Design of broadband achromatic far-infrared metalens based on chalcogenide glass using parameterized topology optimization
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2025-0003
-
摘要:
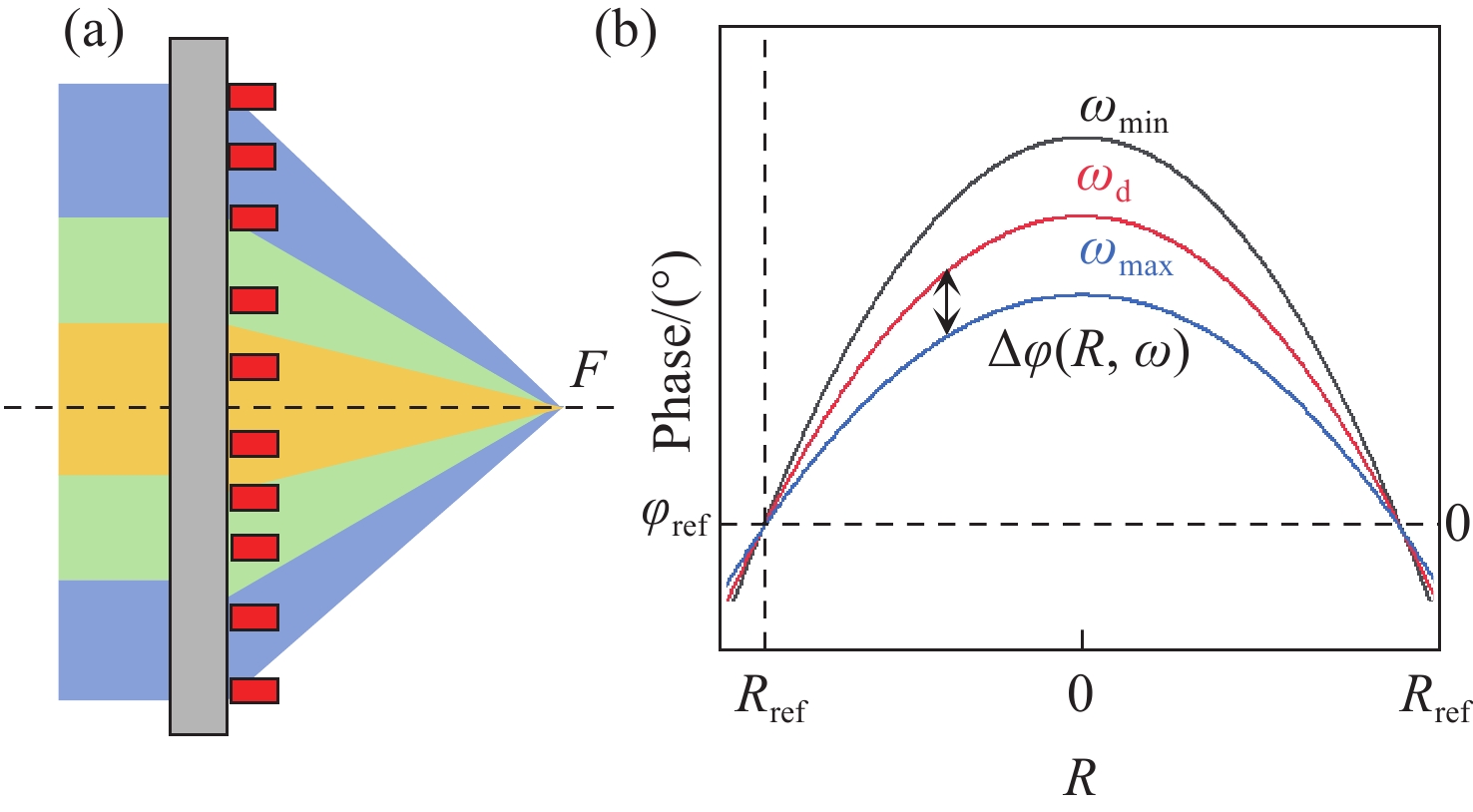
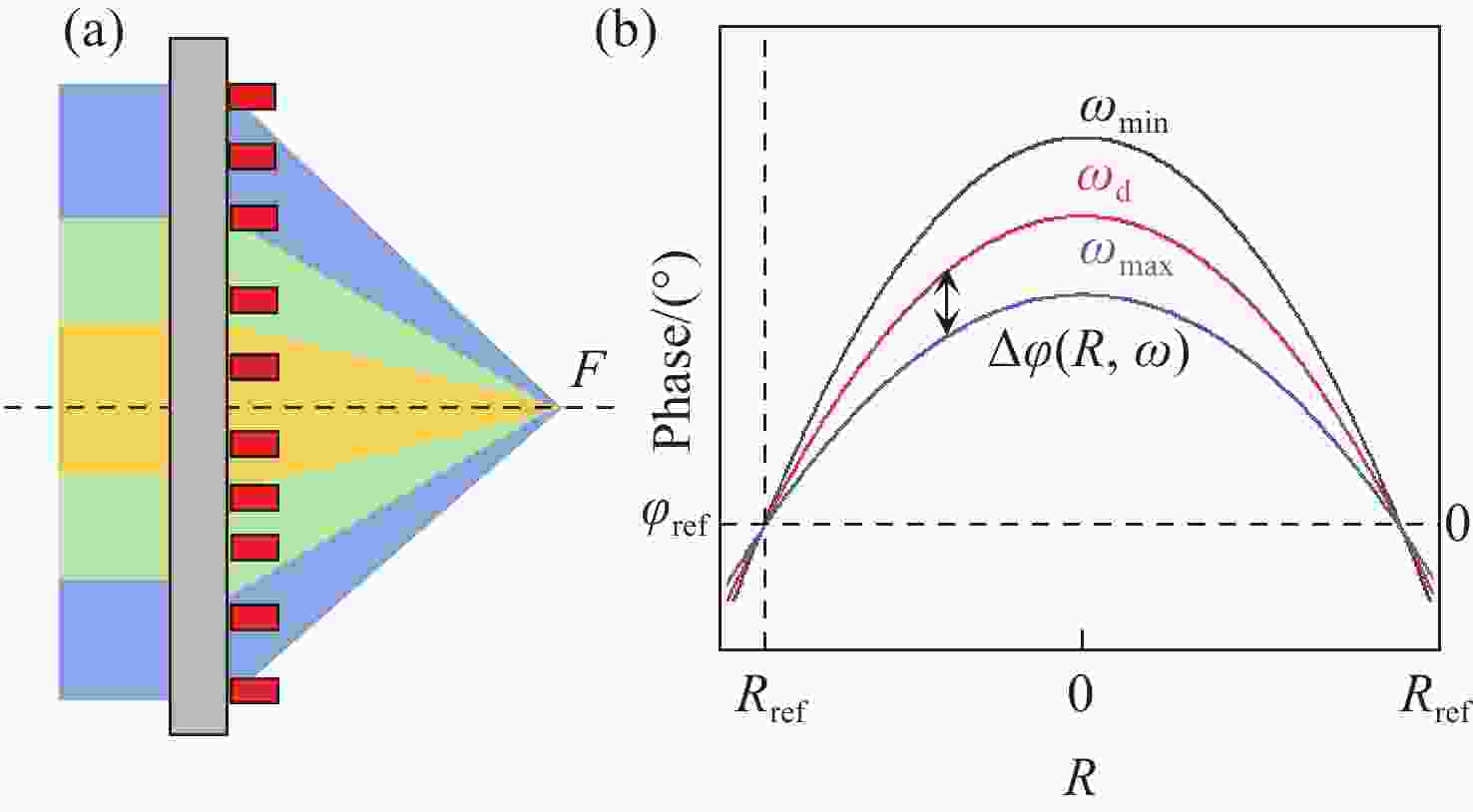
超透镜技术在小型化、集成化红外成像系统中有着广泛的应用。然而,由于单元结构的色散较高,导致超透镜经常出现色差,使得宽带消色差红外成像难以实现。该文章构建了基于硫系玻璃的6种不同单元结构,并对其相位色散参数进行分析,建立数据库。在此基础上,采用色差补偿和参数化伴随拓扑优化的方法,在远红外波段将这6种单元结构排列组合,设计出数值孔径为0.5的宽带消色差超透镜。仿真结果表明,该超透镜在9~11µm的工作波长范围内实现了近衍射极限聚焦,具有良好的消色差性能,全波长具有为54%~58%的平坦的聚焦效率。
Abstract:Metalens technology has been applied extensively in miniaturized and integrated infrared imaging systems. However, due to the high phase dispersion of unit structures, metalens often exhibits chromatic aberration, making broadband achromatic infrared imaging challenging to achieve. In this paper, six different unit structures based on chalcogenide glass are constructed, and their phase-dispersion parameters are analyzed to establish a database. On this basis, using chromatic aberration compensation and parameterized adjoint topology optimization, a broadband achromatic metalens with a numerical aperture of 0.5 is designed by arranging these six unit structures in the far-infrared band. Simulation results show that the metalens achieves near diffraction-limited focusing within the operating wavelength range of 9−11 µm, demonstrating the good performance of achromatic aberration with flat focusing efficiency of 54%−58% across all wavelengths.
-
Key words:
- metalens /
- chalcogenide glass /
- topology optimization /
- high efficiency /
- long wave infrared /
- broadband operation
-
Figure 3. (a) Phase simulation results of unit structure. (b) Distributions of the phase-dispersion parameters for the solid square column structure, where red cross and blue point represent the phase-dispersion parameters of an actual square column structure and the theoretical structure, respectively. (c) Database of the phase-dispersion parameters for all unit structures. (d) Distributions of the phase-dispersion parameters of the initial structure closest to theoretical structures for each position
Table 1. Summary of performances for broadband achromatic metalens
NA Operating wavelength/µm Diameter/µm Average focusing efficiency Polarization Ref. 0.6 0.45−0.75 6 45% Insensitive [11] 0.6 0.63 20 65% Circular [10] 0.11 0.62 112 45% Circular [24] 0.38 3−5 30 46.5% Insensitive [8] 0.56 0.64 10.2 50% Circular [25] 0.82 15.5 50 72% Circular [26] 0.54 8.6−11.4 191.4 38.2% Circular [27] 0.5 9−11 204 56% (54%−58%) Insensitive This paper -
[1] AHMAD M, LI J N, ZHOU R Y, et al. Ultrathin ring-shaped metasurface for a multiview 3D display[J]. Applied Optics, 2024, 63(19): 5217-5222. [2] WU ZH X, ZOU Y Y, DENG H, et al. Broadband devices for a polarization converter based on optical metasurfaces[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 61(24): 7119-7124. doi: 10.1364/AO.464801 [3] OU K, YU F L, LI G H, et al. Mid-infrared polarization-controlled broadband achromatic metadevice[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(37): eabc0711. [4] CHEN J, YU F L, LIU X S, et al. Polychromatic full-polarization control in mid-infrared light[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2023, 12(1): 105. [5] WANG J X, YU F L, CHEN J, et al. Continuous‐spectrum–polarization recombinant optical encryption with a dielectric metasurface[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(41): 2304161. [6] LI Y P, LUO J CH, JI R N, et al. Long wavelength infrared metalens fabricated by photolithography[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2024, 43(5): 603-608. (in Chinese). [7] KHORASANINEJAD M, SHI Z, ZHU A Y, et al. Achromatic metalens over 60 nm bandwidth in the visible and metalens with reverse chromatic dispersion[J]. Nano Letters, 2017, 17(3): 1819-1824. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b05137 [8] WANG SH M, WU P C, SU V C, et al. Broadband achromatic optical metasurface devices[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 187. [9] XIE Y, ZHANG J Q, WANG SH Y, et al. Broadband achromatic polarization-insensitive metalens in the mid-wave infrared range[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 61(14): 4106-4112. [10] SANG D, XU M F, PU M B, et al. Toward high‐efficiency ultrahigh numerical aperture freeform metalens: from vector diffraction theory to topology optimization[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2022, 16(10): 2200265. [11] MANSOUREE M, MCCLUNG A, SAMUDRALA S, et al. Large-scale parametrized metasurface design using adjoint optimization[J]. ACS Photonics, 2021, 8(2): 455-463. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.0c01058 [12] PHAN T, SELL D, WANG E W, et al. High-efficiency, large-area, topology-optimized metasurfaces[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2019, 8: 48. [13] CHRISTIANSEN R E, SIGMUND O. Inverse design in photonics by topology optimization: tutorial[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2021, 38(2): 496-509. [14] LIN Z, LIU V, PESTOURIE R, et al. Topology optimization of freeform large-area metasurfaces[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(11): 15765-15775. [15] CHEN F T, CRAIGHEAD H G. Diffractive lens fabricated with mostly zeroth-order gratings[J]. Optics Letters, 1996, 21(3): 177-179. [16] LALANNE P, ASTILEAN S, CHAVEL P, et al. Blazed binary subwavelength gratings with efficiencies larger than those of conventional échelette gratings[J]. Optics Letters, 1998, 23(14): 1081-1083. doi: 10.1364/OL.23.001081 [17] ARBABI A, HORIE Y, BALL A J, et al. Subwavelength-thick lenses with high numerical apertures and large efficiency based on high-contrast transmitarrays[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 7069. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8069 [18] YU N F, GENEVET P, KATS M A, et al. Light propagation with phase discontinuities: generalized laws of reflection and refraction[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6054): 333-337. doi: 10.1126/science.1210713 [19] BAYATI E, ZHAN A L, COLBURN S, et al. Role of refractive index in metalens performance[J]. Applied Optics, 2019, 58(6): 1460-1466. doi: 10.1364/AO.58.001460 [20] YANG J J, FAN J A. Analysis of material selection on dielectric metasurface performance[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(20): 23899-23909. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.023899 [21] JENSEN J S, SIGMUND O, REVIEWS P. Topology optimization for nano‐photonics[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2011, 5(2): 308-321. [22] SELL D, YANG J J, DOSHAY S, et al. Large-angle, multifunctional metagratings based on freeform multimode geometries[J]. Nano Letters, 2017, 17(6): 3752-3757. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b01082 [23] LIAO W P, LIU H L, LIN Y F, et al. I-line photolithographic metalenses enabled by distributed optical proximity correction with a deep-learning model[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(12): 21184-21194. doi: 10.1364/OE.456469 [24] ZHAN A L, COLBURN S, TRIVEDI R, et al. Low-contrast dielectric metasurface optics[J]. ACS Photonics, 2016, 3(2): 209-214. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.5b00660 [25] ELSAWY M M R, GOURDIN A, BINOIS M, et al. Multiobjective statistical learning optimization of RGB metalens[J]. ACS Photonics, 2021, 8(8): 2498-2508. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.1c00753 [26] WEI H M, HU W C, PANG F F. Inverse design of high-performance near-infrared polymer metalens[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2024, 44(8): 0822002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS231859 [27] WU H, YI Y T, ZHANG N, et al. Inverse design broadband achromatic metasurfaces for longwave infrared[J]. Optical Materials, 2024, 148: 114923. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2024.114923 -





 下载:
下载: