Calculation of orbit external heat flow and radiation characteristics of space target
-
摘要:
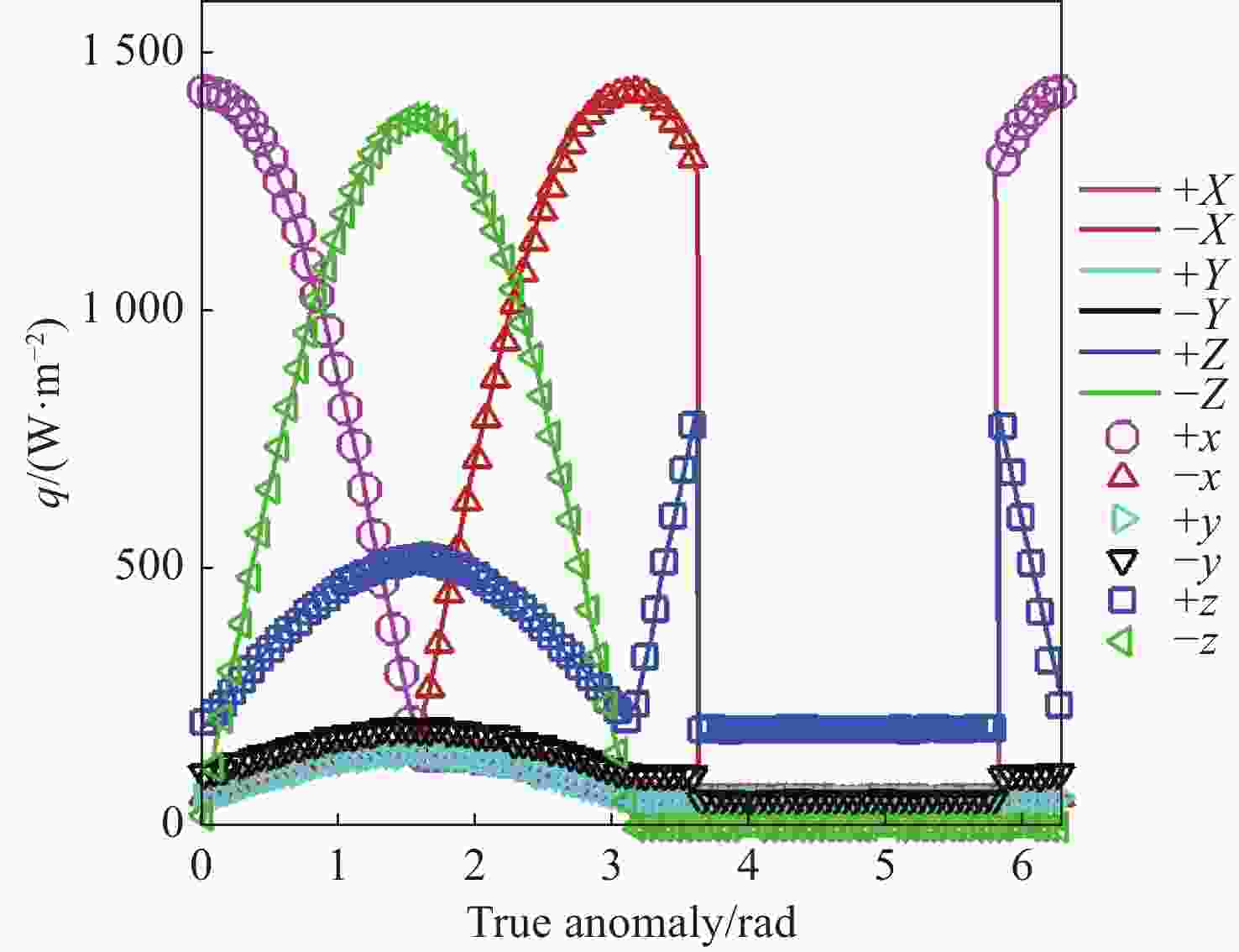
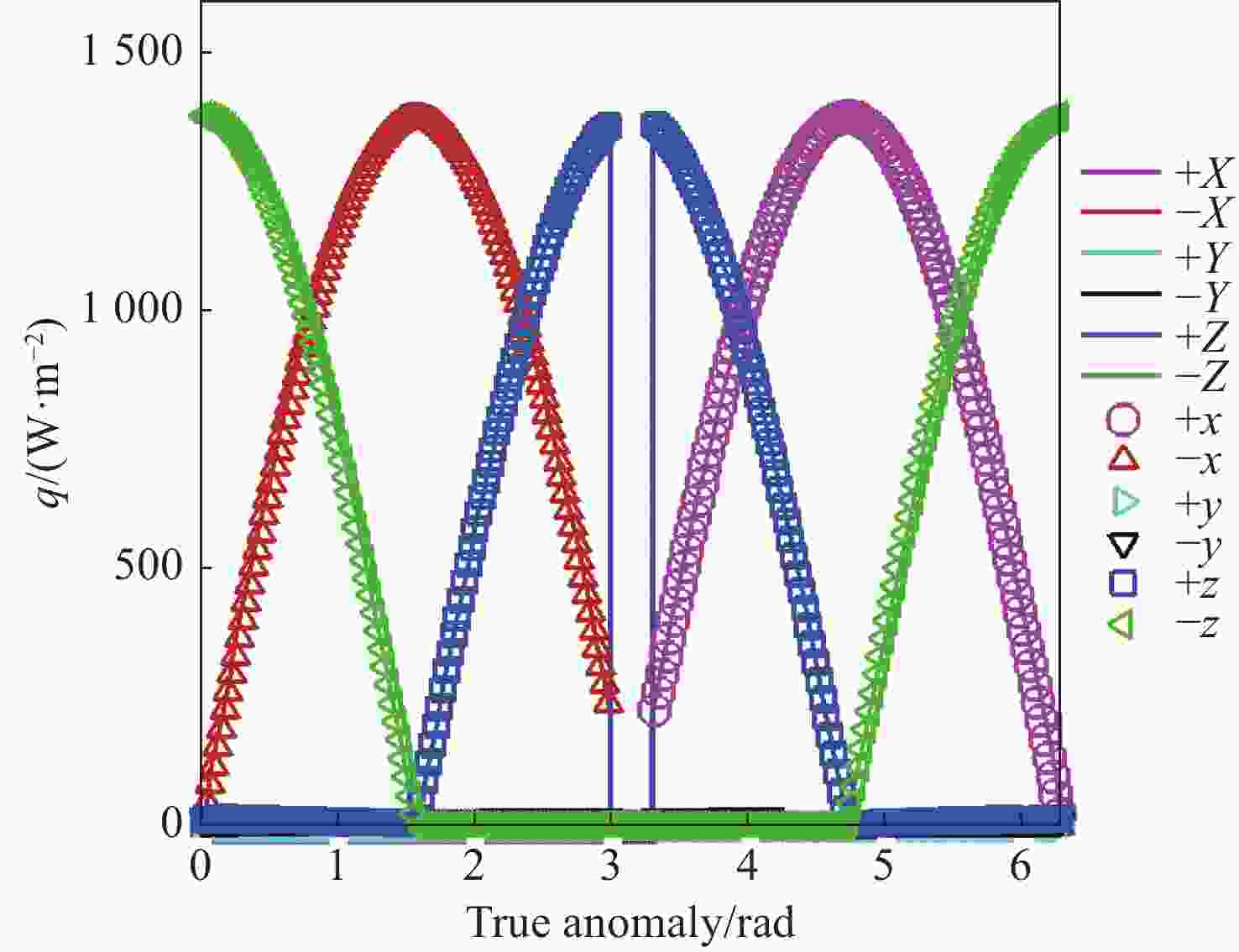
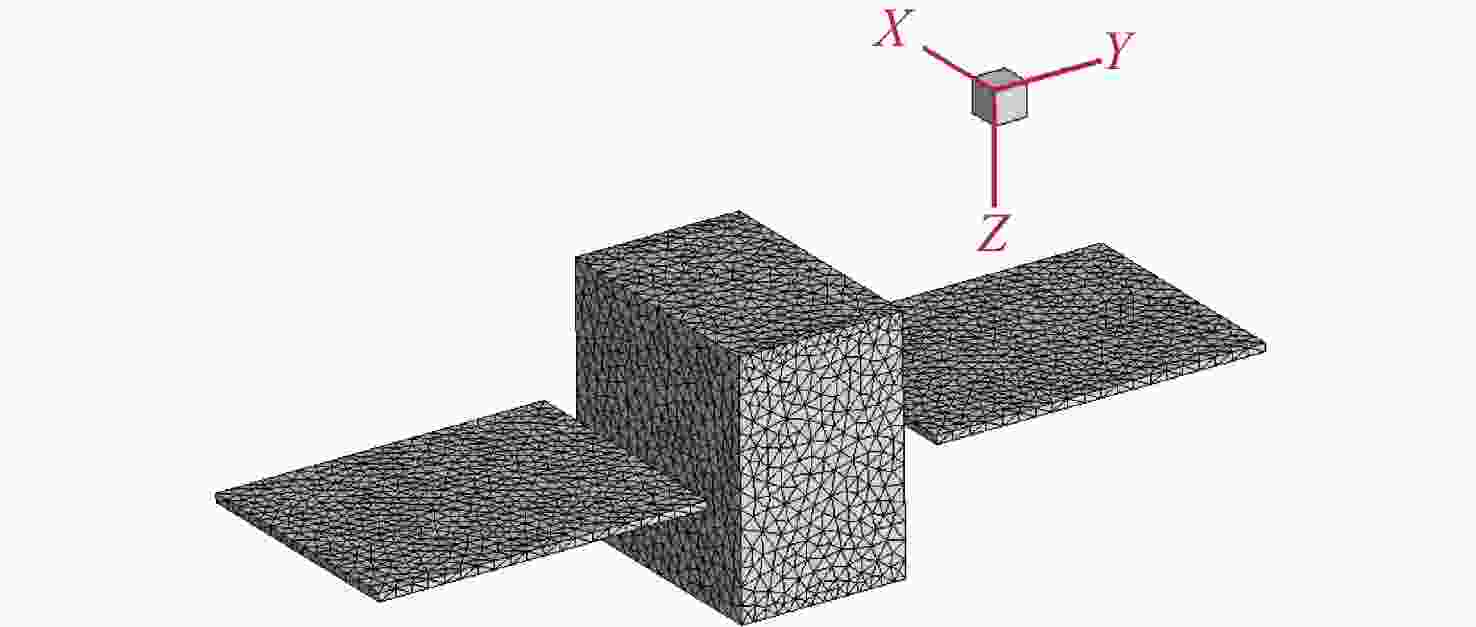
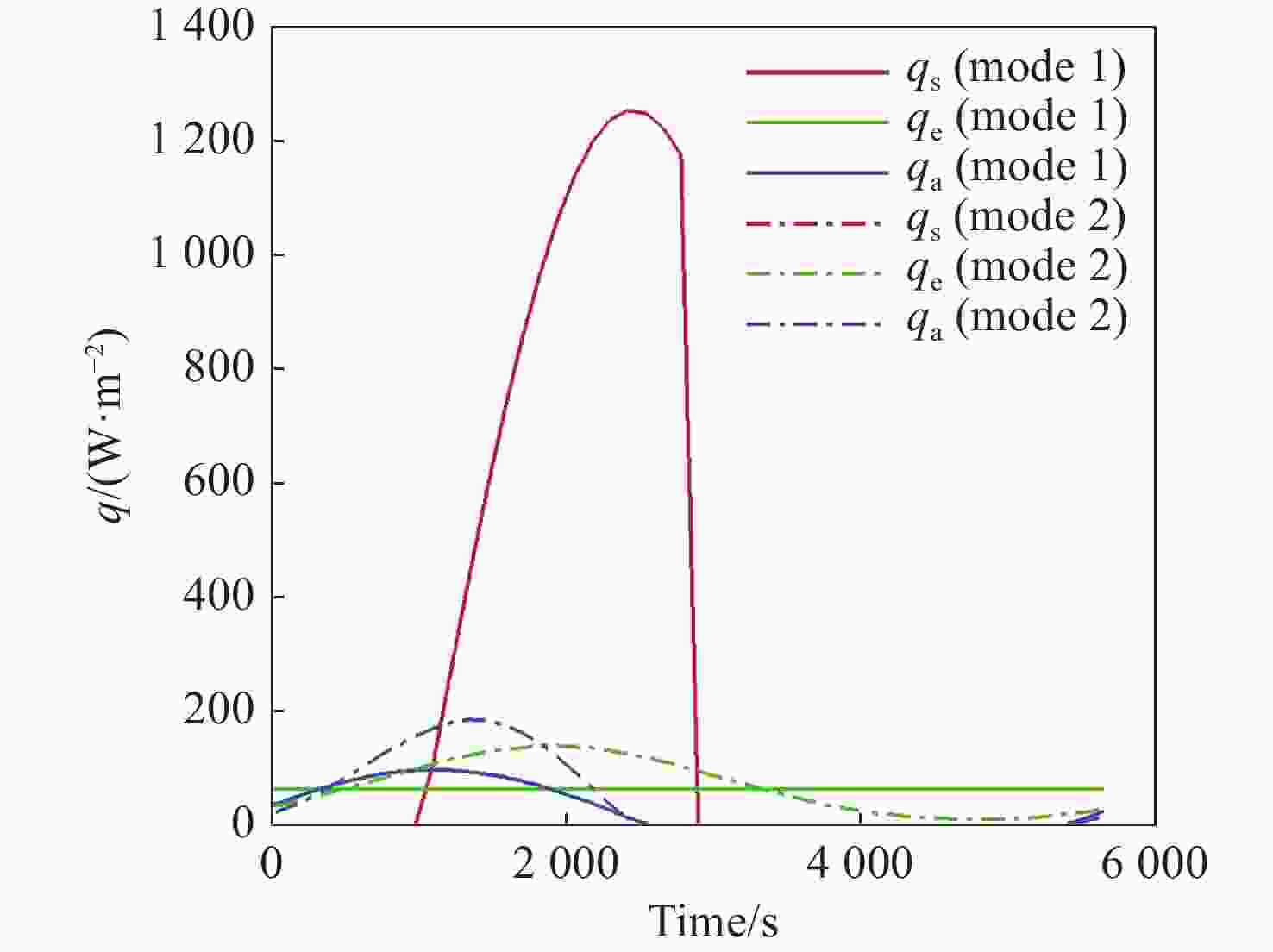
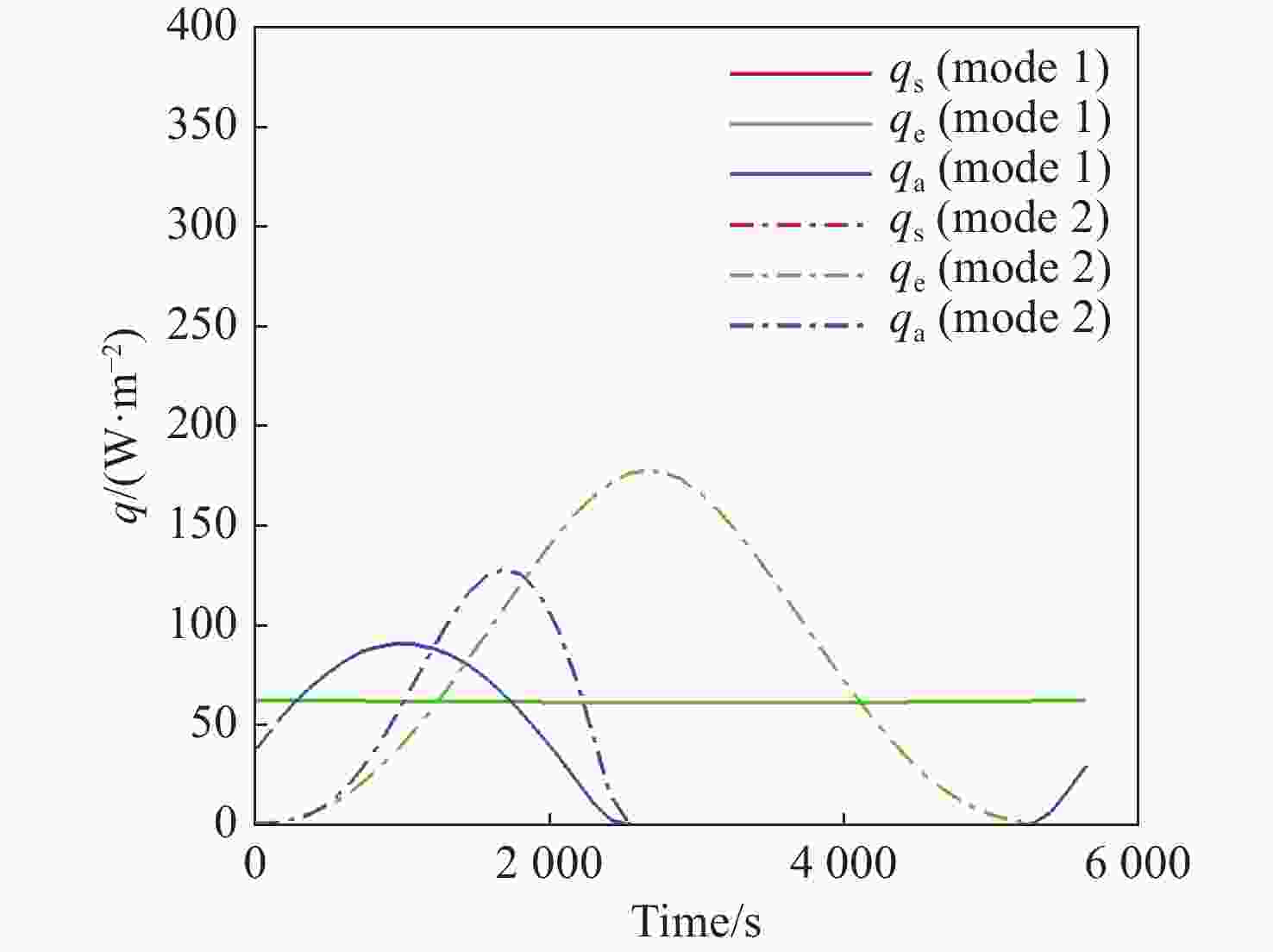
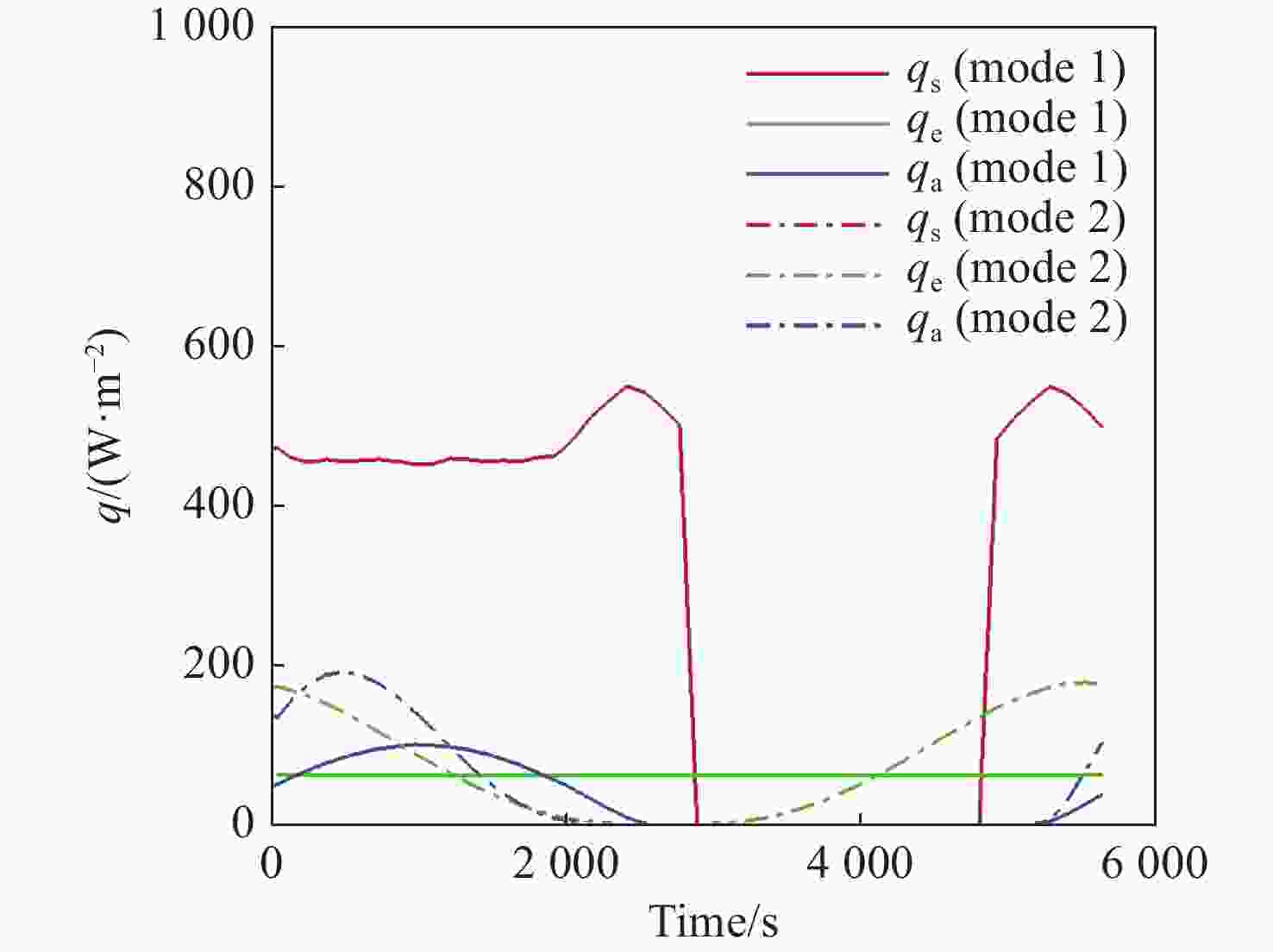
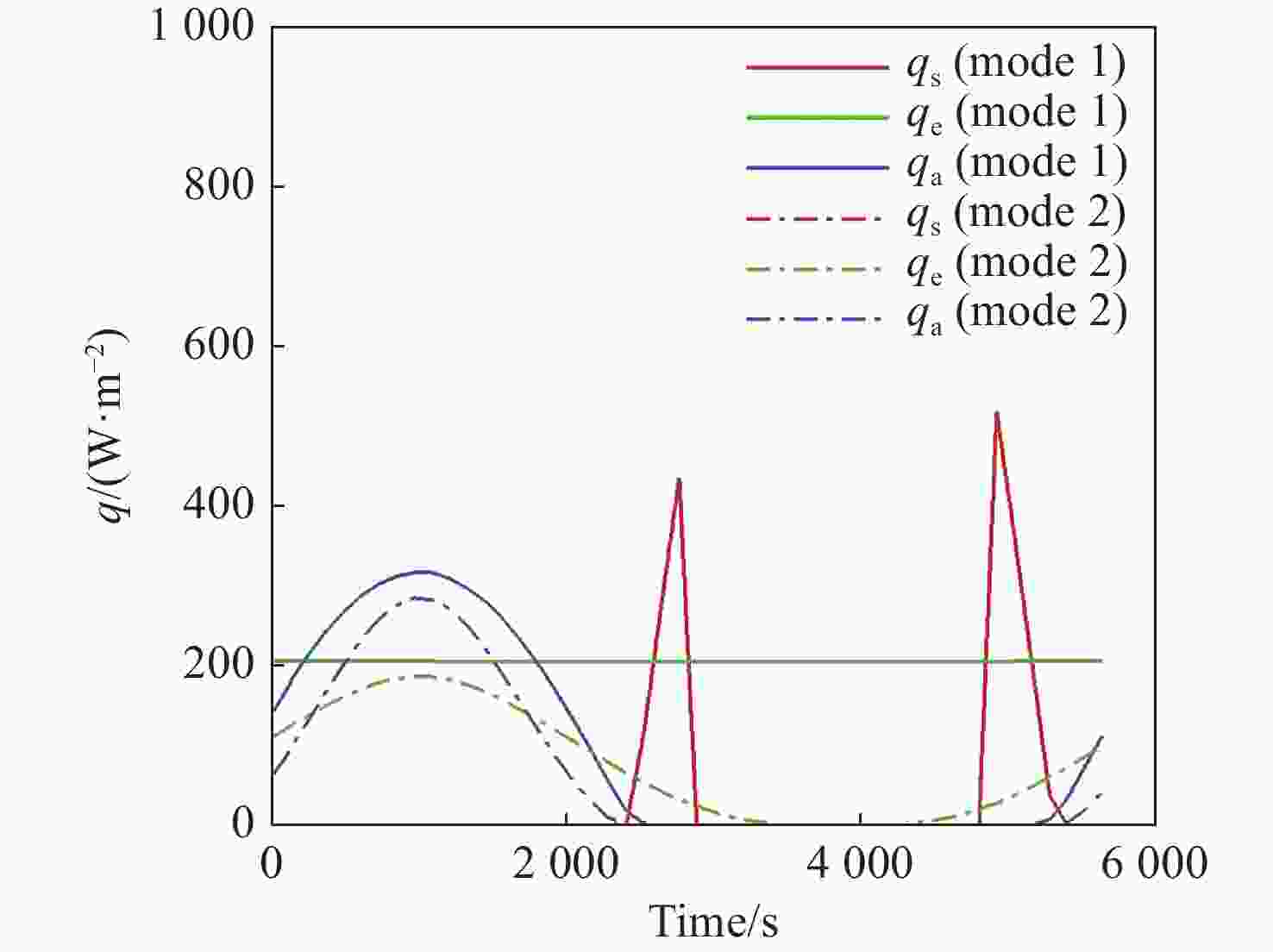
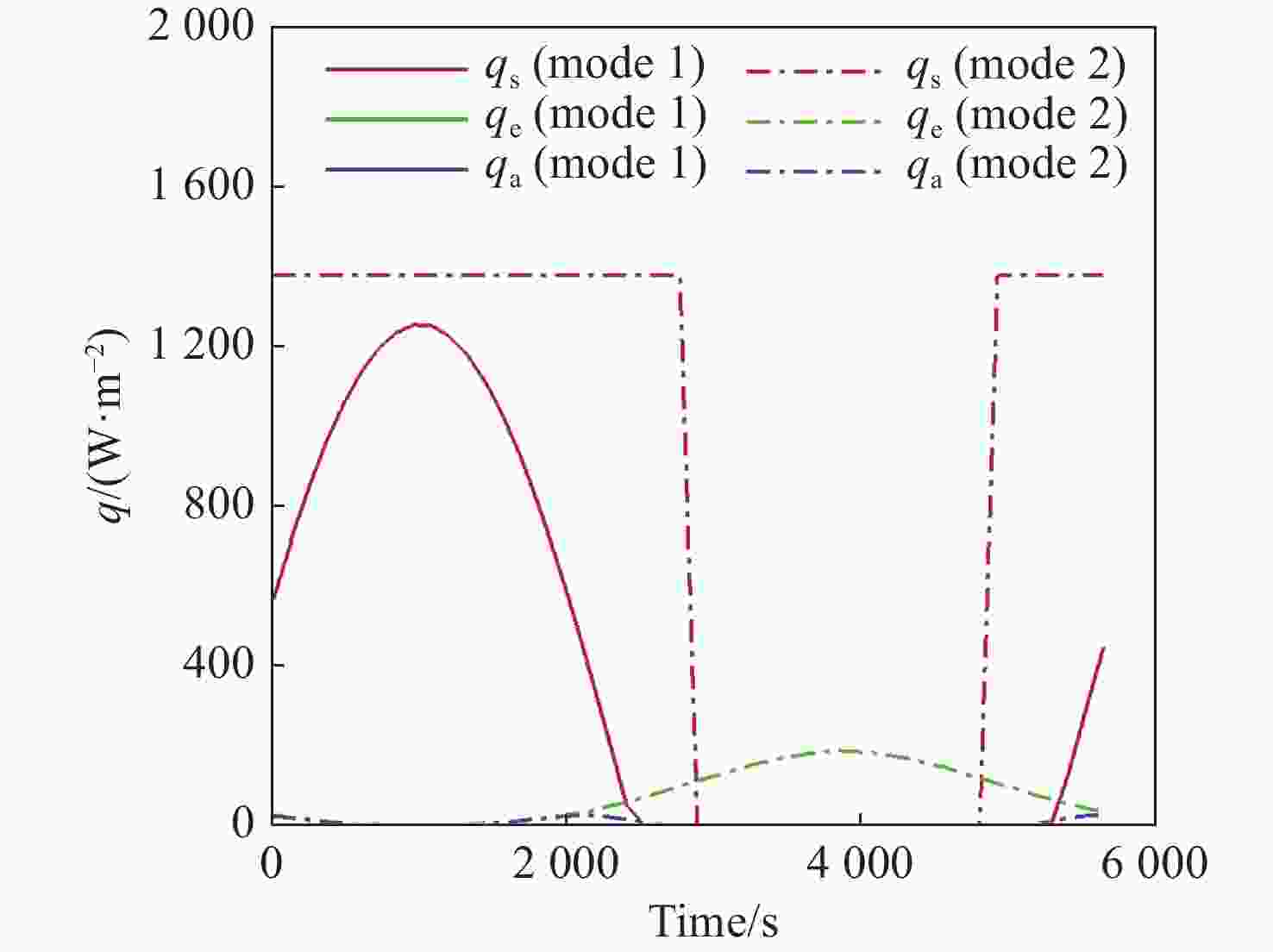
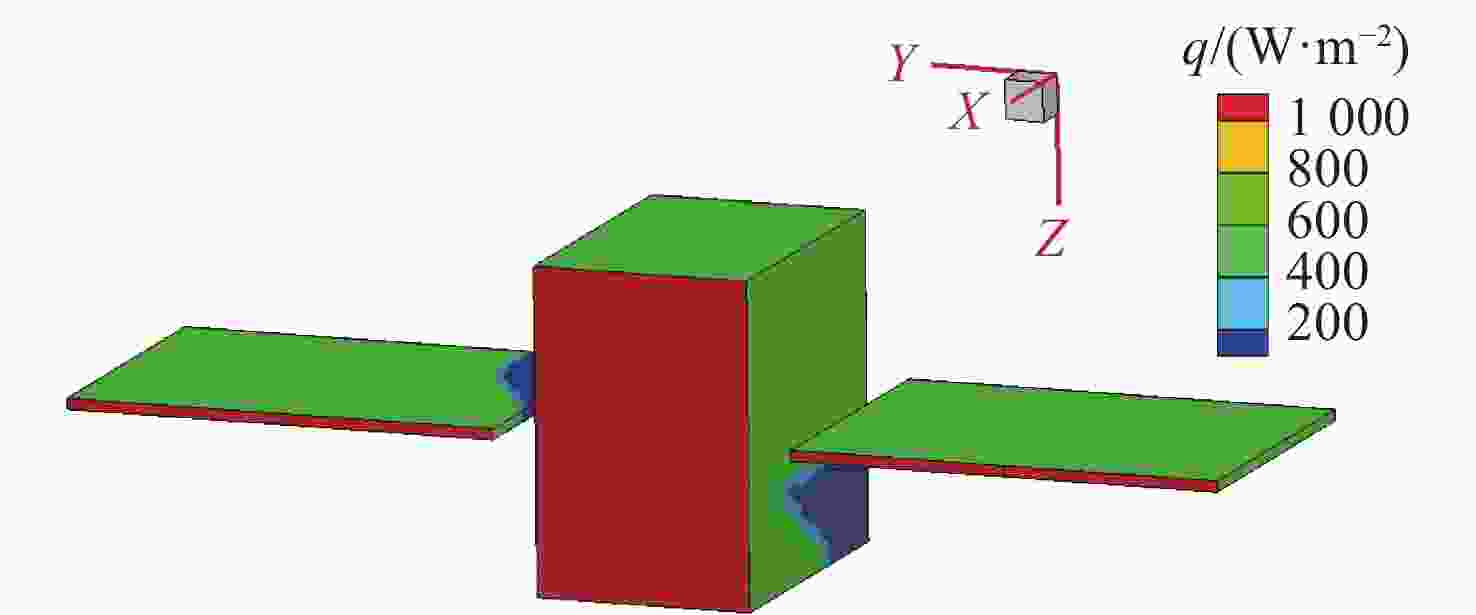
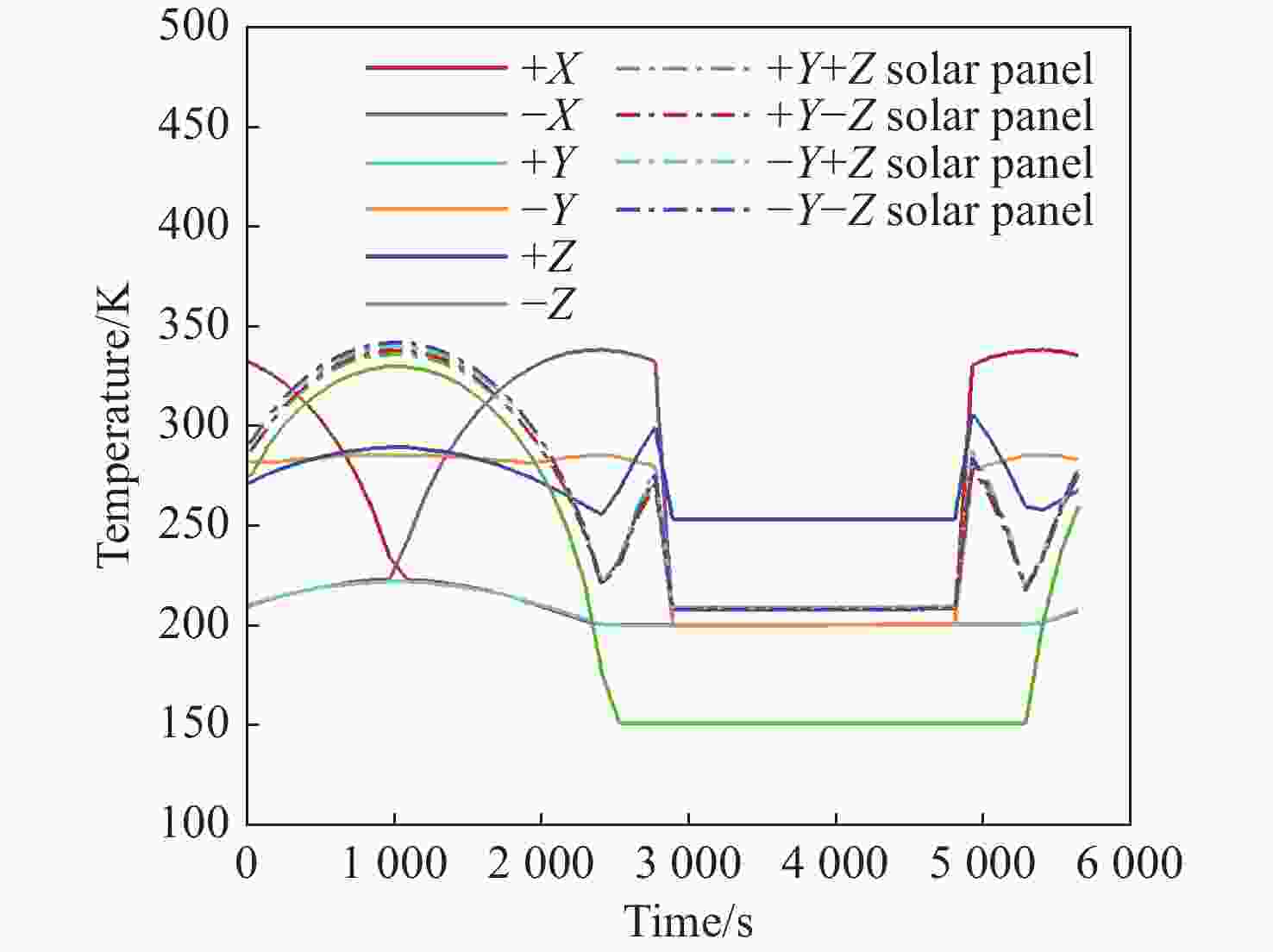
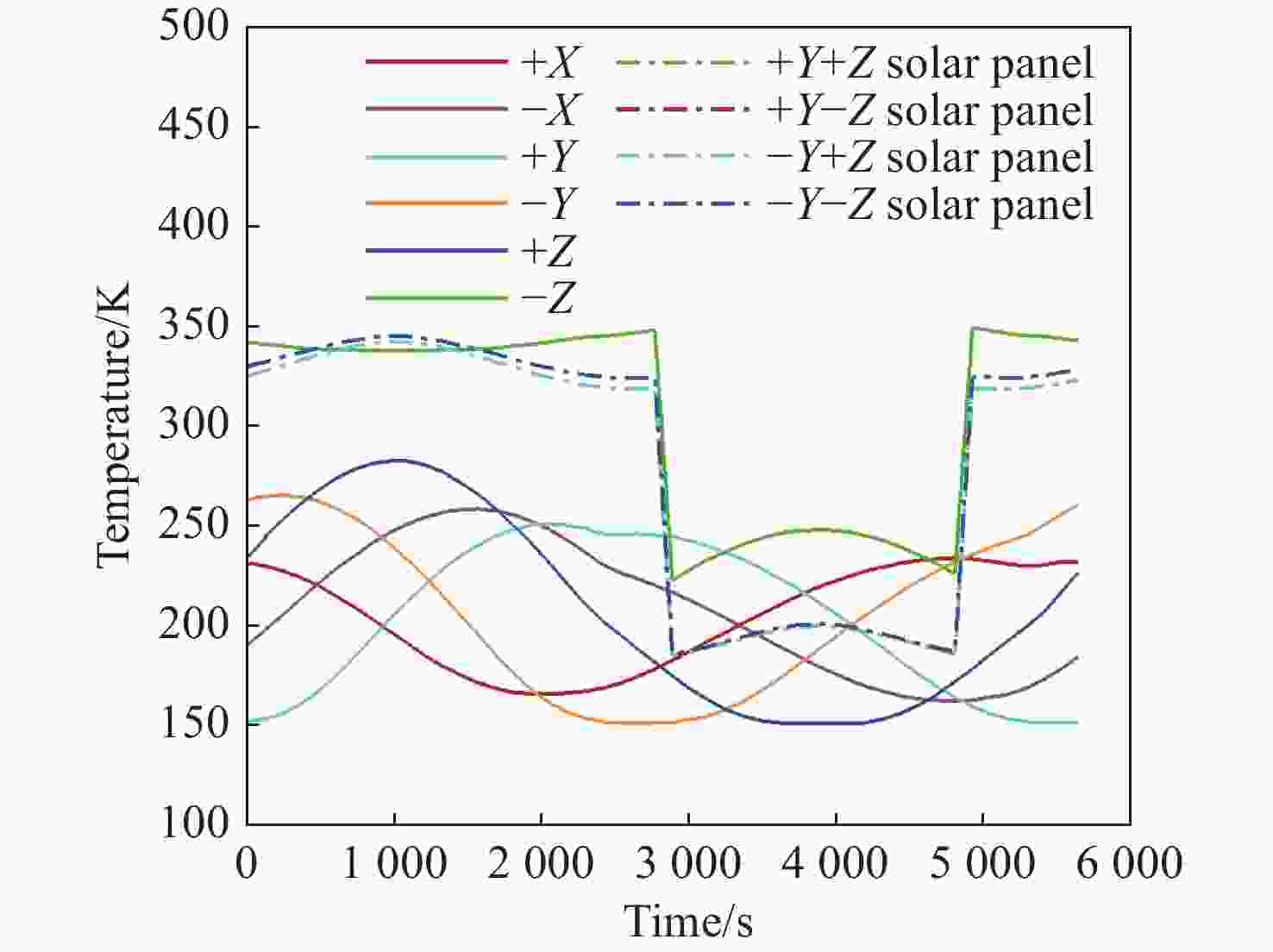
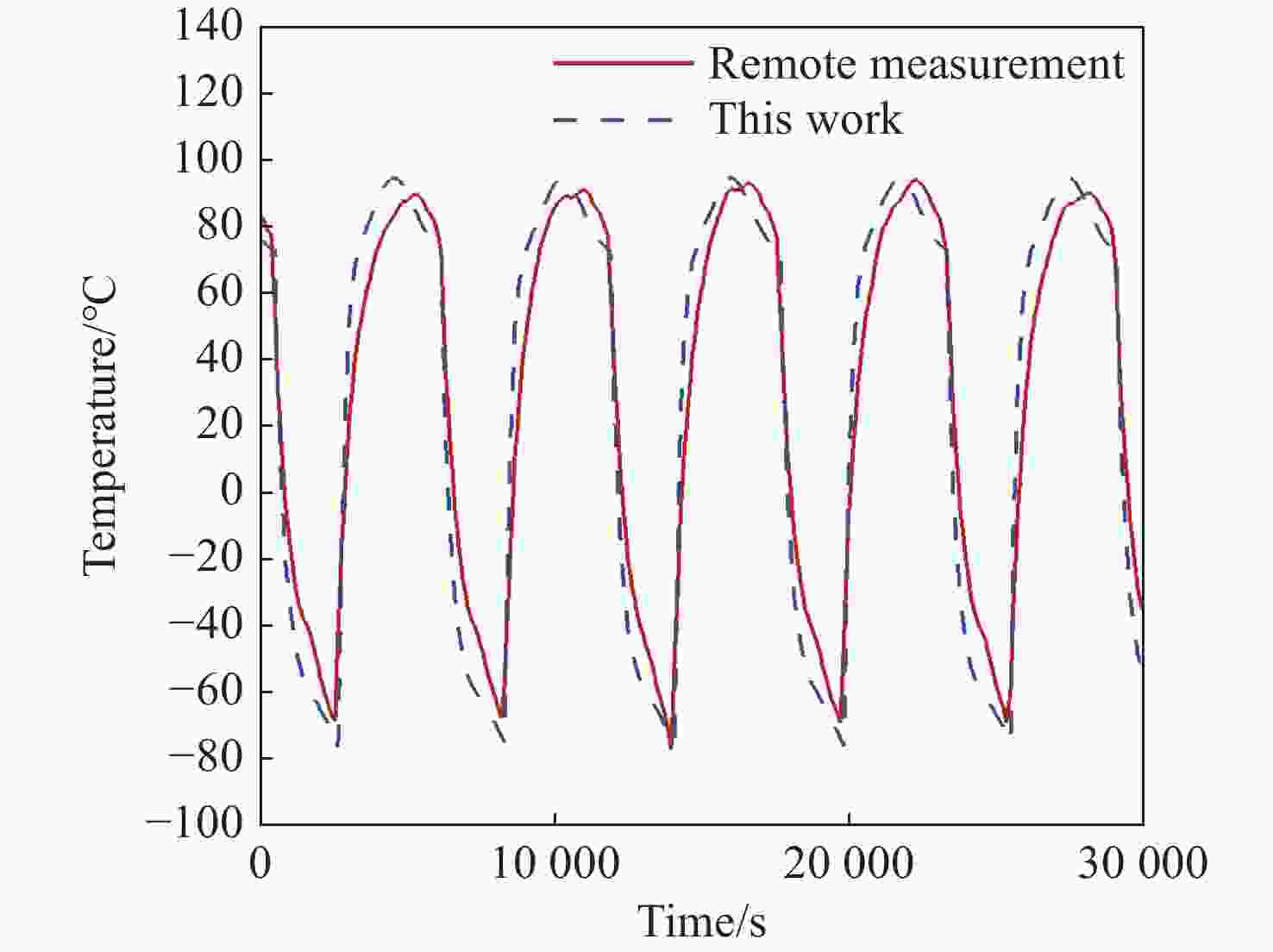
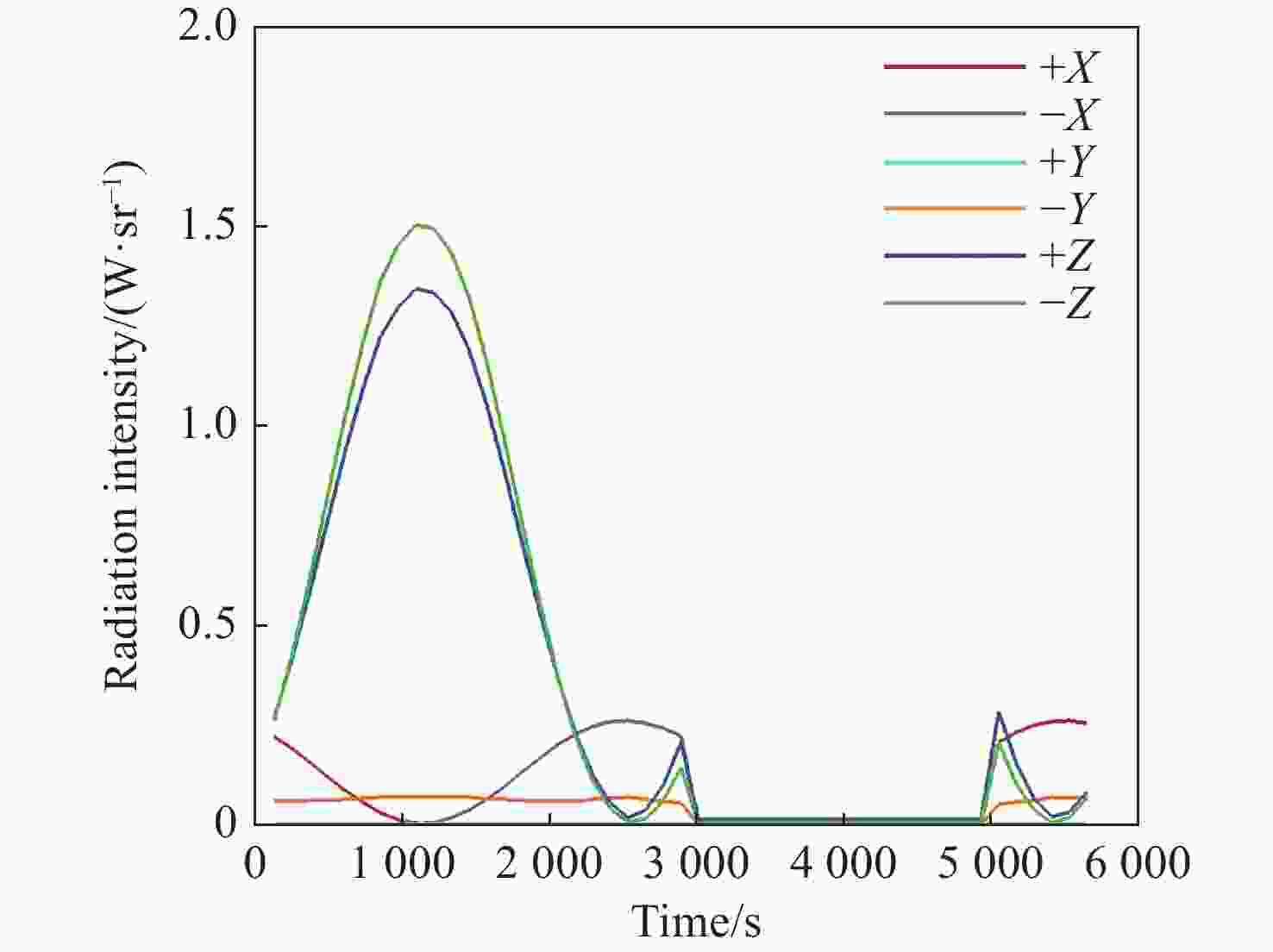
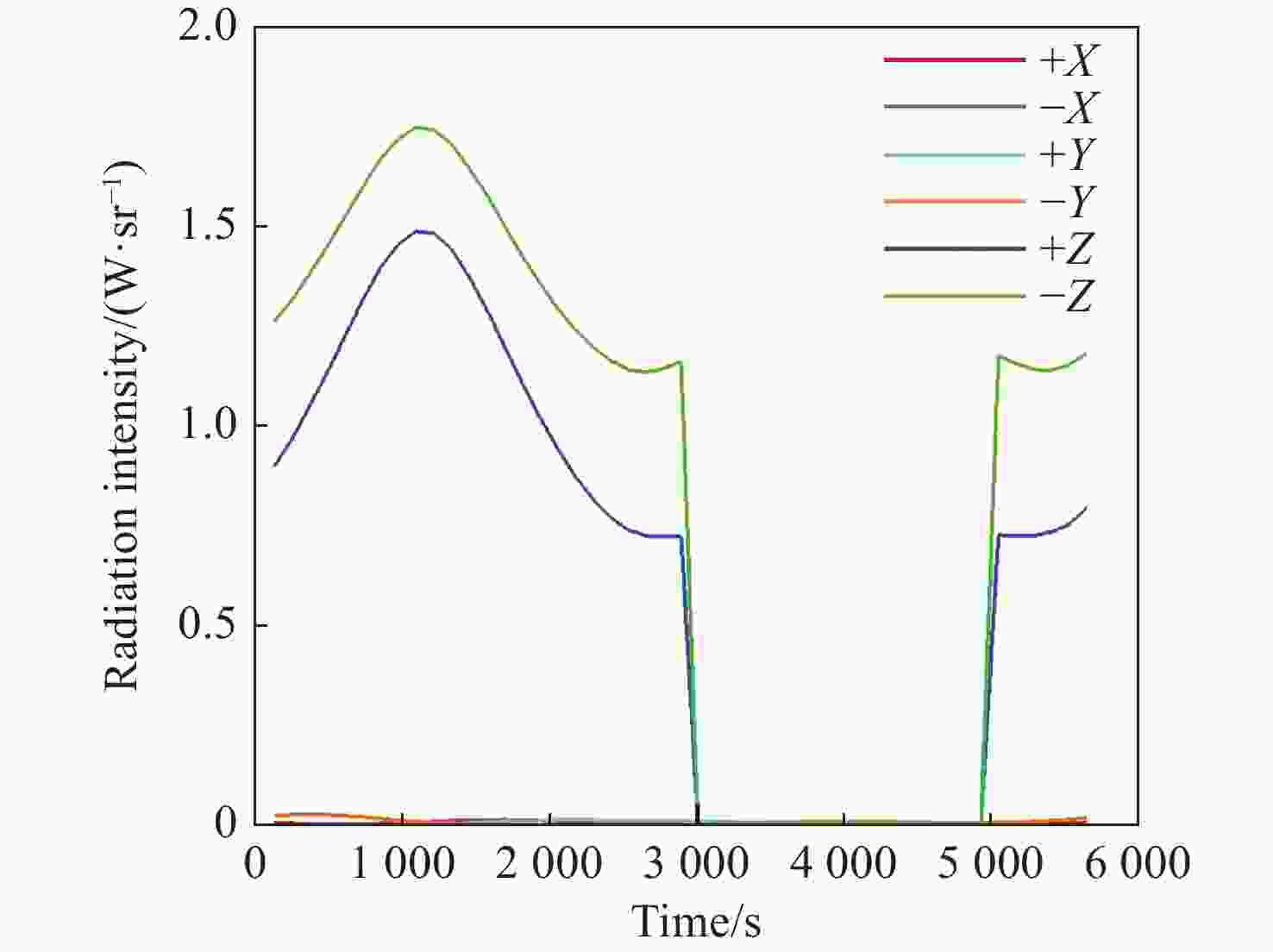
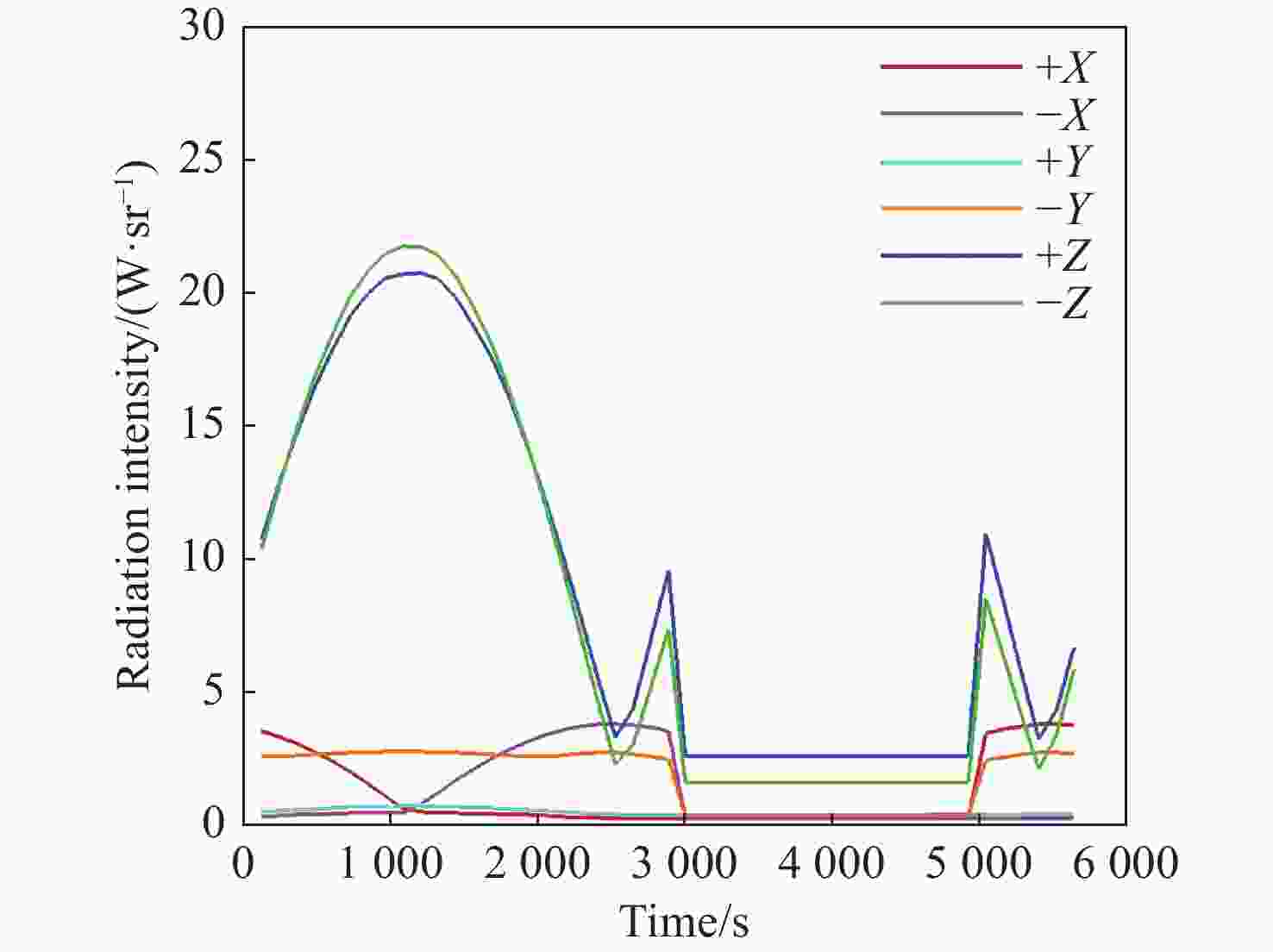
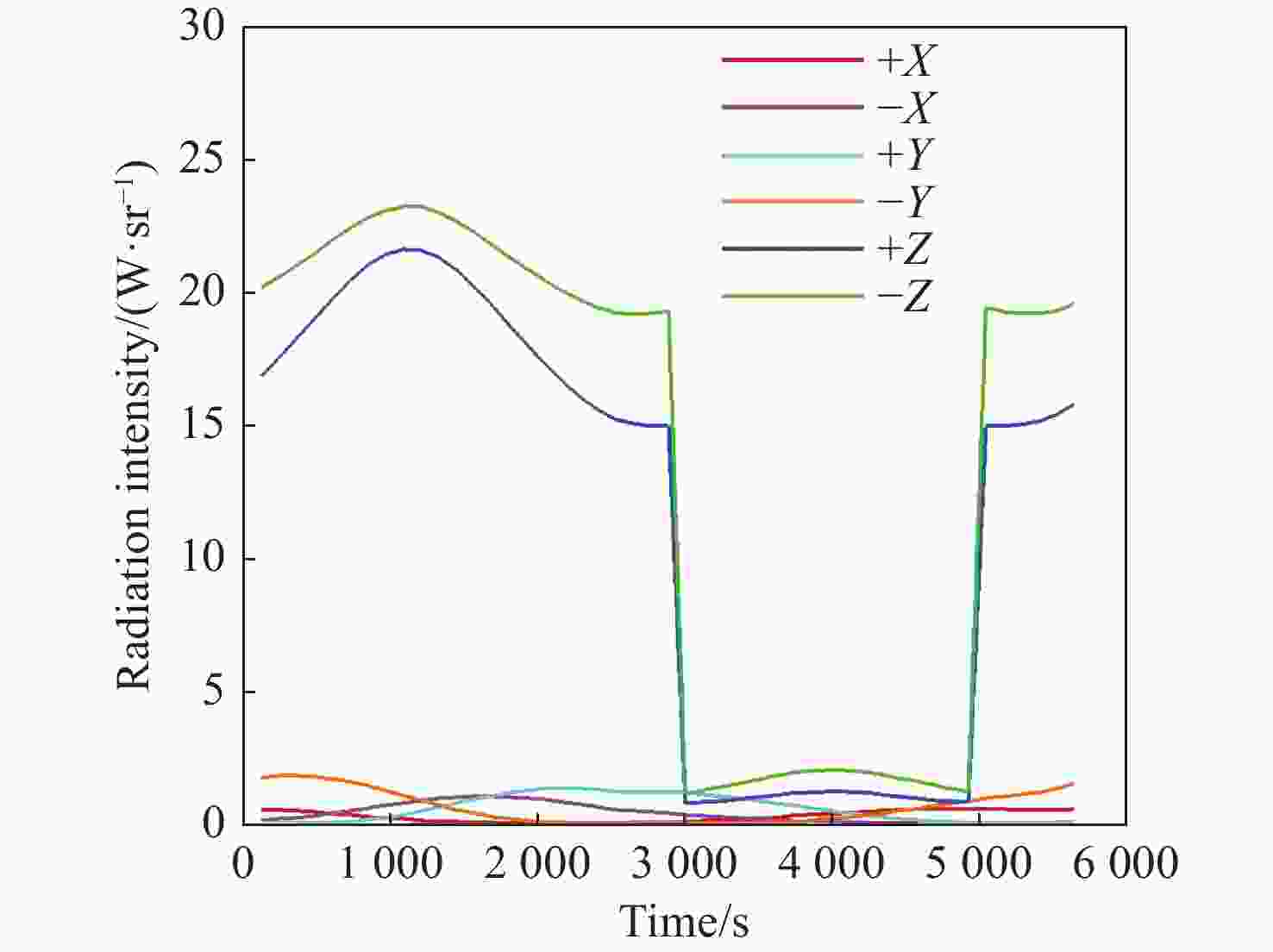
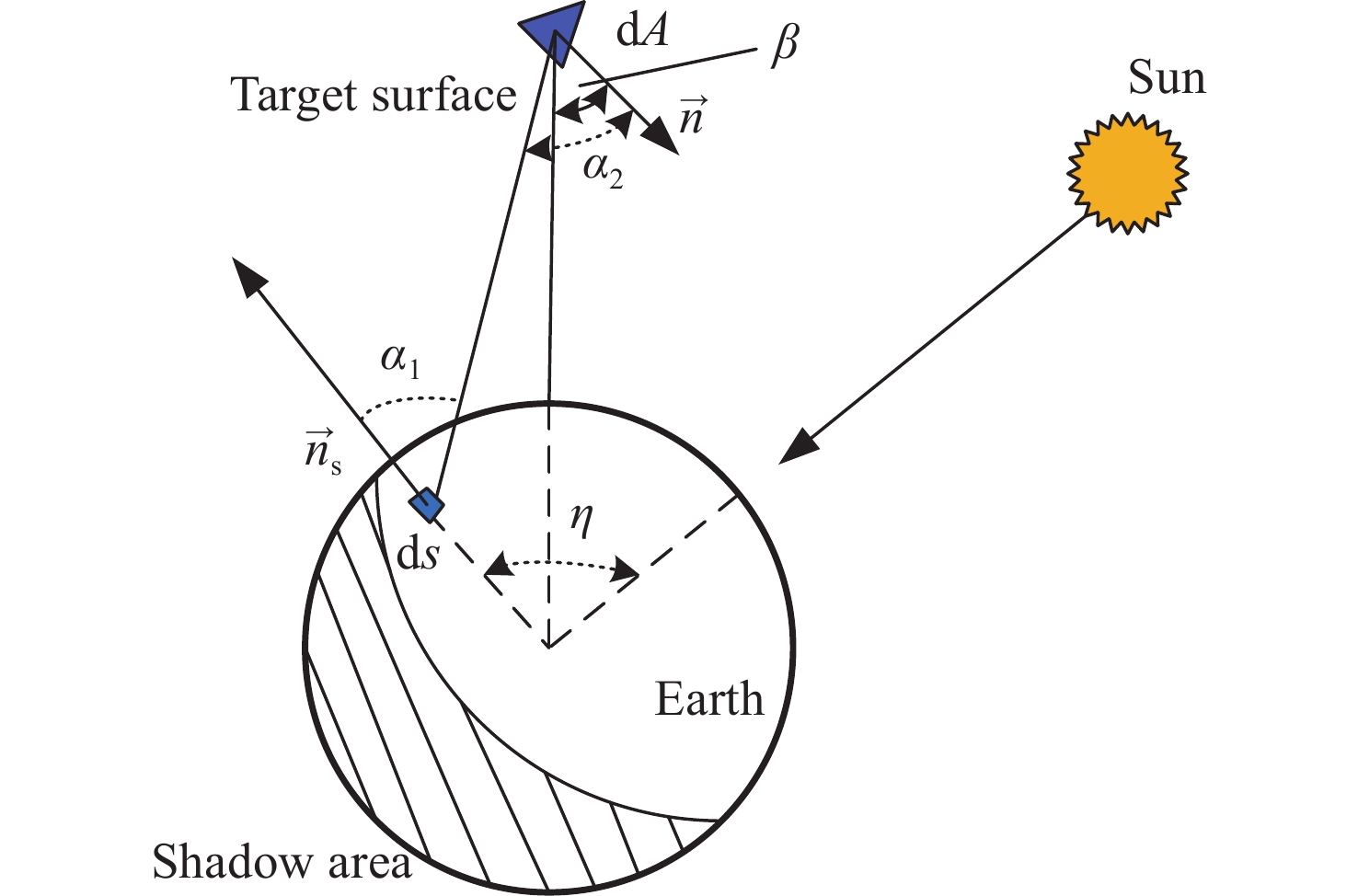
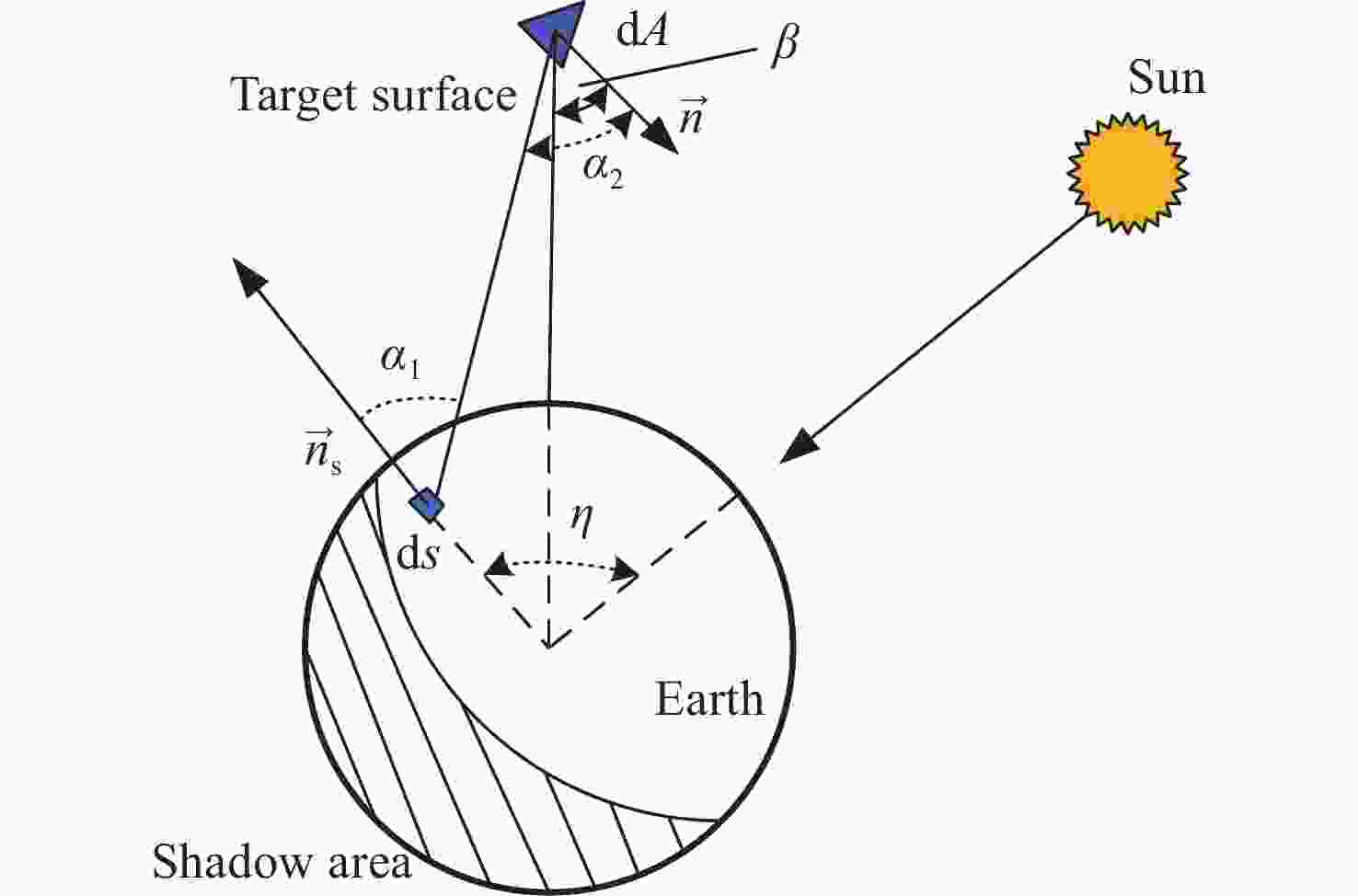
本文针对空间目标受到的太阳辐射、地球辐射、地球反照辐射,采用蒙特卡洛(Monte Carlo)法,基于非结构四面体网格编写了仿真程序,并对计算结果进行了对比验证。进一步地,对太阳同步轨道卫星受到的轨道外热流,采用带帆板的网格对有无遮挡情况下各表面受到的轨道外热流进行了分析。结果显示,在对地模式下考虑遮挡后,−
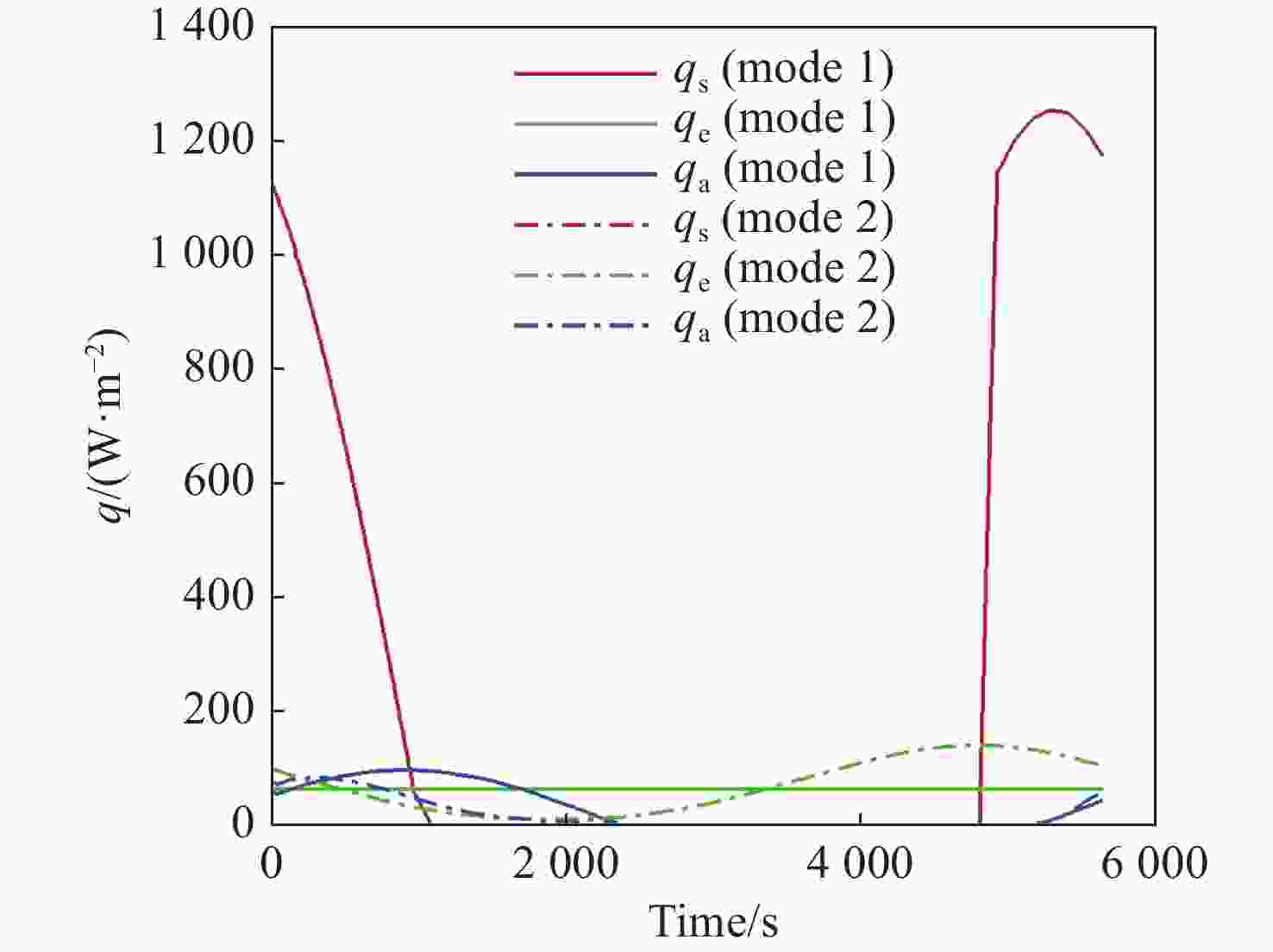
Y 表面平均热流值降低了53.79 W/m2,+Y −Z 侧帆板表面平均热流值降低了32.05 W/m2。结合表面材料属性,分析了各表面的温度特性,并结合帆板温度的在轨遥测数据,验证了计算的准确性。最后,计算了两种模式下各方向的红外辐射强度。结果表明,不同观测模式下各表面受热流的影响不同,对地模式下各表面温度随时间变化较大,而对日模式下各表面热流较为稳定。两种模式下,太阳能帆板的温度较高,辐射强度较大,具有明显的红外特征,便于开展红外观测。Abstract:In this paper, the solar radiation, the earth radiation and the earth albedo radiation received by the space target are simulated by Monte Carlo simulation method, and the simulation program is written based on the unstructured tetrahedral grid, and the calculation results are compared and verified. Furthermore, for the orbit external heat flow received by the sun-synchronous orbit satellite, the grid with solar panels is used to analyze the orbit external heat flow received by each surface with or without occlusion. The results show that the average heat flow value of −
Y surface decreases by 53.79 W/m2 after considering occlusion in the earth-pointing mode. The average surface heat flow value of +Y −Z side panel decreased by 32.05 W/m2. The temperature characteristics of each surface are given combined with the properties of surface materials, and the accuracy of the calculation is verified by combining with the on-orbit telemetry data of the solar panel temperature. Finally, the infrared radiation intensity in each direction of the two modes is calculated. The results show that the influence of heat flow on the surface is different under different observation modes. The temperature of each surface varies greatly over time in the earth-pointing mode, while the heat flow on each surface is relatively stable in the sun-pointing mode. Under both modes, the temperature of the solar panel is higher, the radiation intensity is larger, and it has obvious infrared characteristics, which facilitates infrared observation. -
表 1 表面材料热参数[15]
Table 1. Thermal parameters of surface material
表面 材料 吸收率 发射率 本体 氟46 0.35 0.68 太阳帆板 电池片 0.82 0.81 背板 0.88 0.86 表 2 典型位置地球红外角系数随平板俯仰角变化对比
Table 2. Comparison of earth infrared angular coefficients varying with plate pitch angle at typical positions
$\beta $/(°) 本文结果 Ref [16]结果 0 0.9129 0.9118 30 0.7961 0.7961 60 0.5673 0.5639 90 0.3139 0.3125 120 0.1107 0.1100 150 0.0081 0.0077 180 0.0000 0.0000 表 3 各平面一个轨道周期内的平均外热流
Table 3. Average external heat fluxes of each surface in one orbital period
W/m2 Surface Mode 1 Mode2 +X 390.51 87.92 −X 373.86 116.75 +Y 89.96 100.83 −Y 408.43 120.34 +Z 346.37 148.28 −Z 399.60 972.33 +Y+Z solar panel 342.52 148.17 +Y−Z solar panel 367.55 972.22 −Y+Z solar panel 346.43 148.29 −Y−Z solar panel 399.60 972.23 -
[1] 谷牧, 任栖锋, 周金梅, 等. 基于地基观测的时序卫星红外光谱建模与分析[J]. 物理学报,2019,68(5):059501. doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20181933GU M, REN Q F, ZHOU J M, et al. Modeling and analyzing of time-resolved satellite infrared spectrum based on ground-based detector[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2019, 68(5): 059501. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20181933 [2] 郑鸿儒, 马岩, 范林东, 等. 高空离轨发动机流场红外辐射特性研究[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(2):260-267.ZHENG H R, MA Y, FAN L D, et al. Infrared radiation characteristics of high-altitude off-orbit engine plume[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(2): 260-267. (in Chinese) [3] 易桦, 黄兴, 江海. 一种圆轨道航天器外热流通用计算方法[J]. 航天器工程,2021,30(5):53-58.YI H, HUANG X, JIANG H. Common calculation method for orbital heat flux of spacecraft on circular orbit[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2021, 30(5): 53-58. (in Chinese) [4] GARZÓN A, TAMI J A, CAMPOS-JULCA C D, et al. Effect of beta angle and contact conductances on the temperature distribution of a 3U CubeSat[J]. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 2022, 29: 101183. doi: 10.1016/j.tsep.2021.101183 [5] 李志松, 马昌健, 毛云杰, 等. 微纳卫星在轨温度场快速分析[J]. 航天器环境工程,2021,38(2):122-129.LI ZH S, MA CH J, MAO Y J, et al. Rapid analysis of temperature field for orbiting nanosatellites[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2021, 38(2): 122-129. (in Chinese) [6] 李世俊, 陈立恒, 冯文田, 等. 太阳同步轨道二维变姿态空间相机的外热流计算[J]. 红外与激光工程,2018,47(9):0917008. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201847.0917008LI SH J, CHEN L H, FENG W T, et al. Calculation of external heat fluxes on space camera with two-dimensional changing attitudes in sun-synchronous orbit[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47(9): 0917008. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA201847.0917008 [7] 吴愉华, 陈立恒, 李行, 等. 地球静止轨道变姿态空间相机的外热流计算[J]. 红外与激光工程,2019,48(6):0604001. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.0604001WU Y H, CHEN L H, LI H, et al. Computation of external heat fluxes on space camera with attitude change in geostationary orbit[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2019, 48(6): 0604001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.0604001 [8] ATAR C, AKTAŞ M. Advances in thermal modeling and analysis of satellites[J]. Gazi University Journal of Science, 2022, 35(1): 42-58. doi: 10.35378/gujs.840191 [9] 韩玉阁, 宣益民. 卫星的红外辐射特征研究[J]. 红外与激光工程,2005,34(1):34-37.HAN Y G, XUAN Y M. Infrared feature of the satellite[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2005, 34(1): 34-37. (in Chinese) [10] 潘晴, 王平阳, 包轶颖, 等. 基于反向蒙特卡罗法的飞行器在轨外热流计算[J]. 上海交通大学学报,2012,46(5):750-755,761.PAN Q, WANG P Y, BAO Y Y, et al. On-orbit external heat flux calculation of spacecraft based on reverse Monte Carlo method[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2012, 46(5): 750-755,761. (in Chinese) [11] 刘巨. 太阳同步圆轨道空间相机瞬态外热流计算[J]. 中国光学,2012,5(2):148-153.LIU J. Calculation of transient space heat fluxes for space cameras working in sun-synchronous circle orbit[J]. Chinese Optics, 2012, 5(2): 148-153. (in Chinese) [12] 闵桂荣. 卫星热控制技术[M]. 北京: 中国宇航出版社, 1991: 61-65.MIN G R. Satellite Thermal Control Technology[M]. Beijing: China Aerospace Press, 1991: 61-65. (in Chinese) [13] 侯增褀, 胡金刚. 航天器热控制技术[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 2007: 340-347.HOU Z Q, HU J G. Spacecraft Thermal Control Technology[M]. Beijing: China Science and Technology Press, 2007: 340-347. (in Chinese) [14] 丁少华, 刘书峰, 陈小文, 等. 空间目标温度特性分析及仿真[J]. 红外,2011,32(5):19-22.DING SH H, LIU SH F, CHEN X W, et al. Analysis and simulation of temperature characteristics of space target[J]. Infrared, 2011, 32(5): 19-22. (in Chinese) [15] 王盈, 黄建明, 魏祥泉. 空间目标在轨红外成像仿真[J]. 红外与激光工程,2015,44(9):2593-2597.WANG Y, HUANG J M, WEI X Q. Infrared imaging simulation of space target in orbit[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2015, 44(9): 2593-2597. (in Chinese) [16] 赵立新. 轨道空间外热流计算的一种新方法[J]. 光学 精密工程,1995,3(6):80-85.ZHAO L X. A new method to calculate the heat flux in spacecraft orbits[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 1995, 3(6): 80-85. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: