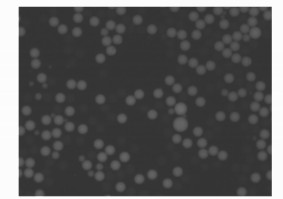
Recognition of dense fluorescent droplets using an improved watershed segmentation algorithm
-
摘要: 基于数字微滴图像检测法的数字聚合酶链式反应(PCR)在检测时获取的荧光微滴图像呈密集分布、具有低亮度、低对比度等特点,导致其识别正确率较低。为了实现对密集分布的荧光微滴的正确识别,本文提出一种基于改进的分水岭分割算法的荧光微滴识别方法,首先利用直方图均衡化和高斯滤波对图像进行预处理,然后使用局部自适应阈值分割从背景中提取目标,降低对图像灰度信息的依赖,最后结合微滴形状类圆、尺寸较均匀的特点定义微滴黏连度函数,降低了分水岭分割中的错误分割比例。对比实验表明,与传统的基于距离变换分水岭分割法相比较,本文算法的正确率为97.34%,高于对照方法的85.9%,验证了本文算法的优越性。Abstract: Fluorescent droplet images acquired during droplet digital Polymerase Chain Reaction(PCR) detection have dense distribution, low brightness and low contrast, resulting in poor recognition accuracy. In order to correctly identify densely distributed fluorescent droplets, a fluorescent droplet recognition method based on an improved watershed segmentation algorithm is proposed. First, the image is preprocessed using histogram equalization and Gauss filtering, then the local adaptive threshold segmentation method is used to extract the targets from the background, thereby reducing the dependence on image gray level information. Finally, the algorithm combines the prior knowledge of the droplets with a circular and uniform size to define the droplet adhesion function, which reduces the error rate in the watershed segmentation. The experiment results show that compared with the traditional distance-based watershed segmentation method, the accuracy of the proposed algorithm is 97.34%, which is higher than the 85.9% accuracy of its counterpart.
-
表 1 微滴分割算法性能对照
Table 1. Performance comparison of different droplet segmentation methods
方法 阳性欠分割率/% 阳性过分割率/% 阴性欠分割率/% 阴性过分割率/% 平均正确率/% 本文方法 0.24 0.62 5.32 0 97.34 对照方法 0.81 0.20 21.59 1.06 85.90 -
[1] VOGELSTEIN B, KINZLER K W. Digital PCR[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1999, 96(16):9236-9241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.16.9236 [2] 彭年才.数字PCR:原理、技术及应用[M].北京:科学出版社, 2017.PENG N C. Digital PCR:Theory, Technology & Application[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 2017.(in Chinese) [3] SOLIMAN K. Cell Profiler:novel automated image segmentation procedure for super-resolution microscopy[J]. Biological Procedures Online, 2015, 17:11. doi: 10.1186/s12575-015-0023-9 [4] CLARKE M L, BURTON R L, HILL A N, et al.. Low-cost, high-throughput, automated counting of bacterial colonies[J]. Cytometry, 2010, 77A(8):790-797. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.20864 [5] GEISSMANN Q. Open CFU, a new free and open-source software to count cell colonies and other circular objects[J]. PLoSOne, 2013, 8(2):e54072. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054072 [6] CHOUDHRY P. High-throughput method for automated colony and cell counting by digital image analysis based on edge detection[J]. PLoSOne, 2016, 11(2):e0148469. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148469 [7] 王浩, 张叶, 沈宏海, 等.图像增强算法综述[J].中国光学, 2017, 10(4):438-448. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9522.shtmlWANG H, ZHANG Y, SHEN H H, et al.. Review of image enhancement algorithms[J]. Chinese Optics, 2017, 10(4):438-448.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9522.shtml [8] 但唐仁, 田景全, 高延军, 等.低强度X射线影像系统的噪声分析及图像去噪处理[J].发光学报, 2002, 23(6):615-618. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7032.2002.06.017DAN T R, TIAN J Q, GAO Y J, et al.. Imaging filter and noise analyse based on low intense X-ray image system[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2002, 23(6):615-618.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7032.2002.06.017 [9] 杨名宇, 李刚.利用区域信息的航拍图像分割[J].中国光学, 2014, 7(5):779-785. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9170.shtmlYANG M Y, LI G. Aerial image segmentation with region information[J]. Chinese Optics, 2014, 7(5):779-785.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9170.shtml [10] 张永梅, 巴德凯, 邢阔.基于模糊阈值的自适应图像分割方法[J].计算机测量与控制, 2016, 24(4):126-128, 136. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjzdclykz201604038ZHANG Y M, BA D K, XING K. A method of fuzzy threshold for adaptive image segmentation[J]. Computer Measurement & Control, 2016, 24(4):126-128, 136.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjzdclykz201604038 [11] BRESSON X, ESEDOGLU S, VANDERGHEYNST P, et al.. Fast global minimization of the active contour/snake model[J]. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 2007, 28(2):151-167. doi: 10.1007/s10851-007-0002-0 [12] VINCENT L, SOILLE P. Watersheds in digital spaces:an efficient algorithm based on immersion simulations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1991, 13(6):583-598. doi: 10.1109/34.87344 [13] SOILLE P. Morphological image analysis applied to crop field mapping[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2000, 18(13):1025-1032. doi: 10.1016/S0262-8856(00)00043-3 [14] 刘聪, 董文飞, 张涛, 等.微滴式数字PCR中低浓度荧光微滴分类[J].光学 精密工程, 2018, 26(3):647-653. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201803017LIU C, DONG W F, ZHANG T, et al.. Identification of florescent droplets at low concentrations for droplet digital PCR[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2018, 26(3):647-653.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201803017 [15] 游迎荣, 范影乐, 庞全.基于距离变换的粘连细胞分割方法[J].计算机工程与应用, 2005, 41(20):206-208. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2005.20.061YOU Y R, FAN Y L, PANG Q. Separate algorithm for overlapping cell images based on distance transformation[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2005, 41(20):206-208.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2005.20.061 -






 下载:
下载: