Study on long wavelength infrared broadband metasurface absorber via hybrid resonant mode
-
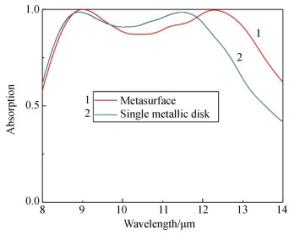
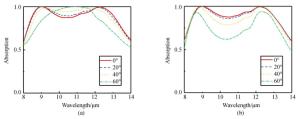
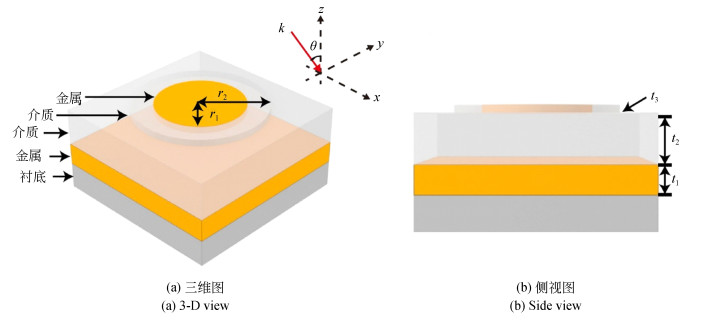
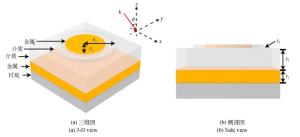
摘要: 为了满足红外探测器件集成化和对红外宽光谱范围吸收的需求,设计了一种工作在长波红外波段(8~14 μm)的超宽带、高吸收、极化不敏感的超材料吸收器。通过在金属-介质-金属三层异质的超材料吸收器结构的顶部金属周围镶嵌一层介质形成超表面,以增加谐振强度和吸收带宽。在8~13.6 μm的带宽范围内,该结构有超过90%的平均吸收率,覆盖了大部分长波红外大气窗口波段,对红外探测领域有着重要意义。研究结果表明:镶嵌的金属-介质组成的介质波导模式和谐振腔模式的结合以及传播型表面等离激元模式的激发是形成宽带高吸收的主要原因,并且谐振模式的谐振波长可以通过相关参数来进行调控。本文的研究结果为可调谐宽带长波红外吸收材料的设计提供参考,该设计方法可推广到中波红外波段、甚至长波红外或其它波段。Abstract: In order to meet the requirements of integration of infrared devices and the wideband absorption of infrared light, a novel ultra-broadband, high-absorbance and polarization-independent metamaterial absorber working in the long-wave infrared region (8~14 μm) is designed.By inserting a dielectric layer around the top metal of a metal-dielectric-metal metamaterial absorber to form a metasurface, the resonance intensity and absorption bandwidth can be improved.The structure has an average absorptivity greater than 90% in the range of 8.0 μm to 13.6 μm, covering most of the long-wave infrared atmospheric window bands, which is of great significance to infrared devices. The results indicate that the excitation of Propagating Surface Plasmon (PSP) modes and embedded cavity modes generated by the combination of dielectric-loaded surface plasmon polaritons waveguide and cavity modes contribute to broadband absorption.Moreover, the resonant wavelength of the resonance mode can be tuned by relevant parameters.The results of this paper provide a reference for the design of tunable broadband long-wavelength infrared(LWIR) absorbers. It is suggested that this design method can be extended to the medium wavelength infrared band, the very long-wavelength infrared band and others.
-
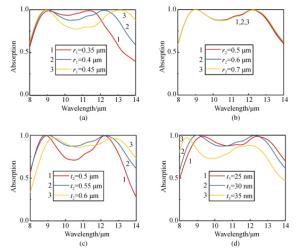
图 4 结构参数对吸收性能的影响:(a)金属圆盘半径(r1),(b)介质圆盘半径(r2), (c)介质间隔层厚度(t2), (d)金属圆盘厚度(t3)
Figure 4. Effects of the geometric parameters on the absorption performance: (a) the radius of the metallic nanodisk (r1), (b) the radius of the dielectric nanodisk (r2), (c)the thickness of the dielectric (t2), (d) the thickness of the metallic nanodisk (t3)
-
[1] 梁秋群.金属纳米结构表面等离激元杂化和吸收特性的研究[D].北京: 中国科学院大学, 2015. http://www.irgrid.ac.cn/handle/1471x/1004792LIANG Q Q. Study on plasmon hybridization and optical absorption properties of metallic nanostructures[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015. (in Chinese) http://www.irgrid.ac.cn/handle/1471x/1004792 [2] 曹水艳.表面等离子体结构聚焦和吸收特性的研究[D].北京: 中国科学院大学, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80139-1014218233.htmCAO SH Y. Study on the property of focusing and absorption of plasmonic nanostructures[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2013. (in Chinese) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80139-1014218233.htm [3] 陈超瑜, 马妍, 方群.微流控器官芯片的研究进展[J].分析化学, 2019, 47(11):1711-1720. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxhx201911001CHEN CH Y, MA Y, FANG Q. Advances in microfluidic organ-on-a-chip systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(11):1711-1720. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxhx201911001 [4] 范一强, 王洪亮, 高克鑫, 等.模块化微流控系统与应用[J].分析化学, 2018, 46(12):1863-1871. doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.181552FAN Y Q, WANG H L, GAO K X, LIU J J, et al.. Applications of modular microfluidics technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 46(12):1863-1871. doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.181552 [5] FANG X, MACDONALD K F, ZHELUDEV N I. Controlling light with light using coherent metadevices:all-optical transistor, summator and invertor[J]. Light:Science & Applications, 2015, 4, 292. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=16eab71e1f25f2ab335dcbb0754a012d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [6] LANDY N I, SAJUYIGBE S, MOCK J J, et al.. Perfect metamaterial absorber[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 100(20):207402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.207402 [7] GRANT J, MA Y, SAHA S, et al.. Polarization insensitive, broadband terahertz metamaterial absorber[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(17):3476-3478. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.003476 [8] 王月, 安西涛, 任伟, 等.纳米金膜及金壳表面局域等离激元对上转换荧光波长的选择调控[J].发光学报, 2019, 40(6):743-750. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fgxb201906006WANGY, AN X T, REN W, et al.. Wavelength Dependent Modulation of Upconversion Luminescence via Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance of Gold Nanofilm and Nanoshell[J].Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2019, 40(6):743-750. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fgxb201906006 [9] 李雪, 张然, 袁新芳, 等.基于金纳米棒@二氧化硅表面等离子体共振增强的有机太阳能电池[J].发光学报, 2018, 39(11):1579-1583. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fgxb201811013LI X, ZHANG R, YUAN X F, et al.. Surface Plasmon Resonance-enhanced Organic Solar Cells Based on Au Nanorods@SiO2 Core-shell Structures[J].Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2018, 39(11):1579-1583. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fgxb201811013 [10] 安西涛, 王月, 牟佳佳, 等.超薄金壳包覆NaYF4:Yb, Er@SiO2纳米结构的可控合成与表面增强上转换荧光[J].发光学报, 2018, 39(11):1505-1512. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fgxb201811003AN X T, WANG Y, MOU J J, et al..Controllable Synthesis and Surface-enhanced Upconversion Luminescence of Ultra-thin Gold Shell Coated NaYF4:Yb, Er@SiO2 Nanostructures[J].Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2018, 39(11):1505-1512. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fgxb201811003 [11] MAIER T, BRVCKL H. Wavelength-tunable microbolometers with metamaterial absorbers[J]. Optics Letters, 2009, 34(19):3012-3014. doi: 10.1364/OL.34.003012 [12] MAIER T, BRUECKL H. Multispectral microbolometers for the midinfrared[J]. Optics Letters, 2010, 35(22):3766-3768. doi: 10.1364/OL.35.003766 [13] MA W, JIA D L, WEN Y ZH, et al.. Diode-based microbolometer with performance enhanced by broadband metamaterial absorber[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(13):2974-2977. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.002974 [14] LIU X L, TYLER T, STARR T, et al.. Taming the blackbody with infrared metamaterials as selective thermal emitters[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2011, 107(4):045901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.045901 [15] MA W, WEN Y ZH, YU X M, et al.. Broadband metamaterial absorber at mid-infrared using multiplexed cross resonators[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(25):30724-30730. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.030724 [16] ADOMANIS B M, WATTS C M, KOIRALA M, et al.. Bi-layer metamaterials as fully functional near-perfect infrared absorbers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2015, 107(2):021107. doi: 10.1063/1.4926416 [17] GUO W L, LIU Y X, HAN T CH. Ultra-broadband infrared metasurface absorber[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(18):20586-20592. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.020586 [18] DAI SH W, ZHAO D, LI Q, et al.. Double-sided polarization-independent plasmonic absorber at near-infrared region[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(11):13125-13133. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.013125 [19] HUBAREVICH A, KUKHTA A, DEMIR H V, et al.. Ultra-thin broadband nanostructured insulator-metal-insulator-metal plasmonic light absorber[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(8):9753-9761. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.009753 [20] WU SH L, GU Y, YE Y, et al.. Omnidirectional broadband metasurface absorber operating in visible to near-infrared regime[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(17):21479-21489. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.021479 [21] HAN Q, FU Y Q, JIN L, et al.. Germanium nanopyramid arrays showing near-100% absorption in the visible regime[J]. Nano Research, 2015, 8(7):2216-2222. doi: 10.1007/s12274-015-0731-0 [22] PALIK E D. Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids. Volume III[M]. New York:Academic Press, 1998. [23] HAI L D, QUIV D, TUNG N H, et al.. Conductive polymer for ultra-broadband, wide-angle, and polarization-insensitive metamaterial perfect absorber[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(25):33253-33262. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.033253 [24] CHEN H T. Interference theory of metamaterial perfect absorbers[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(7):7165-7172. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.007165 -





 下载:
下载: