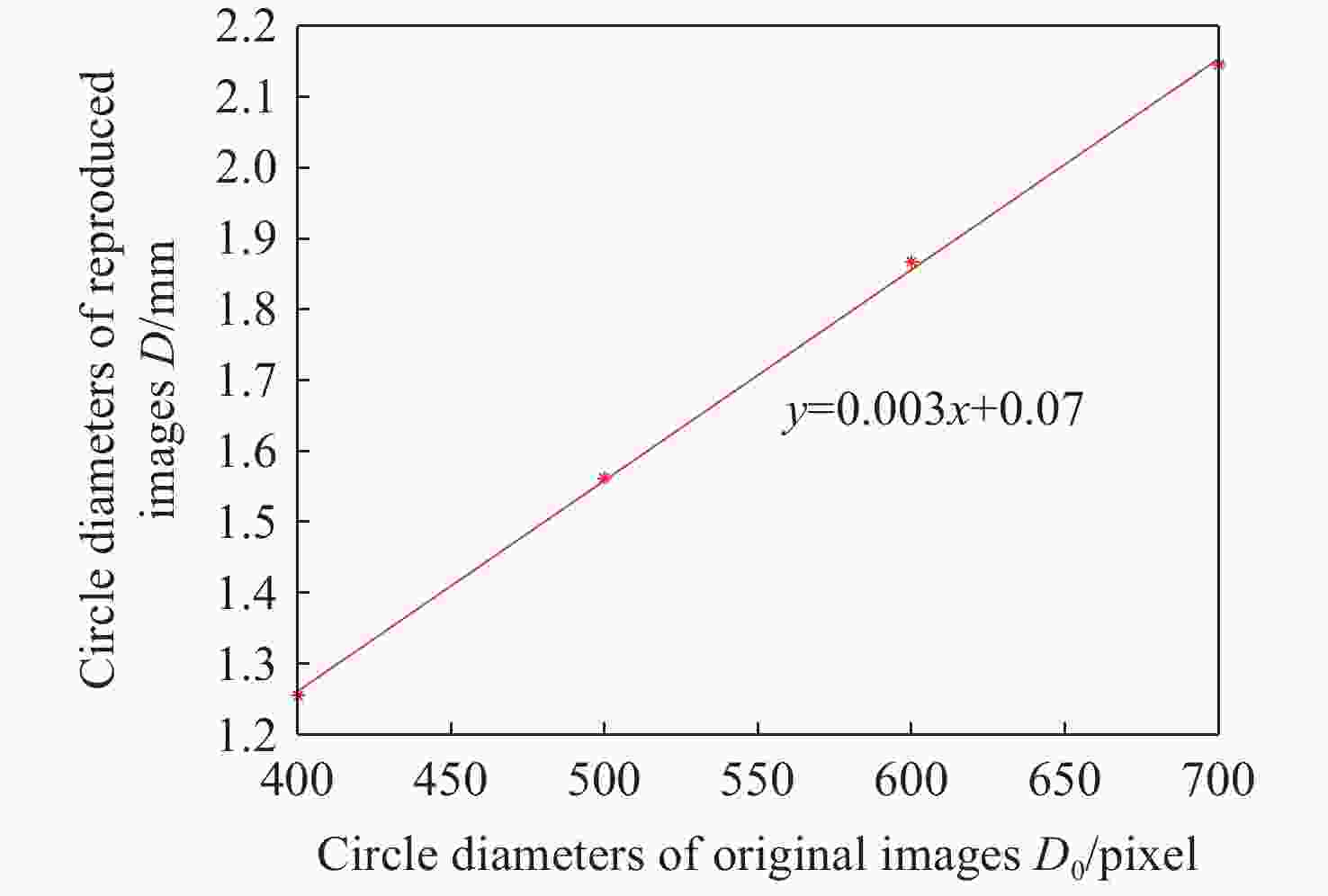
Table 7. Ring diameters of the reproduction images corresponding to the ring diameters of the different original images tested experimentally
Ring diameter of
the original images
D0 (pixel)Pixel occupied by
ring diameters in
reproduction
images (pixel)Ring diameter of
reproduction images
D (mm)Fitting
slope
(mm/pixel)400 448 1.2544 0.0030 500 558 1.5624 600 667 1.8676 700 766 2.1448 表 8 实验测试的不同采样间隔对应的再现图像圆环直径值
Table 8. The ring diameters values of the reproduction images corresponding to the different sampling intervals tested experimentally
Sampling
coefficient
NSampling
interval d
(μm)Pixel occupied by ring
diameters of reproduction
images (pixel)Ring diameter of
reproduction images
D (mm)1 12.5 702 2.1448 2 25 396 1.1088 4 50 241 0.6748 8 100 162 0.4536 -
[1] GABOR D. A new microscopic principle[J]. Nature, 1948, 161(4098): 777-778. doi: 10.1038/161777a0 [2] GOODMAN J W, LAWRENCE R W. Digital image formation from electronically detected holograms[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1967, 11(3): 77-79. doi: 10.1063/1.1755043 [3] LOHMANN A W, PARIS D P. Binary fraunhofer holograms, generated by computer[J]. Applied Optic, 1967, 6(10): 1739-1748. doi: 10.1364/AO.6.001739 [4] GERCHBERG R W, SAXTON W O. A practical algorithm for the determination of phase from image and diffraction plane pictures[J]. Optik, 1972, 35(2): 237-246. [5] 王晓诗. 基于迭代的高质量纯相位全息图生成算法[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2023.WANG X SH. The algorithm based on iteration for generation of phase-only hologram with high quality[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science & Technology, 2023. (in Chinese). [6] 高乾程. 基于相位优化的计算全息显示研究[D]. 芜湖: 安徽工程大学, 2023.GAO Q CH. Research on computer-generated holographic display based on phase optimizatio[D]. Wuhu: Anhui Polytechnic University, 2023. (in Chinese). [7] 刘珂瑄, 吴佳琛, 何泽浩, 等. 基于深度学习的计算全息显示进展[J]. 液晶与显示,2023,38(6):819-828. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2023-0081LIU K X, WU J CH, HE Z H, et al. Progress of learning-based computer-generated holography[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2023, 38(6): 819-828. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2023-0081 [8] 唐旭. 关于计算全息显示中散斑降噪方法研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌航空大学, 2023.TANG X. Research on speckle noise reduction method in computational holographic display[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang Hangkong University, 2023. (in Chinese). [9] 邬明仁. 基于扩散模型的计算全息方法研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2024.WU M R. Research on computer-generated holography method based on diffusion model[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2024. (in Chinese). [10] 高云舒. 基于液晶空间光调制器的可编程波长选择开关的技术研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2020.GAO Y SH. Research on programmable wavelength selective switch based on liquid crystal spatial light modulator[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2020. (in Chinese). [11] KOLLIN J S, BENTON S A, JEPSEN M L. Real-time display of 3-D computed holograms by scanning the image of an acousto-optic modulator[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1989, 1136: 178-185. doi: 10.1117/12.961683 [12] SANDO Y, BARADA D, YATAGAI T. Full-color holographic 3D display with horizontal full viewing zone by spatiotemporal-division multiplexing[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(26): 7622-7626. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.007622 [13] BUSKE P, HOFMANN O, BONNHOFF A, et al. High fidelity laser beam shaping using liquid crystal on silicon spatial light modulators as diffractive neural networks[J]. Optics express, 2024, 32(5): 7064-7078. doi: 10.1364/OE.507630 [14] MINIKHANOV T Z, ZLOKAZOV E Y, STARIKOV R S, et al. Phase modulation time dynamics of the liquid-crystal spatial light modulator[J]. Measurement Techniques, 2024, 66(12): 935-939. doi: 10.1007/s11018-024-02309-x [15] MA B H, YAO B L, LI Z, et al. Generation of three-dimensional optical structures by dynamic holograms displayed on a twisted nematic liquid crystal display[J]. Applied Physics B, 2013, 110(4): 531-537. doi: 10.1007/s00340-012-5289-x [16] ZHU W X, GAO F L, FU Q Q, et al. Multi-mode vector light field generation using modified off-axis interferometric holography and liquid crystal spatial light modulators[J]. Photonics, 2023, 11(1): 33. doi: 10.3390/photonics11010033 [17] 肖瑞. 基于全息光学元件的增强现实三维显示[D]. 北京: 北京邮电大学, 2023.XIAO R. Augmented reality 3D display based on holographic optical element[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2023. (in Chinese). [18] XU K, LI X R. Light field modulation algorithms for spatial light modulators: a review[J]. Current Nanoscience, 2024, 21(2): 182-200. doi: 10.2174/0115734137276125231201113602 [19] 马宁涛. 计算全息再现像质量提升技术的研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州轻工业大学, 2023.MA N T. Research on quality improvement technology of computer-generated holographic image[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University of Light Industry, 2023. (in Chinese). [20] 王化宾, 何渝, 赵立新. 基于改进Gerchberg-Saxton算法的全息双面光刻方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2023,60(16):1609001.WANG H B, HE Y, ZHAO L X. Holographic double-sided photolithography based on improved gerchberg-saxton algorithm[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(16): 1609001. (in Chinese). [21] CHEN Q, TANG M Y, SUN CH L, et al. 83-3: inverse design of liquid crystal phase modulators for 2D/3D switchable display based on deep learning[J]. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, 2024, 55(1): 1159-1162. doi: 10.1002/sdtp.17745 [22] 武耀霞. 相位型全息分划板的复制技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安工业大学, 2019.WU Y X. Research on replication technology of phase holographic reticle[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an Technological University, 2019. (in Chinese). [23] 林培秋. 基于纯相位型液晶空间光调制器的相息图三维显示的研究[D]. 金华: 浙江师范大学, 2010.LIN P Q. Study on three-dimensional display from kinoform based phase-only liquid crystal spatial light modulator[D]. Jinhua: Zhejiang Normal University, 2010. (in Chinese). [24] 颜树华. 衍射微光学设计[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2011.YAN SH H. Design of Diffractive Micro-optics[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2011. (in Chinese). [25] 吴嘉元, 韩军, 王谦豪, 等. 利用达曼光栅灰度图去除零级光干扰[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2024,61(4):185-192.WU J Y, HAN J, WANG Q H, et al. Removal of zero-order beam interference using Dammann grating grayscale map[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2024, 61(4): 185-192. (in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: