Formation of interface defects of ZnO/ZnS core-shell nanowires and its optical properties investigations
-
摘要: ZnO/ZnS核壳纳米结构因具有优异的光电特性,在光电子领域极具应用前景,其依靠核壳结构界面处载流子的束缚效应可更加有效地控制载流子的产生、传输和复合过程。为讨论ZnO/ZnS核壳结构界面状态及其相应的光学特性,生长了不同程度硫粉硫化的ZnO/ZnS核壳纳米线,再利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、透射电子显微镜(TEM)及光致发光光谱(PL)等测试表征手段,分析并讨论经过不同程度硫粉硫化后的ZnO/ZnS核壳纳米线界面处的结构及其光学性质的变化。通过分析ZnO/ZnS核壳结构形貌发现,ZnS成功包覆ZnO纳米线。随着硫化程度的增加,ZnO核结构被破坏,并在核壳界面处引入缺陷,导致形成具有不同结晶质量的ZnO/ZnS核壳纳米线结构,从而会影响ZnO/ZnS核壳纳米线的光学性质。结果表明,ZnO/ZnS核壳界面处缺陷较少时,对载流子的产生和传输具有一定的束缚作用,可以抑制非辐射复合效应,提高材料光学性能;当界面缺陷增加时,形成的缺陷能级则会降低材料的光学性能。Abstract: ZnO/ZnS core-shell nanostructures have great application prospects in optoelectronic area due to their excellent optoelectronic properties. They rely mainly on the binding effect of carriers at the interface of the core-shell structure to more effectively control carrier generation, transmission and recombination processing. In order to discuss the interfacial state of ZnO/ZnS core-shell structure and its corresponding optical properties, ZnO/ZnS core-shell nanowires with different amounts of sulfur powder vulcanization were grown and then characterized using scanning electron microscopy(SEM), transmission electron microscopy(TEM), Photoluminescence spectroscopy(PL). Analysis and discussion were conducted for the structure and optical properties of the ZnO/ZnS core-shell nanowire interface after sulfurization with different amounts of sulfur powder. By analyzing the morphology of the ZnO/ZnS core-shell structure, it was found that ZnS successfully coated ZnO nanowires and with the increase of vulcanization degree, the ZnO core structure was destroyed and defects were introduced at the core-shell interface, resulting in forming ZnO/ZnS core-shell structure with different crystal qualities. The structure affects the optical properties of ZnO/ZnS core-shell nanowires. The results show that when few defects appear at the interface of the ZnO/ZnS core shell, they have a binding effect on the generation and transport of carriers, thus inhibiting the non-radiative composite effect and improving the optical properties of the material. When the interface defects increase, the formed defect energy level reduces the optical properties of the material.
-
Key words:
- core-shell nanostructures /
- localized states /
- interface defects /
- photoluminescence
-
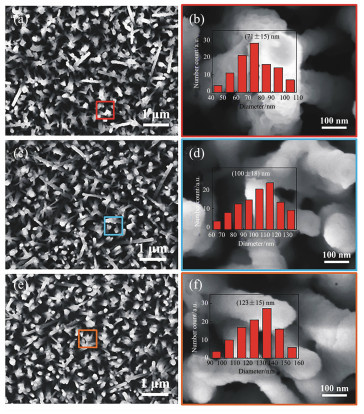
图 3 纯ZnO纳米线(a)及不同剂量硫粉(b)2 mg,(c)5 mg,(d)10 mg硫化的ZnO/ZnS核壳纳米线HRTEM图像,插图为ZnO纳米线和ZnS纳米颗粒的晶格条纹间距
Figure 3. HRTEM images of(a)pure ZnO nanowires and ZnO/ZnS core-shell nanowires with different amounts of sulfur powder (b)2 mg, (c)5 mg, (d)10 mg; inset shows the lattice fringe space of ZnO nanowires and ZnS nanoparticles
图 4 (a) 10 K时ZnO纳米线及不同剂量硫粉硫化的ZnO/ZnS核壳纳米线PL光谱,(b)10 K时UV区域光谱图,(c)ZnO纳米线及经过不同剂量硫粉硫化后10 K时UV区域PL光谱强度及半峰宽,(d)ZnO/ZnS硫化过程球棍模型
Figure 4. (a)PL spectra of ZnO nanowires and ZnO/ZnS core-shell nanowires with different amounts of sulfur powder at 10 K, (b)UV region spectra at 10 K, (c)PL spectral intensities and FWHMs of ZnO nanowires and ZnO/ZnS core-shell nanowires with different amounts of sulfur powder at 10 K, (d)ZnO/ZnS ball model with different sulfurization degrees
-
[1] MA X M, YE H G, DUAN X Y, et al.. Abnormal gas pressure sensitivity of the visible emission in ZnO quantum dots prepared by improved sol-gel method:the role of surface polarity[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(48):29992-29997. doi: 10.1039/C7RA01917C [2] HUAN X, WANG M, WILLINGER M G, et al.. Assembly of three-dimensional hetero-epitaxial ZnO/ZnS core/shell nanorod and single crystalline hollow ZnS nanotube arrays[J]. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(8):7333-7339. doi: 10.1021/nn3024514 [3] 黄海平, 吕连连, 陈重镇, 等.基于多壁碳纳米管-氧化钨纳米复合材料的多巴胺电化学传感器[J].分析化学, 2018, 46(5):765-772. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxhx201805021HUANG H P, LV L L, CHEN ZH ZH, et al.. Electrochemical dopamine sensor based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes-tungsten oxide nanocomposites[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 46(5):765-772.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxhx201805021 [4] CHEN R, YE Q L, HE T CH, et al.. Exciton localization and optical properties improvement in nanocrystal-embedded ZnO core-shell nanowires[J]. Nano Letters, 2013, 13(2):734-739. doi: 10.1021/nl304433m [5] YAN J, FANG X SH, ZHANG L D, et al.. Structure and cathodo luminescence of individual ZnS/ZnO biaxial nanobelt heterostructures[J]. Nano Letters, 2008, 8(9):2794-2799. doi: 10.1021/nl801353c [6] JEONG S, KIM M W, JO Y R, et al.. Crystal-structure-dependent piezotronic and piezo-phototronic effects of ZnO/ZnS core/shell nanowires for enhanced electrical transport and photosensing performance[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(34):28736-28744. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=14df30801a3c78981b77df93b7e7457a [7] 胡明江, 崔秋娜, 虞婷婷, 等.基于氧化锌/聚苯胺复合材料的薄膜型甲醇传感器研究[J].分析化学, 2018, 46(8):1201-1207. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fxhx201808007HU M J, CUI Q N, YU T T, et al.. Research on film-type methanol sensor based on ZnO/polyaniline nanocomposites[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 46(8):1201-1207.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fxhx201808007 [8] FANG X, WEI ZH P, YANG Y H, et al.. Ultraviolet electroluminescence from ZnS@ZnO core-shell nanowires/p-GaN introduced by exciton localization[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(3):1661-1666. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=6144c9beed5f1a60124b2cc6fb307a1e [9] FANG X, WANG X Y, TANG J L, et al.. Synthesis and characterization of ZnO/Ag-doped ZnO core-shell nanowires[J]. Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Letters, 2015, 7(8):643-647. doi: 10.1166/nnl.2015.1976 [10] RAI S C, WANG K, DING Y, et al.. Piezo-phototronic effect enhanced UV/visible photodetector based on fully wide band gap type-Ⅱ ZnO/ZnS core/shell nanowire array[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(6):6419-6427. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b02081 [11] MARANA N L, LAPORTA F A, LONGO E, et al.. Theoretical study on band alignment mechanism for the ZnO/ZnS interface of core/shell structures[J]. Current Physical Chemistry, 2016, 5(4):327-336. doi: 10.2174/187794680504160308170920 [12] WANG K, CHEN J J, ZENG Z M, et al.. Synthesis and photovoltaic effect of vertically aligned ZnO/ZnS core/shell nanowire arrays[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 96(12):123105. doi: 10.1063/1.3367706 [13] GU X Q, ZHANG SH, ZHAO Y L, et al.. Band alignment of ZnO/ZnS heterojunction prepared through magnetron sputtering and measured by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy[J]. Vacuum, 2015, 122:6-11. doi: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2015.09.005 [14] MYONG S Y, BAIK S J, LEE C H, et al.. Extremely transparent and conductive ZnO:Al thin films prepared by photo-assisted metal/organic chemistry vapor deposition(photo-MOCVD) using AlCl3(6H2O) as new doping material[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1997, 36(Part 2, No.8B):L1078-L1081. doi: 10.1143/JJAP.36.L1078 [15] YAN CH L, XUE D F. Conversion of ZnO nanorod arrays into ZnO/ZnS nanocable and ZnS nanotube arrays via an in situ chemistry strategy[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2006, 110(51):25850-25855. doi: 10.1021/jp0659296 [16] SULIEMAN K M, HUANG X T, LIU J P, et al.. One-step growth of ZnO/ZnS core-shell nanowires by thermal evaporation[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2006, 16(1):89. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=540822789c8b9e3f19d31339e25d1448 [17] LI R X, WEI ZH P, ZHAO F H, et al.. Investigation of localized and delocalized excitons in ZnO/ZnS core-shell heterostructured nanowires[J]. Nanophotonics, 2017, 6(5):1093-1100. [18] LI R X, WEI ZH P, FANG X, et al.. Localized-state-dependent electroluminescence from ZnO/ZnS core shell nanowires GaN heterojunction[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2018, 1(4):1641-1647. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.8b00123 [19] FANG X, WEI ZH P, CHEN R, et al.. Influence of exciton localization on the emission and ultraviolet photoresponse of ZnO/ZnS core-shell nanowires[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(19):10331-10336. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=84eac0581090bcbe41cba8d1bf03c404 [20] WANG Y B, FANG X, LI R X, et al.. Surface sulfurization of ZnO/ZnS core shell nanowires and shell layers dependent optical properties[J]. Journal of Materials Science:Materials in Electronics, 2018, 29(9):7924-7929. doi: 10.1007/s10854-018-8792-y [21] FANG X, LI J H, ZHAO D X, et al.. Phosphorus-doped p-type ZnO nanorods and ZnO nanorod p-n homojunction LED fabricated by hydrothermal method[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2009, 113(50):21208-21212. doi: 10.1021/jp906175x [22] DLOCZIK L, ENGELHARDT R, ERNST K, et al.. Hexagonal nanotubes of ZnS by chemical conversion of monocrystalline ZnO columns[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2001, 78(23):3687-3689. doi: 10.1063/1.1376427 [23] SHUAI X M, SHEN W Z. A facile chemical conversion synthesis of ZnO/ZnS core/shell nanorods and diverse metal sulfide nanotubes[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(14):6415-6422. doi: 10.1021/jp2005716 [24] TARISH S, WANG ZH J, Al-HADDAD A, et al.. Synchronous formation of ZnO/ZnS core/shell nanotube arrays with removal of template for meliorating photoelectronic performance[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119(3):1575-1582. doi: 10.1021/jp510835n [25] ZHAO X, FENG J, LIU J, et al.. Metal-organic framework-derived ZnO/ZnS heteronano structures of efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen production[J]. Advanced Science, 2018, 5(4):1700590. doi: 10.1002/advs.201700590 [26] 王泽岚, 周艳芬, 孟哲, 等.核壳聚苯胺选择性磁性固相萃取-高效液相色谱-质谱法测定牛奶中痕量磺胺类药物[J].分析化学, 2019, 47(1):119-128. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxhx201901016WANG Z L, ZHOU Y F, MENG ZH, et al.. Determination of trace sulfonamides antibiotics in milk using polyaniline silicon magnetic composite selective magnetic solid phase extraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(1):119-128.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxhx201901016 [27] 翟英娇, 李金华, 陈新影, 等.镉掺杂氧化锌纳米花的制备及其光催化活性[J].中国光学, 2014, 7(1):124-130. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9105.shtmlZHAI Y J, LI J H, CHEN X Y, et al.. Synthesis and characterization of Cd-doped ZnO nanoflowers and its photocatalytic activity[J]. Chinese Optics, 2014, 7(1):124-130.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9105.shtml [28] CHEN Y N, XU S J, ZHENG C C, et al.. Nature of red luminescence band in research-grade ZnO single crystals:a "self-activated" configurational transition[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 105(4):041912. doi: 10.1063/1.4892356 [29] HU Y, QIAN H H, LIU Y, et al.. A microwave-assisted rapid route to synthesize ZnO/ZnS core-shell nanostructures via controllable surface sulfidation of ZnO nanorods[J]. CrystEngComm, 2011, 13(10):3438-3443. doi: 10.1039/c1ce05111c [30] 冯仕, 李金钗, 冯秀丽.ZnO/ZnS核-壳纳米杆的制备及其光学性质[J].武汉大学学报(理学版), 2009, 55(5):535-538. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-8836.2009.05.008FENG SH, LI J CH, FENG X L. Preparation of ZnO/ZnS core-shell nanorods and its optical properties[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2009, 55(5):535-538.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-8836.2009.05.008 -






 下载:
下载: