Calculation and measurement of infrared atmospheric transmittance at different altitudes
-
摘要: 为了得到不同海拔地区的大气透过率,探索大气透过率随海拔高度的变化规律,利用数值模拟、软件计算和实地测量方法分别对阿里(5 km)、德令哈(3 km)和怀柔(0 km)3个不同海拔地区在4.605~4.755 μm波段25 km以下的大气透过率进行了计算和测量。结果表明:红外大气透过率随海拔高度增加而增加;采用数值模拟计算得到3个地方的大气透过率分别为0.709、0.572和0.555;采用软件计算得到的透过率分别为0.849、0.766和0.596;采用实测方法得到的透过率分别为0.805、0.766和0.673;阿里地区海拔较高,相对湿度较低,能见度高,大气透过率最好。该结论对国内天文红外观测及空间红外目标辐射特性测量具有重要的借鉴意义。Abstract: In order to obtain atmospheric transmittance and study its variation with different altitudes, using methods of mathematical models, software simulations, and actual measurement, we calculate and measure the atmospheric transmittance in the range of 4.605~4.755 μm wavelengths at Ali(5 km), Delingha(3 km) and Huairou(0 km), three different altitudes below 25 km. Results indicate that the infrared atmospheric transmittance increases with altitude. With mathematical model the calculated atmospheric transmittances are 0.709, 0.572 and 0.555, respectively. With software simulations the calculated atmospheric transmittances are 0.849, 0.766 and 0.596, respectively. With actual measurement the obtained atmospheric transmittances are 0.805, 0.766 and 0.673. Due to higher altitude, lower relative humidity, high visibility, the atmospheric transmittance at Ali is the highest one. This conclusion has important reference significance for domestic astronomical infrared observation and spatial infrared target radiation characteristics measurement.
-
表 1 海平面水汽含量与平均大气透过率的关系(4.6~4.8 μm处)[11]
Table 1. The relationship between the water vapor content in the sea level and the average atmosphere transmittance(from 4.6~4.8 μm)[11]
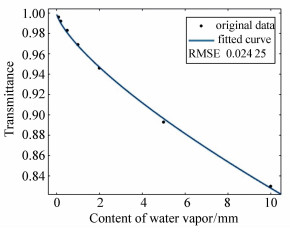
λ/μm Water vapor content/mm 0.1 0.2 0.5 1.0 2.0 5.0 10.0 4.6 0.996 0.992 0.983 0.969 0.946 0.893 0.830 4.7 0.992 0.985 0.970 0.949 0.916 0.845 0.760 4.8 0.975 0.959 0.926 0.889 0.837 0.733 0.621 表 2 海平面二氧化碳含量与大气平均透过率的关系(4.6~4.8 μm处)[14]
Table 2. The relationship between the content of Carbon dioxide in the sea level and the average atmosphere transmittance(from 4.6~4.8 μm)[14]
λ/nm Path length/km 0.1 0.2 0.5 1.0 2.0 5.0 10.0 20.0 50.0 4.6 1 1 0.999 0.998 0.996 0.991 0.982 0.969 0.939 4.7 1 0.999 0.996 0.991 0.982 0.955 0.917 0.855 0.719 4.8 0.990 0.981 0.956 0.920 0.865 0.754 0.634 0.486 0.261 表 3 3个地区大气透过率数值模拟计算结果
Table 3. Calculation results of atmospheric transmittance in three regions with mathematical models
地点 波长/μm τH2O τCO2 τSC τ τav Ali 4.6 0.872 0.982 0.9998 0.857 4.7 0.743 0.913 0.9998 0.678 0.709 4.8 0.291 0.028 0.9998 0.008 Delingha 4.6 0.770 0.978 0.9985 0.752 4.7 0.582 0.894 0.9985 0.519 0.572 4.8 0.128 0.016 0.9985 0.002 Huairou 4.6 0.804 0.966 0.953 0.740 4.7 0.625 0.839 0.953 0.500 0.555 4.8 0.148 0.003 0.953 0.0005 表 4 3个地方大气透过率结果对照表
Table 4. Comparison of atmospheric transmittance results in three regions
mathematical model software simulation actual measurement Ali 0.709 0.849 0.805 Delingha 0.572 0.766 0.766 Huairou 0.555 0.596 0.673 -
[1] 路远, 凌永顺.红外辐射大气透射比的简易计算[J].红外技术, 2003, 25(5):45-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8891.2003.05.012LU Y, LING Y SH. The simple method to calculate the atmospheric transmittance of infrared radiation[J]. Infrared Technology, 2003, 25(5):45-49.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8891.2003.05.012 [2] 宋腾飞, 刘顺庆, 张雪飞.利用日晕光度计反演大气水汽含量[J].气象科技, 2013, 41(1):46-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2013.01.009SONG T F, LIU SH Q, ZHANG X F. Measurement of total precipitable water in atmosphere with sky brightness monitor[J]. Meteorological Science and Technology, 2013, 41(1):46-50.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2013.01.009 [3] 魏合理, 陈秀红, 饶瑞中.通用大气辐射传输软件(CART)介绍[J].大气与环境光学学报, 2007, 2(6):446-450. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6141.2007.06.006WEI H L, CHEN X H, RAO R ZH. Introduction to the combined atmospheric radiative transfer software CART[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2007, 2(6):446-450.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6141.2007.06.006 [4] WALDEN V P, TOWN M S, HALTER B, et al.. First measurements of the infrared sky brightness at dome C, antarctica[J]. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 2005, 117(829):300-308. doi: 10.1086/427988 [5] 王浩, 何枫, 靖旭, 等.昼夜观测恒星整层大气透过率测量研究[EB/OL].(2018-10-30)[2018.11.20] http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/12.1261.TN.20181029.0846.014.html.WANG H, HE F, JING X, et al.. Study on measurement of total atmospheric transmittance in daytime and night observation stars[EB/OL].(2018-10-30)[2018.11.20].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/12.1261.TN.20181029.0846.014.html.(in Chinese) [6] BHATTACHARYYA J C, SCARIAKK, SINGH J, et al. Atmospheric extinction measurements at Leh in near infrared bands[J]. Bulletin of the Astronomical Society of India, 1990, 18(18):1-6. [7] LIOUKN, BOHRENC. An introduction to atmospheric radiation[J]. Physics Today, 1981, 34(7):66-67. doi: 10.1063/1.2914664 [8] 赵志军, 许方宇, 魏超群, 等.红外整层大气透过率测量方法研究[J].红外技术, 2018, 40(7):718-722. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwjs201807017ZHAO ZH J, XU F Y, WEI CH Q, et al.. Study on measurement method for total infrared atmospheric transmittance[J]. Infrared Technology, 2018, 4(7):718-722.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwjs201807017 [9] 陈双远, 许方宇, 王飞翔, 等.中红外大气背景辐射测量设备及误差分析[J].光学学报, 2019, 39(3):0301001.CHEN SH Y, XU F Y, WANG F X, et al.. Measurement equipment and error analysis of mid-infrared atmospheric background radiation[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(3).(in Chinese) [10] 康大勇, 成斌, 高俊光.地空红外探测距离推算方法探讨[J].光电技术应用, 2009, 24(1):29-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1255.2009.01.008KANG D Y, CHENG B, GAO J G. Differentiation algorithm method of ground-air infrared detection range[J]. Electro-Optic Technology Appliction, 2009, 24(1):29-32.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1255.2009.01.008 [11] 刘林华, 董士奎, 余其铮, 等.红外1~14μm波长间隔0.1μm上大气平均透过率(Ⅱ)水蒸汽的透过率[J].哈尔滨工业大学学报, 1999, 31(6):75-78.LIU L H, DONG SH K, YU Q ZH, et al.Atmospheric mean transmittance in wavelength interval 0.1μm from infrared 1 to 14μm, (Ⅱ) transmittance of water vapor[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 1999, 31(6):75-78. (in Chinese) [12] ZHANG Y C, CHEN Y M, FU X B, et al.. The research on the effect of atmospheric transmittance for the measuring accuracy of infrared thermal imager[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2016, 77:375-381.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=76ccaf8ddb2ba7c78451c29152e5cbf4 [13] 张建奇, 方小平.红外物理[M].西安:西安电子科技大学出版社, 2007.ZHANG J Q, FANG X P. Infrared Physics[M]. Xian:Xidian University Press, 2007.(in Chinese) [14] 刘林华, 董士奎, 余其铮, 等.红外1~14μm波长间隔0.1μm上大气平均透过率(Ⅰ)二氧化碳的透过率[J].哈尔滨工业大学学报, 1998, 30(5):8-12.LIU L H, DONG SH K, YU Q ZH, et al.. Atmospheric mean transmittance in wavelength interval 0.1μm from infrared 1 to 14μm, (Ⅰ) transmittance of carbon dioxide[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 1998, 30(5):8-12.(in Chinese) [15] 赵志军, 许方宇, 高玲, 等.3~5μm红外天空亮度测量的多元定标模型[J].红外与激光工程, 2017, 46(10):1004004. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc201710038ZHAO ZH J, XU F Y, GAO L, et al.. Multivariate calibration model for measurement of 3-5μm infrared sky brightness[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46(10):1004004.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc201710038 [16] 赵志军, 许方宇, 徐世春, 等.大气红外辐射及消光特性实测研究[J].光学学报, 2018, 38(4):0401004-4-5. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201804004ZHAO ZH J, XU F Y, XU SH CH, et al.. Measurement of atmospheric infrared radiance and extinction characteristics[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(4):0401004-4-5.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201804004 -






 下载:
下载: