-
摘要:
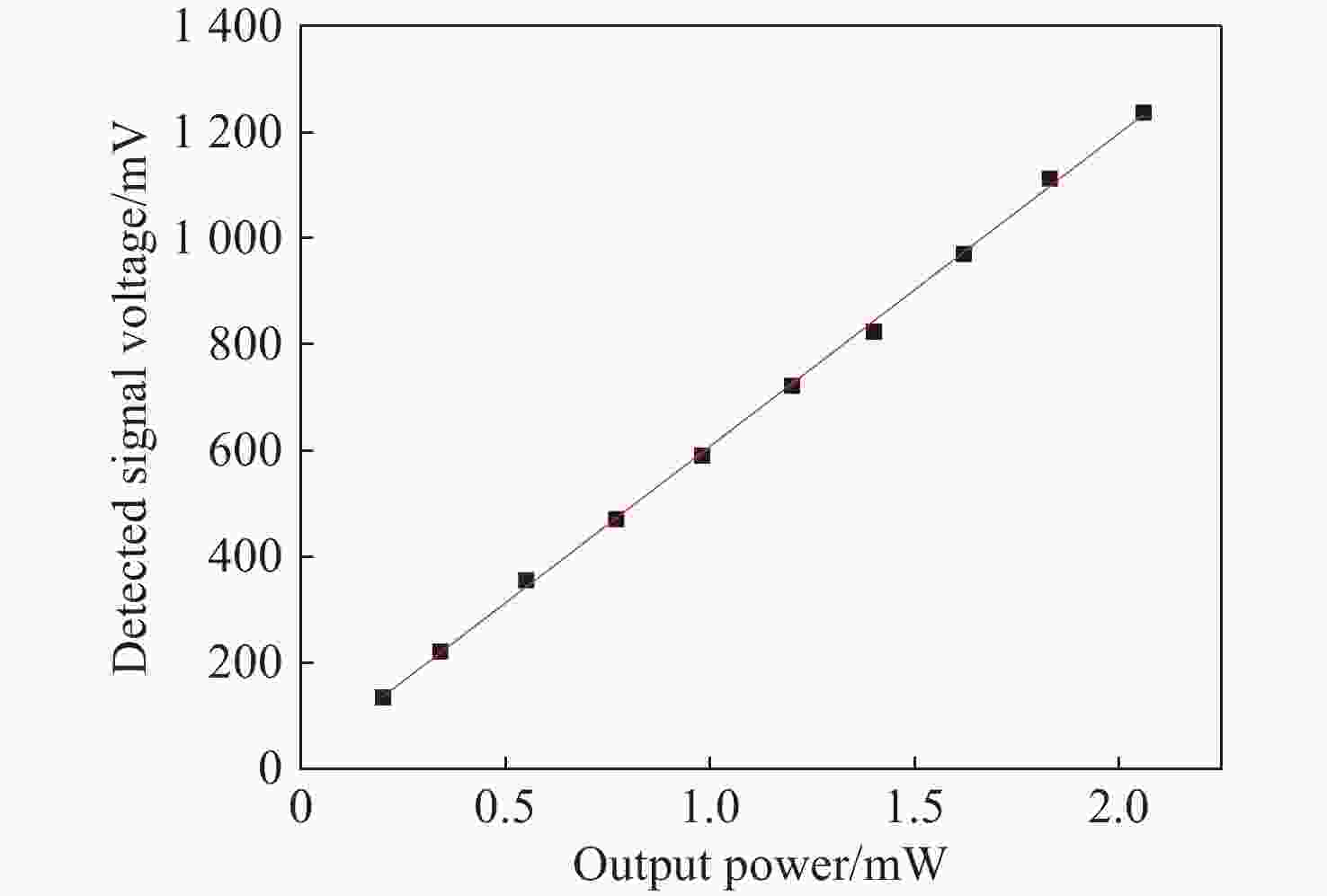
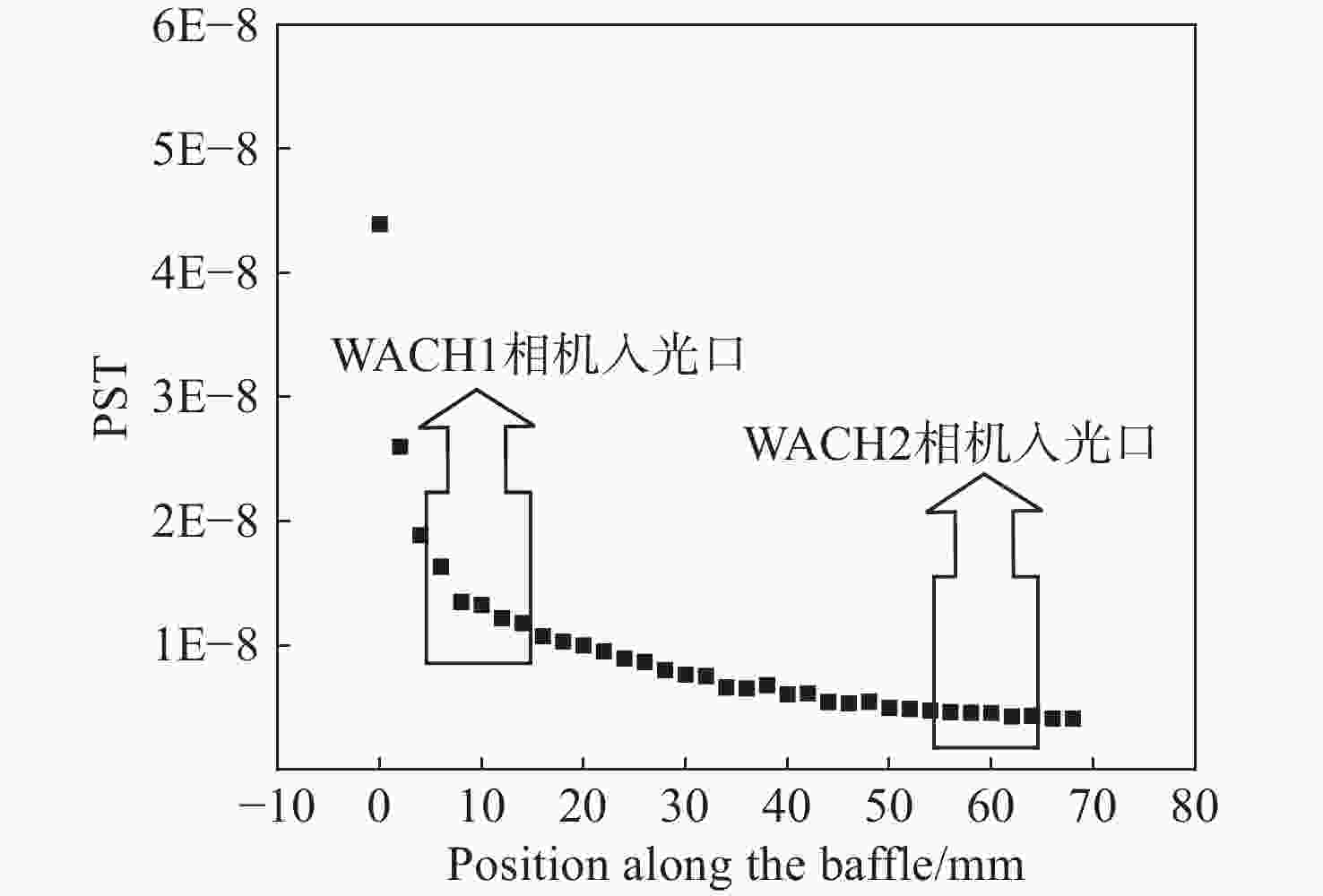
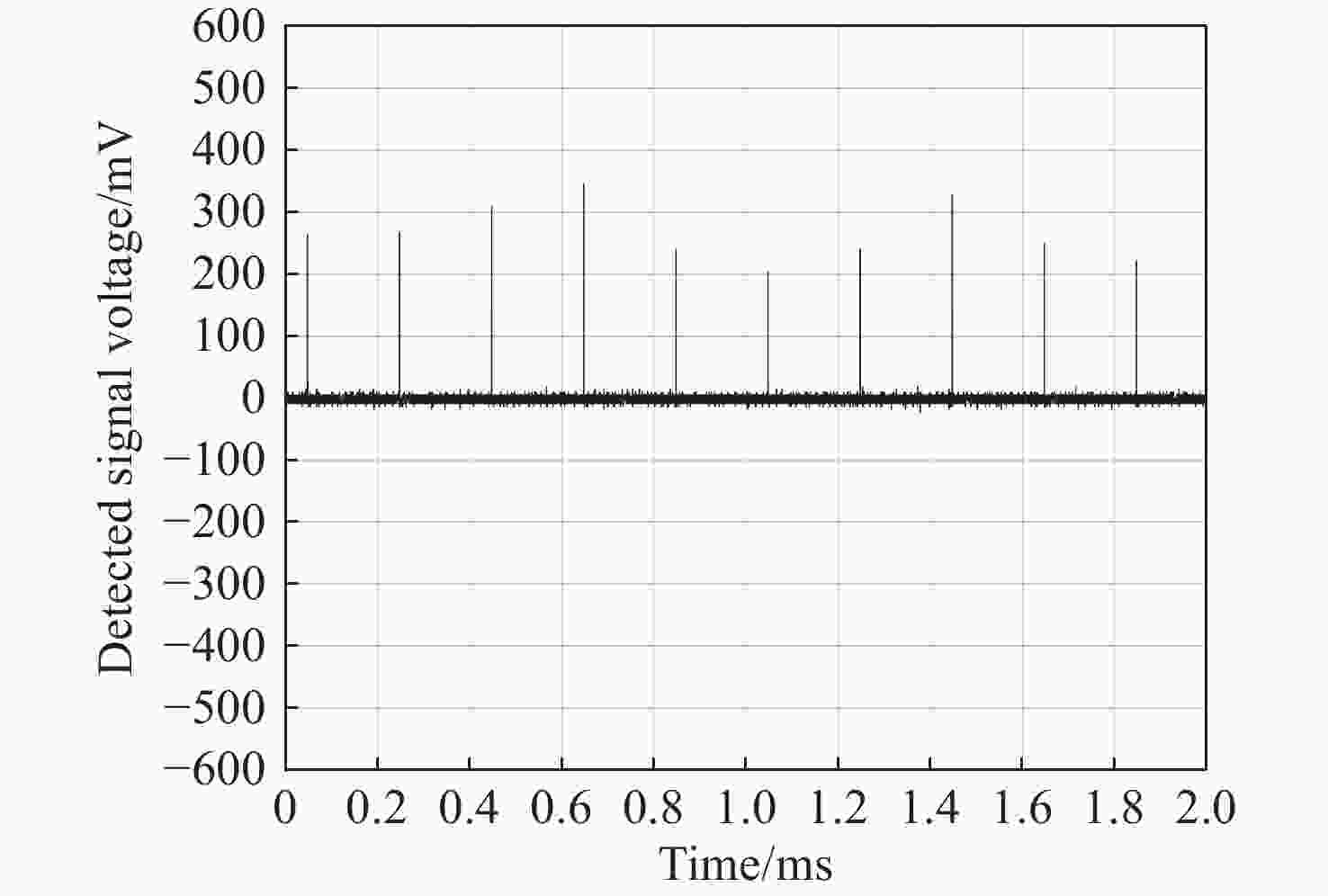
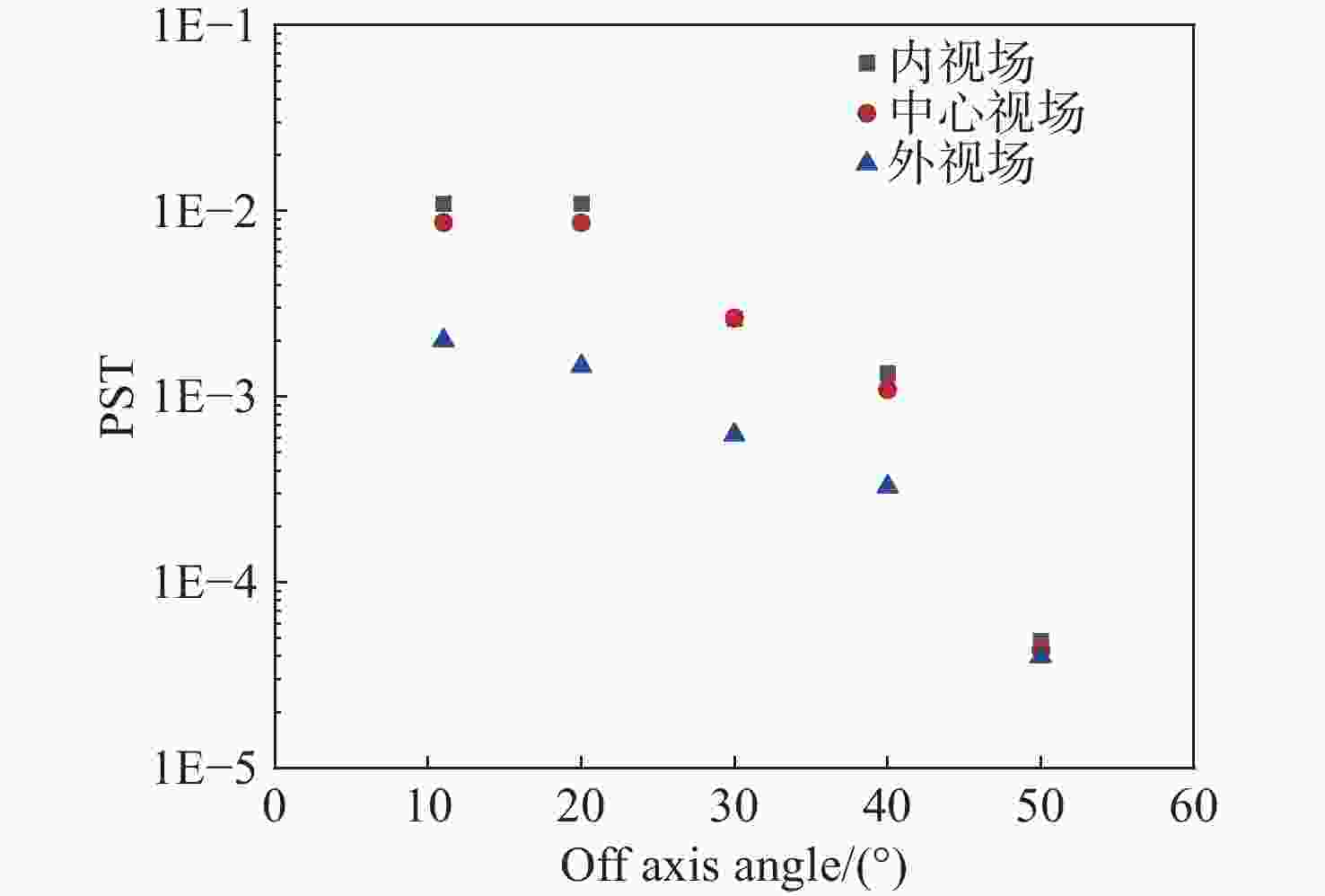
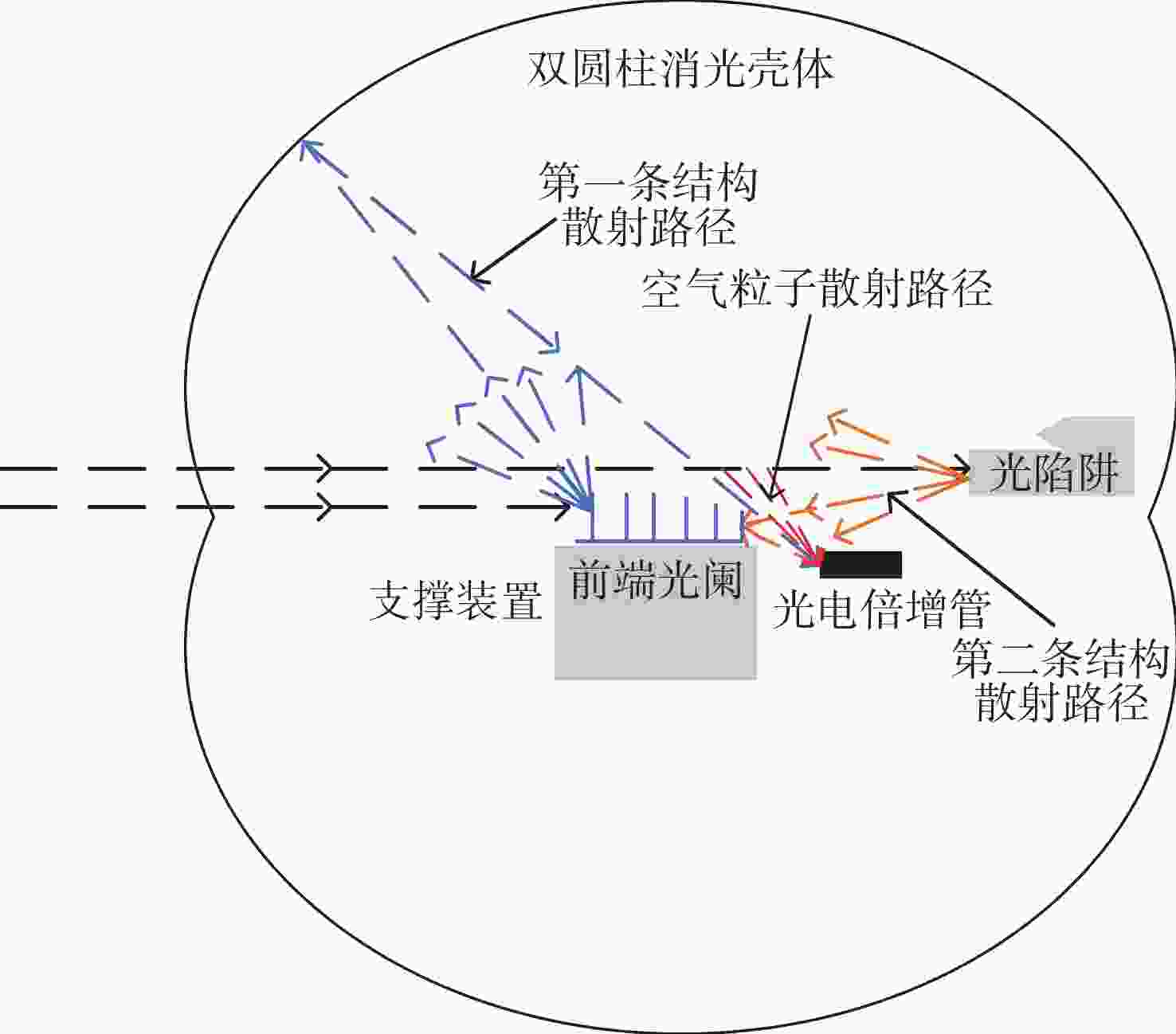
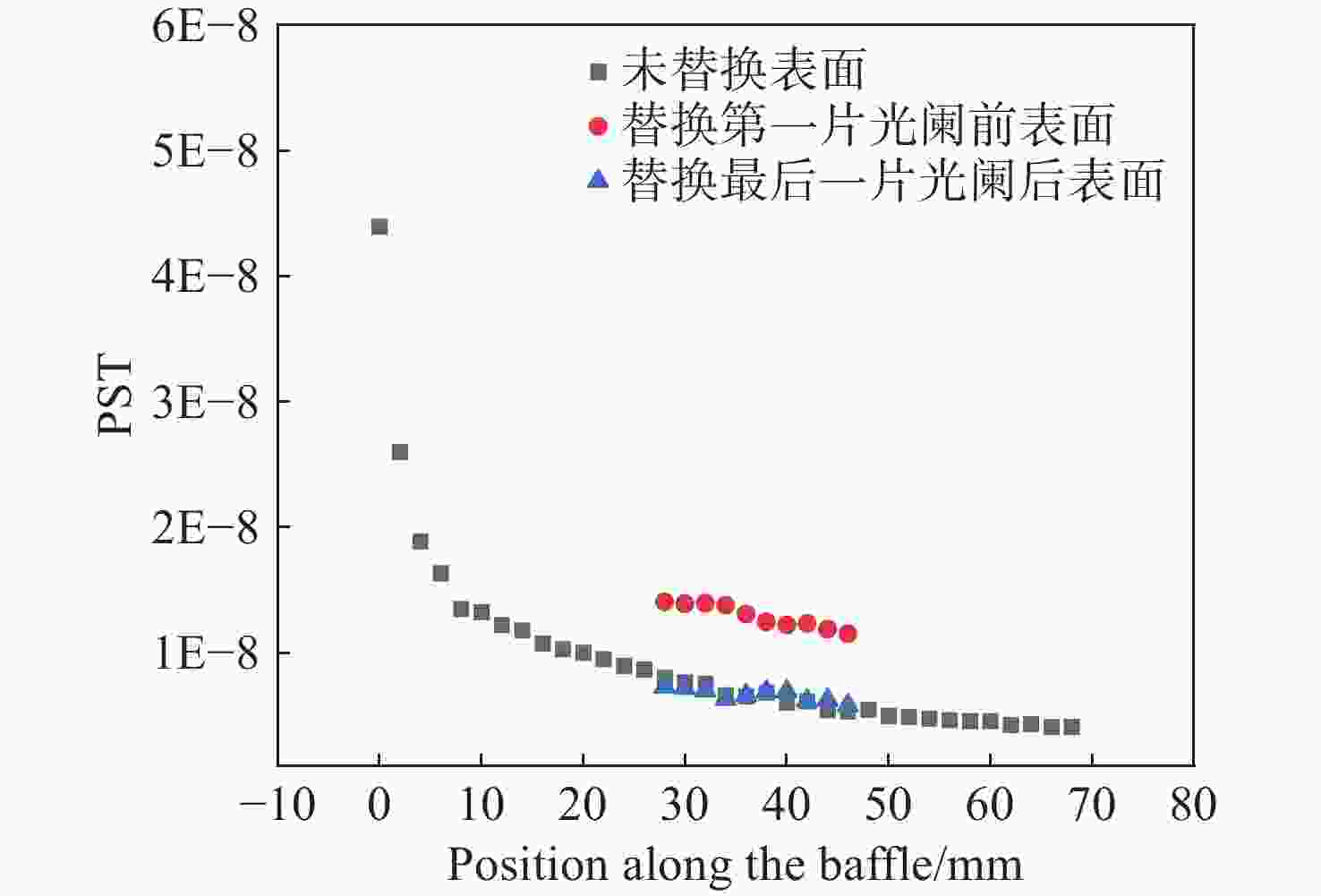
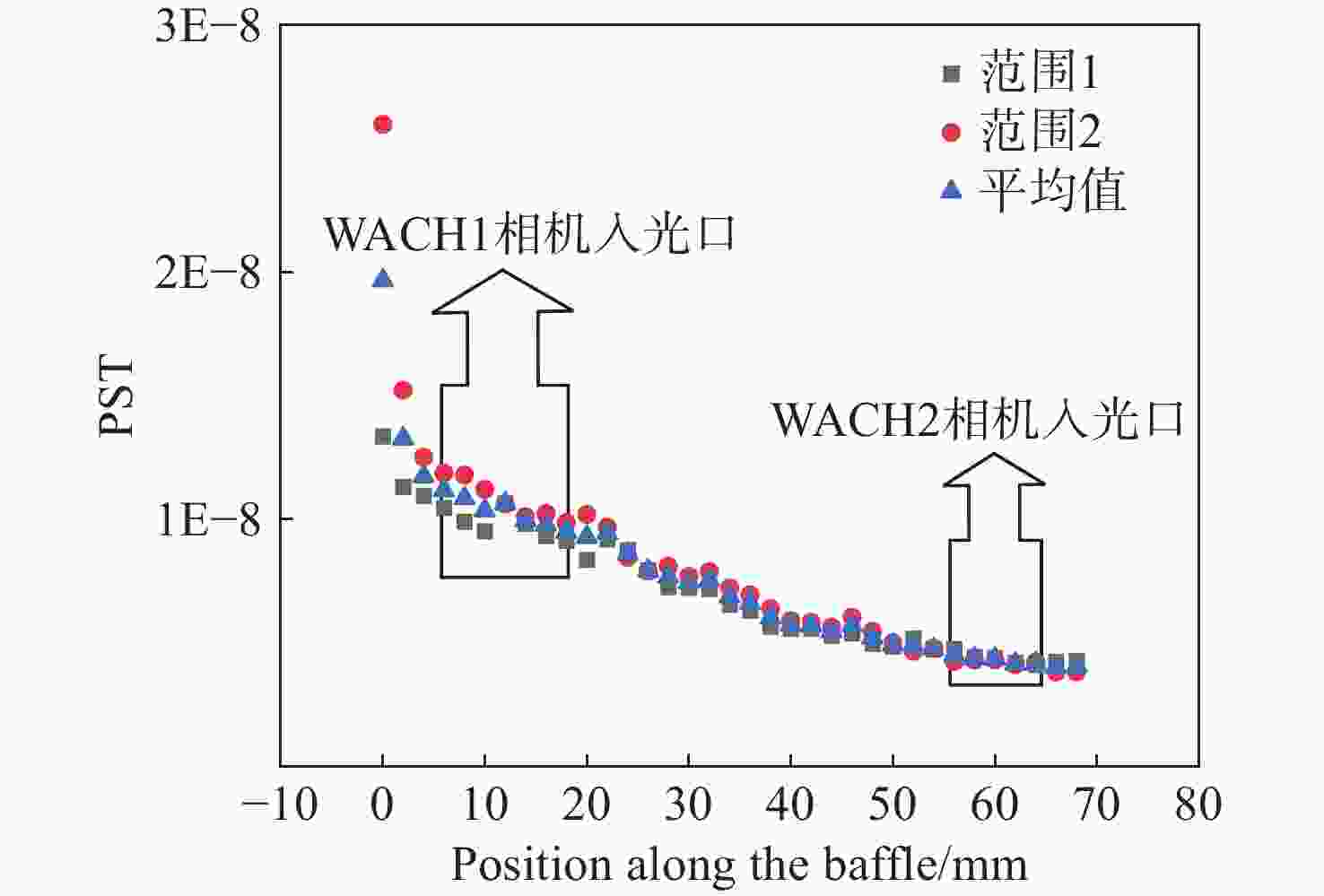
为了对日球成像仪太阳杂光抑制能力进行定量化评价,开展了日球成像仪太阳杂光抑制能力的测试方法研究和实验验证。提出了一种通过将前端光阑与相机进行分段测试,进而实现在实验室条件下测试日球成像仪太阳杂光抑制能力的方法,避免了真空测试环境下空间受限引起的结构散射误差对测试精度的影响问题。利用该方法在实验室条件下对一台日球成像仪太阳杂光抑制能力进行测试。测试结果表明:日球成像仪前端光阑的PST在WACH1相机处为1.4×10−8,在WACH2处为4.3×10−9。对测试结果进行误差分析,其中随机误差为21.6%,系统误差导致WACH1处PST测试误差为1.1×10−8,在WACH2处为4.2×10−9,测试精度满足高杂光抑制比的日球成像仪测试要求,证明了该测试方法的可行性和准确性。本文研究为日球成像仪太阳杂光抑制能力测试提供了一种新的途径。
Abstract:In order to quantitatively assess the solar stray light suppression capability of the heliospheric imager, a testing approach and experimental validation were investigated. In this paper, we proposed a method to test the solar stray light suppression capability of the heliospheric imager under laboratory circumstances by conducting segmented tests of the front-end baffle and the camera. This approach circumvented the issue that the structural scattering caused by the test under vacuum conditions would be overly large and influence the accuracy of the test results. The proposed method was then employed to assess the effectiveness of a heliospheric imager in suppressing solar stray light under laboratory conditions. The experimental results indicate that the PST of the front-end diaphragm of the heliosphere imager is 1.4×10−8 at WACH1 and 4.3×10−9 at WACH2. The error analysis of the test results reveal that the random error is 21.6%, and the PST resulting from the sum of system errors is 1.1×10−8 at WACH1 and 4.2×10−9 at WACH2. The test accuracy meets the requirements, demonstrating the feasibility and accuracy of the test method. The study presented in this paper offers a novel means to test the solar stray light suppression capability of heliospheric imager.
-
Key words:
- heliospheric imager /
- stray light test /
- error analysis
-
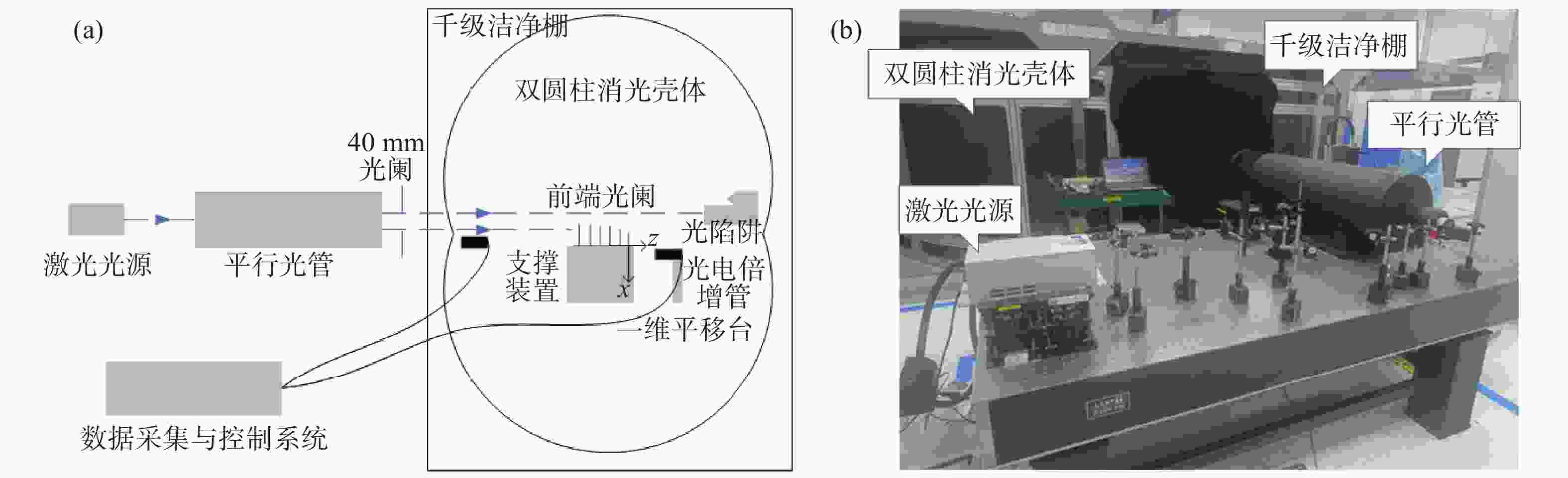
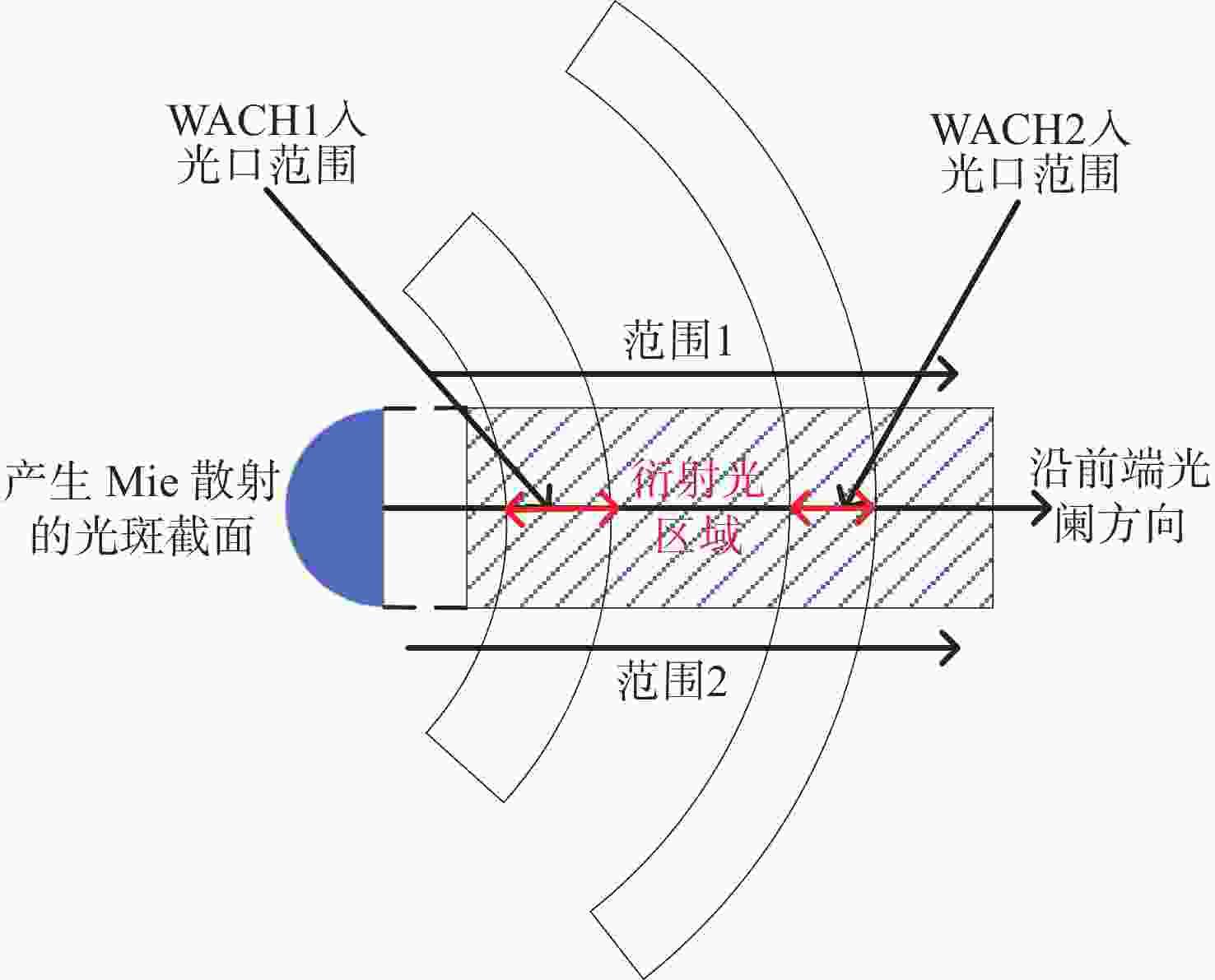
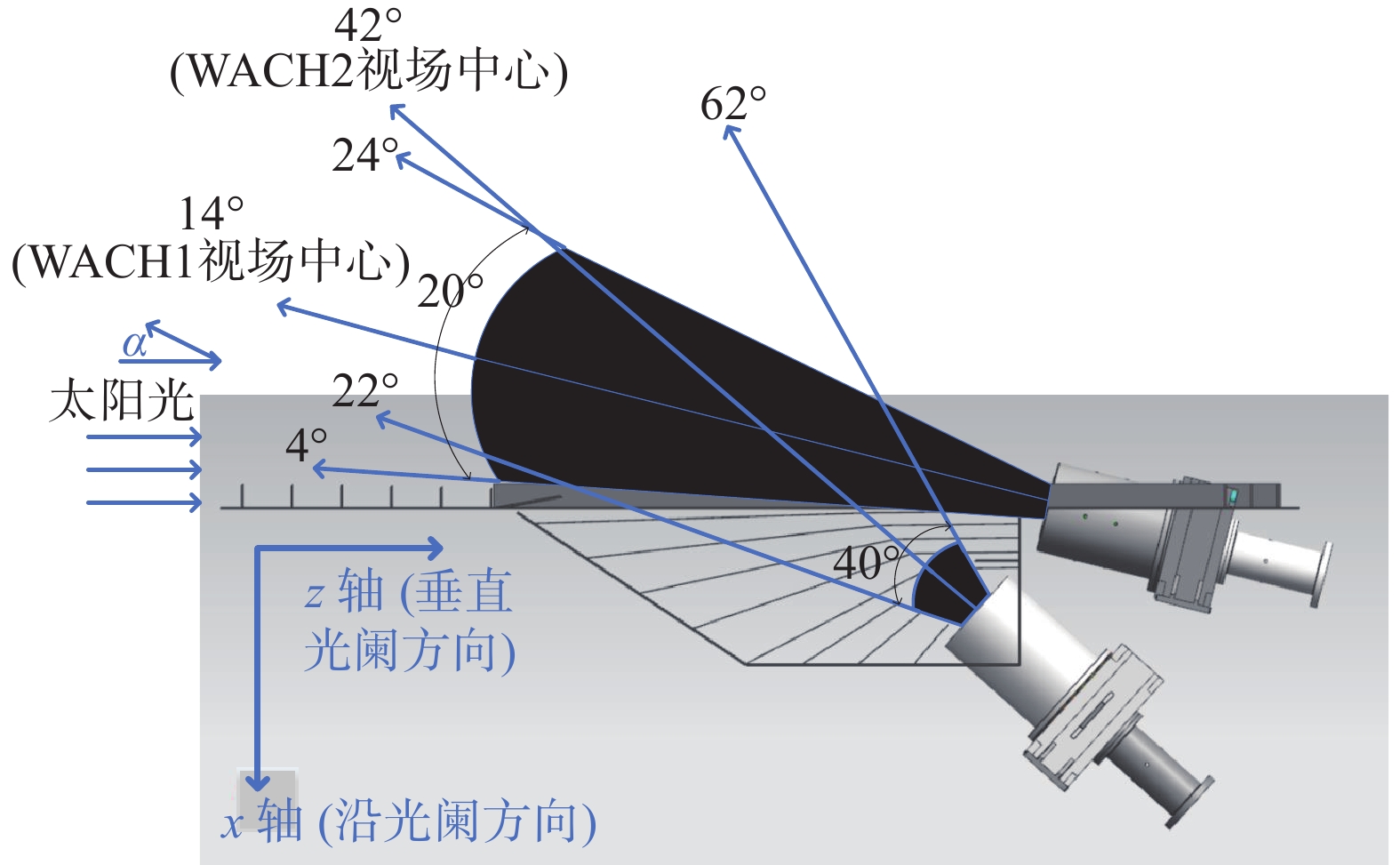
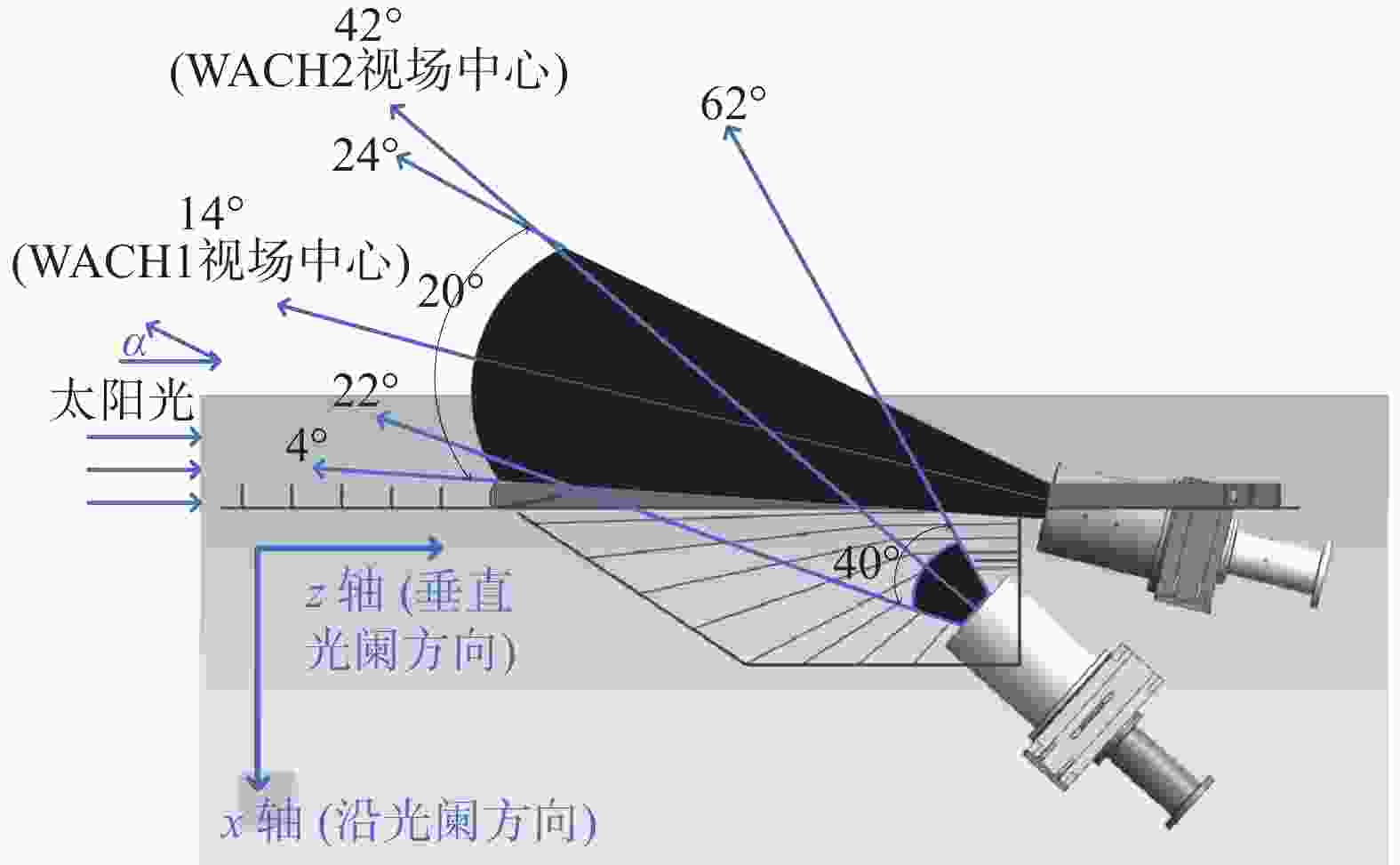
图 1 本文所测试的日球层成像仪示意图,其中蓝色箭头所指角度均为相机视场边缘或视场中心与太阳光线的夹角,WACH1全视场角为20°,WACH2全视场角为40°
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the heliospheric imager tested in this paper. The angles indicated by the blue arrows are the angles between the edge of the camera's field of view or the center of the field of view and the sun's rays. The WACH1 full field of view is 20°, and the WACH2 full field of view is 40°
-
[1] DEFISE J M, HALAIN J P, MAZY E, et al. Design of the heliospheric imager for the STEREO mission[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2001, 4498: 63-72. doi: 10.1117/12.450079 [2] ZIMBARDO G, YING B, NISTICÒ G, et al. A high-latitude coronal mass ejection observed by a constellation of coronagraphs: solar orbiter/metis, STEREO-A/COR2, and SOHO/LASCO[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2023, 676: A48. [3] BRAGA C R, VOURLIDAS A, LIEWER P C, et al. Coronal mass ejection deformation at 0.1 au observed by WISPR[J]. Astrophysical Journal, 2022, 938: 13. doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ac90bf [4] 徐亮. 大口径光学系统杂散光测试关键技术研究[D]. 西安: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所), 2019.XU L. Research on key techniques of stray light measurement for large aperture optical systems[D]. Xi’an: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Xi’an Institute of Optics & Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2019. (in Chinese). [5] 王虎, 陈钦芳, 马占鹏, 等. 杂散光抑制与评估技术发展与展望(特邀)[J]. 光子学报,2022,51(7):0751406. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20225107.0751406WANG H, CHEN Q F, MA ZH P, et al. Development and prospect of stray light suppression and evaluation technology (invited)[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2022, 51(7): 0751406. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/gzxb20225107.0751406 [6] GROCHOCKI F, FLEMING J. Stray light testing of the OLI telescope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7794: 77940W. doi: 10.1117/12.862225 [7] FAN X W, ZOU G Y, QIU Y L, et al. Optical design of the visible telescope for the SVOM mission[J]. Applied Optics, 2020, 59(10): 3049-3057. doi: 10.1364/AO.386177 [8] EYLES C J, HARRISON R A, DAVIS C J, et al. The heliospheric imagers onboard the STEREO mission[J]. Solar Physics, 2009, 254(2): 387-445. doi: 10.1007/s11207-008-9299-0 [9] VOURLIDAS A, HOWARD R A, PLUNKETT S P, et al. The wide-field imager for solar probe plus (WISPR)[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2016, 204(1): 83-130. [10] 冷荣宽, 王上, 王智, 等. 空间引力波探测前向杂散光测量和抑制[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(5):1081-1088. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0251LENG R K, WANG SH, WANG ZH, et al. Measurement and suppression of forward stray light for spaceborne gravitational wave detection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(5): 1081-1088. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0251 [11] THERNISIEN A F R, HOWARD R A, KORENDYKE C, et al. Stray light analysis and testing of the SoloHI (solar orbiter heliospheric imager) and WISPR (wide field imager for solar probe) heliospheric imagers[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10698: 106980E. [12] ZHANG T Y, GAO T Y, WANG D, et al. Calculation of diffraction by a multi-vane baffle based on boundary wave diffraction theory[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2024, 13189: 1318911. [13] 王维, 陆琳, 张天一, 等. 10−9量级高灵敏度点源透射比测试设备研究[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(2):390-396. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0050WANG W, LU L, ZHANG T Y, et al. A 10−9-order point source transmission test facility[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(2): 390-396. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0050 [14] 曹智睿, 付跃刚, 田浩. 空气洁净度对点源透射比测试准确度的影响[J]. 光子学报,2016,45(1):0112002. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20164501.0112002CAO ZH R, FU Y G, TIAN H. The impact for the air cleanliness to the precision of PST test[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2016, 45(1): 0112002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/gzxb20164501.0112002 [15] 曾瑾, 王战虎, 李欣耀, 等. 基于双柱罐结构的三波段杂散光PST测试装置[J]. 红外,2017,38(4):12-16,22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8785.2017.04.003ZENG J, WANG ZH H, LI X Y, et al. Three-band stray-light test facility for point source transmission based on double cylindrical chamber[J]. Infrared, 2017, 38(4): 12-16,22. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8785.2017.04.003 [16] 肖鹏益, 刘铭鑫, 闫磊, 等. 鬼像影响下的调制传递函数计算模型[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(5):1183-1191.XIAO P Y, LIU M X, YAN L, et al. An MTF calculation model under the influence of ghost images[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(5): 1183-1191. (in Chinese). [17] KEMP J C, WYATT C L. Terrestrial measurement of the performance of high-rejection optical baffling systems[J]. Optical Engineering, 1977, 16: 412-416. -





 下载:
下载: