-
摘要:
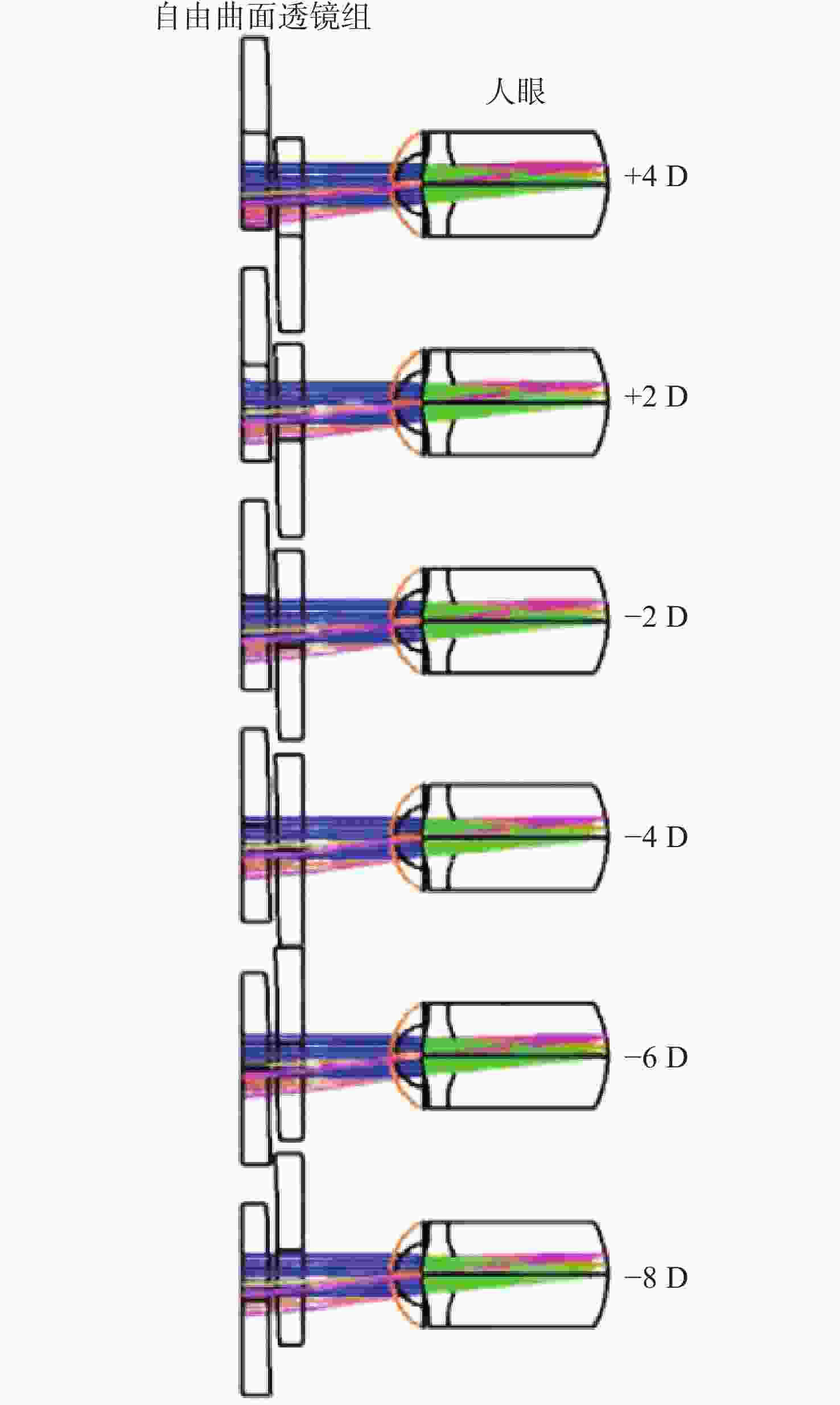
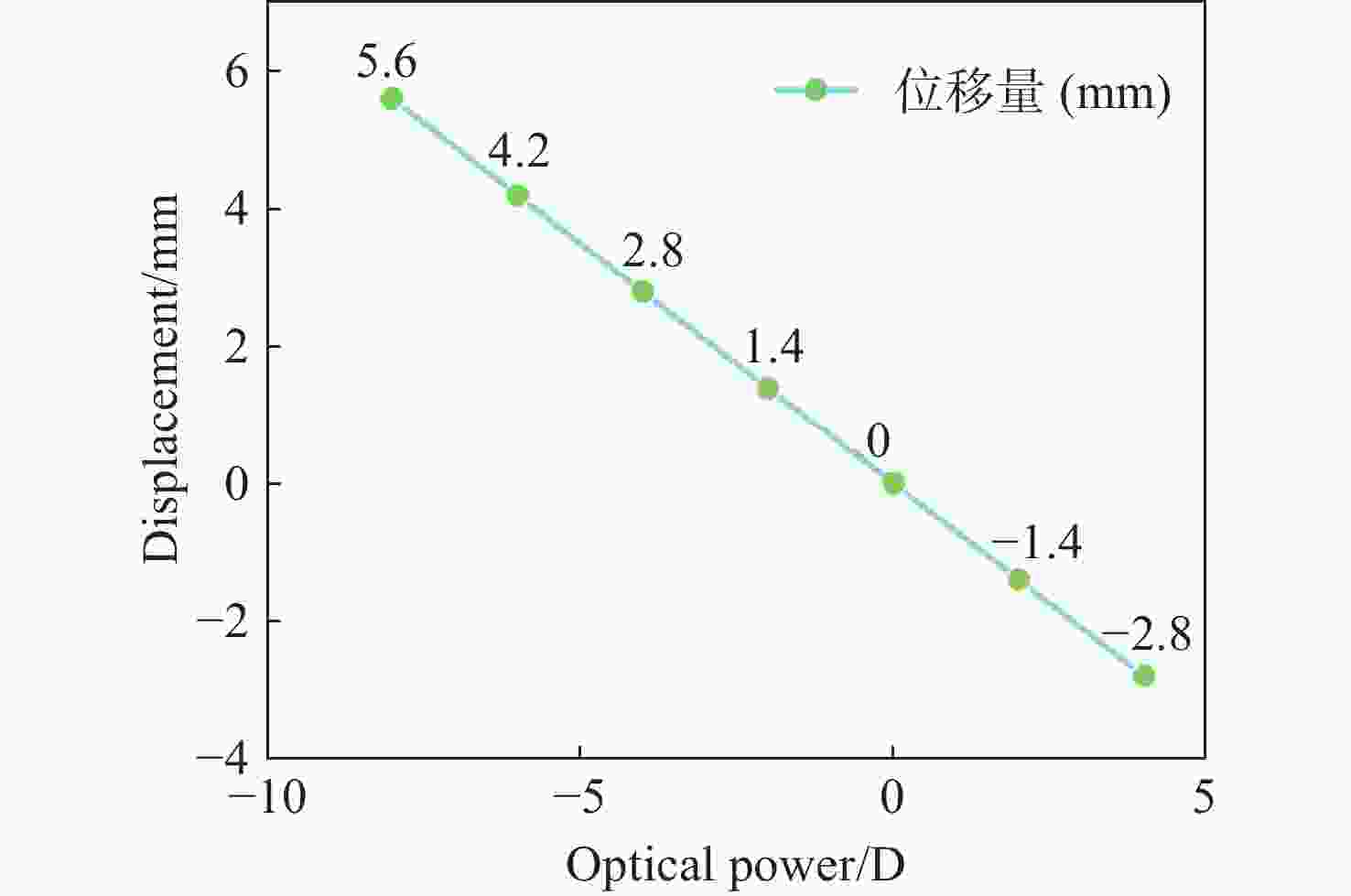
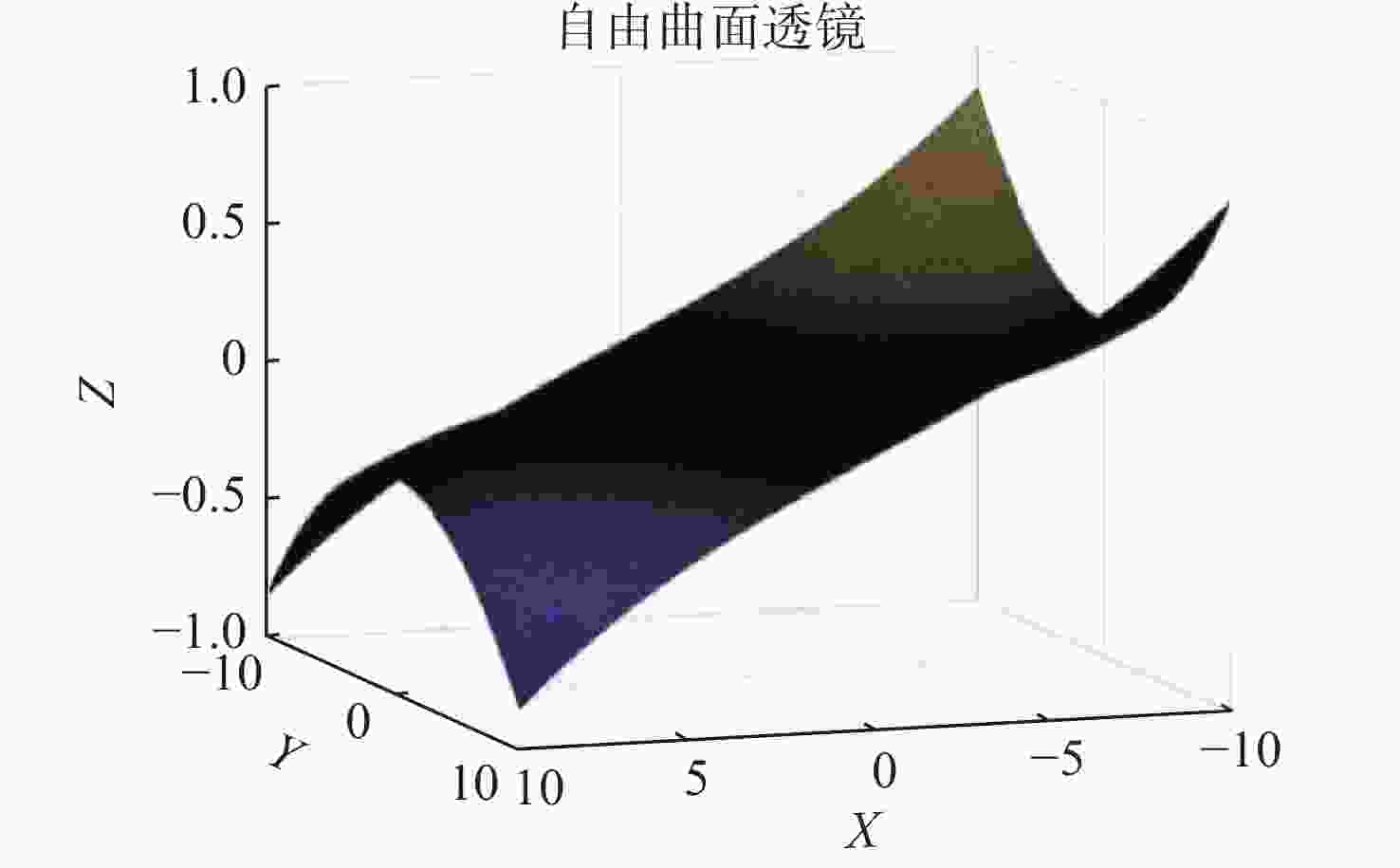
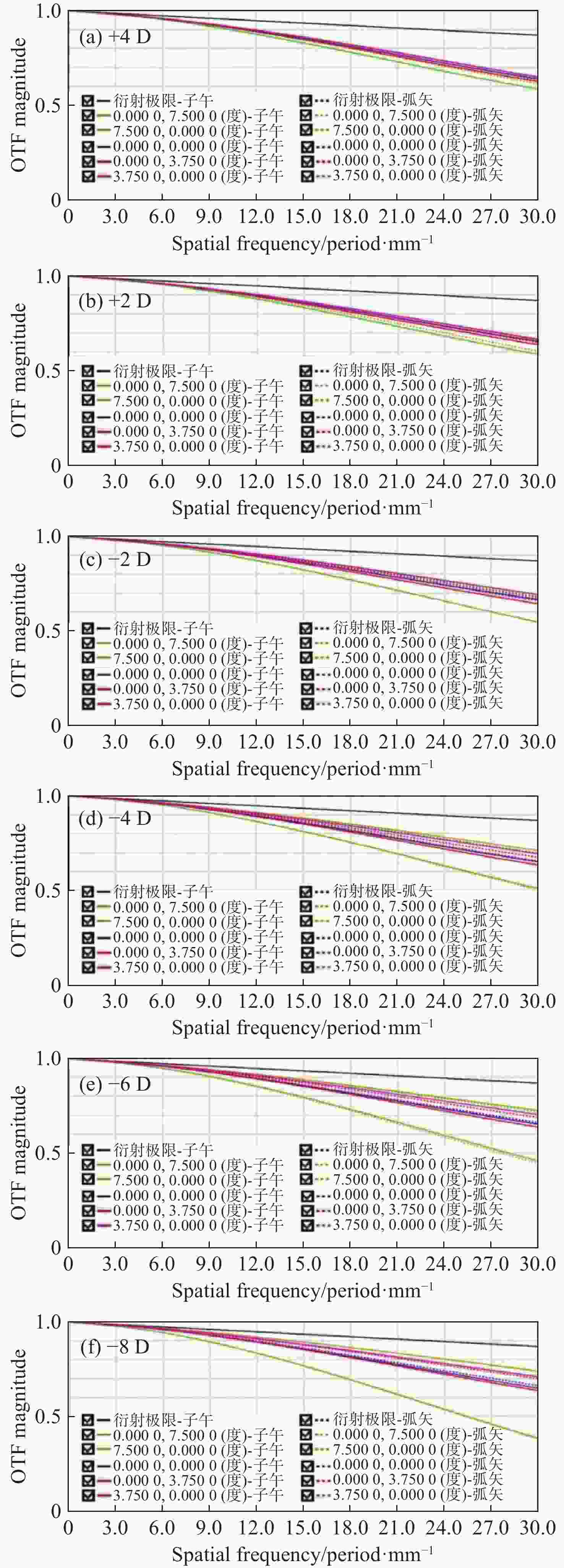
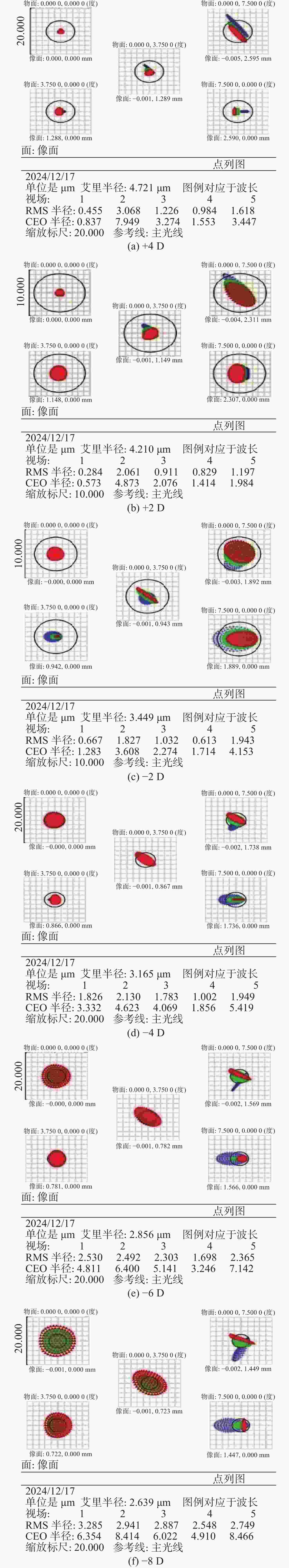
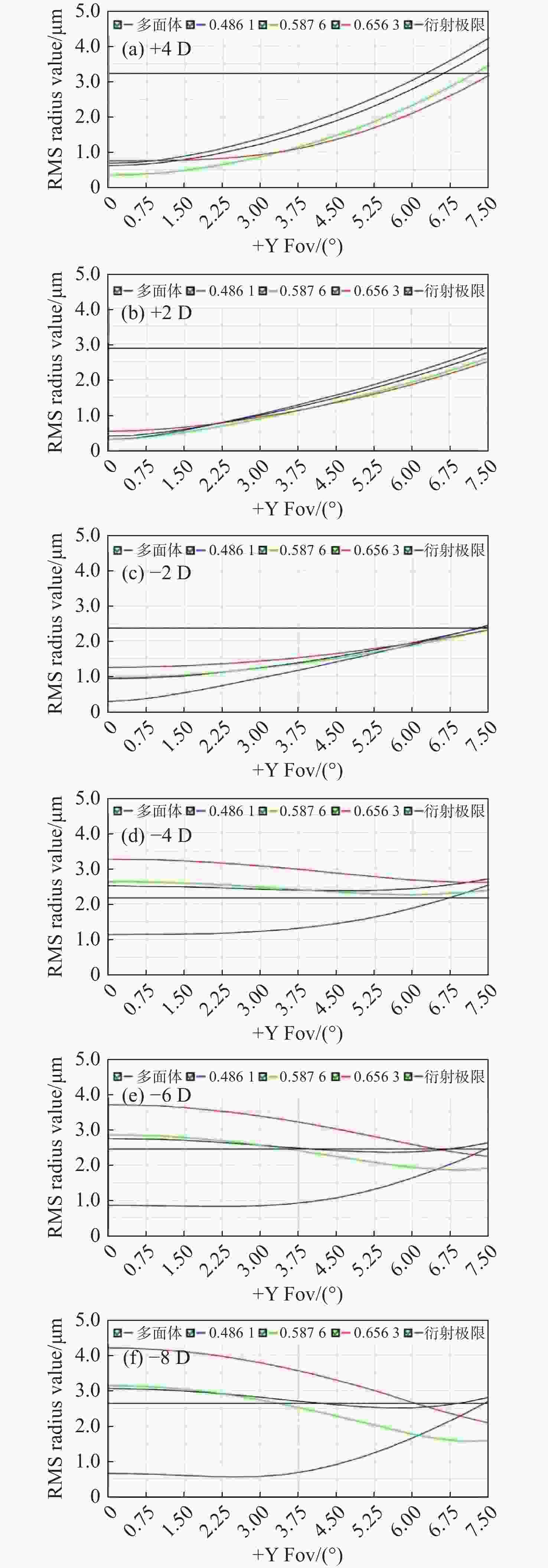
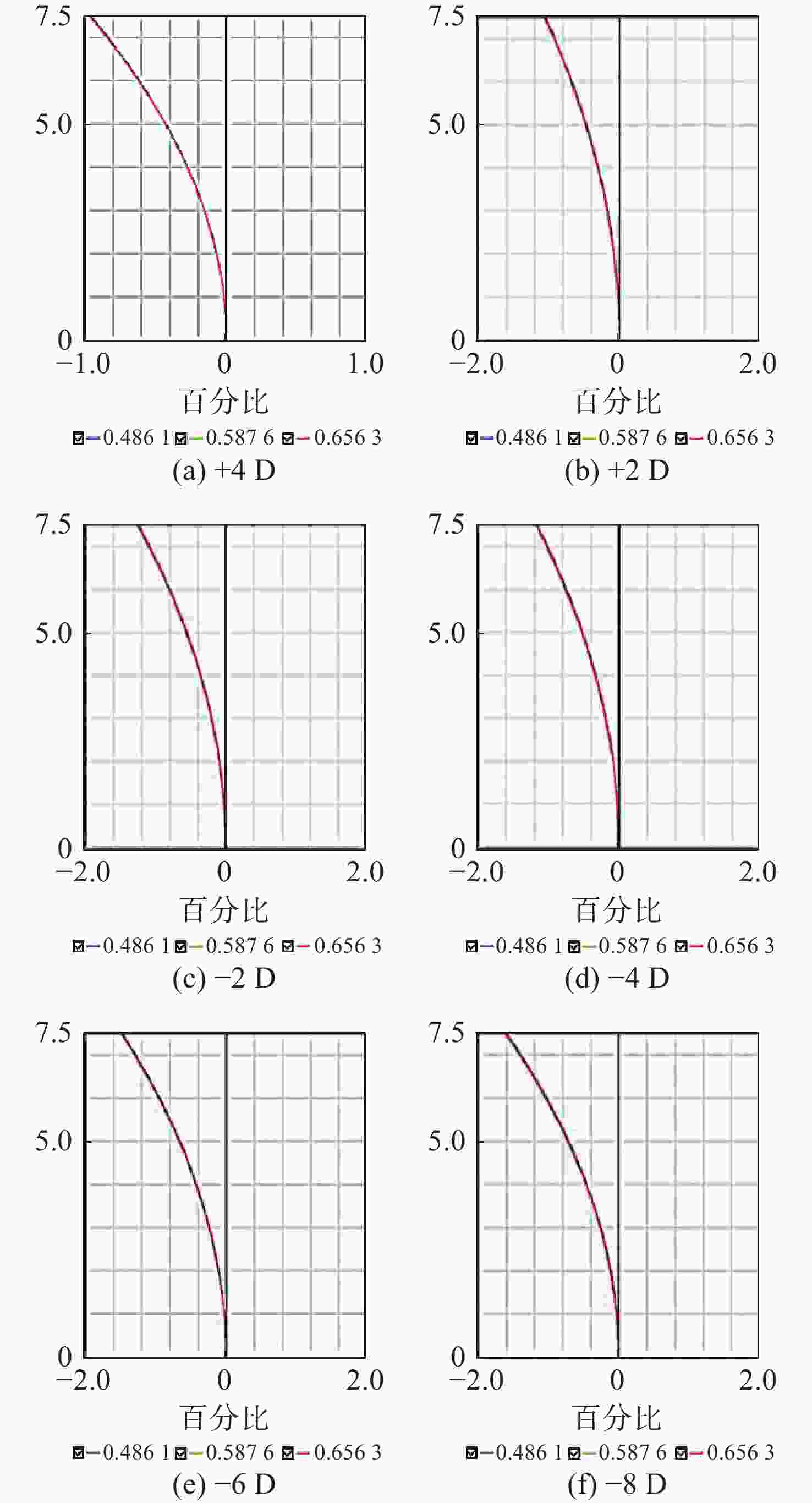
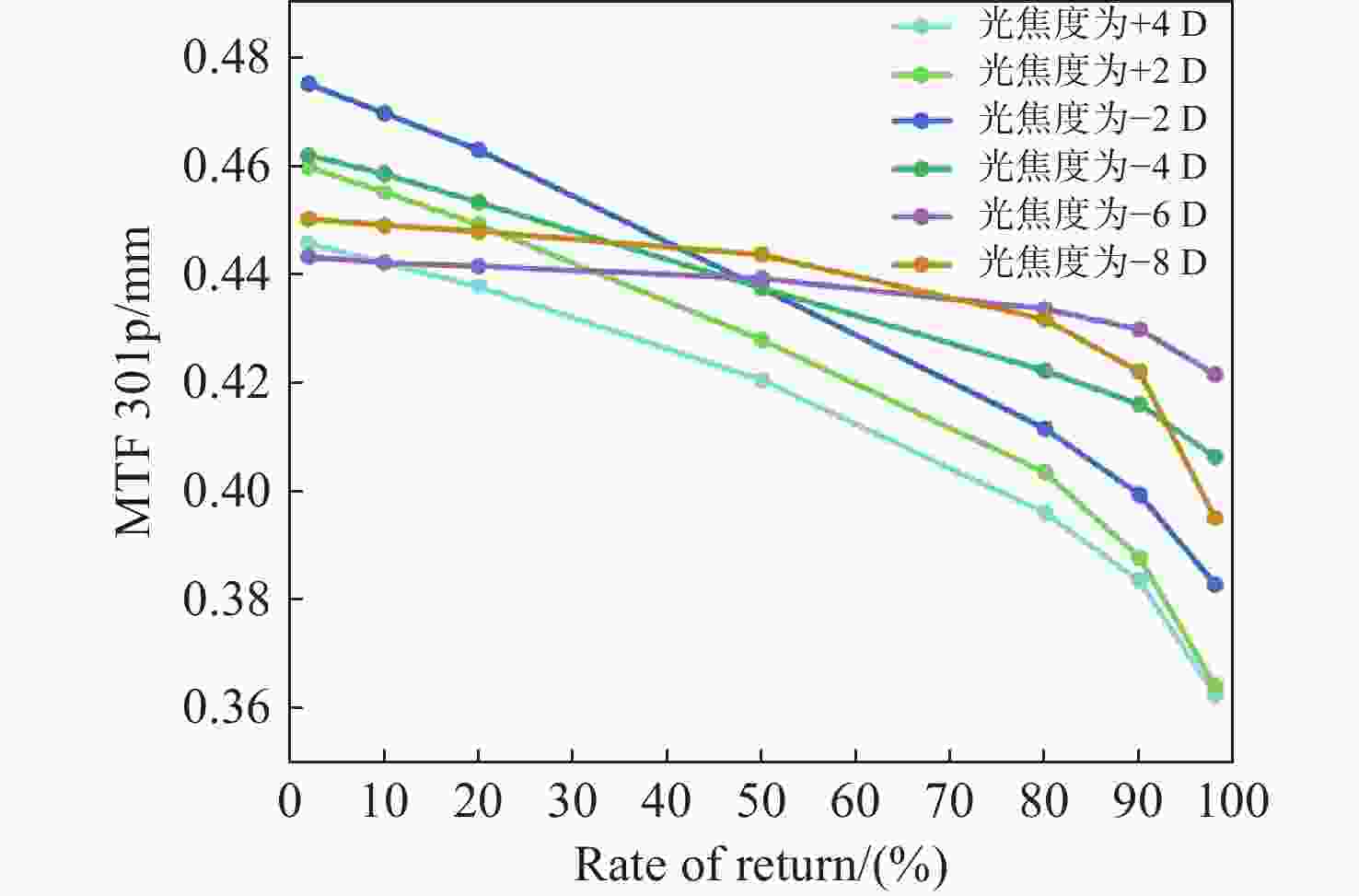
当前市面上的视觉训练产品大多采用电子屏幕显示远近大小交替变化的物体,通过观看屏幕刺激睫状肌,进行视功能训练,但该方法存在蓝光辐射,对人眼构成潜在危害。针对此问题,本文设计了一种基于Varifocal变焦结构的视光学系统。该系统通过控制两组垂直于光轴的镜片的横向移动实现光焦度连续变倍,模拟物体远近的变化,刺激睫状肌进行调节训练。本文首先分析了可变焦距透镜的面型限制,加入可变焦距球面效应方程优化Alvarez透镜基础面型,并采用Zemax软件进行设计。所设计的透镜面型由三阶XY多项式自由曲面表征,其中两组透镜最大相对垂轴偏移量为5.6 mm,实现屈光度在+4D~−8D的连续变倍。设计结果表明,全视场调制传递函数在奈奎斯特频率30 lp/mm处均大于0.3,均方根(RMS)半径值接近于艾里斑半径值,畸变均小于2%,该光学系统成像质量较好。
Abstract:Most of the current visual training products available on the market use electronic screens to display objects of varying dimensions and distances, thereby stimulating the ciliary muscle through looking at the screen for visual function training. However, this method involves blue light radiation, which poses a potential hazard to the human eye. To address this issue, a visual optical system based on a Varifocal zoom structure has been designed. The system achieves continuous magnification of optical power by manipulating the lateral movement of two sets of lenses perpendicular to the optical axis. This simulates changes in object distance and stimulating ciliary muscle regulation training. This paper first derives the surface shape limits of variable focal length lenses, incorporates the variable focal length spherical effect equation to optimize the basic surface shape of Alvarez lenses, and uses Zemax software for design. The designed lens surface is characterized by a third-order XY polynomial free-form surface, with a maximum relative vertical axis offset of 5.6 mm between the two groups of lenses, achieving continuous magnification of refractive power between +4D and −8D. The design results indicate that the full-field modulation transfer function exceeds 0.3 at a Nyquist frequency of 30 lp/mm, with root mean square (RMS) radius values approaching the Airy spot radius value and distortion below 2%. The imaging quality of this optical system is satisfactory.
-
Key words:
- progressive multifocal /
- optical power /
- Varifocal /
- Alvarez lens /
- free-form surface
-
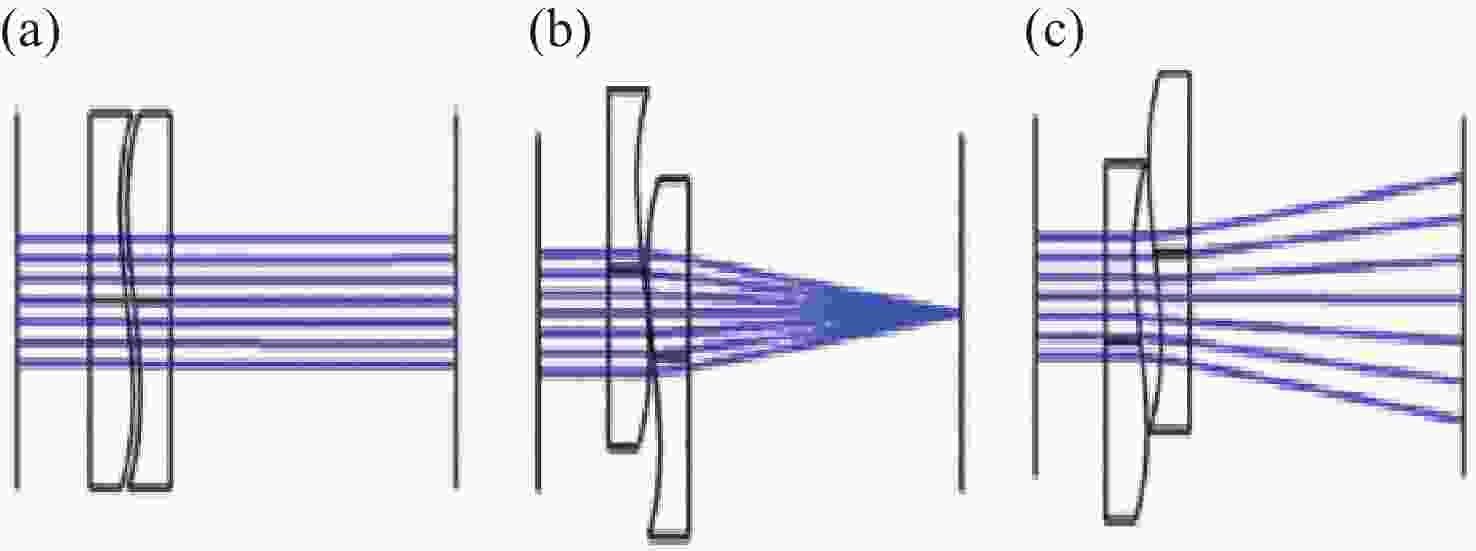
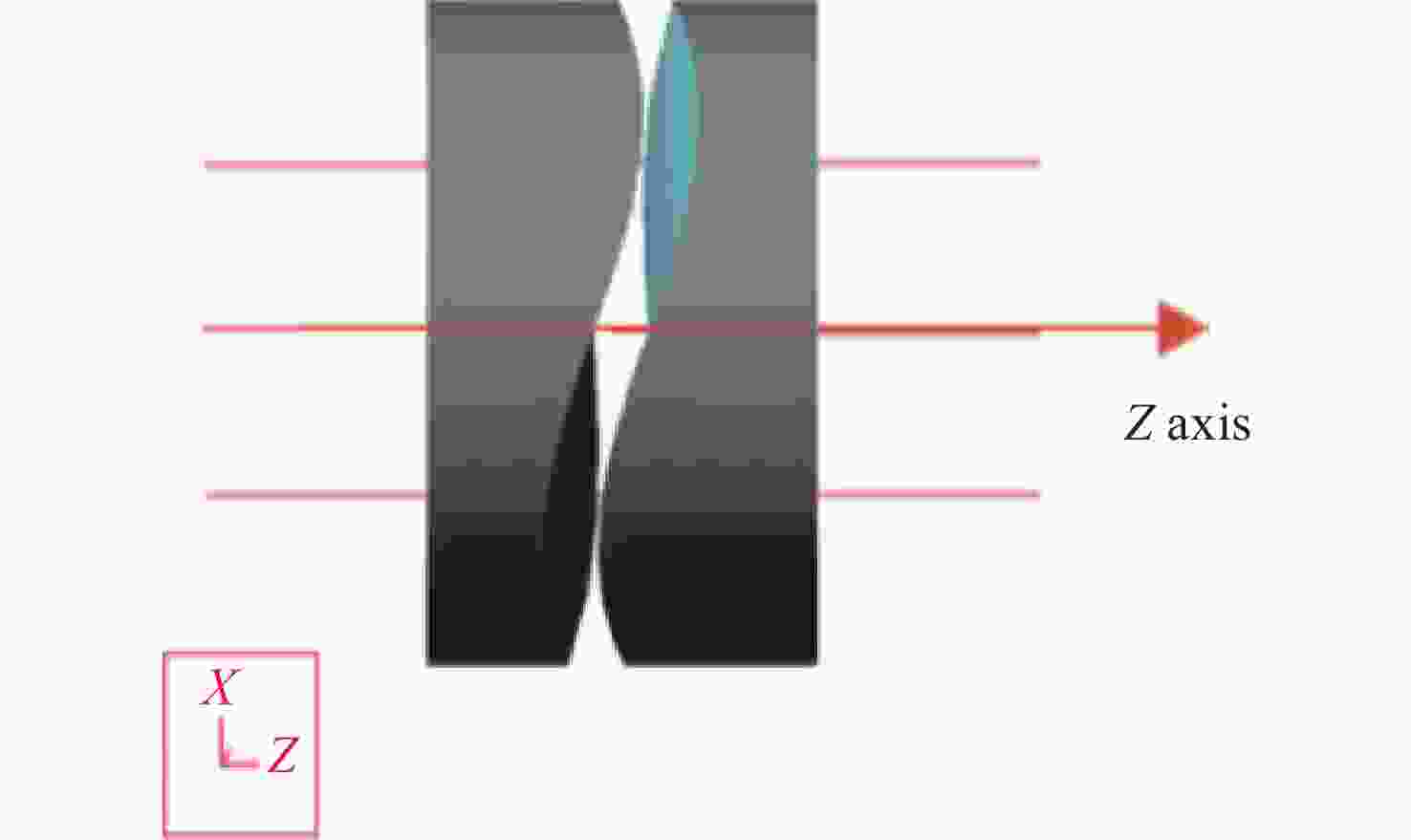
图 1 Alvarez透镜[11}
Figure 1. Alvarez lens[11]
表 1 连续变焦光学系统参数指标
Table 1. Parameters and indicators of continuous zoom optical system
Parameter Value Wavelength/nm 486~656 Full field of view /(°) 15 Entrance pupil diameter/mm 4 Focal power variation +4D~−8D Distortion/% <2% MTF 30line pairs >0.3 表 2 连续变焦光学系统基本参数
Table 2. Basic parameters of continuous zoom optical system
Type A Radius Thickness Material Standard - 无限 3 APL5014CL XY polynomial − 0.0006 −3.940E-09 1 XY polynomial − 0.0006 −3.940E-09 3 APL5014CL Standard - 无限 12 Standard
(角膜)- 6.896 0.6 Nd:1.377
Vd:55Standard
(液状体)- 3.365 3 Nd:1.335
Vd:55Standard(stop)
(瞳孔)- 10.100 0 Standard
(晶状体)- 10.485 4 Nd:1.405
Vd:55Even Aspheric
(玻璃体)- −5.673 17.25 Nd:1.335
Vd:55Standard
(视网膜)−12.5 0 表 3 XY多项式自由曲面系数
Table 3. XY polynomial free-form surface coefficients
Coefficient Value X3 2.11×10−4 XY2 6.31×10−4 X2 2.01×10−5 Y2 1.38×10−6 X 3.48×10−5 表 4 系统公差设置
Table 4. System tolerance settings
Type Operator Item Target Index tolerances TIND Index 0.0005 TABB Abbe 0.3 Surface tolerances TIRR Irregularity 0.5 TFRN Radius/fringe 3 TTHI Thickness/mm 0.002 TSDX(Y) Decenter/mm 0.02 TSTX(Y) Tilt/° 0.0167 Element tolerances TEDX(Y) Decenter/mm 0.015 TETX(Y) Tilt/° 0.0167 -
[1] 王婉珠, 李爱华, 倪连红. VTS4疗法联合传统综合疗法治疗屈光不正性弱视的效果[J]. 中国医学创新,2023,20(15):107-110.WANG W ZH, LI A H, NI L H. Effect of VTS4 therapy combined with traditional comprehensive therapy in the treatment of ametropia amblyopia[J]. Medical Innovation of China, 2023, 20(15): 107-110. (in Chinese). [2] 迟英杰, 王华君, 李霄, 等. 视觉训练系统联合传统综合疗法对屈光不正性弱视治疗的临床效果评价[J]. 中华实验眼科杂志,2022,40(6):451-457.CHI Y J, WANG H J, LI X, et al. Clinical evaluation of vision therapy system 4 combined with traditional comprehensive training for ametropic amblyopia[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Ophthalmology, 2022, 40(6): 451-457. (in Chinese). [3] 黄艳, 李雪瑶, 刘庆. 视觉功能训练系统在屈光性弱视患儿治疗中的应用效果[J]. 中国卫生标准管理,2023,14(13):1-5.HUANG Y, LI X Y, LIU Q. Effectiveness of visual function training system in the treatment of children with refractive amblyopia[J]. China Health Standard Management, 2023, 14(13): 1-5. (in Chinese). [4] 杨翠. 基于IPMC驱动的可变焦微透镜的研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2021.YANG C. Research on variable focal microlens driven by IPMC[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2021. (in Chinese). [5] HAO Q, CHEN CH X, CAO J, et al. Ultra-wide varifocal imaging with selectable region of interest capacity using Alvarez lenses actuated by a dielectric elastomer[J]. Photonics Research, 2022, 10(7): 1543-1551. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.455331 [6] 卞旭琪. 自由曲面变焦成像系统的研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2017.DIAN X Q. Research on freeform varifocal optical imaging systems[D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2017. (in Chinese). [7] ALVAREZ L W. Two-element variable-power spherical lens: US, 3305294[P]. 1967-02-21. [8] BARBERO S, RUBINSTEIN J. Adjustable-focus lenses based on the Alvarez principle[J]. Journal of Optics, 2011, 13(12): 125705. doi: 10.1088/2040-8978/13/12/125705 [9] HOU CH L, XIN Q, ZANG Y. Optical zoom system realized by lateral shift of Alvarez freeform lenses[J]. Optical Engineering, 2018, 57(4): 045103. [10] 蒋婷婷, 冯华君, 李奇. 自由曲面变焦的内调焦式光学系统设计[J]. 红外与激光工程,2021,50(4):20200290. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200290JIANG T T, FENG H J, LI Q. Design on internal focusing optical system with zoom lens of freeform[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(4): 20200290. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200290 [11] 蒋婷婷, 徐之海, 李奇. 基于五阶自由曲面垂轴偏移的空间相机变焦方法[J]. 飞控与探测,2023,6(2):18-22.JIANG T T, XU ZH H, LI Q. Zooming method for space cameras based on lateral shift of fifth-order free-form lenses[J]. Flight Control & Detection, 2023, 6(2): 18-22. (in Chinese). [12] 欧阳琦, 柳萌遥, 宁妍, 等. 基于Alvarez透镜的紧凑型红外连续变倍系统设计[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2024,61(10):1022001.OUYANG Q, LIU M Y, NING Y, et al. Design of a compact infrared continuous optical zoom system based on Alvarez lenses[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2024, 61(10): 1022001. (in Chinese). [13] CAMPBELL C E. Conditions under which two-element variable power lenses can be created. Part 1. Theoretical analysis[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2011, 28(10): 2148-2152. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.28.002148 [14] CAMPBELL C E. Conditions under which two-element variable power lenses can be created. Part 2. Application to specific designs[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2011, 28(10): 2153-2159. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.28.002153 [15] 罗宇杰. 紧凑型无盲区全景成像光学系统及其变焦组件设计研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018.LUO Y J. Design of compact non-blind area PAL system and its zoom elements[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018. (in Chinese). [16] 禹静. 自由曲面镜片评价方法的研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2015.YU J. Study on evaluation method of freeform spectacle lenses[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2015. (in Chinese). [17] 华芳芳, 禹静, 李东升. 渐进多焦点镜片光学系统MTF评价的仿真分析[J]. 光学技术,2018,44(6):709-716.HUA F F, YU J, LI D SH. Research on MTF evaluation method of progressive addition lenses[J]. Optical Technique, 2018, 44(6): 709-716. (in Chinese). [18] 张梅. 基于个性化眼光学结构的人眼色差的研究[D]. 天津: 南开大学, 2010.ZHANG M. Research on chromatic aberration of human eye based on individual eye[D]. Tianjin: Nankai University, 2010. (in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: