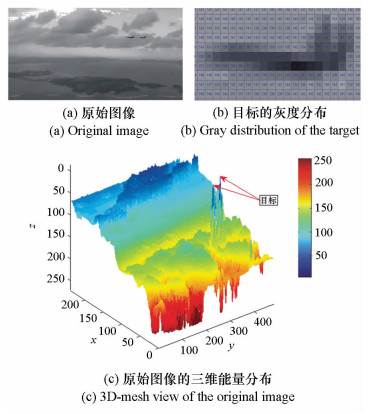
-
摘要: 为了在复杂天空背景下检测出低空慢速小目标,本文研究了“低小慢”目标的视觉显著性区域特征,融合扫描线填充算法,提出了一种动态背景下“低小慢”目标自适应实时检测技术。首先,根据图像的亮度对比度获取显著性图。接着,使用形态学梯度提取显著性特征,通过三帧差分算法得到种子点。然后,使用扫描线填充算法进行生长,结合提出的自适应双高斯算法分割出前景。最后,根据候选目标的面积占比变化、质心距离变化、宽高比差异剔除虚假目标,完成检测。为了验证算法的有效性,本文选取了7组复杂天空背景的视频序列进行测试,并与其他优秀检测算法进行了对比。结果表明,本文提出的算法对运动目标检测的平均运行时间为0.040 9 s,平均检测准确率为89.97%,相比于其他算法的平均运算时间减少了0.35 s,检测的平均准确率提高了24.5%。算法在复杂背景下具有较好的稳定性和较强的鲁棒性。Abstract: In order to detect LSS(Low, Small and Slow) targets in complex sky backgrounds, we study the visual salient region characteristics of the LSS target and scan line filling algorithm and propose an adaptive real-time detection technology for LSS targets in dynamic complex backgrounds. Firstly, a saliency map is obtained based on the Luminance Contrast(LC) of the image. Secondly, the morphological gradient is used to extract the saliency feature and the seed points of the scan line filling algorithm are obtained by the three frame difference algorithm. Then, the scan line filling algorithm is used to grow the image and the foreground is segmented using the proposed adaptive double Gauss threshold segmentation algorithm. Finally, according to the change of the object's area of occupation, the center distance and the aspect ratio of the candidate target, the false targets are eliminated and detection is completed. In order to verify the effectiveness of the algorithm, 7 test groups of complex sky background video sequences are selected and compared with other excellent detection algorithms. The results show that the running time of the proposed algorithm for moving object detection is 0.040 9 s and the accuracy rate is 89.97%. When compared with other algorithms, the average running time is reduced by 0.35 s, and the average accuracy of detection is enhanced by 24.5%. The algorithm has good stability and is robust in target detection in complex backgrounds.
-
Key words:
- computer vision /
- visual saliency /
- scan line filling /
- curve fitting /
- adaptive threshold segmentation
-
表 1 剔除虚警流程
Table 1. Eliminating false alarm process
input:候选目标集合R output:目标集合T 1.ti={ri}, T={ϕ} Δ初始化 2. For i=1, ri∈R 3. if 
4. 
Δ更新目标集合 5. else 6. Texist=T Δ剔除虚警 7. End for 表 2 实验中的测试视频
Table 2. Test sequences in our experiments
视频 帧数 SCR Video 1 76 <1 Video 2 69 1~1.5 Video 3 249 1.5~2 Video 4 90 2~3 Video 5 22 >3 Video 6 64 >3 Video 7 101 >3 表 3 检测准确率Pd及虚警率Pfa
Table 3. Detection accuracy and false alarm rate (%)
视频 准确率 虚警率 Vibe PBAS Ours Vibe PBAS Ours Video 1 26.3 65. 8 81.6 77.2 35.8 5.1 Video 2 30.4 72.5 87.0 82.4 76.5 4.6 Video 3 32.1 80.3 84.3 65.3 11.2 0.9 Video 4 23.3 80 87.8 86.5 3.5 0.3 Video 5 45. 5 90.9 100 40.7 4.6 0 Video 6 62.5 78.1 100 33.5 4.8 0 Video 7 59.4 84.2 89.1 20.9 6.5 6.2 表 4 算法的时间复杂度
Table 4. Average time consumption and total time consumption of the proposed algorithm
视频 帧数 平均耗时(s/frame) 总耗时/s Vibe PBAS Ours Vibe PBAS Ours Video 1 76 0.362 0.396 0.042 27.512 30.096 3.05 Video 2 69 0.346 0.389 0.048 24.081 26.841 3.31 Video 3 249 0.372 0.412 0.047 96.682 102.588 11.61 Video 4 90 0.329 0.386 0.046 29.61 34.74 4.102 Video 5 22 0.349 0.391 0.045 7.678 8.602 0.988 Video 6 64 0.354 0.397 0.043 22.656 25.408 2.764 Video 7 101 0.371 0.403 0.047 37.471 40.703 4.770 -
[1] HU J, YU Y, LIU F. Small and dim target detection by background estimation[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2015, 73:141-148. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jgyhw201710023 [2] YANG W P, LU X P, LI J CH, et al.. Fast algorithm of infrared small target detection in jitter background[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2015, 9476:947614. [3] DENG H, LIU J G, CHEN ZH. Infrared small target detection based on modified local entropy and EMD[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2010, 8(1):24-28. doi: 10.3788/COL20100801.0024 [4] KIM S, YANG Y, LEE J, et al.. Robust scale invariant small target detection using the Laplacian scale-space theory[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 6969:696911. doi: 10.1117/12.786354 [5] 姜志国, 韩冬兵, 袁天云, 等.基于全自动控制显微镜的自动聚焦算法研究[J].中国图象图形学报, 2004, 9(4):396-401. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8961.2004.04.003JIANG ZH G, HAN D B, YUAN T Y, et al.. Study on auto focusing algorithm for automatic microscope[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2004, 9(4):396-401.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8961.2004.04.003 [6] ABDELKAWY E, MCGAUGHY D. Small infrared target detection using two-dimensional fast orthogonal search(2D-FOS)[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 5094:179-185. doi: 10.1117/12.487378 [7] 解婷, 陈忠, 马荣毅.一种基于PGF、BEMD和局部逆熵的新型红外小目标检测方法[J].红外与毫米波学报, 2017, 36(1):92-101. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyhmb201701017XIE T, CHEN ZH, MA R Y. A novel method for infrared small target detection based on PGF, BEMD and LIE[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2017, 36(1):92-101.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyhmb201701017 [8] BAI X ZH, ZHOU F G. Analysis of new top-hat transformation and the application for infrared dim small target detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2010, 43(6):2145-2156. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2009.12.023 [9] WANG P, TIAN J W, GAO CH Q. Infrared small target detection using directional highpass filters based on LS-SVM[J]. Electronics Letters, 2009, 45(3):156-158. doi: 10.1049/el:20092206 [10] REED I S, GAGLIARDI R M, STOTTS L B. Optical moving target detection with 3-D matched filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2002, 24(4):327-336. [11] GUARIGLIA E. Entropy and fractal antennas[J]. Entropy, 2016, 18(3):84. doi: 10.3390/e18030084 [12] SHEN X M, DENG L. Game theory approach to discrete H∞filter design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1997, 45(4):1092-1095. doi: 10.1109/78.564201 [13] 刘伟宁.基于小波域扩散滤波的弱小目标检测[J].中国光学, 2011, 4(5):503-508. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1531.2011.05.015LIU W N. Dim target detection based on wavelet field diffusion filter[J]. Chinese Optics, 2011, 4(5):503-508.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1531.2011.05.015 [14] 刘希佳, 陈宇, 王文生, 等.小目标识别的小波阈值去噪方法[J].中国光学, 2012, 5(3):248-256. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1531.2012.03.009LIU X J, CHEN Y, WANG W SH, et al.. Denoising algorithm of wavelet threshold for small target detection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2012, 5(3):248-256.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1531.2012.03.009 [15] CASELLES V, KIMMEL R, SAPIRO G. Geodesic active contours[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1997, 22(1):61-79. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjyjyfz200302024 [16] LIU ZH J, CHEN CH Y, SHEN X B, et al.. Detection of small objects in image data based on the nonlinear principal component analysis neural network[J]. Optical Engineering, 2005, 44(9):9093604. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d66c10351f8cf89b2fb5386e8beca31f [17] 郭文佳, 朱晓辉, 王向军.野外图像监测中地平线附近的弱小目标的实时检测[C].光电技术与系统文选——中国光学学会光电技术专业委员会成立二十周年暨第十一届全国光电技术与系统学术会议论文集, 中国光学学会, 2005.GUO W J, ZHU X H, WANG X J. Real-time detection of weak and small targets near the horizon in field image monitoring[C]. Optoelectronic Technology of China Institute of Optics and Optoelectronic Technology Specialized Committee Establishment 20th Anniversary and National Photoelectric Technology And System Academic Conference, Chinese Optical Society, 2005.(in Chinese) [18] 胡谋法, 王书宏, 李超, 等.空时域联合去相关检测可见光背景下的运动小目标[C].光电技术与系统文选——中国光学学会光电技术专业委员会成立二十周年暨第十一届全国光电技术与系统学术会议论文集, 中国光学学会, 2005.HU M F, WANG SH H, LI CH, et al.. Detection of small moving targets in the visible light background by the joint spatio-temporal correlation detection[C]. Optoelectronic Technology of China Institute of Optics and Optoelectronic Technology Specialized Committee Establishment 20th Anniversary and National Photoelectric Technology and System Academic Conference, Chinese Optical Society, 2005.(in Chinese) [19] 洪普, 王群, 阮建斌, 等.复杂背景红外弱点目标检测[C].中国光学学会2010年光学大会论文集, 中国光学学会, 2010.HONG P, WANG Q, RUAN J B, et al.. Infrared weak target detection in complex background[C]. A Collection of the 2010 Optical Conference of the Chinese Academy of Optics, hinese Optical Society, 2010.(in Chinese) [20] 姚成乾, 陈伟.基于改进粒子算法的红外弱小目标检测研究[J].激光与光电子学进展, 2017, 54(11):111101. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jgygdzxjz201711017YAO CH Q, CHEN W. Infrared dim target detection based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2017, 54(11):111101.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jgygdzxjz201711017 [21] 刘靳, 姬红兵.基于移动式加权管道滤波的红外弱小目标检测[J].西安电子科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 34(5):743-747. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2007.05.013LIU J, JI H B. Detection method for small targets in the IR image based on the variable weighted pipeline filter[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2007, 34(5):743-747.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2007.05.013 [22] 黄宇, 张晓芳, 俞信.光子成像静止点目标的管道滤波探测方法[J].中国光学, 2013, 6(1):73-79. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8893.shtmlHUANG Y, ZHANG X F, YU X. Pipeline filtering detection of stationary point targets in photon images[J]. Chinese Optics, 2013, 6(1):73-79.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8893.shtml [23] NIE H SH, HUANG ZH J, DIAO J T, et al.. A wiener filter based infrared small target detecting and tracking method[C]. Proceedings of 2010 International Conference on Intelligent System Design and Engineering Application, IEEE, 2010: 184-187. [24] ZHAI Y, SHAH M. Visual attention detection in video sequences using spatiotemporal cues[C]. Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, ACM, 2006: 815-824. [25] 王晓阳, 彭真明, 张萍, 等.局部对比度结合区域显著性红外弱小目标检测[J].强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27(9):32-38. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qjgylzs201509006WANG X Y, PENG ZH M, ZHANG P, et al.. Infrared small dim target detection based on local contrast combined with region saliency[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27(9):32-38.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qjgylzs201509006 [26] 毋亚北, 王卫华, 吴巨红, 等.基于形态学梯度的红外目标检测[J].光电工程, 2012, 39(9):81-85. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gdgc201209015WU Y B, WANG W H, WU J H, et al..IR target detection based on morphological gradient[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2012, 39(9):81-85.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gdgc201209015 [27] ZHANG Y Z, WANG X Y, QU B. Three-frame difference algorithm research based on mathematical morphology[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2012, 29:2705-2709. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2012.01.376 [28] GONZALEZ R C, WOODS R E. Digital Image Processing[M]. RUAN Q Q, RUAN Y ZH, trans. 2nd ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2007. [29] 肖丽君, 于哲舟, 周栩, 等.基于对称差分算法的视频运动目标分割[J].吉林大学学报(理学版), 2008, 46(4):691-696. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-5489.2008.04.025XIAO L J, YU ZH ZH, ZHOU X, et al.. Moving object segmentation based on symmetrical differencing algorithm in video sequences[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Science Edition), 2008, 46(4):691-696.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-5489.2008.04.025 [30] 范宏深, 倪国强, 冯煜芳.复杂背景可见光图像中弱小目标探测的新算法[J].光电工程, 2004, 31(6):48-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2004.06.014FAN H SH, NI G Q, FENG Y F. A new algorithm for small and dim target detection of visible image under heavy clutters[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2004, 31(6):48-51.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2004.06.014 [31] WU Y F, SUN H J, LIU P X. A novel fast detection method of infrared LSS-target in complex urban background[J]. International Journal of Wavelets, Multiresolution and Information Processing, 2018, 16(1):1850008. doi: 10.1142/S021969131850008X [32] BARNICH O, VAN DROOGENBROECK M. ViBE: A powerful random technique to estimate the background in video sequences[C]. Proceedings of 2009 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, IEEE, 2009: 945-948. [33] HOFMANN M, TIEFENBACHER P, RIGOLL G. Background segmentation with feedback: the pixel-based adaptive segmenter[C]. Proceedings of 2012 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, IEEE, 2012: 38-43. [34] 王敏敏, 孙胜利.并行压缩成像系统的压缩域小目标检测[J].光学 精密工程, 2016, 34(10):2549-2556. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201610025WANG M M, SUN SH L. Small target detection in compressed domain of parallel compression imaging system[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2016, 34(10):2549-2556.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201610025 [35] 李正周, 曹雷, 邵万兴, 等.基于空时混沌分析的海面小弱目标检测[J].光学 精密工程, 2018, 26(1):193-199. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201801023LI ZH ZH, CAO L, SHAO W X, et al.. Detection of small and weak targets in sea surface based on spatio temporal chaos analysis[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2018, 26(1):193-199.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201801023 -






 下载:
下载: