-
摘要:
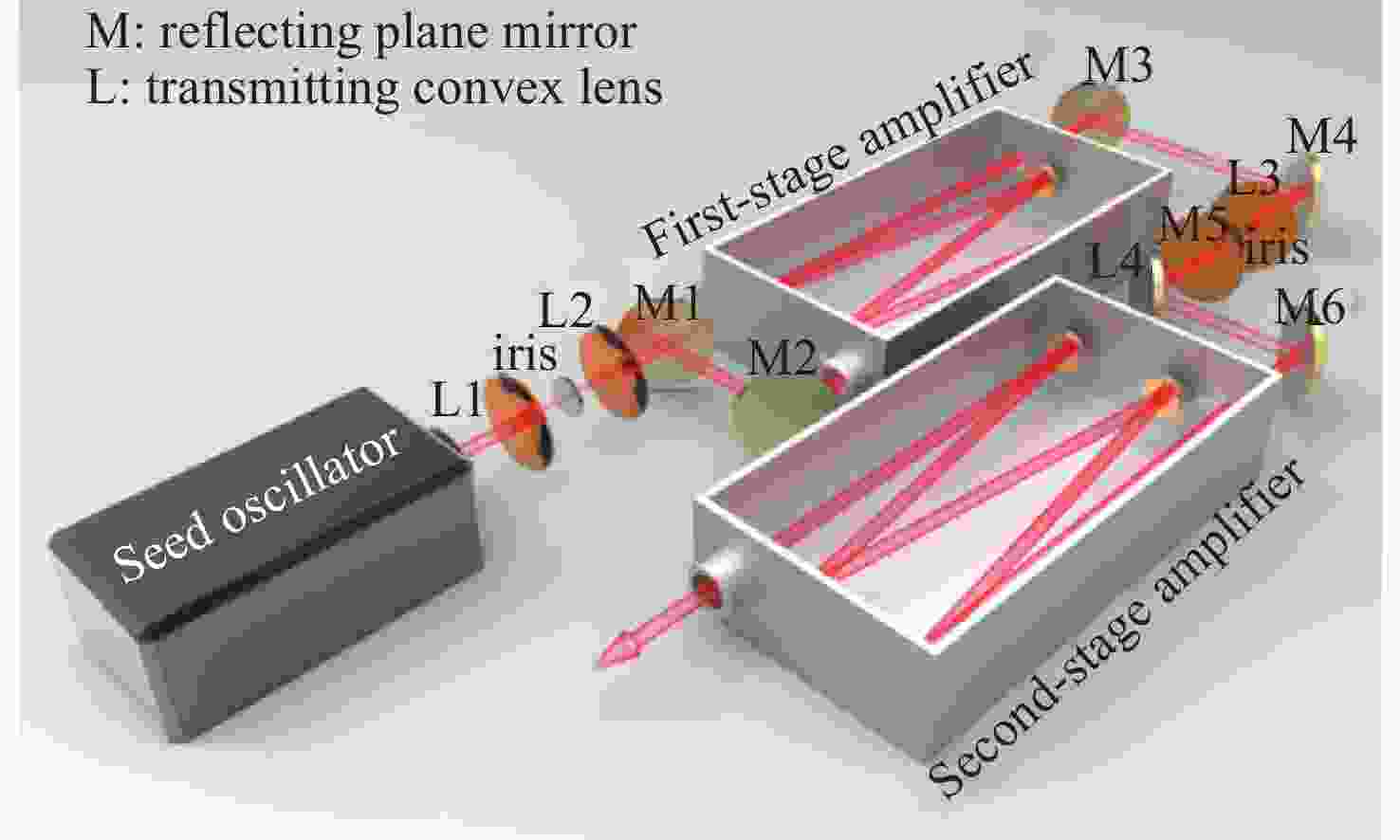
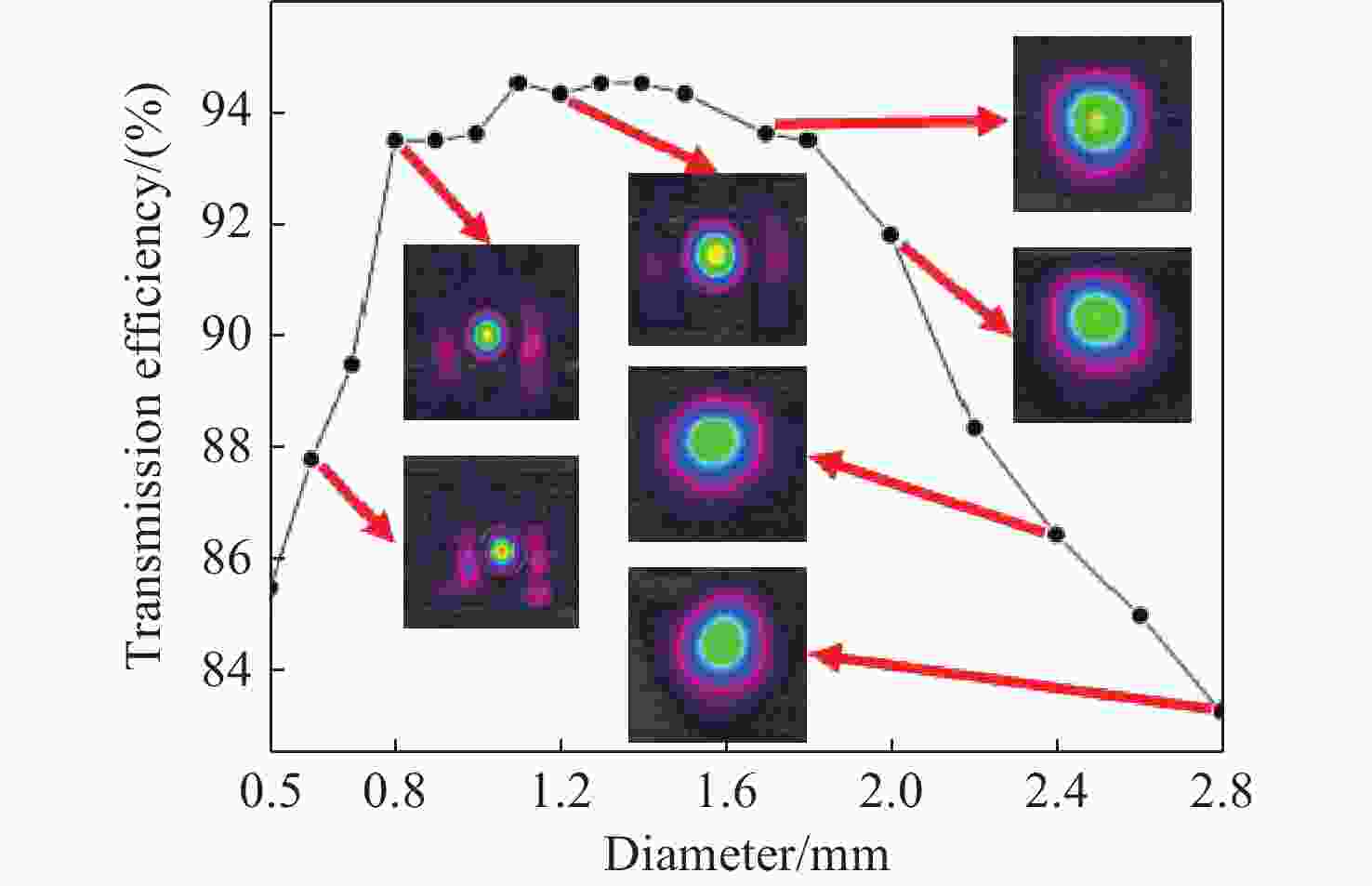
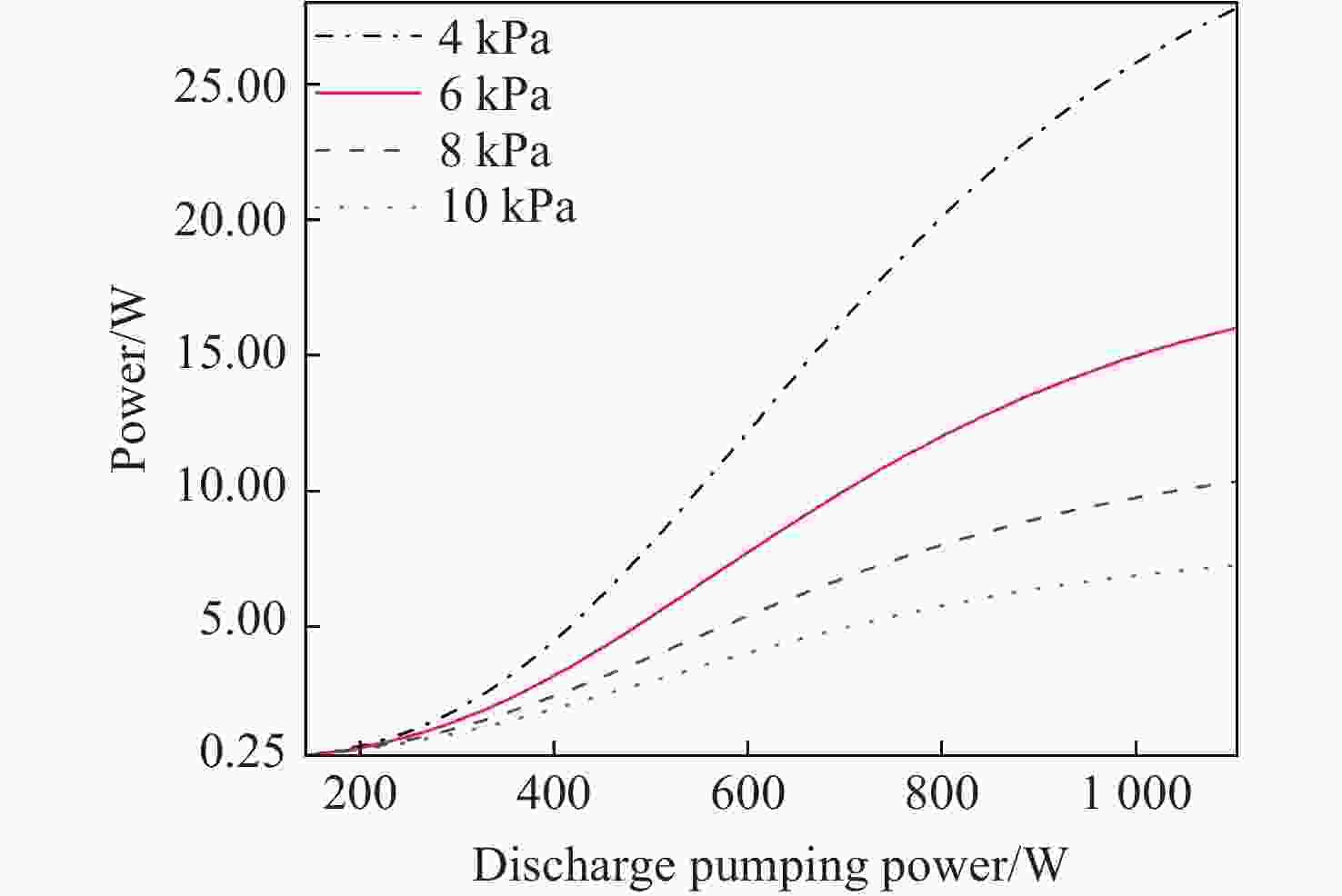
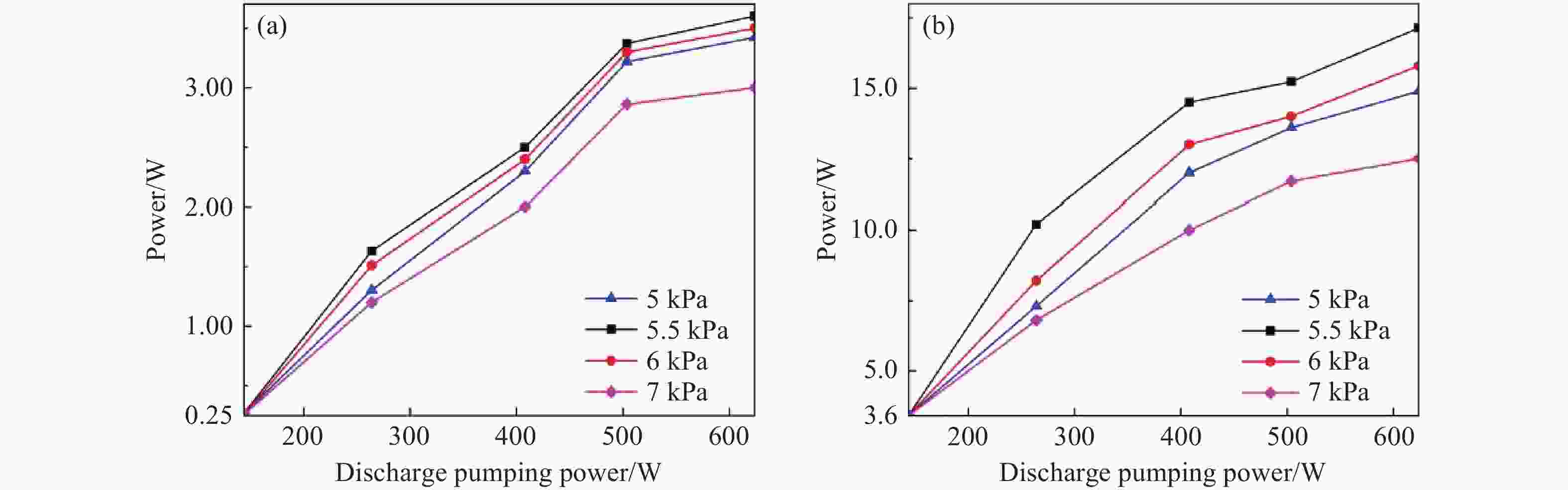
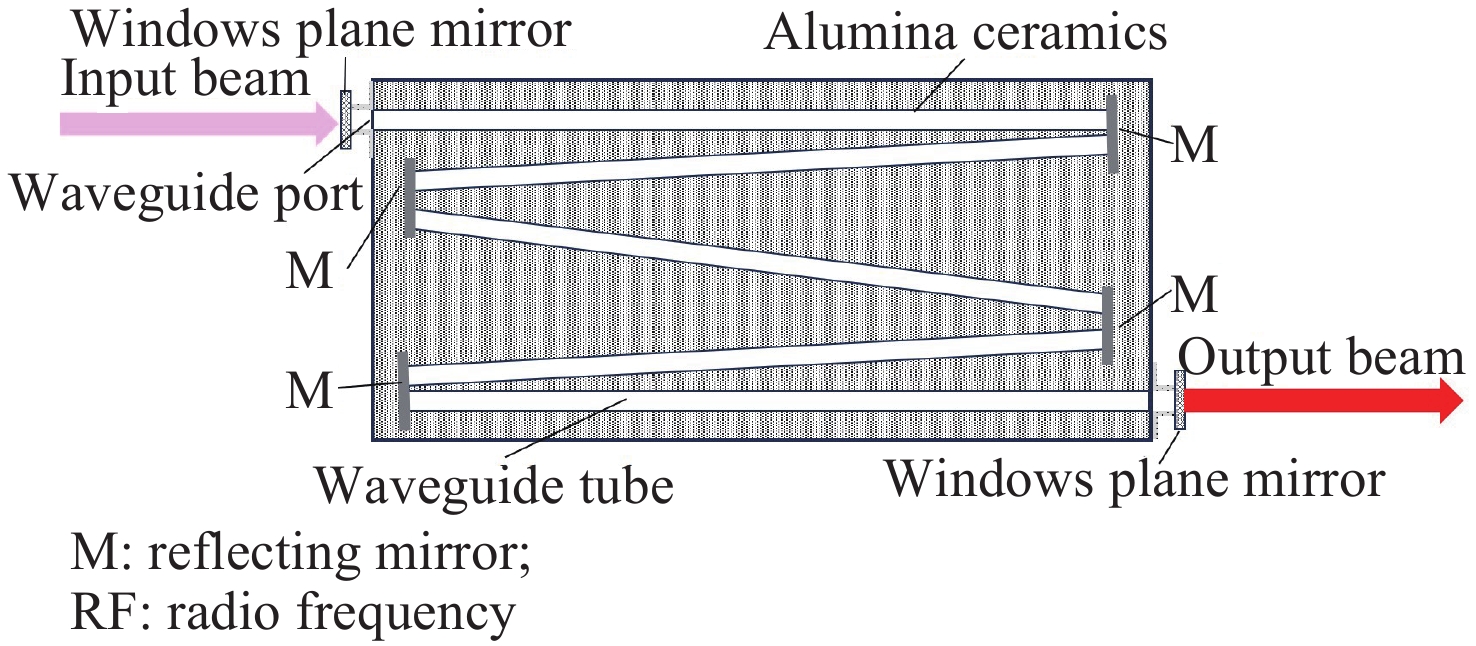
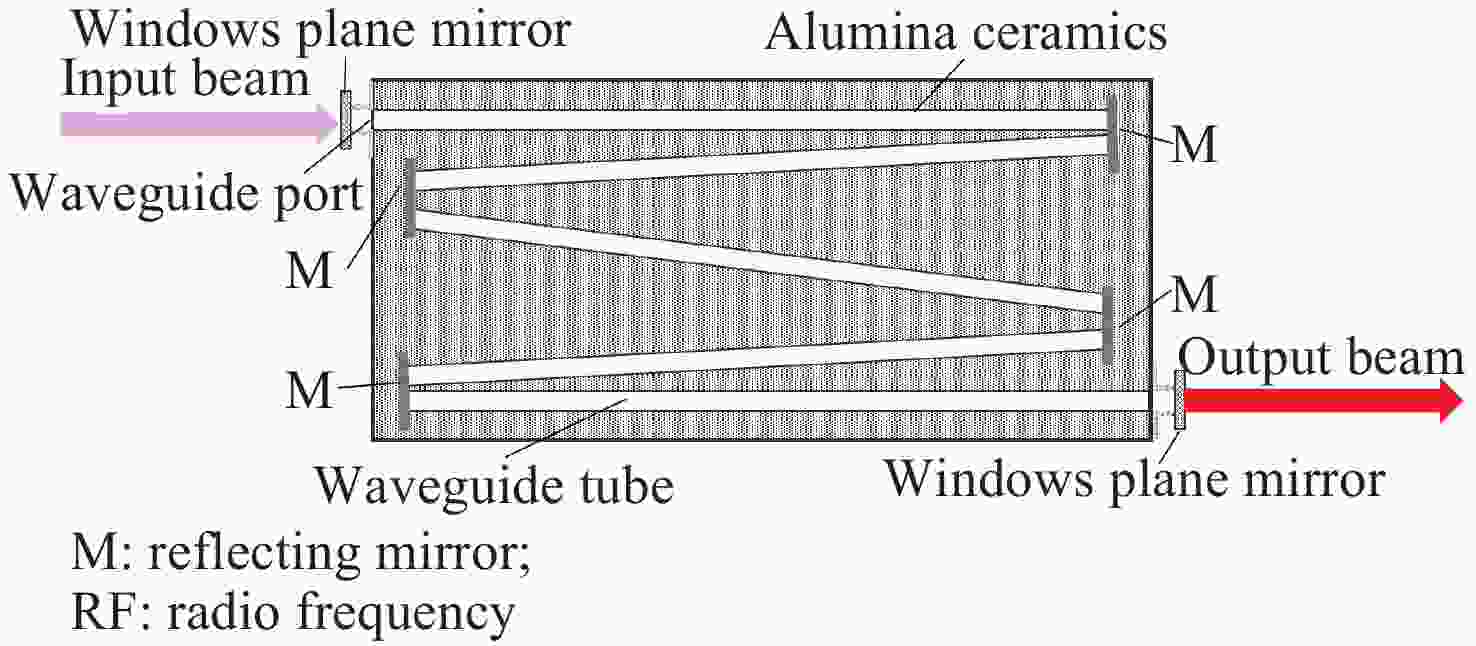
面向极紫外光刻光源对高功率、高光束质量CO2种子激光的应用需求,本文开展了基于射频波导体制的CO2激光放大技术研究。一方面,分析了射频波导放大器的静态插入损耗与输出光束质量随入射光参数的变化关系,确定了最佳模式匹配参数。另一方面,建立了多级射频波导放大仿真模型,理论计算了工作气压与放电泵浦功率等参数对放大倍率的影响规律,在实验上,引入增益介质调控技术,实现了激光系统放大性能的优化。实验结果表明:在2.5 m的波导长度下,传输效率达到了91.4%,输出光束在水平方向与竖直方向上的光束质量因子分别为1.03与1.05;二级射频波导放大系统的总放大倍率达到了68倍,最终获得了重复频率50 kHz、脉冲宽度20 ns、平均功率17.1 W、高光束质量的CO2激光输出。
Abstract:Toward the application demand for high-power, high-beam-quality CO2 seed lasers in extreme ultraviolet lithography light sources, the amplification characteristics were investigated based on a RF waveguide architecture. The static insertion loss and output beam quality of the RF waveguide amplifier were measured as function of incident beam parameters. A numerical model was developed to simulate the multi-stage RF waveguide amplification and to evaluate the effects of the gas pressure and the discharge pumping power on gain. The technology of regulating with gain medium was implemented to optimize the amplification performance in the experiment. Experimentally, optimal mode-matching conditions were identified with a waveguide length of 2.5 m, yielding a transmission efficiency of 91.4%. The beam quality factors of the output beam in the horizontal and vertical directions were 1.03 and 1.05, respectively. An overall gain factor of 68× was achieved in a dual-stage RF waveguide amplifier. The system delivered CO2 laser emission with a repetition rate of 50 kHz, a pulse duration of 20 ns, and an average output power of 17.1 W, satisfying the design criteria and demonstrating its suitability for high-power, high-beam-quality seed laser applications.
-
Key words:
- CO2 laser /
- master oscillator power amplifier /
- mode-matching /
- gain medium regulation
-
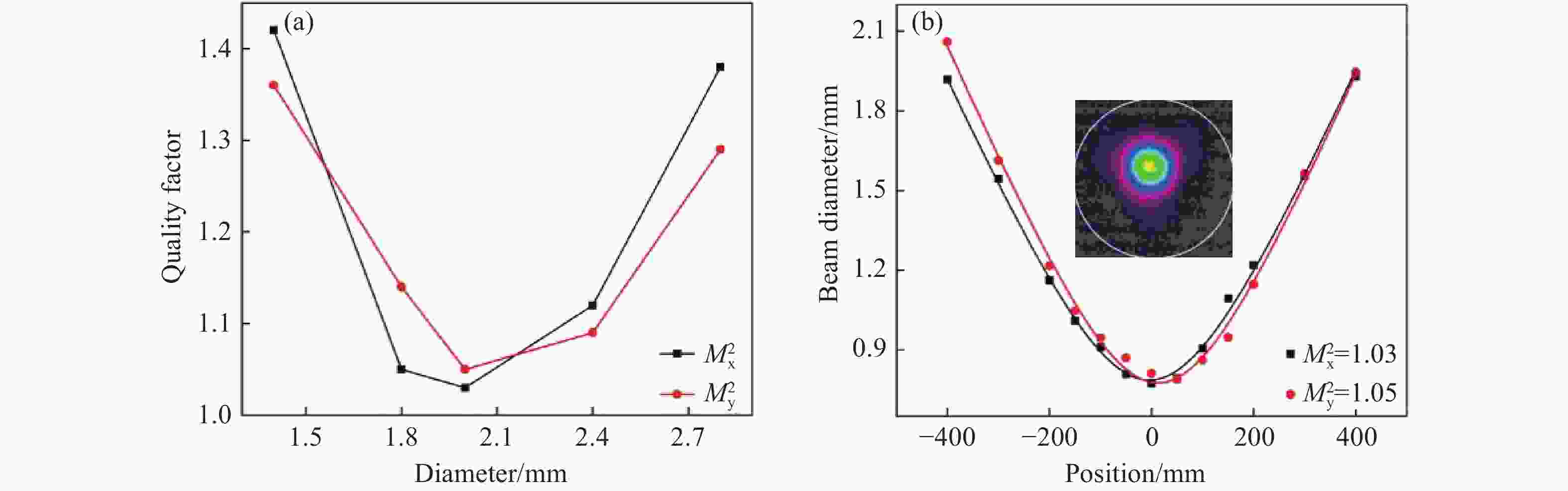
图 4 光束质量因子测量结果。(a)光束质量因子随入射光束直径的变化关系;(b)入射直径为2 mm时测量结果,插图为光束强度分布图
Figure 4. Measurement results of the beam quality factor. (a) Relationship between the beam quality factor and the diameter of the incident beam; (b) Measurement results when the incident diameter is 2 mm, with the inset showing the beam intensity distribution
-
[1] . YANG Y X, LIU K X, GAO Y H, et al. Advancements and challenges in inverse lithography technology: a review of artificial intelligence-based approaches[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2025, 14(1): 250. [2] 王佶, 赵昆. 高重复频率极紫外光源的产生和光谱技术研究进展[J]. 中国激光, 2024, 51(7): 0701002. doi: 10.3788/CJL231498WANG J, ZHAO K. Research progress in generation and spectral technology of high-repetition-rate extreme-ultraviolet-light sources[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2024, 51(7): 0701002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL231498 [3] 付轹文, 林楠. 面向极紫外光刻光源液滴锡靶的光学测量与检测进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2025, 62(13): 1300006. doi: 10.3788/LOP242388FU L W, LIN N. Progress in optical measurement and detection of tin droplets for extreme ultraviolet lithography light sources[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2025, 62(13): 1300006. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/LOP242388 [4] SHEN W H, LU Q P, SONG Y, et al. Study on tin contamination deposition mechanism on collector mirror surfaces in LPP-EUV light sources based on hydrodynamics and particle simulation theory[J]. Vacuum, 2025, 233: 114024. doi: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2025.114024 [5] 游聪, 黄维, 林高洁, 等. 基于遗传算法的快轴流CO2激光放大器的参数优化[J]. 中国激光, 2024, 51(7): 0701016. doi: 10.3788/CJL231509YOU C, HUANG W, LIN G J, et al. Optimization of fast axial flow CO2 laser amplifier parameters based on genetic algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2024, 51(7): 0701016. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL231509 [6] 黄盼, 赵崇霄, 董祝君, 等. 射频轴快流CO2激光器动态L型阻抗匹配网络设计[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2025, 18(5): 1155-1163. doi: 10.37188/CO.2024-0096HUANG P, ZHAO CH X, DONG ZH J, et al. Design of dynamic L-type impedance matching network in RF excited fast axial flow CO2 lasers[J]. Chinese Optics, 2025, 18(5): 1155-1163. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2024-0096 [7] RAZEGHI M, BAI Y B, WANG F H. High-power, high-wall-plug-efficiency quantum cascade lasers with high-brightness in continuous wave operation at 3-300μm[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2025, 14(1): 252. [8] ZHANG R R, GAO Y, PAN Q K, et al. Experimental study on optical isolation characteristics of SF6 for a high-repetition-rate nanosecond CO2 laser[J]. Applied Optics, 2025, 64(8): 1949-1955. doi: 10.1364/AO.544457 [9] 杜彤耀. 高损伤阈值空间光调制器关键技术及应用研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2023: 38-62.DU T Y. Research on key technology and application of high laser damage threshold spatial light modulator[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2023: 38-62. (in Chinese). [10] HUMMLER K, ZHU Q SH, BEHM K, et al. High-power EUV light sources (>500W) for high throughput in next-generation EUV lithography tools[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2024, 12953: 129530V. [11] IWAMOTO F, UENO Y, NAGAI S, et al. Development progress of Gigaphoton’s LPP EUV light source for inspection systems[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2024, 12953: 1295313. doi: 10.1117/12.3010135 [12] NOWAK K M, SUGANUMA T, ENDO A, et al. Efficient and compact short pulse MOPA system for laser-produced-plasma extreme-UV sources employing RF-discharge slab-waveguide CO2 amplifiers[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 7005: 70051Q. doi: 10.1117/12.782606 [13] SCHAFGANS A A, BROWN D J, FOMENKOV I V, et al. Performance optimization of MOPA pre-pulse LPP light source[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2015, 9422: 94220B. doi: 10.1117/12.2087421 [14] NOWAK K M, OHTA T, SUGANUMA T, et al. Multiline short-pulse solid-state seeded carbon dioxide laser for extreme ultraviolet employing multipass radio frequency excited slab amplifier[J]. Optics Letters, 2013, 38(6): 881-883. doi: 10.1364/OL.38.000881 [15] BRANDT D C, FOMENKOV I V, FARRAR N R, et al. CO2/Sn LPP EUV sources for device development and HVM[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2013, 8679: 86791G. [16] 叶静涵, 朱子任, 白进周, 等. 高气压同位素CO2皮秒激光脉冲放大输出特性理论研究[J]. 中国激光, 2023, 50(11): 1101017. doi: 10.3788/CJL221558YE J H, ZHU Z R, BAI J ZH, et al. Theoretical research on output characteristics of high-pressure isotope CO2 picosecond pulse laser amplification[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2023, 50(11): 1101017. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL221558 [17] 肖龙胜, 唐霞辉, 秦应雄, 等. 2 kW射频板条CO2激光器输出光束整形特性研究[J]. 中国激光, 2014, 41(4): 0402008. doi: 10.3788/CJL201441.0402008XIAO L SH, TANG X H, QIN Y X, et al. Shaping characteristics of output beam of 2 kW radio frequency slab CO2 laser[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2014, 41(4): 0402008. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201441.0402008 [18] 张冉冉. 短脉冲CO2激光放大与噪声光隔离技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2021: 20-28.ZHANG R R. Study on technology of short pulse CO2 laser amplification and noise isolation[D]. Changchun: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2021: 20-28. (in Chinese). [19] GORDON I E, ROTHMAN L S, HARGREAVES R J, et al. The HITRAN2020 molecular spectroscopic database[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 2022, 277: 107949. doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2021.107949 [20] ILUKHIN B I, UDALOV Y B, KOCHETOV I V, et al. Theoretical and experimental investigation of a waveguide CO2 laser with radio-frequency excitation[J]. Applied Physics B, 1996, 62(2): 113-127. doi: 10.1007/BF01081112 -





 下载:
下载: