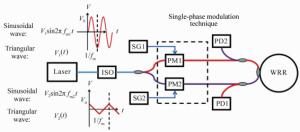
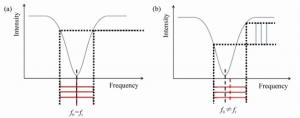
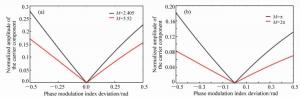
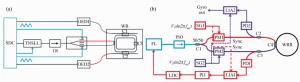
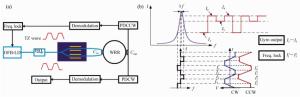
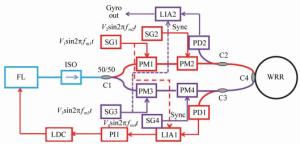
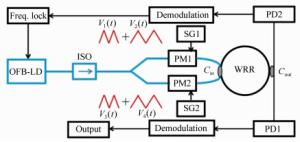
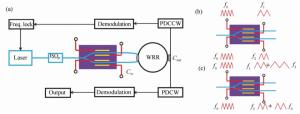
Phase modulation techniques for suppressing backscattering noise in resonator integrated optic gyroscopes
doi: 10.3788/CO.20191206.1403
-
摘要: 在谐振式集成光学陀螺系统中,相位调制技术被广泛用于检测陀螺旋转信号。本文详细介绍了近几年来国内外学者为提高陀螺精度、抑制陀螺噪声所提出的相位调制技术。文章首先从理论上分析了谐振环中的背散射噪声,发现载波抑制是抑制背散射噪声的关键因素。然后,详细介绍了近几年来为提高陀螺精度而提出的两类相位调制技术,分别是单相位调制技术和双相位调制技术,并分析比较了其技术原理、噪声抑制能力以及系统的鲁棒性和复杂度。新型的边带锁定技术可以有效抑制陀螺中的背散射噪声。最后通过总结这些相位调制技术的优缺点发现,在陀螺系统中除了需要借助于相位调制技术抑制背反射噪声外,提高对其他类型噪声的抑制是集成光学陀螺性能进一步提高的关键。Abstract: Phase modulation technology is widely used in detecting the rotational signal of gyro in resonator integrated optic gyroscopes in order to improve the sensitivity and suppress noises. This paper we review various phase modulation techniques that have been proposed by many researchers in recent years. The influences of backscattering noises on the performance of RIOG are introduced firstly. Various improved phase modulation techniques are proposed by different research groups. The advantages and limitations of these modulation techniques are investigated. The modulation techniques include two broad categories:namely, single-phase modulation technique (SPMT) and double phase modulation technique (DPMT). Compared with SPMT, DPMT can further improve accuracy and system robustness of RIOGs. High precision sideband locking technology is the latest emerging modulation method that is expected to fulfill performance requirements in the fields of aerospace and defense.
-
Key words:
- gyroscopes /
- phase modulation /
- optical sensing and sensors /
- resonators
-
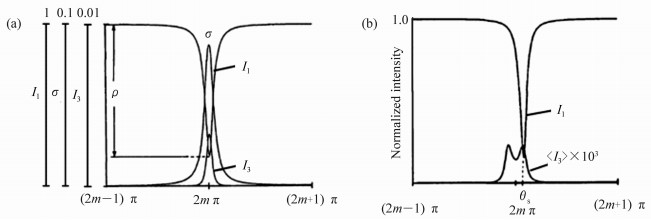
Figure 7. (Color online)(a)Sketch map of the demodulation method of the trapezoidal phase modulation technique[18], (b)intensity modulation output from resonator under trapezoidal phase modulation
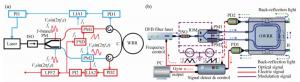
Figure 8. (Color online) Schematic illustration of a RIOG based on the DSPM technique[21]
Figure 9. (Color online)Schematic illustration of a RIOG based on the DTPM[20]
Figure 10. (Color online) Schematic illustration of a RIOG based on the phase difference traversal(PDT) method[22]
Table 1. RIOGs based on different phase modulation techniques with the best bias stability
Phase Modulation technique Waveform Resonator finesse Measured short term bias stability (deg/s) Measured long term bias stability (deg/s) System complexity System robustness SPMT sinusoidal[10] - 0.46 - low low SPMT triangular[17] 56 - 0.717 08 low low SPMT trapezoidal[18] 82 - 0.09 low low SPMT sideband locking technique[27] 59 - 0.004 2 low high DPMT triangular[20] 59 - 0.22 medium high DPMT sinusoidal[21] 46.3 0.01 - high high DPMT triangular(PDT)[22] 82 0.005 5 0.013 low medium DPMT sinusoidal wave and sawtooth-wave[23] 34 - 0.05 high medium DPMT triangular wave and sawtooth-wave[7] 59 0.22 - medium medium -
[1] SAGNAC G. L'éther lumineux démontré par léffet du vent relatif d'éther dans un interférométre en rotation uniforme[J]. Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, 1913, 157:708-719. [2] SUZUKI K, TAKIGUCHI K, HOTATE K. Integrated optical ring-resonator gyro using a silica planar lightwave circuit[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1999, 3541:66-75. doi: 10.1117/12.339114 [3] FEI Y, YANG T SH, LI ZH F, et al.. Design of the low-loss waveguide coil for interferometric integrated optic gyroscopes[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2017, 38(4):044009. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/4/044009 [4] DELL'OLIO F, TATOLI T, CIMINELLI C, et al.. Recent advances in miniaturized optical gyroscopes[J]. Journal of the European Optical Society-Rapid Publications, 2014, 9:14013. doi: 10.2971/jeos.2014.14013 [5] SANDERS S J, STRANDJORD L K, MEAD D. Fiber optic gyro technology trends-a Honeywell perspective[C]. Proceedings of 2002 15th Optical Fiber Sensors Conference Technical Digest, IEEE, 2002: 5-8. [6] FREIER L, LAZNICKA O, GILMORE J, et al.. A fiber-optic rotation sensor for NASA space missions[J]. AAS Guidance and Control, 1992, 91. [7] FENG L SH, LEI M, LIU H L, et al.. Suppression of backreflection noise in a resonator integrated optic gyro by hybrid phase-modulation technology[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(8):1668-1675. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.001668 [8] CIMINELLI C, DELL'OLIO F, ARMENISE M N, et al.. High performance InP ring resonator for new generation monolithically integrated optical gyroscopes[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(1):556-564. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.000556 [9] YU X H, MA H L, JIN ZH H, et al.. Resonator fiber optic gyroscope with an all digitalized system[C]. Proceedings of 2010 3rd International Symposium on Systems and Control in Aeronautics and Astronautics, IEEE, 2010: 815-818. [10] IWATSUKI K, HOTATE K, HIGASHIGUCHI M. Effect of Rayleigh backscattering in an optical passive ring-resonator gyro[J]. Applied Optics, 1984, 23(21):3916-3924. doi: 10.1364/AO.23.003916 [11] MA H L, HE Z Y, HOTATE K. Sensitivity improvement of waveguide-type optical passive ring resonator gyroscope by carrier suppression[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2009, 7503:750353. doi: 10.1117/12.835029 [12] SUZUKI K, TAKIGUCHI K, HOTATE K. Monolithically integrated resonator microoptic gyro on silica planar lightwave circuit[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2000, 18(1):66-72. doi: 10.1109/50.818908 [13] MA H L, ZHANG X L, JIN ZH H, et al.. Waveguide-type optical passive ring resonator gyro using phase modulation spectroscopy technique[J]. Optical Engineering, 2006, 45(8):080506. doi: 10.1117/1.2280645 [14] ZHANG X L, MA H L, JIN ZH H, et al.. Open-loop operation experiments in a resonator fiber-optic gyro using the phase modulation spectroscopy technique[J]. Applied Optics, 2006, 45(31):7961-7965. doi: 10.1364/AO.45.007961 [15] YAN Y CH, WANG L L, MA H L, et al.. Hybrid air-core photonic bandgap fiber ring resonator and implications for resonant fiber optic gyro[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2015, 9655:96550I. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=CC0215031297 [16] YING D Q, MA H L, JIN ZH H. Resonator fiber optic gyro using the triangle wave phase modulation technique[J]. Optics Communications, 2008, 281(4):580-586. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2007.10.012 [17] YU H, ZHANG C, FENG L, et al.. Limitation of rotation sensing in IORG by Rayleigh backscattering noise[J]. Europhysics Letters, 2011, 95(6):64001. doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/95/64001 [18] WANG J J, FENG L SH, TANG Y CH, et al.. Resonator integrated optic gyro employing trapezoidal phase modulation technique[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(2):155-158. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0234104520/ [19] MAO H, MA H L, JIN ZH H, et al.. Resonator micro-optic gyroscope based on the double phase modulation technique[C]. Proceedings of CLEO/QELS: 2010 Laser Science to Photonic Applications, IEEE, 2010: 1-2. [20] ZHI Y ZH, FENG L SH, WANG J J, et al.. Reduction of backscattering noise in a resonator integrated optic gyro by double triangular phase modulation[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(1):114. doi: 10.1364/AO.54.000114 [21] MAO H, MA H L, JIN ZH H. Polarization maintaining silica waveguide resonator optic gyro using double phase modulation technique[J]. Optics Express, 2011, 19(5):4632-4643. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.004632 [22] WANG J J, FENG L SH, WANG Q W, et al.. Suppression of backreflection error in resonator integrated optic gyro by the phase difference traversal method[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(7):1586-1589. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.001586 [23] MA H L, ZHANG J J, WANG L L, et al.. Double closed-loop resonant micro optic gyro using hybrid digital phase modulation[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(12):15088-15097. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.015088 [24] JIN ZH H, YU X H, MA H L. Closed-loop resonant fiber optic gyro with an improved digital serrodyne modulation[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(22):26578-26588. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.026578 [25] LEFÈVRE H C. The fiber-optic gyroscope:challenges to become the ultimate rotation-sensing technology[J]. Optical Fiber Technology, 2013, 19(6):828-832. doi: 10.1016/j.yofte.2013.08.007 [26] DELL'OLIO F, INDIVERI F, CIMINELLI C, et al.. Optoelectronic gyroscope based on a high-Q InGaAsP/InP ring resonator: preliminary results of the system test[C]. Proceedings of 2014 16th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks, IEEE, 2014: 1-4. [27] LIU N, NIU Y X, FENG L SH, et al.. Suppression of backscattering induced noise by the sideband locking technique in a resonant fiber optic gyroscope[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2018, 16(1):010608. doi: 10.3788/COL201816.010608 [28] LEFÈVRE H C. The Fiber-optic Gyroscope[M]. London:Artech House, 2014. [29] TENCH R, DELAVAUX J M, TZENG L, et al.. Performance evaluation of waveguide phase modulators for coherent systems at 1.3 and 1.5μm[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 1987, 5(4):492-501. doi: 10.1109/JLT.1987.1075535 [30] FEI Y, HE Y M, LI ZH F, et al.. Backreflections in resonant micro-optic gyroscope[J]. Journal of Physics Communications, 2018, 2(9):095010. doi: 10.1088/2399-6528/aad065 [31] YAN Y CH, CHEN Y, MA H L, et al.. Polarization-fluctuation induced drift in resonator micro optic gyro[C]. Proceedings of 2012 Asia Communications and Photonics Conference, IEEE, 2012: 1-3. [32] FEI Y, HE Y M, WANG X D, et al.. Analysis of resonance asymmetry phenomenon in resonator integrated optic gyro[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2018, 27(8):084213. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/27/8/084213 [33] LI X H, ZHANG J J, MA H L, et al.. Test and analysis of the optical kerr-effect in resonant micro-optic gyros[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2014, 6(5):6601007. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dfedeed3687d3cd0d90139057c8c5beb [34] MA H L, YAN Y CH, CHEN Y, et al.. Improving long-term stability of a resonant micro-optic gyro by reducing polarization fluctuation[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2012, 4(6):2372-2381. doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2012.2232908 [35] MA H L, CHANG X, YANG ZH H, et al.. Full investigation of the backscattering in resonator fiber optic gyro[J]. Optics Communications, 2011, 284(19):4480-4484. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2011.06.018 [36] KAISER T J, CARDARELLI D, WALSH J G. Experimental developments in the RFOG[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1991, 1367:121-126. doi: 10.1117/12.24736 [37] WANG X J, KISHI M, HE Z Y, et al.. Closed loop resonator fiber optic gyro with precisely controlled bipolar digital serrodyne modulation[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2012, 8351:83513G. doi: 10.1117/12.914427 [38] MA H L, HE Z Y, HOTATE K Z. Reduction of backscattering induced noise by carrier suppression in waveguide-type optical ring resonator gyro[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2011, 29(1):85-90. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2010.2092751 [39] LEI M, FENG L SH, ZHI Y ZH. Impact of inflection points on the performance of resonator integrated optic gyro[J]. Optik, 2014, 125(1):508-510. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fa343d2a6490fcd203ab718f2a0c07f5 [40] WANG J J, FENG L SH, WANG Q W, et al.. Reduction of angle random walk by in-phase triangular phase modulation technique for resonator integrated optic gyro[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(5):5463-5468. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.005463 [41] EZEKIEL S, BALSAMO S R. Passive ring resonator laser gyroscope[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1997, 30(9):478-480. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLHY/NSTL_HYCC027669952/ [42] LEI M, FENG L SH, ZHI Y ZH. Sensitivity improvement of resonator integrated optic gyroscope by double-electrode phase modulation[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(30):7214-7219. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.007214 [43] MOELLER R P, BURNS W K. 1.06-μm all-fiber gyroscope with noise subtraction[J]. Optics Letters, 1991, 16(23):1902-1904. doi: 10.1364/OL.16.001902 [44] 郭丽君, 宁亮, 孔梅, 等.谐振式集成光学陀螺解调特性分析[J].中国光学, 2014, 7(4):651-656. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9148.shtmlGUO L J, NING L, KONG M, et al.. Demodulation characteristics of resonator integrated optical gyro[J]. Chinese Optics, 2014, 7(4):651-656.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9148.shtml [45] JIN ZH H, ZHANG G H, MAO H, et al.. Resonator micro optic gyro with double phase modulation technique using an FPGA-based digital processor[J]. Optics Communications, 012, 285(5):645-649. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ef431c61e998320eb58cd7e231dd1ea7 -





 下载:
下载: