-
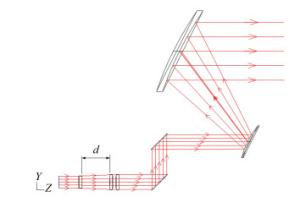
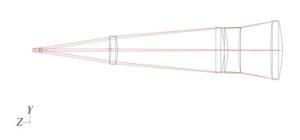
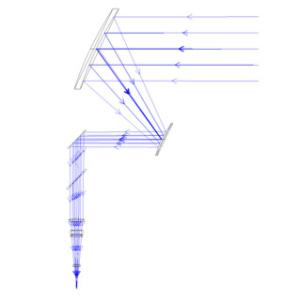
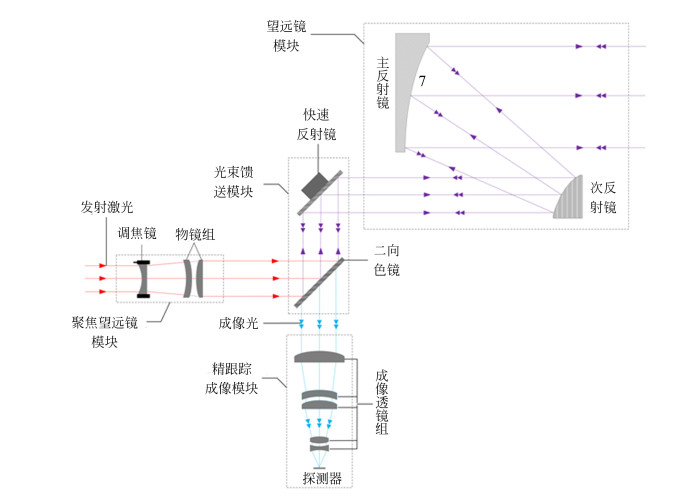
摘要: 高能激光系统的主要工作方式是利用其精跟踪模块将发射激光传输聚焦至闭环跟踪条件下的目标上,使之受到毁伤或失效。为实现该工作方式,本文研究设计了一套共孔径光学收发装置。该装置的发射系统主要由离轴两反式主望远镜模块、伽利略透射式调焦望远镜模块和光束馈送模块共同组成二级扩束系统,接收系统主要由离轴两反式主望远镜模块、精跟踪成像模块和光束馈送模块共同组成长焦距光学系统,其中光束馈送模块由二向色镜、快速反射镜等光学元件组成。以非相干空间合束的基模高斯光作为激光光源,利用光学设计软件对该装置进行了优化设计。对于发射系统,获得了激光经过调焦望远镜模块不同的调焦量调制后,传输至0.5~5 km处的光斑分布情况,且激光波前像差RMS值均优于λ/20;对于接收系统,由各模块一同构成的成像光学系统的性能经优化后接近衍射极限,其中系统传递函数在70 lp/mm时大于0.6,最后通过样机实验也验证了设计的正确性。本文的设计和实验结果证实了该共孔径光学收发装置结构合理,性能可靠,满足高能激光系统的工程应用需求。Abstract: The working principle of high energy laser systems is focusing the transmitting laser beam onto target while the target is tracked in a closed-loop using a fine tracking module, so that the target can be damaged or invalidated. In order to achieve this, an optical device with a co-aperture is designed for high-energy laser systems. The emitting system of this device is a two-stage beam expander consisted of an off-axis two-trans primary telescope module, a Galileo transmission telescope module for focusing, and a beam-feeding module. The receiver of this device is a long-focus optical system consisted of the same off-axis two-trans primary telescope module, an imaging module for fine tracking, and the same beam-feeding module, which is composed of a dichroic mirror, a fast mirror and other optical elements. Using an incoherent combination laser in space as laser source, we use optical design software in both the sequential mode and the non-sequential mode to design and simulate this device. The simulation results show that for the emitting system, the distribution of the spot at 0.5~5 km is obtained after the laser is modulated by different focusing quantities in the focusing telescope module. The RMS value of the laser wavefront is found to be better than λ/20 in the emitting system. In addition, the performance of the imaging optical system approaches the diffraction limit after optimizing, and the system transfer function is greater than 0.6 at 70 lp/mm. A prototype experiment is carried out to verify the correctness and rationality of this design. The results of this paper confirm that this optical transceiver possesses reasonable structure and reliable performance, which meets the engineering requirements of high-energy laser system applications.
-
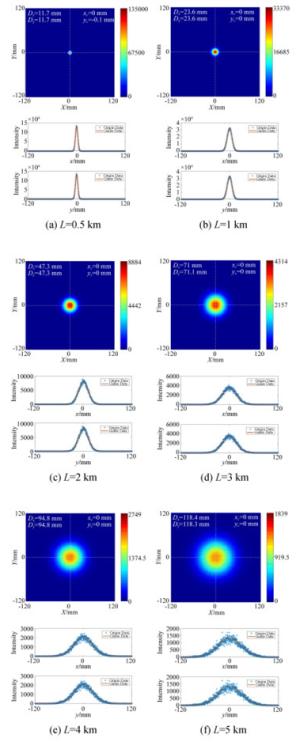
表 1 优化后各聚焦距离下的d, Δ, RMS值
Table 1. d, Δ and RMS values corresponding to different focusing distances after optimizing
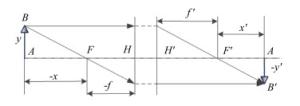
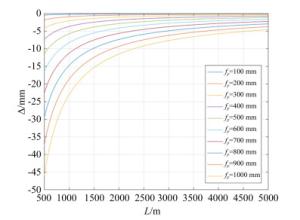
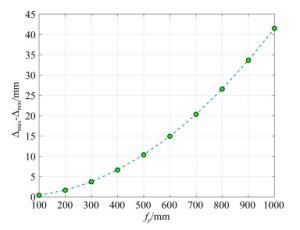
参数类型 参数值 L/km 0.5 1 2 3 4 5 ∞ d/mm 137.78 125.91 119.96 117.98 116.99 116.39 114 Δ/mm 23.78 11.91 5.96 3.98 2.99 2.39 0 RMS/λ 0.019 0.016 0.013 0.012 0.011 0.011 0.009 表 2 入射激光参数
Table 2. Parameters of incident laser
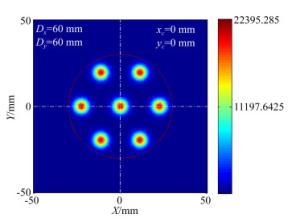
参数类型 参数值 合束激光数目 7 合束激光直径/mm 60 设计波长/nm 1 070~1 090 单束激光发散角/mrad 0.12 表 3 成像接收系统参数
Table 3. Parameters of imaging receiving system
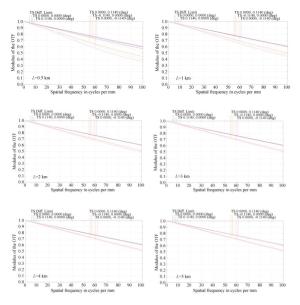
参数类型 参数值 视场/(′) ±6.6 入瞳直径/mm 320 设计波长/nm 780~840 有效焦距/mm 1 200 表 4 不同物距对应的弥散圆半径最大值
Table 4. Maximum RMS radius corresponding to different object distances
L/km 0.5 1 2 3 4 5 RMS Radius/μm 2.203 0.976 0.961 0.837 0.782 0.753 Airy Radius/μm 3.7 3.7 3.7 3.7 3.7 3.7 表 5 激光发射系统公差分析
Table 5. Tolerance analysis of emitting system
公差类型 公差名称 聚焦望远镜模块 光束馈送模块 望远镜模块 各透镜 快反镜 分色镜 主反射镜 次反射镜 加工公差 折射率 0.001 — — — — 阿贝数 1% — — — — 光圈数 1 1 1 0.5 0.5 不规则度 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2 厚度 0.03 mm 0.03 mm 0.03 mm 0.01 mm 0.01 mm X轴偏心 0.02 mm — — — — Y轴偏心 0.02 mm — — — — X轴倾斜 42″ — — — — Y轴倾斜 42″ — — — — 装调公差 X轴偏心 0.02 mm 0.02 mm 0.02 mm 0.01 mm 0.01 mm Y轴偏心 0.02 mm 0.02 mm 0.02 mm 0.01 mm 0.01 mm X轴倾斜 42″ 42″ 42″ 30″ 16″ Y轴倾斜 42″ 42″ 42″ 30″ 16″ 表 6 成像接收系统公差分析
Table 6. Tolerance analysis of receiving system
公差类型 公差名称 精跟踪成像模块 光束馈送模块 望远镜模块 透镜各表面 快反镜 分色镜 主反射镜 次反射镜 加工公差 折射率 0.001 — 0.001 — — 阿贝数 1% — 1% — — 光圈数 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 不规则度 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2 厚度 0.04 mm 0.03 mm 0.03 mm 0.01 mm 0.01 mm X轴偏心 0.02 mm — 0.03 mm — — Y轴偏心 0.02 mm — 0.03 mm — — X轴倾斜 42″ — 42″ — — Y轴倾斜 42″ — 42″ — — 装调公差 X轴偏心 0.03 mm 0.03 mm 0.03 mm 0.01 mm 0.01 mm Y轴偏心 0.03 mm 0.03 mm 0.03 mm 0.01 mm 0.01 mm X轴倾斜 42″ 42″ 42″ 30″ 16″ Y轴倾斜 42″ 42″ 42″ 30″ 16″ 表 7 聚焦光斑直径
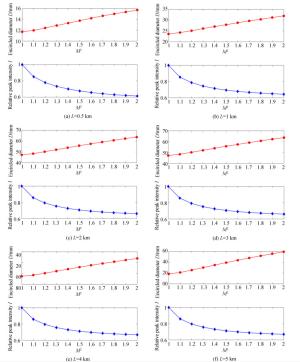
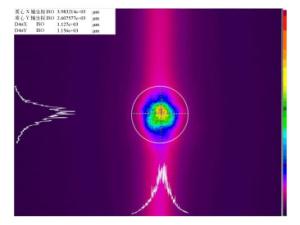
Table 7. Diameter of focusing spot
L(km) k (Dx, Dy)
(测量值)(Dx, Dy)
(实际值)(Dx, Dy)
(设计值)1 22 (1127 μm, 1156 μm) (24.79 mm, 25.43 mm) (23.6 mm, 23.6 mm) -
[1] 伊炜伟, 屈长虹, 任国光.战术机载激光武器[J].激光与红外, 2018, 48(2): 131-139. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2018.02.001YI W W, QU CH H, REN G G. Tactical airborne laser weapon[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2018, 48(2): 131-139. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2018.02.001 [2] 何奇毅, 宗思光.舰载激光武器发展进展与思考[J].激光与红外, 2017, 47(12): 1455-1460. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2017.12.001HE Q Y, ZONG S G. Research progress and consideration of shipborne laser weapon[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2017, 47(12): 1455-1460. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2017.12.001 [3] 张岩岫, 王冰, 雷萍, 等.高能激光对抗系统的发展现状与趋势[J].光电技术应用, 2018, 33(6): 24-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1255.2018.06.005ZHANG Y X, WANG B, LEI P, et al.. Development situation and trend of high energy laser countermeasure system[J]. Electro-Optic Technology Application, 2018, 33(6): 24-28. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1255.2018.06.005 [4] 李晶, 车英, 王加安, 等.折反射共光路多谱段激光雷达光学系统设计[J].中国激光, 2018, 45(5): 267-272. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgjg201805037LI J, CHE Y, WANG J A, et al.. Optical system design for multi-spectral laser radar with refraction and reflection in co-path[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2018, 45(5): 267-272. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgjg201805037 [5] 金光, 李艳杰, 钟兴, 等.空间成像与激光通信共口径光学系统设计[J].光学 精密工程, 2014, 22(8): 2067-2074. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201408013JIN G, LI Y J, ZHONG X, et al.. Design of co-aperture optical system for space imaging and laser communication[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2014, 22(8): 2067-2074. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201408013 [6] 谢桂娟, 吴健, 李长桢.一种反射共孔径式激光测距光学系统设计[J].激光与红外, 2017, 47(5): 606-612. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2017.05.016XIE G J, WU J, LI CH ZH. Design of reflective laser ranging optical system with common aperture[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2017, 47(5): 606-612. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2017.05.016 [7] 李艳杰, 金光, 张元, 等.成像与激光发射系统的共口径设计与实验[J].中国光学, 2015, 8(2): 220-226. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9252.shtmlLI Y J, JIN G, ZHANG Y, et al.. Co-aperture optical system for imaging and laser transmitting[J]. Chinese Optics, 2015, 8(2): 220-226. (in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9252.shtml [8] 刘琳, 李林.近距离激光武器光学系统特性分析[J].激光与红外, 2018, 48(1): 109-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2018.01.020LIU L, LI L. Feature analysis on optical system of close range laser weapon[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2018, 48(1): 109-112. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2018.01.020 [9] 曹秋生.战术激光武器聚焦发射特性计算研究[J].电光系统, 2017(3): 1-5. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92484X/201703/673739285.htmlCAO Q SH. Computational research on focused emission characteristics of tactical laser weapon[J]. Electronic and Electro-Optical Systems, 2017(3): 1-5. (in Chinese) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92484X/201703/673739285.html [10] 王效才.强激光武器系统光学总体考虑[J].应用光学, 1996, 17(6): 8-13. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/95241X/199606/2236541.htmlWANG X C. Optical general considerations of powerful laser weapon system[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 1996, 17(6): 8-13. (in Chinese) http://www.cqvip.com/qk/95241X/199606/2236541.html [11] 郭劲.战术激光武器系统若干关键技术分析及发展研究[J].光学 精密工程, 1996, 4(1): 7-14. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-924X.1996.01.002GUO J. Key technology analyse and develop researching of the tactical laser weapon system[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 1996, 4(1): 7-14. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-924X.1996.01.002 [12] STATON R, PAWLAK R. Laser Weapon System (LaWS) adjunct to the Close- In Weapon System (CIWS)[J]. Leading Edge, 2012, 7(4): 36-43. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=mfqtfpRtgHDH6nSBcxz3xNT0+fjqfF+eTjXbaxL7ndI= [13] 李怡勇, 王建华, 李智.高能激光武器发展态势[J].兵器装备工程学报, 2017, 38(6): 1-6. doi: 10.11809/scbgxb2017.06.001LI Y Y, WANG J H, LI ZH. Development situation of high-energy laser weapons[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2017, 38(6): 1-6. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11809/scbgxb2017.06.001 [14] 赵延仲, 宋丰华, 孙华燕. 1.06 μm脉冲激光高倍率变焦的扩束发射光学系统设计[J].红外与激光工程, 2007, 36(6): 891-895. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2007.06.032ZHAO Y ZH, SONG F H, SUN H Y. Optical design of 1.06μm pulse laser expanding system with high rate variable focus[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2007, 36(6): 891-895. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2007.06.032 [15] 郑盼, 杨应平, 郜洪云, 等.基于伽利略结构的二级激光扩束系统的设计[J].应用光学, 2008, 29(3): 347-350. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2082.2008.03.007ZHENG P, YANG Y P, GAO H Y, et al.. Design of two-level laser beam expander based on Galilean structure[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2008, 29(3): 347-350. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2082.2008.03.007 [16] 赵阳, 巩岩.折反射式连续变倍扩束系统的设计[J].光电工程, 2010, 37(4): 77-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2010.04.015ZHAO Y, GONG Y. Design of catadioptric variable focus beam expanding optical system[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2010, 37(4): 77-82. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2010.04.015 [17] 卢政伟, 邵帅, 马亚坤.复合式无遮拦激光扩束器的设计[J].中国光学, 2018, 11(4): 582-589. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9478.shtmlLU ZH W, SHAO SH, MA Y K. Design of a composite laser beam expander without obscuration[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(4): 582-589. (in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9478.shtml [18] 亓红群, 段开椋, 蒲继雄.光纤激光及其相干合成光场的准确分析[J].激光技术, 2009, 33(6): 600-603. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jgjs200906008QI H Q, DUAN K L, PU J X. Accurate analysis of coherent beam combining of fiber laser[J]. Laser Technology, 2009, 33(6): 600-603. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jgjs200906008 [19] 冯国英, 周寿桓, 高春清.激光模场及光束质量表征[M].北京:国防工业出版社, 2016.FENG G Y, ZHOU SH H, GAO CH Q. Laser Mode Field and Beam Quality Characterization[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2016. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: