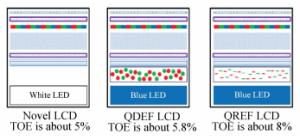
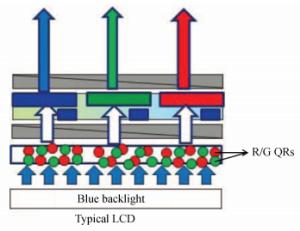
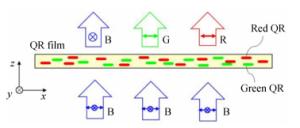
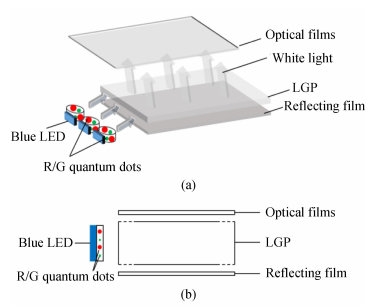
-
摘要: 量子点材料因具有发光波长可调,色度纯,量子效率高等优异特性而受到广泛关注,在光致发光高色彩显示方面有着巨大的应用潜力。本文综述了量子点背光技术的研究进展,主要对比了QDs On-Chip、QDs On-Surface及QDs On-Edge 3种量子点背光主流技术的基本原理及结构,并分析了它们在液晶显示领域的应用,未来前景及面临的挑战;然后介绍了几种新型的量子点背光技术,并对两种量子点背光新技术进行重点说明:一种是采用低温注塑成型工艺将量子点与高分子材料均匀混合为一体,用于制备直下式背光的量子点体散射型结构扩散板;另一种新技术是采用丝网印刷或喷墨打印工艺将量子点转印至导光板表面,形成应用于侧入式背光的量子点网点微结构导光板。这两种背光都具有制备工艺简单、成本低、生产效率高等特点,对高色域液晶显示的研究及发展意义深远。Abstract: Quantum dots (QDs) have received widespread attention because of their adjustable emitted wavelength of light, color purity and high quantum efficiency, which have great potential in applications requiring high-color-quality displays with photoluminescence. In this paper, the progress of QD backlights based on each QDs on-chip, QDs on-surface and QDs on-edge are reviewed, including their principle, structures and current applications. Then, several other novel QD backlight structures are also introduced, prompting a proposal for two novel QD backlight technologies. One is the QDs scattering diffusion plate, which is prepared by injecting molding with a mixture of QDs and polymer at a low temperature. The other is a QD microstructure light guide plate, which is fabricated by transferring QDs on the surface of a light guide plate through screen printing or inkjet printing. Both of these two QD plates can achieve high color gamut while being simple to process, being low in cost and holding high production efficiency. These have wide applications in high color gamut liquid crystal displays.
-
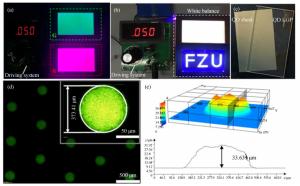
图 13 (a) 5.5英寸红、绿单色量子点导光板背光模型[58];(b)5.5英寸白平衡量子点背光模组和字符图案背光模型[58];(c)量子点膜片与量子点网点导光板示意图[58];(d)量子点散射网点的荧光显微镜局部放大图[58];(e)单个量子点散射网点的三维图像及其相应轮廓[58]
Figure 13. (a) Backlight module of 5.5-inch red/green monochromatic QDs[58]; (b) backlight module of 5.5-inch white-balance QDs and the specific partition backlight for the characters "FZU"[58]; (c)shematic diagrams of QD sheet and QD LGP[58]; (d) partial magnification of fluorescence microscope of the quantum dots microstructure array[58]; (e) 3D image and the corresponding profile of a single QD microstructure[58]
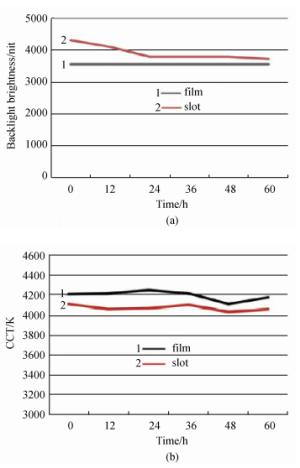
表 1 量子点槽结构与量子点膜片结构背光对比表[38]
Table 1. Backlight contrast table of QDs slot structure and QDEF structure[38]
Structure CIE(X, Y) CCT/K Lum/nit QDs Usage/num Film-a (0.354 09, 0.296 48) 4 226.8K 3 235.3 4.78×1019 Slot-b (0.359 32, 0.304 66) 4 070.7K 6 765.7 3.58×1017 表 2 LCD各背光技术对比
Table 2. Contrast of different LCD backlight technologies

YAG荧光粉
技术On-chip
结构On-edge
结构On-surface
结构量子点槽
结构量子点棒
技术量子点扩
散板技术量子点网点
微结构技术典型
结构光学硅胶
+荧光粉光学硅胶
+量子点细玻璃管
+量子点阻隔膜+量子
点层+阻隔膜光学封装胶
+量子点量子点棒 聚合物+
量子点导光油墨
+量子点色域
(NTSC)72% 82%~90% 100% 110% - - >120% >120% 工作
温度高温
(150℃)高温
(150℃)较高温度 较低温度
(室温)较高温度 较低温度
(室温)较高温度 较低温度
(室温)寿命 较高 低 较高 较高 - 较高 - - 量子点
用量无 少
(10kg/年)较少
(1t/年)多
(100t/年)少 - 少 少 结构 不改背光
结构不改背光
结构需增加
组件需增加
组件不改背光
结构不改背光
结构不改背光
结构不改背光
结构结构
利用率低 高 中 低 高 高 中 高 成本 低 芯片成本高 较低 较高 较低 较高 较高 较低 工艺 简单 复杂 简单 简单 简单 复杂 简单 简单 -
[1] PAN J W, HU Y W. Design of a hybrid light guiding plate with high luminance for backlight system application[J]. Journal of Display Technology, 2013, 9(12): 965-971. doi: 10.1109/JDT.2013.2276744 [2] 王海雄, 李积彬. LCD导光板微结构成型技术及发展趋势[J].液晶与显示, 2012, 27(4): 486-492. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yjyxs201204011WANG H X, LI J B. Molding technologies of micro-structure on light guide plate of LCD and trends[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2012, 27(4): 486-492. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yjyxs201204011 [3] REINERT-WEISS C J, BAUR H, AL NUSAYER S A, et al. Development of active matrix LCD for use in high-resolution adaptive headlights[J]. Journal of the Society for Information Display, 2017, 25(2): 90-97. doi: 10.1002/jsid.534 [4] LAI L P, ZHUANG Q R, LIANG D J. Design of an efficient projector for LED flat lamp without light guide plate[J]. Optoelectronics Letters, 2013, 9(6): 441-445. doi: 10.1007/s11801-013-3131-2 [5] SHEN X, ZHANG D F, FAN X W, et al. Fabrication and characterization of YAG: Ce phosphor films for white LED applications[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2016, 27(1): 976-981. doi: 10.1007/s10854-015-3841-2 [6] JI S H, LEE H C, YOON J M, et al. P.91: adobe RGB LCD monitor with 3 primary colors by deep green color filter technology[J]. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, 2013, 44(1): 1332-1334. doi: 10.1002/j.2168-0159.2013.tb06483.x [7] LUO ZH Y, CHEN Y, XU D M, et al. Is quantum-dot LCD ready for prime time?[C]. Proceedings of IEEE Photonics Conference, IEEE, 2014: 40-41. [8] LUO ZH Y, CHEN Y, WU S T. Wide color gamut LCD with a quantum dot backlight[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(22): 26269-26284. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.026269 [9] CHEN J, GENSLER S, YUREK J. Quantum dots for ultra-high color gamuts in LCDs[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2015: 1-3. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/276458774_Quantum_dots_for_ultra-high_color_gamuts_in_LCDs [10] LUO ZH Y, XU D M, WU S T. Emerging quantum-dots-enhanced LCDs[J]. Journal of Display Technology, 2014, 10(7): 526-539. doi: 10.1109/JDT.2014.2325218 [11] JANG E, JUN S, JANG H, et al. White-Light-Emitting diodes with quantum dot color converters for display backlights[J]. Advanced Materials, 2010, 22(28): 3076-3080. doi: 10.1002/adma.201000525 [12] CHEN J, HARDEV V, HARTLOVE J, et al. A high-efficiency wide-color-gamut solid-state backlight system for LCDs using quantum dot enhancement film[J]. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, 2012, 43(1): 895-896. doi: 10.1002/j.2168-0159.2012.tb05931.x [13] COE-SULLIVAN S. The quantum dot revolution: marching towards the mainstream[J]. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, 2016, 47(1): 239-240. doi: 10.1002/sdtp.10648 [14] BOURZAC K. Quantum dots go on display[J]. Nature, 2013, 493(7432): 283. doi: 10.1038/493283a [15] 季洪雷, 周青超, 潘俊, 等.量子点液晶显示背光技术[J].中国光学, 2017, 10(5): 666-680. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9531.shtmlJI H L, ZHOU Q CH, PAN J, et al. Advances and prospects in quantum dots based backlights[J]. Chinese Optics, 2017, 10(5): 666-680. (in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9531.shtml [16] 金一政, 彭笑刚.量子点显示——中国显示行业"换道超车"的曙光[J].浙江大学学报(理学版), 2016, 43(6): 635-637. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zjdxxb201606002JIN Y ZH, PENG X G. Quantum-dots based display technology-the opportunity for Chinese display industry[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition), 2016, 43(6): 635-637. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zjdxxb201606002 [17] 史冬梅, 杨斌.量子点材料与显示技术发展现状与趋势[J].科技中国, 2017(12): 8-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5129.2017.12.004SHI D M, YANG B. Current development and trend of quantum dot materials and display technology[J]. Technology China, 2017(12): 8-10. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5129.2017.12.004 [18] 马赐强. 2017全球量子点显示器市场发展现状及未来市场概述[EB/OL].[2017-06-19]. https://wenku.baidu.com/view/2bd18dbfbb0d4a7302768e9951e79b89680268d6.html?re=view.MA C Q, 2017 global quantum dot display market development status and future market overview[EB/OL].[2017-06-19]. https://wenku.baidu.com/view/2bd18dbfbb0d4a7302768e9951e79b89680268d6.html?re=view. (in Chinese) [19] KIM S W, IM S H, KIM S W. Performance of light-emitting-diode based on quantum dots[J]. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(12): 5205-5214. doi: 10.1039/c3nr00496a [20] KURTIN J, PUETZ N, THEOBALD B, et al. Quantum dots for high color gamut LCD displays using an On-Chip LED solution[J]. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, 2014, 45(1): 146-148. doi: 10.1002/j.2168-0159.2014.tb00040.x [21] GRINOLDS D D, BROWN P R, HARRIS D K, et al. Quantum-dot size and thin-film dielectric constant: precision measurement and disparity with simple models[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(1): 21-26. doi: 10.1021/nl5024244 [22] TWIETMEYER K, SADASIVAN S. Design considerations for highly efficient edge-lit quantum dot displays[J]. Journal of the Society for Information Display, 2016, 24(5): 312-322. doi: 10.1002/jsid.436 [23] STECKEL J S, HO J, HAMILTON C, et al. Quantum dots: the ultimate down-conversion material for LCD displays[J]. Journal of the Society for Information Display, 2015, 23(7): 294-305. doi: 10.1002/jsid.313 [24] SONG W S, YANG H. Efficient white-light-emitting diodes fabricated from highly fluorescent copper indium sulfide core/shell quantum dots[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2012, 24(10): 1961-1967. doi: 10.1021/cm300837z [25] ZHAO Y M, RIEMERSMA C, PIETRA F, et al. High-temperature luminescence quenching of colloidal quantum dots[J]. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(10): 9058-9067. doi: 10.1021/nn303217q [26] COE-SULLIVAN S, LIU W H, ALLEN P, et al. Quantum dots for LED downconversion in display applications[J]. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology, 2013, 2(2): R3026-R3030. doi: 10.1149/2.012302jss [27] COUNCIL of the EU. Restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment (RoHS) Directive 2002/95/EC[R]. Council of the EU, 2003. [28] ZHANG F, ZHONG H ZH, CHEN CH, et al. Brightly luminescent and color-tunable colloidal CH3NH3PbX3 (X =Br, I, Cl) quantum dots: potential alternatives for display technology[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(4): 4533-4542. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b01154 [29] HUANG H L, ZHAO F CH, LIU L G, et al. Emulsion synthesis of size-tunable CH3NH3PbBr3 quantum dots: an alternative route toward efficient light-emitting diodes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(51): 28128-28133. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26652661 [30] BAI Z L, ZHONG H ZH. Halide perovskite quantum dots: potential candidates for display technology[J]. Science Bulletin, 2015, 60(18): 1622-1624. doi: 10.1007/s11434-015-0884-y [31] CHEN X M, ZHANG F, GE Y, et al. Centimeter-sized Cs4PbBr6 crystals with embedded CsPbBr3 nanocrystals showing superior photoluminescence: nonstoichiometry induced transformation and light-emitting applications[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(16): 1706567. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201706567 [32] CHEN J, KAN SH H, LEE E, et al. Quantum dot enabled high color gamut LCDs[J]. Proceedings of the SPIE, 2015, 9385: 93850F, doi: 10.1117/12.2086918. [33] THIELEN J, LAMB D, LEMON A, et al. Correlation of accelerated aging to in-device lifetime of quantum dot enhancement film[J]. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, 2016, 47(1): 336-339. doi: 10.1002/sdtp.10673 [34] ZHOU Q CH, BAI Z L, LU W G, et al. In situ fabrication of halide perovskite nanocrystal-embedded polymer composite films with enhanced photoluminescence for display backlights[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(41): 9163-9168. doi: 10.1002/adma.201602651 [35] KIM G, SHIH Y C, SHI F G. Optimal design of a quantum dot color conversion film in LCD backlighting[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2017, 23(5), doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2017.2677898. [36] KONG Y L, BOULOGNE F, KIM H, et al. Deposition of quantum dots in a capillary tube[J]. Langmuir, 2015, 31(45): 12560-12566. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b03443 [37] CHENG M C, SU Y CH, HSIAO V K S. Optically switchable photoluminescence using liquid-crystal dispersed quantum dots in film and capillary tube[J]. Proceedings of SPLE, 2011, 8114: 811419. doi: 10.1117/12.897945 [38] 顾宝, 盛欣, 叶志成.量子点应用于液晶显示背光的研究[J].激光与光电子学进展, 2015, 52(2): 222-228. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JGDJ201502030.htmGU B, SHENG X, YE ZH CH. Research on quantum dot apply to LCD backlight[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2015, 52(2): 222-228. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JGDJ201502030.htm [39] MOKARI T, ROTHENBERG E, POPOV I, et al. Selective growth of metal tips onto semiconductor quantum rods and tetrapods[J]. Science, 2004, 304(5678): 1787-1790. doi: 10.1126/science.1097830 [40] SHIEH F, SAUNDERS A E, KORGEL B A, et al. General shape control of colloidal CdS, CdSe, CdTe quantum rods and quantum rod heterostructures[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2005, 109(18): 8538-8542. doi: 10.1021/jp0509008 [41] SRIVASTAVA A K, ZHANG W L, SCHNEIDER J, et al. Photo-Aligned quantum rod dispersed liquid crystal polymer films[J]. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, 2016, 47(1): 602-604. doi: 10.1002/sdtp.10754 [42] SUZUKI M, KISHIMOTO T, HIRAYAMA Y, et al. Quantum rod containing film development for display applications[J]. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, 2016, 47(1): 340-343. doi: 10.1002/sdtp.10674 [43] CHEN H W, HE J, WU S T. Recent advances on quantum-dot-enhanced liquid-crystal displays[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2017, 23(5), doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2017.2649466. [44] OKUMURA T, TAGAYA A, KOIKE Y, et al. Highly-efficient backlight for liquid crystal display having no optical films[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2003, 83(13): 2515-2517. doi: 10.1063/1.1613051 [45] OKUMURA T, ISHIKAWA T, TAGAYA A, et al. Optical design of liquid crystal display backlighting with highly scattering optical transmission polymer[J]. Journal of Optics A: Pure and Applied Optics, 2003, 5(5): S269-S275. doi: 10.1088/1464-4258/5/5/377 [46] TAGAYA A, KOIKE Y. Highly scattering optical transmission polymers for bright display[J]. Macromolecular Symposia, 2000, 154(1): 73-82. doi: 10.1002/1521-3900(200004)154:1<73::AID-MASY73>3.0.CO;2-Z [47] 叶勤, 唐振方, 张杰, 等.体散射液晶导光板的光线追迹模拟[J].光学学报, 2006, 26(11): 1627-1631. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.2006.11.007YE Q, TANG ZH F, ZHANG J, et al. Ray tracing simulation of volume scattering light guide plate for LCD[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2006, 26(11): 1627-1631. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.2006.11.007 [48] 宋孟夏, 刘颖, 郑秀婷, 等.双层复合微结构体散射导光板导光性能的分析[J].塑料, 2015, 44(2): 52-56, 43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1396.2015.02.017SONG M X, LIU Y, ZHENG X T, et al. Analysis on light guide performance of double composite volume scattering light guide plate with microstructure[J]. Plastics, 2015, 44(2): 52-56, 43. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1396.2015.02.017 [49] DONG P W, CAI H ZH, ZHANG Y J, et al. The study of micro-injection molding of thin-wall light guide plate with hemispherical micro structures[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 562-564: 611-614. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.562-564.611 [50] XIE P CH, GOU G, WEN ZH X, et al. Research on the key technology of precision injection molding equipment for light guide plate[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2010, 87-88: 306-310. https://www.scientific.net/AMR.87-88.306 [51] DONG P W, ZHAO ZH L, WU D M, et al. Simulation of injection molding of ultra-thin light guide plate with hemispherical microstructures[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2012, 503: 222-226. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.503.222 [52] JUNG T S, JANG J H, KIM J S. A study on the filling pattern imbalance in high speed injection molding process for thin light guide plate[J]. Polymer (Korea), 2017, 41(1): 30-38. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=518c44ee5e5ca772edcf9fb0c47327f6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [53] YU J C, HSU P K. Integration of stamper fabrication and design optimization of LCD light guides using silicon-based microfeatures[J]. Microsystem Technologies, 2010, 16(7): 1193-1200. doi: 10.1007/s00542-009-0948-5 [54] WANG M W, PANG D CH, TSENG Y E, et al. The study of light guide plate fabricated by inkjet printing technique[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2014, 45(3): 1049-1055. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2013.08.021 [55] 徐胜, 徐玉珍, 陈恩果, 等.基于量子点网点微结构的背光源技术研究[J].海南大学学报自然科学版, 2016, 34(3): 209-214. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hainandxxb201603003XU SH, XU Y ZH, CHEN E G, et al. LED backlight technology based on micro-dot structures mixed with quantum dots[J]. Natural Science Journal of Hainan University, 2016, 34(3): 209-214. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hainandxxb201603003 [56] 黄炳乐, 郭太良, 陈恩果, 等.导光板网点平均密度范围的最优化研究[J].光学学报, 2015, 35(5): 306-312. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201505041HUANG B L, GUO T L, CHEN E G, et al. Study on optimal scale of average netted dot density for light guide plate[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2015, 35(5): 306-312. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201505041 [57] 黄佳敏, 陈恩果, 郭太良.量子点背光源白平衡特性的研究[J].液晶与显示, 2017, 32(2): 77-83. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yjyxs201702001HUANG J M, CHEN E G, GUO T L. White-balance characteristic of quantum-dot backlight[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2017, 32(2): 77-83. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yjyxs201702001 [58] CHEN E G, XIE H X, HUANG J M, et al. Flexible/curved backlight module with quantum-dots microstructure array for liquid crystal displays[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(3): 3466-3482. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.003466 [59] 黄佳敏, 陈恩果, 郭太良.量子点背光源颜色特性的理论研究与验证[C].中国平板显示学术会议论文集, 2016: 1348-1353.HUANG J M, CHEN E G, GUO T L. Theoretical study and verification of the color characteristics of quantum dot backlight[C]. Papers Collection of China Flat Panel Display Academic Conference, 2016: 1348-1353. (in Chinese) [60] 汪江胜, 叶芸, 徐胜, 等.量子点网点导光板的制备及性能研究[J].发光学报, 2017, 38(1): 91-96. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fgxb201701015WANG J SH, YE Y, XU SH, et al. Fabrication and properties of quantum-dots backlight light guide plate[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2017, 38(1): 91-96. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fgxb201701015 [61] 福州大学.一种改善喷墨打印量子点网点导光板的方法: 中国, CN201610828845.9[P]. 2016-09-19.FUZHOU University. A method for improving inkjet printing quantum dots dot light guide plate: CN, CN201610828845.9[P]. 2016-09-19. (in Chinese) [62] 福州大学.一种基于量子点导光板的背光模组: 中国, CN201410285691.4[P]. 2014-06-25.Fuzhou University. A backlight module based on quantum dots light guide plate: CN, CN201410285691. 4[P]. 2014-06-25. (in Chinese) [63] 福州大学.一种喷墨打印量子点导光板网点微结构的方法: 中国, CN201810657132.X[P]. 2018-06-25.Fuzhou University. A method for inkjet printing of dot microstructure of quantum dots light guide plate: CN, CN201810657132. X[P]. 2018-06-25. (in Chinese) -





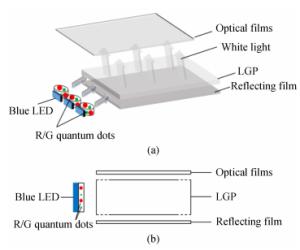
 下载:
下载: