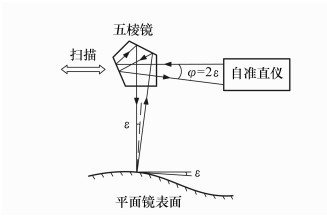
-
摘要: 为了提高大口径平面镜面形检测的精度和效率,提出了一种新的五棱镜扫描法。该方法采用径向扫描的方式,使用一个扫描的五棱镜和一台自准直仪来测量表面倾斜角的差值,然后将被测平面镜的面形表示为Zernike多项式的线性组合,再利用表面倾斜角的差值建立方程组,最后采用最小二乘法计算得到被测平面镜的面形。在检测过程中,该方法还可以对五棱镜在扫描过程中的倾斜变化量进行自动监视和调整,减小了检测误差。误差分析表明,该方法的面形检测精度为7.6 nm rms(均方根误差)。采用该方法对一块1.5 m口径的平面镜进行了面形检测,并与Ritchey-Common法的检测结果进行了对比,两种方法面形结果的差异为7.1 nm rms,小于五棱镜扫描法的面形检测精度。证明了利用该五棱镜扫描法检测大口径平面镜面形的正确性。Abstract: To improve the accuracy and efficiency of the surface shape measurements of large flat mirrors, a new scanning pentaprism method is proposed. In this method, we use a scanning pentaprism and an autocollimator to radially scan and measure the differences between the tilt angles. The surface shape of the flat mirror under test is expressed by a linear combination of Zernike polynomials and an equation set is established on the basis of the angle differences. Finally, the surface shape of the flat mirror can be derived through a least squares calculation. In the measuring process, this method can automatically accommodate changes in the pentaprism tilts during scans, which can reduce measurement errors. The error analysis indicates that the surface shape measurement accuracy by this method is 7.6 nm rms(root-mean-square). This method is used to measure the surface shape of a 1.5 m flat mirror and the result is compared to that of the Ritchey-Common method. The difference between the two surface shape results is 7.1 nm rms, which is less than the surface shape measurement results of the scanning pentaprism method. This proves that it is feasible using the scanning pentaprism method to measure the topographies of large flat mirrors.
-
Key words:
- scanning pentaprism method /
- large flat mirror /
- surface shape /
- tilt angle of surface
-
表 1 各个倾斜误差角的值
Table 1. Values of tilt angle error
倾斜误差角 来源于初始调整 来源于五棱镜扫描时的倾斜 来源于旋转臂的倾斜 来源于被测平面镜的表面倾斜 方和根 αpp <30 μrad <45 μrad <210 μrad — <217 μrad γpp <30 μrad <45 μrad — — <54 μrad αac — — <210 μrad — <210 μrad βac — — <210 μrad — <210 μrad γac — — — — 等于0 μrad αst <30 μrad — — <9 μrad <31 μrad Δαpp — 21 μrad rms — — 21 μrad rms Δγpp — 21 μrad rms — — 21 μrad rms Δαst — — — 3 μrad rms 3 μrad rms 表 2 计算式(15)的一些组成部分
Table 2. Calculations of some components in Equation (15)(μrad)
组成部分 αpp 2αpp αac αst γpp 方和根 2αpp+αac+αst — <434 <210 <31 — <483 αac+αst — — <210 <31 — <212 αac+αpp+γpp <217 — <210 — <54 <307 表 3 计算Eδ的值
Table 3. Calculations of Eδ
式(15)中的项 误差值(nrad rms) Δαpp(2αpp+αac+αst) 10.1 Δγpp(αac+αst) 4.5 Δαst(αac+αpp+γpp) 0.9 方和根 11.1 表 4 计算光束倾斜带来的测量点位置误差
Table 4. Calculations of the position errors caused by beam tilts
光束倾斜角/μrad rms 五棱镜与被测平面镜的距离/mm 测量点位置误差mm rms 来源于αpp:72 0.036 来源于γpp:18 0.009 来源于βac:70 500 0.035 来源于γac:0 0 来源于V0:15 0.008 来源于H0:15 0.008 方和根 0.052 表 5 表面倾角差值的误差汇总
Table 5. The combined error of the surface tilt angle difference
误差来源 误差值/nrad rms 倾斜误差 11.1 自准直仪1的测量误差 70.7 测量点的位置误差 1.7 环境变化带来的误差 38.5 方和根 81.3 -
[1] 赵维谦, 李文宇, 赵齐, 等.被测件随机移相干涉面形测量方法[J].光学 精密工程, 2016, 24(9):2167-2172. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201609010ZHAO W Q, LI W Y, ZHAO Q, et al.. Surface measurement by randomly phase shifting interferometry of measured element[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2016, 24(9):2167-2172.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201609010 [2] ZHU SH, ZHANG X H. Eliminating alignment error and analyzing Ritchey angle accuracy in Ritchey Common test[J]. Optics Communications, 2013, 311:368-374. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2013.08.024 [3] 林冬冬, 胡明勇, 李金鹏, 等.大口径平面镜局部采样瑞奇-康芒检验[J].激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(3):031202. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jgygdzxjz201803038LIN D D, HU M Y, LI J P, et al.. Local sampling Ritchey-Common test for large aperture flat mirror[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2018, 55(3):031202.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jgygdzxjz201803038 [4] 王孝坤.大口径离轴凸非球面系统拼接检验技术[J].中国光学, 2016, 9(1):130-136. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9396.shtmlWANG X K. Measurement of large off-axis convex asphere by systemic stitching testing method[J]. Chinese Optics, 2016, 9(1):130-136.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9396.shtml [5] 郭福东, 唐锋, 卢云君, 等.子孔径拼接干涉的快速调整及测量[J].光学 精密工程, 2017, 25(10):2682-2688. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201710019GUO F D, TANG F, LU Y J, et al.. Rapid adjustment and measurement for subaperture stitching interferometry[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2017, 25(10):2682-2688.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201710019 [6] 于瀛洁, 齐特, 武欣.大尺寸光学元件在位动态干涉拼接测量系统[J].光学 精密工程, 2017, 25(7):1764-1770. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201707009YU Y J, QI T, WU X. On-line dynamic interference stitching measurement system for large optical elements[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2017, 25(7):1764-1770.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201707009 [7] 张磊, 刘东, 师途, 等.光学自由曲面面形检测技术[J].中国光学, 2017, 10(3):283-299. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9523.shtmlZHANG L, LIU D, SHI T, et al.. Optical free-form surfaces testing technologies[J]. Chinese Optics, 2017, 10(3):283-299.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9523.shtml [8] GECKELER R D, ARTEMIEV N A, BARBER S K, et al.. Aperture alignment in autocollimator-based deflectometric profilometers[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2016, 87(5):051906. doi: 10.1063/1.4950734 [9] SIEWERT F, ZESCHKE T, ARNOLD T, et al.. Linear chirped slope profile for spatial calibration in slope measuring deflectometry[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2016, 87(5):051907. doi: 10.1063/1.4950737 [10] QIAN J, SULLIVAN J, ERDMANN M, et al.. Performance of the APS optical slope measuring system[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A:Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2013, 710:48-51. [11] QIAN SH N, GECKELER R D, JUST A, et al.. Approaching sub-50 nanoradian measurements by reducing the saw-tooth deviation of the autocollimator in the Nano-Optic-Measuring Machine[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A:Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2015, 785:206-212. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=310dabb1d03d9d36f183d4aaad684b52 [12] ALCOCK S G, NISTEA L, SAWHNEY K. Nano-metrology:the art of measuring X-ray mirrors with slope errors < 100 nrad[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2016, 87(5):051902. doi: 10.1063/1.4949272 [13] MALLIK P C V, ZHAO CH Y, BURGE J H. Measurement of a 2-meter flat using a pentaprism scanning system[J]. Optical Engineering, 2007, 46(2):023602. doi: 10.1117/1.2700386 [14] YELLOWHAIR J, BURGE J H. Analysis of a scanning pentaprism system for measurements of large flat mirrors[J]. Applied Optics, 2007, 46(35):8466-8474. doi: 10.1364/AO.46.008466 [15] QI E H, HU H X, HU H F, et al.. The application of pentaprism scanning technology on the manufacturing of M3MP[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9682:96821A. [16] 袁理, 张晓辉, 韩冰, 等.五棱镜转动时出射光角度的变化[J].中国光学, 2015, 8(6):1035-1043. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9358.shtmlYUAN L, ZHANG X H, HAN B, et al.. Changes of output light's angles with pentaprism rotation[J]. Chinese Optics, 2015, 8(6):1035-1043.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9358.shtml [17] 朱硕.大口径光学平面镜面形检测技术研究[D].北京: 中国科学院大学, 2014.ZHU SH. Study on technology for large optic flat mirror testing[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014.(in Chinese) [18] GECKELER R D. Optimal use of pentaprisms in highly accurate deflectometric scanning[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2007, 18(1):115-125. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/18/1/014 [19] 费业泰.误差理论与数据处理[M]. 6版.北京:机械工业出版社, 2010.FEI Y T. Error Theory and Data Processing[M]. 6th ed. Beijing:China Machine Press, 2010.(in Chinese) [20] 赖丽萍, 梁德娟, 庄其仁.聚合物光栅生物传感器光信号检测滤波电路[J].光学与光电技术, 2013, 11(1):56-59. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxygdjs201301014LAI L P, LIANG D J, ZHUANG Q R. Filter circuits used for optical signal detection in the polymer grating biosensors[J]. Optics & Optoelectronic Technology, 2013, 11(1):56-59.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxygdjs201301014 [21] 孟浩玉, 王彦, 汪诚伟, 等.基于锁相放大原理的微弱光信号检测系统设计[J].光学与光电技术, 2014, 12(6):88-91. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxygdjs201406021MENG H Y, WANG Y, WANG CH W, et al.. Design of the weak fluorescence signal detection system based on the principle of lock-in amplifier[J]. Optics & Optoelectronic Technology, 2014, 12(6):88-91.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxygdjs201406021 -






 下载:
下载: