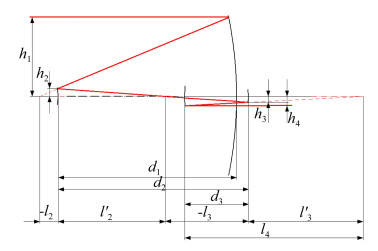
-
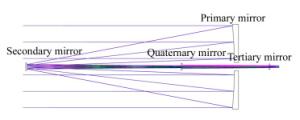
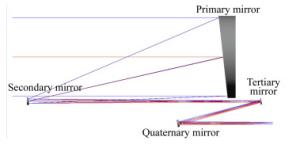
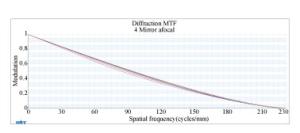
摘要: 空间引力波探测任务采用的是外差法激光干涉测量技术,其对系统的噪声和精度要求极为苛刻。望远镜是引力波探测天文台的重要组成部分,起到激光信号收发的作用,其光学系统应具备大倍率、高像质、杂光抑制能力强,波前误差一致性好的特点。针对上述要求,对大倍率离轴四反无焦光学系统进行了设计和优化。基于初级像差理论阐述了初始结构的求解方法。系统具有中间像面和可用的实出瞳,便于杂光抑制和与后端科学干涉仪的承接。优化过程中,建立了波前一致性优化函数,通过优化设计,系统入瞳直径为200 mm,放大倍率为40倍,科学视场为±8 μrad,波前误差RMS值优于0.005λ,PV值优于0.023λ(λ=1 064 nm),波前一致性残差RMS值优于0.000 8λ(λ=1 064 nm),在捕获视场±200 μrad内的成像质量均接近衍射极限,并对系统公差进行了分析,满足引力波探测的应用需求。Abstract: The space gravitational wave detection is realized by adopting the technology of heterodyne laser interferometry. The accuracy and noise level of the measurement are extremely rigorous. As an important part of space-based gravitational wave observatory, telescope plays the role of laser signal transceiver, and is characterized by high magnification, high image quality, high similarity of wave-front error over the field of view and extraordinary ability to suppress stray light. Aiming at above requirements, methods of design and analysis of the off-axis four-mirror afocal optical system with high magnification are investigated. Based on the theory of primary aberration, the design method of initial structure is explored. The system has an intermediate image plane and an available exit pupil, which facilitates stray light suppression and integration with the scientific interferometer. The wave-front similarity merit function is established. After optimization, the entrance pupil diameter is 200 mm, the magnification is 40. The Root-Mean-Square (RMS) wave-front error is better than 0.005λ and the Peak-to-Valley (PV) value is less than 0.023λ, moreover, the RMS of wave-front similarity residuals are better than 0.000 8λ(λ=1 064 nm) within the ±8 μrad scientific field of view. Over the field of regard for acquisition, the imaging quality is close to the diffraction limit. The tolerance of the system is analyzed and meets the requirements of space-based gravitational wave detection.
-
表 1 光学系统指标
Table 1. Optical system requirements
系统参数 技术指标 光学口径/mm 200 工作波长/nm 1 064 捕获视场/μrad ±200 科学视场/μrad ±8 激光束放大倍数 40 波前质量(科学视场内) ≤λ/30RMS(λ=1 064 nm) 表 2 光学系统的结构参数
Table 2. Structural parameters of optical system
结构参数 取值范围 取值 α1 (0, 1) 0.055 47 α2 (-∞, 0) -0.101 75 α3 (0, ∞) 4.432 66 β1 (-∞, 0) -18.020 53 β2 (-∞, ∞) -1.130 47 表 3 优化后光学系统的设计参数
Table 3. Design parameters of optical system after optimization
半径(mm) 间隔(mm) 二次曲面类型 主镜 -1 075 -507.68 Ellipsoid 次镜 -63.13 591.95 Ellipsoid 三镜 -947.40 -217.58 - 四镜 -543.89 235.46 - 表 4 出瞳波前误差
Table 4. Wave-front errors on exit pupil
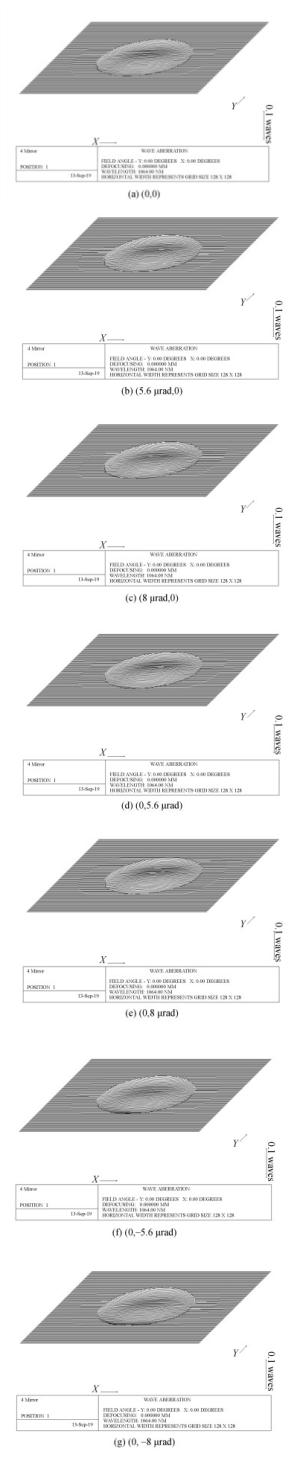
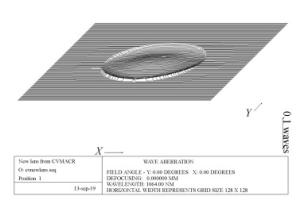
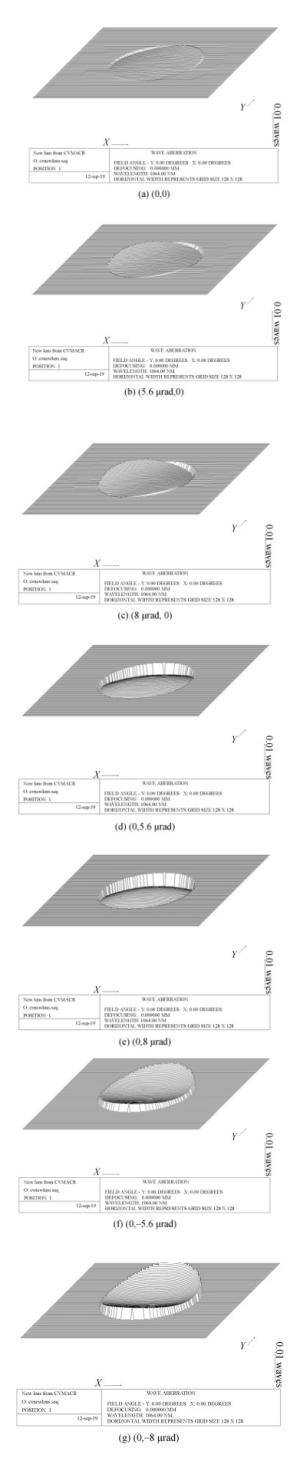
视场(μrad) RMS(λ=1 064 nm) PV(λ=1 064 nm) (0, 0) 0.005λ 0.021λ (5.6, 0) 0.005λ 0.023λ (8.0, 0) 0.005λ 0.023λ (0, 5.6) 0.005λ 0.022λ (0, 8.0) 0.005λ 0.022λ (0, -5.6) 0.004λ 0.021λ (0, -8.0) 0.004λ 0.021λ 表 5 波前一致性残差
Table 5. Wave-front similarity residuals
视场(μrad) RMS(λ=1 064 nm) PV(λ=1 064 nm) (0, 0) 0.000 19λ 0.001λ (5.6, 0) 0.000 35λ 0.003λ (8.0, 0) 0.000 58λ 0.005λ (0, 5.6) 0.000 57λ 0.005λ (0, 8.0) 0.000 79λ 0.007λ (0, -5.6) 0.000 57λ 0.005λ (0, -8.0) 0.000 79λ 0.007λ 表 6 公差分配结果
Table 6. Tolerance allocation of optical system
类型 公差项 主镜 次镜 三镜 四镜 加工公差 曲率半径(mm) 0.1 0.02 0.5 0.1 二次曲面系数 0.000 5 0.001 - - 面形精度(λ=1 064 nm) 1/100λ 1/100λ 1/200λ 1/200λ 装调公差 X向位移(μm) - 5 20 20 Y向位移(μm) - 5 20 20 Z向位移(μm) - 5 20 20 绕X轴倾斜(″) - 20 20 20 绕Y轴倾斜(″) - 20 20 20 绕Z轴倾斜(″) - 40 60 60 表 7 波前误差累积概率
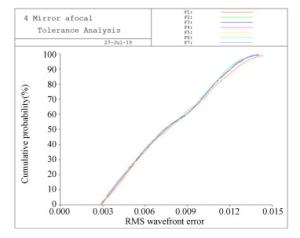
Table 7. Cumulative probability of RMS wave-front error
累积概率 全视场波前误差变化(λ=1 064 nm) 50% 0.005 1λ 84.1% 0.007 6λ 97.7% 0.009 6λ 99.9% 0.011 4λ -
[1] JENNRICH O. LISA technology and instrumentation[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2009, 26(15): 153001. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/26/15/153001 [2] HU W R, WU Y L. The Taiji program in space for gravitational wave physics and the nature of gravity[J]. National Science Review, 2017, 4(5): 685-686. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwx116 [3] LIVAS J C, ARSENOVIC P, CROW J A, et al.. Telescopes for space-based gravitational wave missions[J]. Optical Engineering, 2013, 52(9): 091811. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.52.9.091811 [4] VERLAAN A L, HOGENHUIS H, PIJNENBURG J, et al.. LISA telescope assembly optical stability characterization for ESA[C].International Conference on Space Optics—ICSO 2012. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2017, 10564: 105640K. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258719157_LISA_Telescope_Assembly_Optical_Stability_Characterization_for_ESA [5] 刘河山, 高瑞弘, 罗子人, 等.空间引力波探测中的绝对距离测量及通信技术[J].中国光学, 2019, 12(3):486-492. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zggxyyygxwz201903008LIU H SH, GAO R H, LUO Z R, et al.. Laser ranging and data communication for space gravitational wave detection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(3): 486-492. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zggxyyygxwz201903008 [6] SANKAR S, LIVAS J. Testing and characterization of a prototype telescope for the evolved Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (eLISA)[C]. Space Telescopes and Instrumentation 2016: Optical, Infrared, and Millimeter Wave. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2016, 9904: 99045A. [7] 王智, 沙巍, 陈哲, 等.空间引力波探测望远镜初步设计与分析[J].中国光学, 2018, 11(1):131-151. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zggxyyygxwz201801014WANG ZH, SHA W, CHEN ZH, et al..Preliminary design and analysis of telescope for space gravitational wave detection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(1), 131-151. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zggxyyygxwz201801014 [8] 孙可, 江厚满, 程湘爱.强光辐照下主镜表面散射引起的视场内杂光分布[J].光学 精密工程, 2011, 19(2): 493-499. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201102040SUN K, JIANG H M, CHENG X A. Distribution of in-field stray light due to surface scattering from primary mirror illuminated by intense light[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2011, 19(2): 493-499. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201102040 [9] SHIRI R, STEIN R, MURPHY K, et al.. Fabrication of petal-shaped masks for suppression of the on-axis poisson spot in telescope systems[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2016, 87(4): 043112. doi: 10.1063/1.4945793 [10] 高瑞弘, 刘河山, 罗子人, 等.太极计划激光指向调控方案介绍[J].中国光学, 2019, 12(3): 425-431. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zggxyyygxwz201903002GAO R H, LIU H SH, LUO Z R, et al.. Introduction of laser pointing scheme in the Taiji program[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(3): 425-431. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zggxyyygxwz201903002 [11] SCHUSTER S. Tilt-to-length coupling and diffraction aspects in satellite interferometry[D]. Hannover: Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Universität Hannover, 2017. [12] SCHUSTER S, WANER G, TRÖBS M, et al.. Vanishing tilt-to-length coupling for a singular case in two-beam laser interferometers with Gaussian beams[J]. Applied optics, 2015, 54(5): 1010-1014. doi: 10.1364/AO.54.001010 [13] WANNER G. Complex optical systems in space: numerical modelling of the heterodyne interferometery of LISA Pathfinder and LISA[D]. Hannover: Albert Enstein Institute & University of Hannover, 2010. [14] 马烈, 陈波.三维成像载荷共孔径光学系统设计[J].光学 精密工程, 2018, 26(9): 2326-2333. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201809026MA L, CHEN B. Optical design of a co-aperture system for 3-D remote sensing payload[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2018, 26(9): 2326-2333. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201809026 [15] 梅贵, 翟岩, 曲贺盟, 等.离轴三反系统的无应力装调[J].光学 精密工程, 2015, 23(12): 3414-3421. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201512018MEI G, ZHAI Y, QU H M, et al.. Stress-free alignment of off-axis three-mirror system[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2015, 23(12): 3414-3421. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201512018 [16] 杜福嘉, 李朋辉.低温环境下材料膨胀系数和润滑对望远镜负载扭矩的影响[J].光学 精密工程, 2018, 26(3): 616-623. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201803013DU F J, LI P H. Effect of material expansion coefficient and lubrication on telescope load torque under low temperature[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2018, 26(3): 616-623. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201803013 -





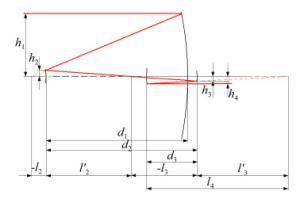
 下载:
下载: