Optical design of an ultra-short-focus projection system with low throw ratio based on a freeform surface mirror
doi: 10.3788/CO.20201302.0363
-
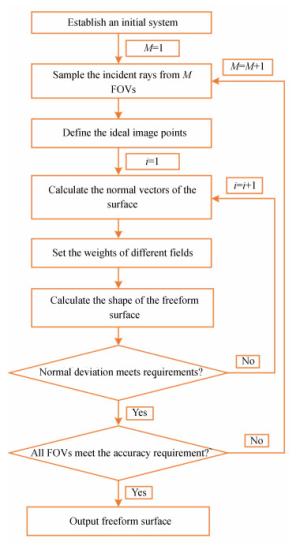
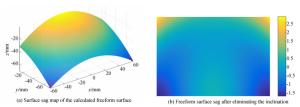
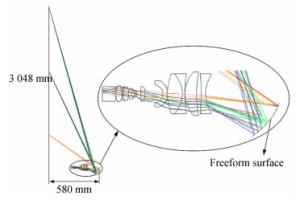
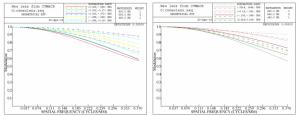
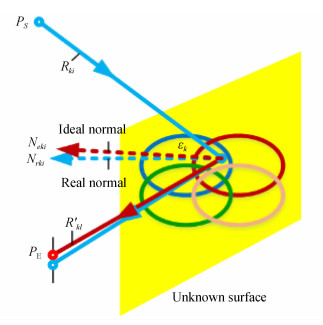
摘要: 为了设计低投射比的超短焦投影物镜,本文采用自由曲面和折反式的光路结构设计了一种具有低投射比的超短焦投影物镜系统。该物镜由一个旋转对称的折射透镜组和一个自由曲面反射镜组成。采用11.938 mm的数字微镜器件(DMD)作为空间光调制器产生图像源。采用法线加权迭代优化的方法计算自由曲面。最后,分析了系统的性能。仿真结果表明:超短焦投影物镜可在580 mm的投影距离处实现3 048 mm尺寸的大屏幕投影,系统的投射比低至0.19,系统的最大畸变小于0.72%。能够满足低投射比超短焦投影物镜的设计要求。该投影系统具有低投射比、低畸变、投影效果好等优点,可为超短焦投影系统的进一步发展提供有益参考。Abstract: In order to design an ultra-short-focus objective lens with a low throw ratio, a system of ultra-short-focus, low-throw-ratio objective lenses is designed using a freeform surface and refractive-reflective optical structure. The objective lenses consist of a rotationally symmetrical refractive lens group and a freeform surface mirror. A 11.938 mm Digital Micromirror Device (DMD) is used as a spatial light modulator to generate the image source. The normal-weighted iterative optimization method is used to calculate the freeform surface. Finally, the performance of the system is analyzed. The simulation results show that the ultra-short-focus projection objective lens can achieve a 3 048 mm screen projection at a distance of 580 mm. The throw ratio of the system is 0.19, which is extraordinarily low, and the maximum distortion of the system is less than 0.72%. This can meet the design requirements of low throw ratio ultra-short-focus projection objective lenses. This projection system is advantageous for its low throw ratio, low distortion and good imaging quality, which can provide a useful reference for the further development of ultra-short-focus projection systems.
-
Table 1. Specifications of the ultra-short-focus projection system
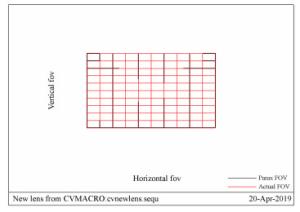
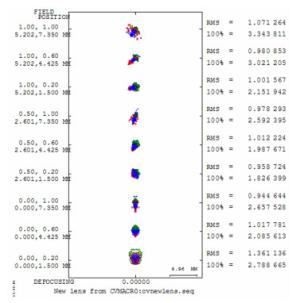
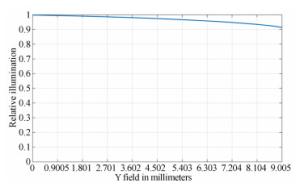
Parameter Specification DMD size 11.938 mm(1 920×1 080) Screen size 3 048 mm Projection distance 580 mm Throw ratio 0.19 Focal length 2.19 mm FOV 156° F number 1.7 Configuration Refractive-reflective combined Distortion < 1% MTF >50%@0.363 lp/mm Relative illumination >90% at all FOVs -
[1] HUANG J W. The optical design of ultra-short throw system for panel emitted theater video system[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2015, 9524:952418. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=7d7ad2f2ac4cedcf5f081d5f63c92cfa&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [2] 冯思悦, 梁静秋, 梁中翥, 等. LED微阵列投影系统设计[J].中国光学, 2019, 12(1):88-96. doi: 10.3788/CO.20191201.0088FENG S Y, LIANG J Q, LIANG ZH ZH, et al.. Design of projection system for a micro-LED array[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(1):88-96. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CO.20191201.0088 [3] ZHENG ZH R, SUN X T, LIU X, et al.. Design of reflective projection lens with Zernike polynomials surfaces[J]. Displays, 2008, 29(4):412-417. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d0aa38f711daf04ce94360173daee6a1 [4] OGAWA J, AGATA K, SAKAMOTO M, et al.. Super-short-focus front projector with aspheric-mirror projection optical system[J]. Journal of the Society for Information Display, 2005, 13(2):111-116. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=79062ce60754ee399205fb29822d9a31 [5] MATSUMOTO S, AMANO R, OKUDA M, et al.. Ultra-short throw distance front projector with mirror-lens hybrid projection optical system[C]. Proceedings of 2008 Digest of Technical Papers-International Conference on Consumer Electronics, IEEE, 2008: 1-2. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4587974?reload=true&arnumber=4587974 [6] NIE Y F, MOHEDANO R, BENÍTEZ P, et al.. Multifield direct design method for ultrashort throw ratio projection optics with two tailored mirrors[J]. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(14):3794-3800. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9e34f0ab78f936b796ad5ddc5baa0677 [7] 杨建明, 刘伟奇, 孟祥翔, 等.同轴超短焦距折反式投影系统设计[J].液晶与显示, 2015, 30(5):864-871. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yjyxs201505020YANG J M, LIU W Q, MENG X X, et al.. Design of coaxial short focal length catadioptric projection system[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2015, 30(5):864-871. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yjyxs201505020 [8] AGÓCS T. Comparison of optical design methods of freeform surfaces for imaging applications[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2015, 9626:962637. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ed29f316e45325b0cb7d392018e0f74a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [9] YANG T, ZHU J, JIN G F. Design of a freeform, dual fields-of-view, dual focal lengths, off-axis three-mirror imaging system with a point-by-point construction-iteration process[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2016, 14(10):100801. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgjg-e201610008 [10] 张磊, 刘东, 师途, 等.光学自由曲面面形检测技术[J].中国光学, 2017, 10(3):283-299. doi: 10.3788/CO.20171003.0283ZHANG L, LIU D, SHI T, et al.. Optical free-form surfaces testing technologies[J]. Chinese Optics, 2017, 10(3):283-299. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CO.20171003.0283 [11] MIÑANO J C, BENÍTEZ P, LIN W, et al.. Overview of the SMS design method applied to imaging optics[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2009, 7429, 74290C. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=CC0210245172 [12] WASSERMANN G D, WOLF E. On the theory of aplanatic aspheric systems[J]. Proceedings of the Physical Society, Section B, 1949, 62(1):2-8. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=66ccfb12dd15260f25442468057cbcf7&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [13] YANG T, JIN G F, ZHU J. Design of image-side telecentric freeform imaging systems based on a point-by-point construction-iteration process[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2017, 15(6):062202. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b1e28b2fb5957a2c5f5a924cbe76368d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [14] ZHU J, WU X F, YANG T, et al.. Generating optical freeform surfaces considering both coordinates and normals of discrete data points[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2014, 31(11):2401-2408. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8da8a7ac574e856d09315a7dcaeccbea -





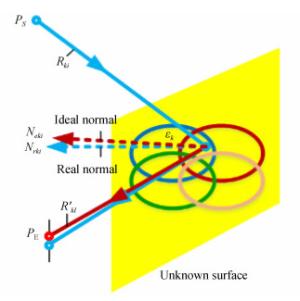
 下载:
下载: