Internal profile reconstruction of microstructures based on near-infrared light transmission reflection interferometry with optical path compensation
doi: 10.3788/CO.20191202.0395
-
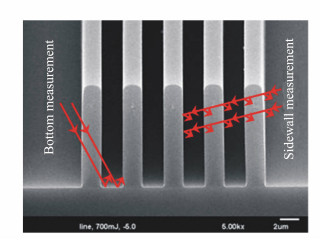
摘要: 高深宽比微结构的底部及侧壁形貌重构是微机电系统领域亟待解决的一个问题。本文提出光程补偿近红外光透射反射干涉技术重构微结构内部形貌的方法,所采用的近红外光干涉技术将白光干涉系统中的光源扩展至近红外光源,将反射干涉技术扩展至透射反射干涉技术,近红外光干涉测量系统由近红外光光源、干涉显微镜、红外光CCD、高精度压电陶瓷和数据采集系统组成。设计了具有两个台阶的GaAs半导体微结构待测样品,采用近红外光垂直扫描干涉法并通过光程补偿,重构了微结构的内部三维形貌,并与扫描电镜结果进行对比。光程补偿近红外光透射反射干涉技术测量的台阶相对高度分别为2.132 μm和0.766 μm,与扫描电镜和近红外光反射干涉测量结果基本一致,分别对应2.16%和2.68%的相对误差。测量结果表明,该测量系统能够测量高深宽比微结构底部及侧壁形貌。
-
关键词:
- 近红外光透射反射干涉 /
- 微结构 /
- 重构内部形貌
Abstract: The bottom and sidewall profile reconstruction of microstructures with a high aspect ratio is a problem that urgently needs to be solved in the field of MEMS(Micro-Electro-Mechanical system). Microstructures profile reconstruction method is presented based on near-infrared light transmission reflection interferometry with optical path compensation(OPC), which is extended from white light to near-infrared light and from reflection interference to transmission interference. The near-infrared light transmission interferometry system is composed of a near-infrared light source, an interference microscope, an infrared light CCD, piezoelectric ceramics with high accuracy and a data acquisition system. A GaAs sample microstructure with two steps was designed and the method of vertical scanning interference of near-infrared light with OPC was adopted to reconstruct the internal profile of a microstructure, which was then compared with the results of scanning electron microscopy(SEM). Test results show that the relative heights of the measured microstructure steps using near-infrared light transmission reflection interferometry were 2.132 μm and 0.766 μm with 2.16% and 2.68% relative errors, respectively, which agree with the results of SEM and that of the near-infrared light reflection interferometer. The measurement system has the ability to reconstruct the bottom and sidewall profile of microstructures with a high aspect ratio. -
表 1 Comparison of relative step heights for different measurement methods
Table 1. Comparison of relative step heights for different measurement methods
Measurement method Step A/μm Error/% Step B/μm Error/% SEM 2.087 0.746 Near-infrared light reflection interference 2.107 0.96 0.759 1.74 Near-infrared transmission interference 2.132 2.16 0.766 2.68 -
[1] TOTSU K, FUJISHIRO K, TANAKA S, et al.. Fabrication of three-dimensional microstructure using maskless gray-scale lithography[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2006, 130-131:387-392. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2005.12.008 [2] ZHANG T, GAO F, JIANG X Q. Surface topography acquisition method for double-sided near-right-angle structured surfaces based on dual-probe wavelength scanning interferometry[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(20):24148-24156. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.024148 [3] HOU P X, LIU C, CHENG H M. Field Emission from Carbon Nanotubes[M]. Nanomaterials Handbook. 2nd Ed. CRC Press, 2017: 255-272. [4] MORITA S, GIESSIBL F J, MEYER E, et al.. Noncontact Atomic Force Microscopy[M]. Berlin:Springer, 2015. [5] 董恺琛, 娄帅, 姚杰, 等.脉冲激光沉积薄膜的残余应力测量[J].光学 精密工程, 2018, 26(1):70-76. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM201801011.htmDONG K CH, LOU SH, YAO J, et al.. Measurement of residual stresses in pulsed laser deposited thin films[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2018, 26(1):70-76.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM201801011.htm [6] TSUDA Y, KITASAKO Y, SADR A, et al.. Effects of brushing timing after erosive challenge on enamel loss in situ: White light interferometer and nanoindentation study[J]. Dental Materials Journal, 2016, 35(4) 613-620. doi: 10.4012/dmj.2015-405 [7] DAO T, THOMAS T, MARX D, et al.. Evaluation of non-destructive etch depth measurement for through silicon vias[C]. 2012 IEEE International Conference on IC Design & Technology, IEEE, 2012: 1-4. [8] ZHOU Y F, CAI H ZH, ZHONG L Y, et al.. Eliminating the influence of source spectrum of white light scanning interferometry through time-delay estimation algorithm[J]. Optics Communications, 2017, 391:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2016.12.006 [9] XUE CH Y, LIU J, CHOU X J, et al.. White-light transmission reflection interference technology application in three-dimensional reconstruction method validation for microstructures[C]. Proceedings of the 3rd International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, IEEE, 2010, 2: 867-870. [10] 刘燕德, 万常斓.芝麻油掺伪的近红外透射光谱检测技术[J].农业机械学报, 2012, 43(7):136-140. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2012.07.025LIU Y D, WAN CH L. Analysis of sesame oil adulteration using near infrared transmission spectroscopy[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(7):136-140.(in Chinese) doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2012.07.025 [11] 秦五昌, 汤修映, 彭彦昆, 等.基于可见/近红外透射光谱的孵化早期受精鸡蛋的判别[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(1):200-204. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201701044.htmQIN W CH, TANG X Y, PENG Y K, et al.. Identification of fertilized chicken eggs based on visible/near-infrared spectrum during early stage of incubation[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(1):200-204.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201701044.htm [12] THOMAS D J. 3D white light interferometry assessment of robotic laser scalpel assisted surgery to minimise scar tissue formation[J]. International Journal of Surgery, 2017, 38:117-118. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2016.12.037 [13] XIAO Y, QIU L R, ZHAO W Q. Laser confocal cylindrical radius measurement method and its system[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(23):6596-6602. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.006596 [14] TAPILOUW A M, CHANG Y W, YU L Y, et al.. Reduction of batwing effect in white light interferometry for measurement of patterned sapphire substrates(PSS) wafer[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9960:996006. doi: 10.1117/12.2236874 [15] TERESCHENKO S, LEHMANN P, GOLLOR P, et al.. Vibration compensated high-resolution scanning white-light Linnik-interferometer[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10329:1032940. doi: 10.1117/12.2270226 -






 下载:
下载: