-
摘要:目的
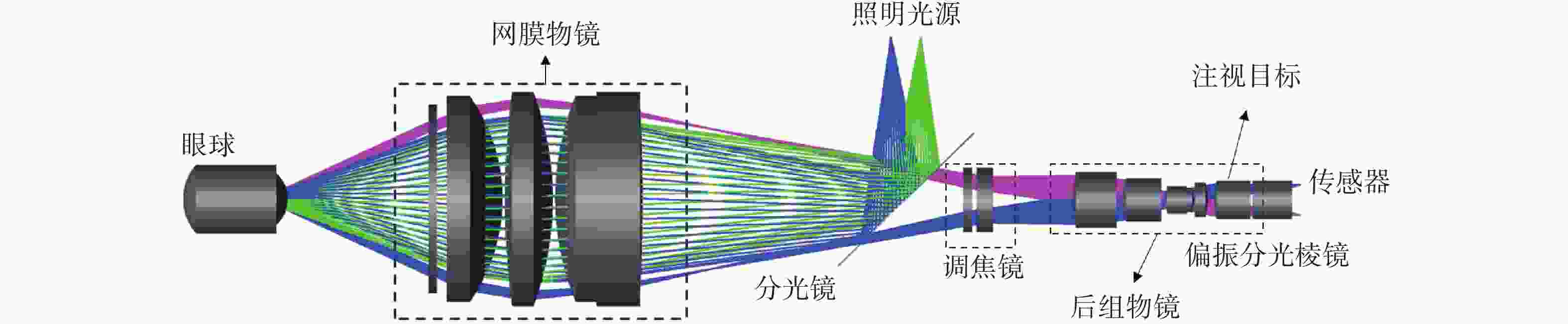
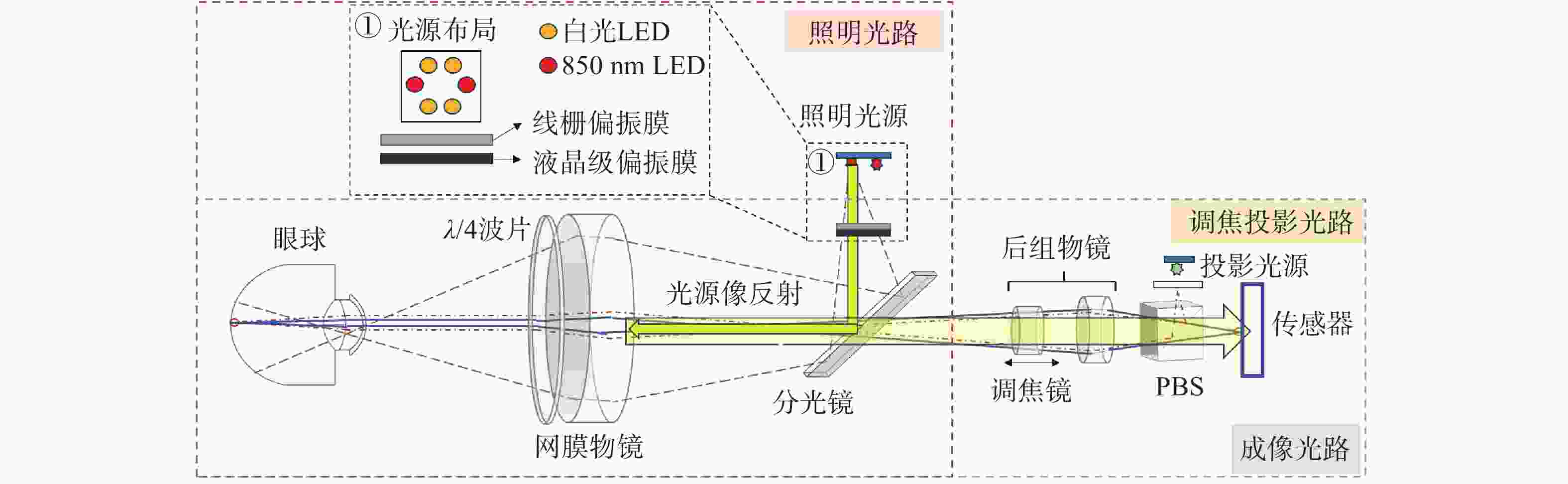
针对传统便携式免散瞳眼底相机存在照明与成像光路相互制约、角膜杂散光干扰严重、视网膜不同区域难以同时清晰成像等问题,本文提出一种新型眼底光学系统设计方案。
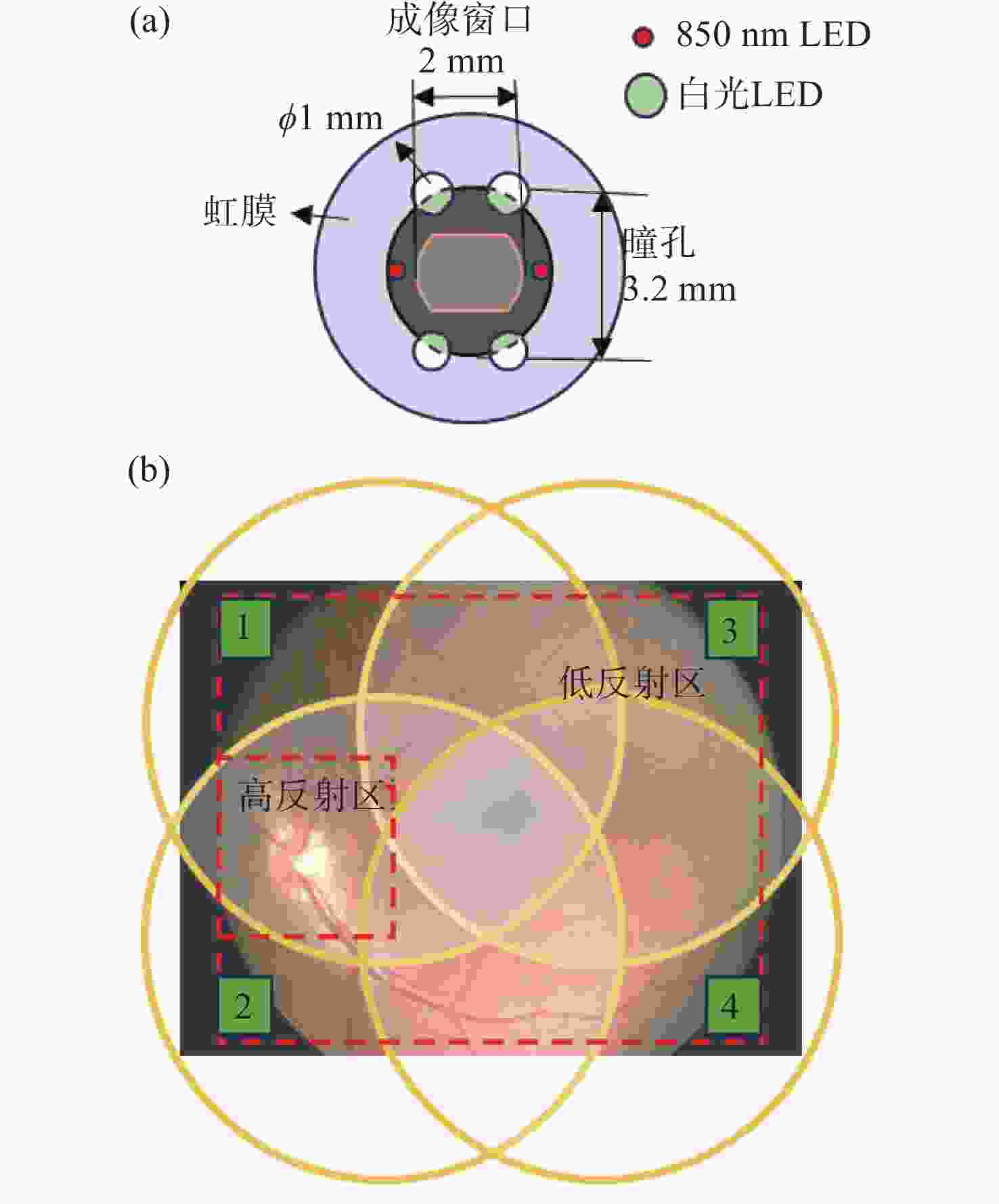
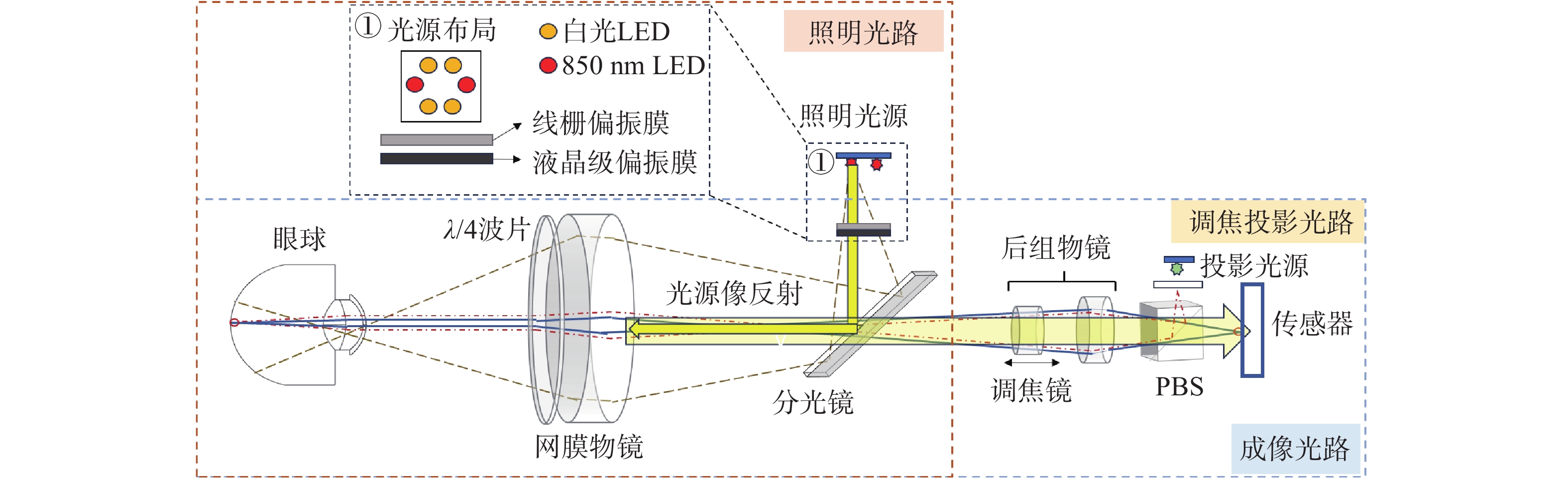
方法该方案采用四点光源矩形布局与分区域亮度可调的照明方式,在3.2 mm瞳孔直径下使角膜杂散光较传统方法减少91.56%,并可实现视盘与黄斑区域的高对比度同步成像。系统通过照明光路与成像光路分离设计,结合线栅与液晶叠层偏振技术,有效抑制光学表面反射杂光。
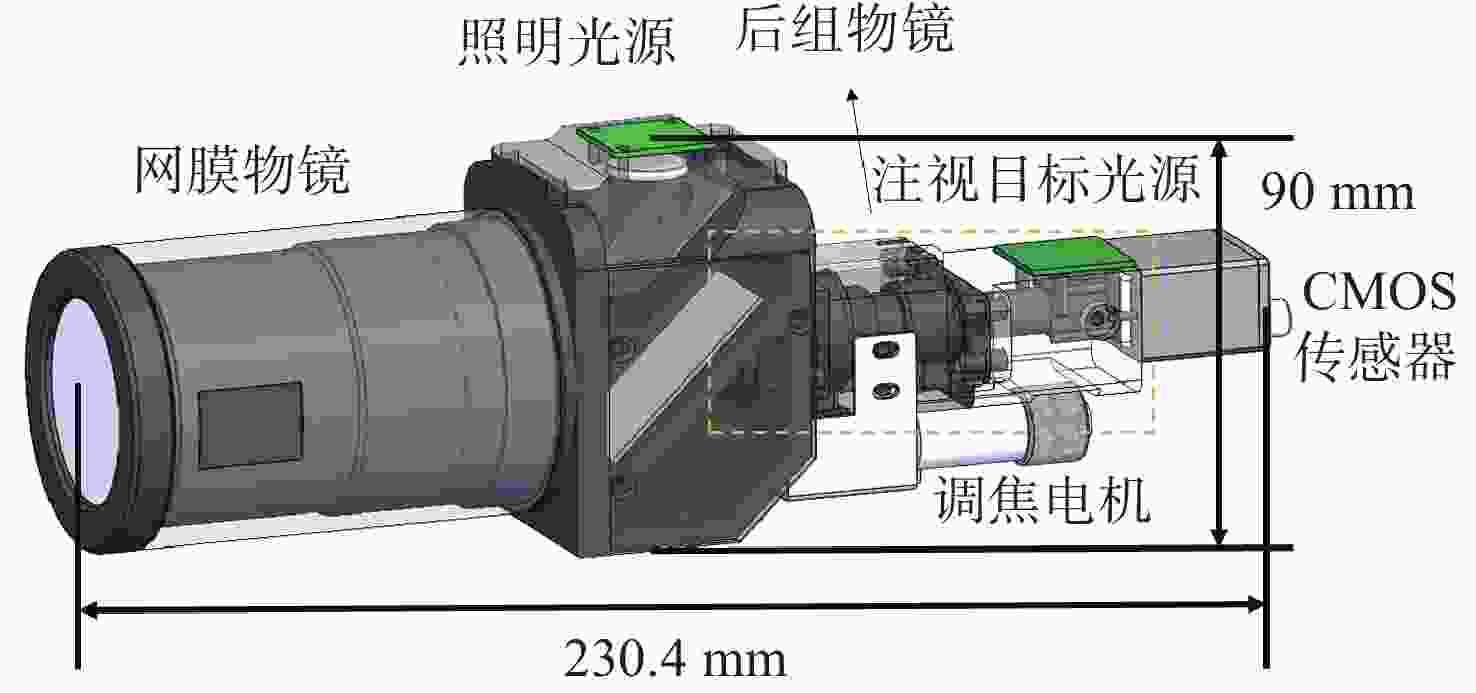
结果在230.4 mm*90 mm紧凑型结构内同步实现53°大视场、±20 D屈光补偿,及6 μm的眼底分辨率。
结论本系统通过单次拍摄人眼即可获得视盘与黄斑细节清晰、对比度优良的视网膜图像。
Abstract:Objetive: To address the inherent limitations of conventional portable non-mydriatic fundus cameras, including the mutual constraints between illumination and imaging optical paths, severe interference from corneal stray light, and the difficulty of achieving simultaneous clear imaging of different retinal regions, this paper proposes a novel fundus optical system design. Method: The proposed system adopts a four-point rectangular illumination layout combined with regionally adjustable illumination intensity. At a pupil diameter of 3.2 mm, the corneal stray light is reduced by 91.56% compared with traditional approaches, enabling high-contrast synchronous imaging of both the optic disc and macular regions. Furthermore, a separated illumination and imaging optical path architecture is employed. By integrating a wire-grid polarizer with a stacked liquid-crystal polarization scheme, stray light caused by optical surface reflections is effectively suppressed. Result: Within a compact system envelope of 230.4 mm × 90 mm, the proposed fundus camera simultaneously achieves a wide field of view of 53°, a refractive error compensation range of ±20 D, and a retinal spatial resolution of 6 μm. Conclusion: The proposed system enables the acquisition of high-contrast retinal images with clearly resolved details of both the optic disc and macula in a single-shot capture, demonstrating its suitability for portable non-mydriatic fundus imaging applications.
-
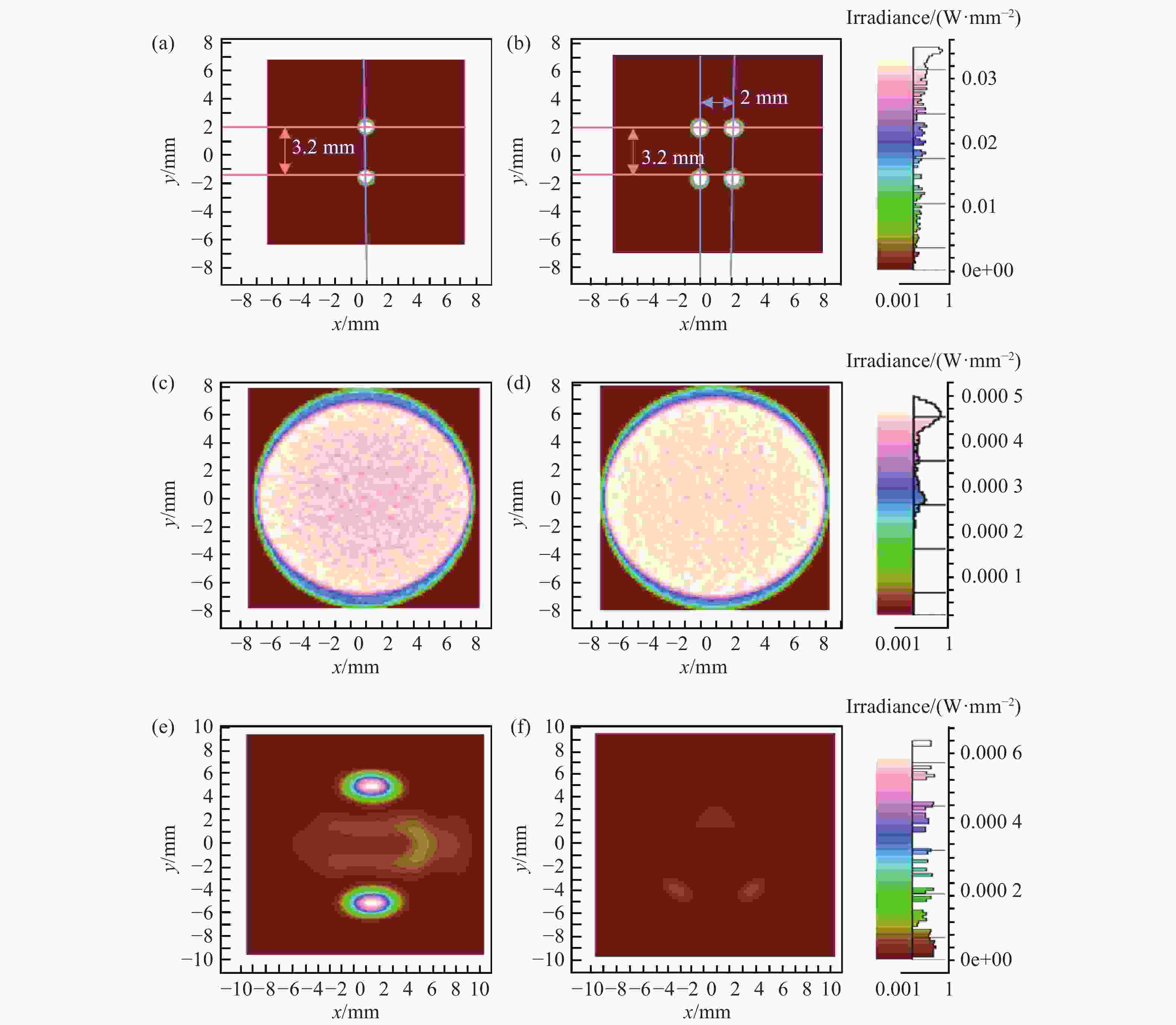
图 5 不同光源布局照明仿真结果对比分析:(a)两点对称照明瞳孔面光场分布;(b)四点矩形照明瞳孔面光场分布;(c)两点对称照明眼底面照度分布;(d)四点矩形照明眼底面照度分布;(e)两点对称照明下传感器接收的角膜杂散光分布;(f)四点矩形照明下传感器接收的角膜杂散光分布。
Figure 5. Comparative analysis of illumination simulation results for different light source configurations. (a) Intensity distribution on the pupil plane under two-point symmetric illumination; (b) Intensity distribution on the pupil plane under four-point rectangular illumination; (c) Irradiance distribution on the fundus plane under two-point symmetric illumination; (d) Irradiance distribution on the fundus plane under four-point rectangular illumination; (e) Distribution of corneal stray light received by the sensor under two-point symmetric illumination; (f) Distribution of corneal stray light received by the sensor under four-point rectangular illumination.
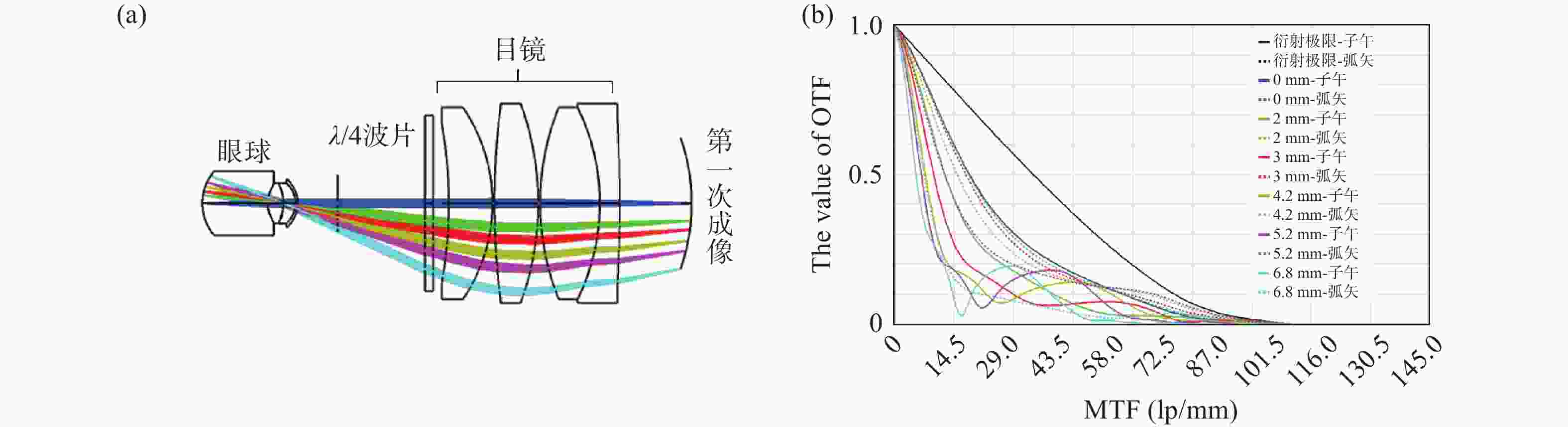
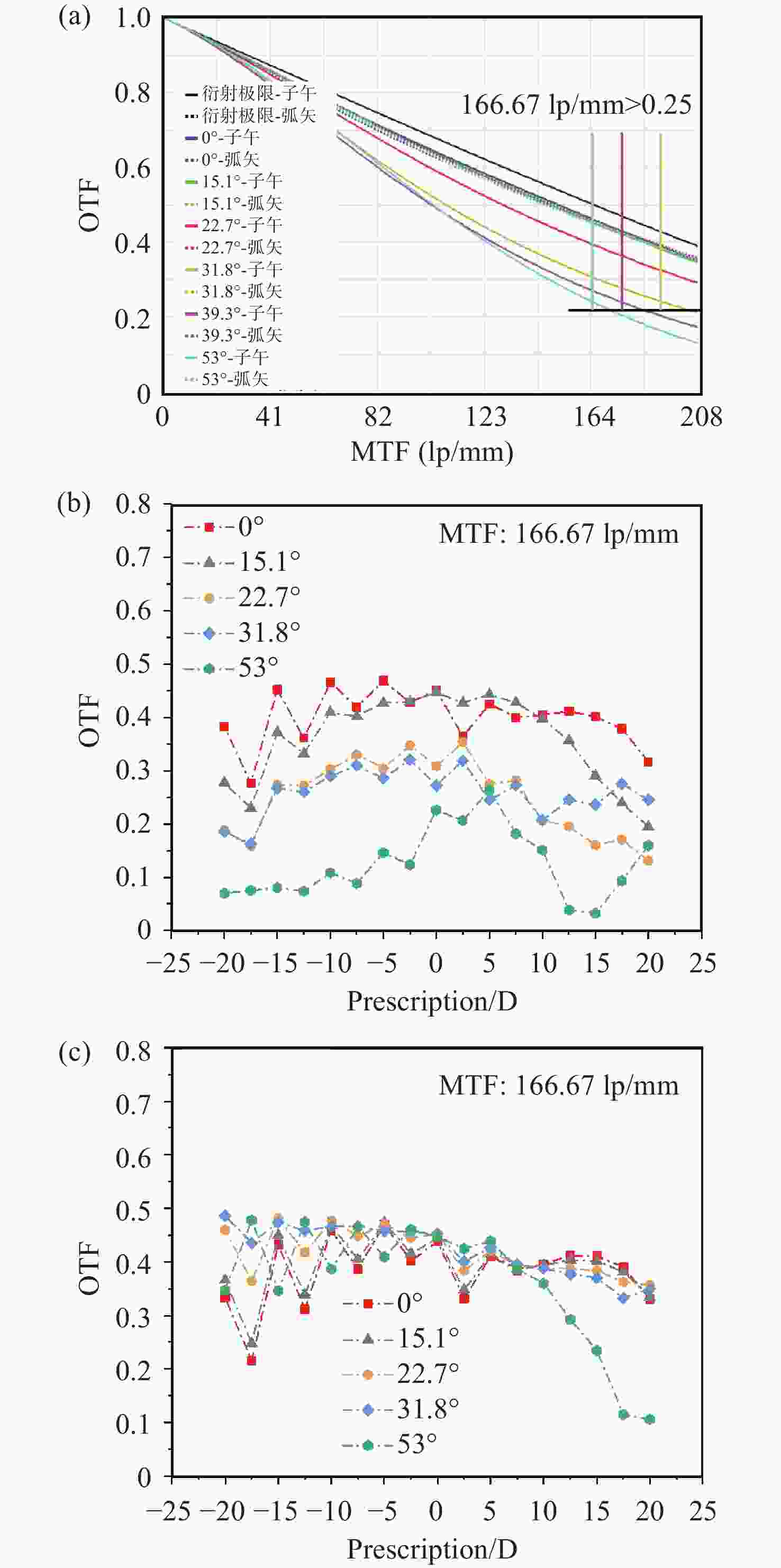
图 6 成像系统像质评价:(a) 0 D下可见光波段的调制传递函数曲线;(b) ±20 D范围内各视场在子午方向上、166.67 lp/mm处的光学传递函数模值;(c) ±20 D范围内各视场在弧矢方向上、166.67 lp/mm处的光学传递函数模值。
Figure 6. Image quality evaluation of the imaging system. (a) MTF curves in the visible wavelength range at 0 D; (b) Magnitude of the optical transfer function (|OTF|) at 166.67 lp/mm in the tangential direction for different fields within a refractive error range of ±20 D; (c) Magnitude of the optical transfer function (|OTF|) at 166.67 lp/mm in the sagittal direction for different fields within a refractive error range of ±20 D.
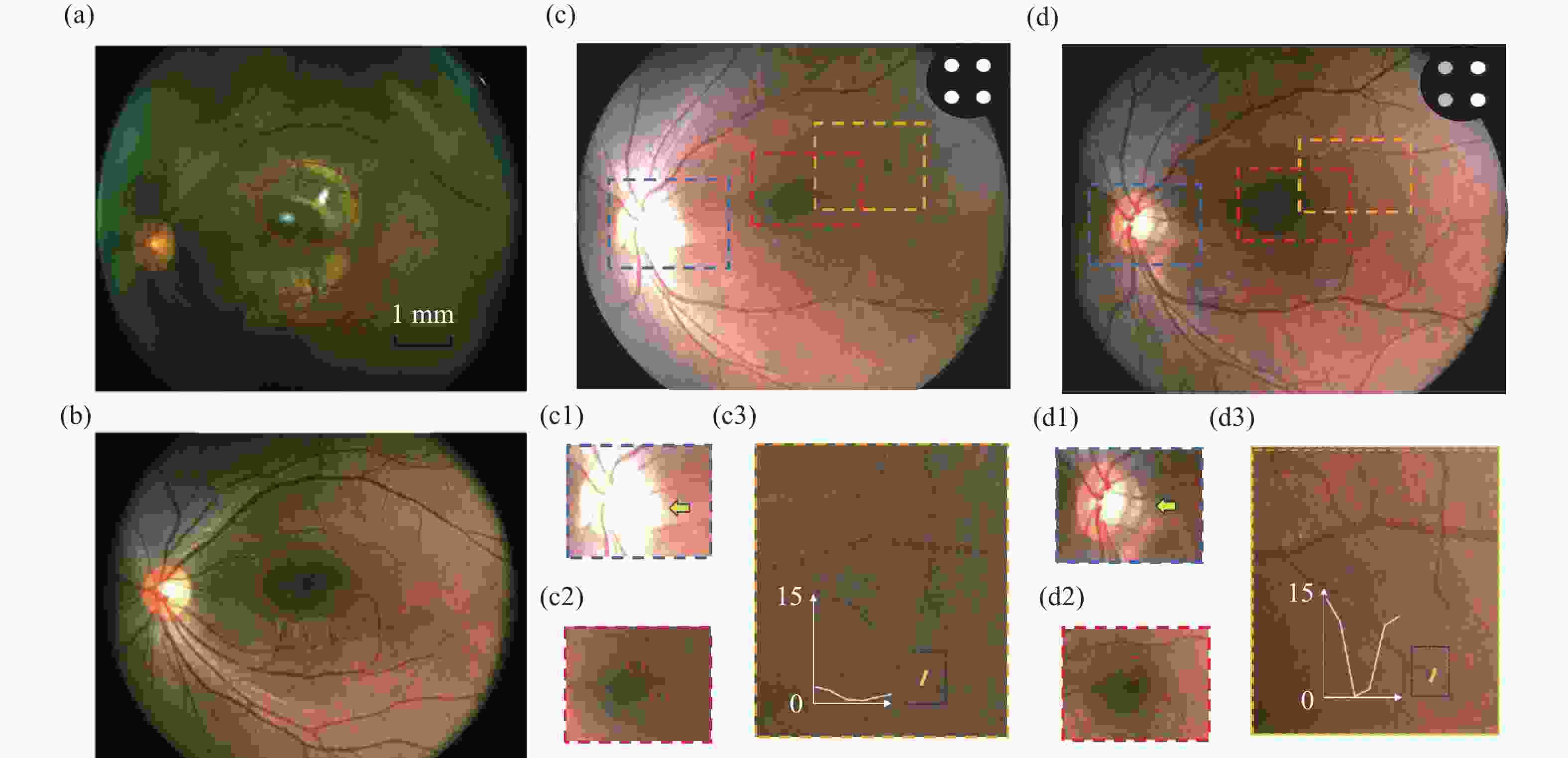
图 8 人眼成像测试:(a)对称两点照明成像;(b)四点矩形照明成像;(c)常规均匀照明的视网膜图像,其中(c1)视盘区域、(c2)黄斑中心凹、(c3)血管对比度局部(沿图中黄色截线所示);(d)区域调光后的视网膜图像,其中(d1)视盘区域、(d2)黄斑中心凹、(d3)血管对比度局部(沿图中黄色截线所示)。
Figure 8. Human eye imaging experiments. (a) Retinal image acquired under two-point symmetric illumination; (b) Retinal image acquired under four-point rectangular illumination; (c) Retinal image acquired under conventional uniform illumination, with (c1) the optic disc region, (c2) the foveal center, and (c3) a local profile of vascular contrast along the yellow line indicated; (d) Retinal image acquired with regionally adjusted illumination, with (d1) the optic disc region, (d2) the foveal center, and (d3) a local profile of vascular contrast along the yellow line indicated.
表 1 眼底相机的设计技术指标
Table 1. Design specifications of the fundus camera.
技术指标 数值 总长(mm) ≤200 视场角(deg) ≥53 入瞳直径(mm) 2 工作波长(nm) 436~656/850 调焦度数范围(D) -20~+20 调制传递函数(MTF) @166.67 lp/mm ≥0.2 表 2 本系统与国内市面上两款相机的性能参数对比
Table 2. Comparison of performance parameters between the proposed system and two commercially available domestic fundus cameras.
工作参数 本系统 AI-FD16aF Kestrel 300 入瞳直径 (mm) 3.2 3.5 3.5 工作距离 (mm) 35±2 - 15±5 分辨率 (lp/mm) ≥80 80 ≥60 视场角 (°) 53 40 35 屈光调节范围 (D) −20~+20 −15~+15 −15~+15 照明方法 四点矩形 单点倾斜照明 单点倾斜照明 尺寸(长*高)(mm*mm) 230*90 280*130 284*145 -
[1] SACHDEVA V, VASSENEIX C, HAGE R, et al. Optic nerve head edema among patients presenting to the emergency department[J]. Neurology, 2018, 90(5): e373-e379. doi: 10.1212/wnl.0000000000004895 [2] 陈蔚霖, 常军, 赵雪惠, 等. 广域眼底相机光学系统的设计与仿真分析[J]. 中国光学, 2020, 13(4): 814-821. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0066CHEN W L, CHANG J, ZHAO X H, et al. Optical system design and simulation of a wide-area fundus camera[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(4): 814-821. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0066 [3] LI B, CHEN H, ZHANG B L, et al. Development and evaluation of a deep learning model for the detection of multiple fundus diseases based on colour fundus photography[J]. British Journal of Ophthalmology, 2022, 106(8): 1079-1086. [4] MILEA D, NAJJAR R P, JIANG ZH B, et al. Artificial intelligence to detect papilledema from ocular fundus photographs[J]. New England Journal of Medicine, 2020, 382(18): 1687-1695. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1917130 [5] LIU L, LIU Y M, YAN X T, et al. Retinal layer segmentation using gradient feature calculation in OCT[J]. Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences, 2024, 17(6): 2450021. doi: 10.1142/S1793545824500214 [6] YAO X CH, SON T, MA J CH. Developing portable widefield fundus camera for teleophthalmology: Technical challenges and potential solutions[J]. Experimental Biology and Medicine, 2022, 247(4): 289-299. doi: 10.1177/15353702211063477 [7] 王晓恒, 薛庆生. 大视场手持式免散瞳眼底照相机光学设计[J]. 光学学报, 2017, 37(9): 0922001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0922001WANG X H, XUE Q SH. Optical design of portable Non-Mydriatic Fundus camera with large field of view[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(9): 0922001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0922001 [8] 江剑宇, 杨波, 万新军, 等. 便携式免散瞳带信标眼底相机光学系统[J]. 光学技术, 2019, 45(2): 240-244. doi: 10.13741/j.cnki.11-1879/o4.2019.02.021JIANG J Y, YANG B, WAN X J, et al. A portable and mydriasis-free fundus optical system with a beacon[J]. Optical Technique, 2019, 45(2): 240-244. (in Chinese). doi: 10.13741/j.cnki.11-1879/o4.2019.02.021 [9] HONG Y, ZENG CH M, XIA CH L, et al. Design of automatic focusing fundus camera[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2021, 11780: 117800J. doi: 10.1117/12.2589586 [10] 杨皓聿, 任文斌, 常献刚, 等. 一种小型眼底相机: 中国, 202011095592.1[P]. 2020-12-08.YANG H Y, REN W B, CHANG X G, et al. Small fundus camera: CN, 202011095592.1[P]. 2020-12-08. (in Chinese). [11] 牟国强, 陈荡荡, 杨皓聿. 一种用于眼底相机调焦的光学系统及眼底相机: 中国, 202410579696.1[P]. 2024-07-02.MOU G Q, CHEN D D, YANG H Y. Optical system for fundus camera focusing and fundus camera: CN, 202410579696.1[P]. 2024-07-02. (in Chinese). [12] HAFIZ F, CHALAKKAL R J, HONG S C, et al. A new approach to non-mydriatic portable fundus imaging[J]. Expert Review of Medical Devices, 2022, 19(4): 303-314. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2022.2070004 [13] REMINGTON L A. Clinical Anatomy and Physiology of the Visual System[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2012: 233-252. [14] YOUSSIF A A A, GHALWASH A Z, GHONEIM A S. A comparative evaluation of preprocessing methods for automatic detection of retinal anatomy[C]. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Informatics & Systems, INFOS, 2007: 24-30. [15] KOLAR R, ODSTRCILIK J, JAN J, et al. Illumination correction and contrast equalization in colour fundus images[C]. 2011 19th European Signal Processing Conference, IEEE, 2011: 298-302. [16] 盖俊帅, 马玉婷, 张运海, 等. 用于眼底视网膜图像的去雾状杂散光算法[J]. 液晶与显示, 2024, 39(8): 1070-1078. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2023-0289GAI J S, MA Y T, ZHANG Y H, et al. Dehazing stray light algorithm for fundus retinal image[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2024, 39(8): 1070-1078. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2023-0289 [17] SAHA S K, XIAO D, KANAGASINGAM Y. A novel method for correcting non-uniform/poor illumination of color fundus photographs[J]. Journal of Digital Imaging, 2018, 31(4): 553-561. doi: 10.1007/s10278-017-0040-0 [18] ROSSI A, RAHIMI M, SON T, et al. Preserving polarization maintaining photons for enhanced contrast imaging of the retina[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2023, 14(11): 5932-5945. doi: 10.1364/BOE.501636 [19] ROSSI A, RAHIMI M, LE D, et al. Portable widefield fundus camera with high dynamic range imaging capability[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2023, 14(2): 906-917. doi: 10.1364/BOE.481096 [20] ZAITSEV M, MACLAREN J, HERBST M. Motion artifacts in MRI: a complex problem with many partial solutions[J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2015, 42(4): 887-901. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24850 [21] DUKE D J, KNAST T, THETHY B, et al. A low-cost high-speed CMOS camera for scientific imaging[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2019, 30(7): 075403. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/ab1832 [22] 罗敬, 陈兴达, 吕凝睿, 等. 光学系统偏振特性影响抑制方法综述[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2025, 18(5): 979-1015. doi: 10.37188/CO.2025-0066LUO J, CHEN X D, LV N R, et al. A review of methods for suppressing the influence of polarization characteristics in optical systems[J]. Chinese Optics, 2025, 18(5): 979-1015. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2025-0066 [23] 史浩东, 许家伟, 张健, 等. 强光背景下主动偏振成像方法[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2024, 17(5): 1075-1086. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0151SHI H D, XU J W, ZHANG J, et al. Active polarization imaging method under strong light background[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(5): 1075-1086. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0151 [24] 邢陈陈, 郑继红, 陈芳芳, 等. 光控取向液晶偏振全息柱透镜的制备及聚焦特性[J]. 液晶与显示, 2024, 39(5): 593-601. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2024-0027XING CH CH, ZHENG J H, CHEN F F, et al. Preparation and focusing characteristics of polarized holographic photo-alignment liquid crystal cylindrical lenses[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2024, 39(5): 593-601. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2024-0027 [25] International Agency for the Prevention of Blindness. Equipment specifications: Fundus camera for diabetic retinopathy screening: non-mydriatic[R]. London: International Agency for the Prevention of Blindness, 2019. [26] 肖志涛, 娄世良, 吴骏, 等. 立体成像眼底相机光学系统设计[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2018, 26(5): 1054-1060. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182605.1054XIAO ZH T, LOU SH L, WU J, et al. Design of optical system for stereo imaging fundus camera[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(5): 1054-1060. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182605.1054 [27] LEE S J, YANG K M, LEE K B, et al. Design of illumination system using characterized illuminances for smartphone-based fundus camera[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2023, 168: 107664. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2023.107664 [28] 长沙鹰瞳健康科技有限公司. AI-FD16aF眼底相机[EB/OL]. (2022-10-12). https://www.chem17.com/product/det ail/37337180.html. (查阅网上资料,未找到本条文献信息且网址打不开,请确认,且请补充引用日期信息).Changsha Eyetong Health Technology Co., Ltd. AI-FD16aF Fundus camera[EB/OL]. (2022-10-12). https://www.chem17.com/product/detail/37337180.html. (in Chinese). [29] 重庆贝奥新视野医疗设备有限公司. 新视野全自动便携式眼底相机Kestrel 300[EB/OL]. (2025-05-19). https://www.lyqbq.com/ydzxj/117.html. (查阅网上资料,未找到引用日期信息,请确认补充).Chongqing Bio New Vision Medical Equipment Co., Ltd. Kestrel 300 Fundus camera[EB/OL]. (2025-05-19). https://www.lyqbq.com/ydzxj/117.html. (in Chinese) (查阅网上资料,未找到对应的英文翻译,请确认). -





 下载:
下载: