-
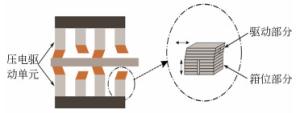
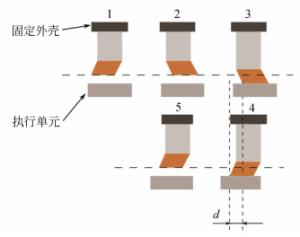
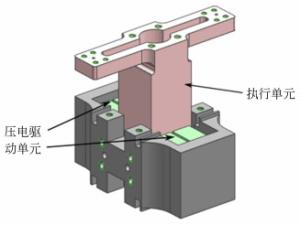
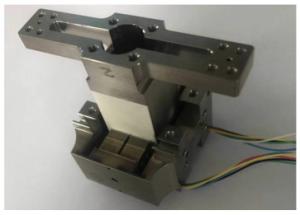
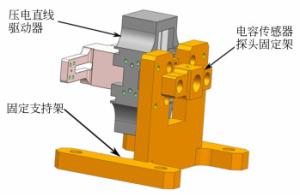
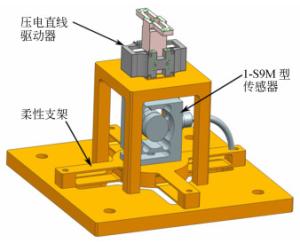
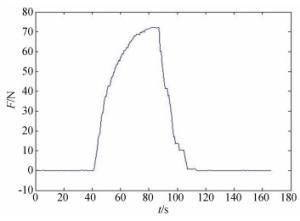
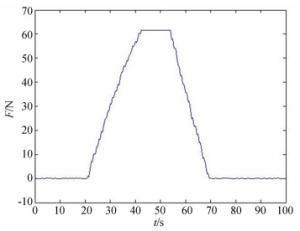
摘要: 为保证空间惯性传感器的正常在轨运行,在发射阶段需保证测试质量固定以避免与周围电容极板的接触碰撞;到达预定轨道后再重新捕获并以最小残余线速度将测试质量释放至精确位置,保持自由悬浮状态。测试质量的捕获定位对驱动器提出高精度的要求。本文针对在太空中捕获定位释放测试质量所用的压电直线驱动器进行了设计定制与性能测试。试验结果表明:该定制的压电驱动器最小步长小于1 nm,但步长稳定性误差较大;150 V工作电压条件最大驱动力达72 N;单步行进驱动力稳定;夹持测试质量过程中,驱动力稳定,稳定性偏差为0.16%。满足捕获、定位、释放机构的使用需求。Abstract: In order to ensure the normal operation of space inertial sensors in orbit, it is necessary to ensure the test mass is fixed during launch to prevent collision with the surrounding capacitor plate. It must grab the test mass after reaching its predetermined orbit and precisely release it in its correct position with minimal residual velocity such that it remains free-floating. In this paper, a piezoelectric linear actuator that is used to grab the test mass is designed, customized and tested for performance. The test results show that the customized piezoelectric actuator can achieve a minimum step size of less than 1 nm, but the step length stability error is large; the maximum driving force at 150 V of input is 72 N; the single stepping drive force is stable; during the process of fixing the test mass, the driving force is stable and the deviation in its stability is 0.16%. These findings meet the needs of the grabbing, positioning, and release mechanisms.
-
Key words:
- precision actuation /
- inchworm motion /
- piezoelectric actuator /
- driving force /
- displacement resolution
-
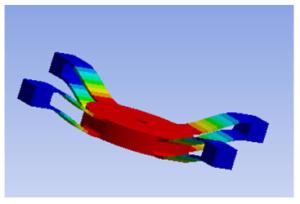
表 1 柔性片不同受力条件下的最大变形及最大应力
Table 1. Maximum deformation and maximum stress of flexible sheet under different forces
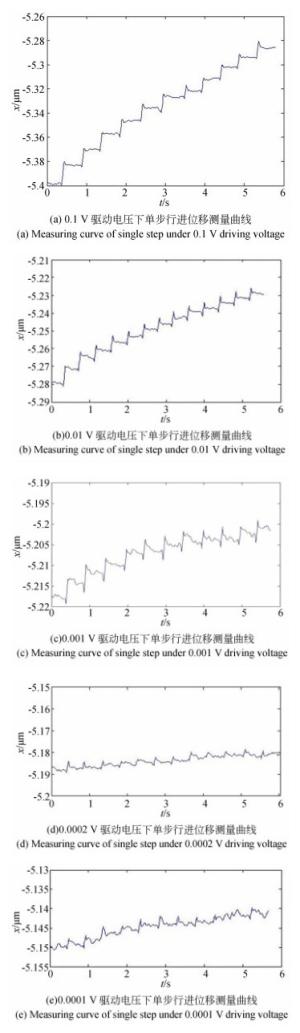
序号 施力大小/N 最大变形/mm 最大应力/MPa 1 10 0.008 428 4.395 5 2 20 0.016 855 8.798 1 3 30 0.025 281 13.207 4 40 0.033 704 17.623 5 50 0.042 124 22.045 6 60 0.050 541 26.473 7 70 0.058 953 30.905 8 80 0.067 360 35.343 9 90 0.075 761 39.786 10 100 0.084 154 44.232 表 2 驱动器不同电压下的平均步长
Table 2. Average step length of actuator at different voltages
序号 驱动电压/V 平均步长/nm 1 0.1 10.23 2 0.01 3.40 3 0.001 1.60 4 0.0002 0.85 5 0.0001 0.81 表 3 不同电压下驱动器的步长稳定性偏差
Table 3. Step stability deviation of actuator under different driving voltages
序号 驱动电压/V 失稳系数/(%) 1 0.1 13.48 2 0.01 13.09 3 0.001 34.06 4 0.0002 58.68 5 0.0001 49.38 -
[1] 罗子人, 白姗, 边星, 等.空间激光干涉引力波探测[J].力学进展, 2013, 43(4):415-447. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/twxjz201501004LUO Z R, BAI SH, BIAN X, et al..Space laser interferometry gravitational wave detection[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2013, 43(4):415-447. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/twxjz201501004 [2] 王智, 马军, 李静秋.空间引力波探测计划-LISA系统设计要点[J].中国光学, 2015, 8(6):980-987. doi: 10.3788/CO.20150806.0980WANG ZH, MA J, LI J Q. Space-based gravitational wave detection mission:design highlights of LISA system[J]. Chinese Optics, 2015, 8(6):980-987. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CO.20150806.0980 [3] 高瑞弘, 刘河山, 罗子人, 等.太极计划激光指向调控方案介绍[J].中国光学, 2019, 12(3):425-431. doi: 10.3788/CO.20191203.0425GAO R H, LIU H SH, LUO Z R, et al..Introduction of laser pointing scheme in the Taiji program[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(3):425-431. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CO.20191203.0425 [4] 赵亚, 姚东, 王智, 等.应用于空间精密测量的全玻璃光纤耦合器的系统设计[J].中国光学, 2019, 12(3):432-440. doi: 10.3788/CO.20191203.0432ZHAO Y, YAO D, WANG ZH, et al..System design of all glass fiber couplers for precise space measurement[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(3):432-440. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CO.20191203.0432 [5] LI Y P, LIU H SH, ZHAO Y, et al..Demonstration of an ultraprecise optical bench for the Taiji space gravitational wave detection path finder mission[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(10):2087. doi: 10.3390/app9102087 [6] 王少鑫, 齐克奇, 王玉坤, 等.电极不对称性对惯性传感器性能损失的研究[J].中国光学, 2019, 12(3):455-462. doi: 10.3788/CO.20191203.0455WANG SH X, QI K Q, WANG Y K, et al..Study on loss of performance in inertial sensors due to electrode asymmetry[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(3):455-462. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CO.20191203.0455 [7] 白彦峥, 田蔚, 周泽兵, 等.高精度空间加速度计及其应用[J].空间科学学报, 2010, 30(6):601-606. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kjkxxb201006014BAI Y ZH, TIAN W, ZHOU Z B, et al..High-precision space-borne accelerometer and its applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2010, 30(6):601-606. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kjkxxb201006014 [8] BORTOLUZZI D, MÁUSLI P A, ANTONELLO R, et al..Modeling and identification of an electro-mechanical system:the LISA grabbing positioning and release mechanism case[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2011, 47(3):453-465. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2010.09.004 [9] BORTOLUZZI D, ZANONI C, VITALE S.Improvements in the measurement of metallic adhesion dynamics[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2015, 52-53:600-613. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2014.06.002 [10] BORTOLUZZI D, BAGLIVO L, BENEDETTI M, et al..Test-mass release phase ground testing for the LISA path finder mission[C]. American Institute of Physics Conference Proceedings of the 6th International LISA Symposium, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, 2006: 556-561. [11] 赵宏伟, 刘建芳, 华顺明, 等.压电型步进精密旋转驱动器[J].光学 精密工程, 2005, 13(3):305-310. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc200503010ZHAO H W, LIU J F, HUA SH M, et al..Piezoelectric-type stepping precision rotary actuator[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2005, 13(3):305-310. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc200503010 [12] 李鹏志.压电促动器的纳米级精度控制及其在光刻物镜中的应用研究[D].长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2019.LI P ZH.Research on nano scale precise control of piezoelectric actuator and its application in lithographic projection lens[D]. Changchun: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences(Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2019. (in Chinese) [13] LI J P, ZHAO H W, QU X T, et al..Development of a compact 2-DOF precision piezoelectric positioning platform based on inchworm principle[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2015, 222:87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2014.12.001 [14] 刘建芳.压电步进精密驱动器理论及实验研究[D].长春: 吉林大学, 2005.LIU J F. Theoretical and experimental study on piezoelectric precision step actuator[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2005. (in Chinese) [15] LI J P, ZHAO H W, QU H, et al..A piezoelectric-driven rotary actuator by means of inchworm motion[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2013, 194:269-276. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2013.02.020 [16] 刘宇阳.步进式压电驱动直线运动系统的研究[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017.LIU Y Y. Research on linear motion system driven by stepping piezoelectric actuator[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017. (in Chinese) [17] 齐克奇, 向阳.光刻物镜波像差检测球面波发生装置的研制[J].仪器仪表学报, 2014, 35(7):1518-1524. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yqyb201407010QI K Q, XIANG Y. Development of spherical wave generating device for lithographic objective wavefront aberration detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2014, 35(7):1518-1524. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yqyb201407010 [18] FU X, XIAO W L, XU L Y. Piezoelectric inchworm-type probe-approaching stepper[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2011, 8321:83210Z. doi: 10.1117/12.903935 [19] 赵余杰, 孙庆龙, 张志豪, 等.压电尺蠖直线电机的设计[J].压电与声光, 2018, 40(2):206-210. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ydysg201902018ZHAO Y J, SUN Q L, ZHANG ZH H, et al..Design of a piezoelectric linear motor based on inchworm motion[J]. Piezoelectrics & Acousto Optics, 2018, 40(2):206-210. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ydysg201902018 [20] 郭文峰, 曲建俊, 曲华杰, 等.箝位体刚度平衡对被动箝位压电驱动器性能的影响[J].光学 精密工程, 2015, 23(3):738-744. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201503018GUO W F, QU J J, QU H J, et al..Influences of balanced stiffness of clamping body on performance of inverse piezoelectric inchworm motor[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2015, 23(3):738-744. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201503018 [21] 赵宏伟, 吴博达, 杨志刚, 等.尺蠖型压电直线驱动器的运动稳定性分析[J].纳米技术与精密工程, 2007, 5(1):49-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6030.2007.01.011ZHAO H W, WU B D, YANG ZH G, et al..Analysis of motion stability for inchworm-type piezoelectric linear actuator[J]. Nanotechnology and Precision Engineering, 2007, 5(1):49-54. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6030.2007.01.011 [22] 李全松.尺蠖型压电直线电动机制作及性能测试[J].微特电机, 2014, 42(6):21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7018.2014.06.006LI Q S. Machining and functional testing of inchworm-type piezoelectric linear motor[J]. Small & Special Electrical Machines, 2014, 42(6):21-24. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7018.2014.06.006 -





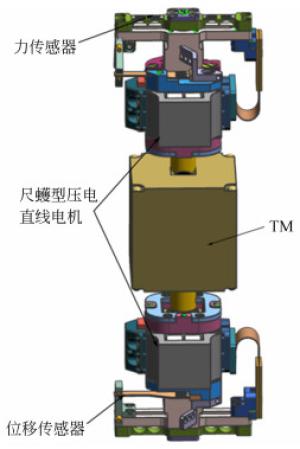
 下载:
下载: