-
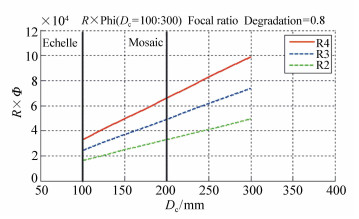
摘要: 为了充分利用LAMOST望远镜,实现对银河系不同星族的分布与整体性研究,以及极端贫金属星元素丰度测定等科学目标,研制了LAMOST高分辨率光谱仪,光谱分辨率R ≥ 30 000,光谱覆盖范围380~740 nm。在充分考虑台址因素与现有条件后,采用中继倍率0.7倍的准白瞳设计方案,使用大芯径光纤、拼接大光栅、棱栅组合式横向色散器、缝前像切分器等措施来满足性能要求。进行了效率估算与杂散光分析,光谱仪本体效率峰值大于30%,杂散光照度占CCD总照度的2.55%,信噪比为16.01 dB。试运行阶段实测了太阳光谱,温度稳定性达到±0.03℃,光谱仪效率峰值约为33.5%,满足稳定、高效的运行要求。Abstract: In order to make full use of the LAMOST telescope, as well as to achieve scientific goals such as the distribution and integrity of different stellar populations in the galaxy or the measurement of elemental abundance in extremely metal-poor stars, a LAMOST high-resolution spectrometer was developed with a spectral resolution of R ≥ 30 000 and spectral coverage range of 380-740 nm. After fully considering the factors of the site and its existing conditions, a quasi-white pupil design scheme with a repeater magnification of 0.7×was applied, using a large-core fiber, a large-diameter tiled-grating, a prism-grating disperser, and an image slicer to meet the perfermence requirment. Efficiency estimation and stray light analysis were performed. The peak efficiency of the spectrograph was more than 30%, the stray light illumination accounted for 2.55% of the total CCD illumination and the signal-to-noise ratio was 16.01dB. The solar spectrum was measured during the trial run with a temperature stability of±0.03℃ and a peak efficiency of approximately 33.5%, thus meeting requirements for stable and efficient operation.
-
Key words:
- spectrograph /
- resolution /
- light efficiency /
- stray light
-
表 1 LAMOST-HRS主要技术指标
Table 1. Main specifications of LAMOST-HRS
项目 参数 光谱分辨率 无限缝下R≥30 000 波长覆盖范围/nm 380~740 狭缝对天空张角/(″) 2.25 准直光束口径/mm 205 中继倍率 0.7× 相机焦比 F/2 阶梯光栅刻线密度/(lp·mm-1) 41.6 横向色散器刻线密度/(lp·mm-1) 500 光效率峰值 >30% 表 2 预估杂散光背景
Table 2. Estimate of background of stray light
鬼像 散射 级次 1级 2级 1级 2级 机械结构 0% 0% 0% 0.01% 光学面 0.07% 0.13% 2.49% 0.04% 表 3 杂散光分析结果
Table 3. Results of stray light analysis
项目 结果 CCD面总照度 3.15E-01 平均照度 5.75E-05 标准差 1.06E-03 杂散光照度 0.79E-02 信噪比 16.01 dB CCD面杂散光百分比 2.55% -
[1] CUI X. Preparing first light of LAMOST[C]. Ground-based and Airborne Telescopes Ⅱ, US, 2008, 7012: 701204 [2] ZHAO G, ZHAO Y H, CHU Y Q, et al.. LAMOST spectral survey-An overview[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2012, 12(7):723-734. doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/12/7/002 [3] BAI Z R, ZHANG H T, YUAN H L, et al.. Sky subtraction for LAMOST[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2017, 17(9), doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/17/9/91. [4] 张凯.LAMOST高分辨率光谱仪的研制进展[C].中国天文学会2014年学术年会论文摘要集, 2014:ZHANG K. Development of LAMOST high resolution spectrometer[C]. The China Astronomical Society 2014 Annual Conference Paper Abstract Collection, 2014.(in Chinese) [5] 崔向群.中国大型光学红外望远镜[C].全国光学测试学术交流会, 2016.CUI X Q. China Large-scale optical infrared telescope[C]. National Optical Testing Academic Conference, 2016.(in Chinese) [6] 武旭华, 朱永田, 王磊.高分辨率阶梯光栅光谱仪的光学设计[J].光学精密工程, 2003, 11(5):442-447. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-924X.2003.05.004WU X H, ZHU Y T, WANG L. Optical design of high resolution echelle spectrograph[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2003, 11(5):442-447.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-924X.2003.05.004 [7] 朱永田.8~10 m级光学/红外望远镜的高分辨率光谱仪[J].天文学进展, 2001, 19(2):336-345.ZHU Y T. High-resolution spectrometer for 8 to 10 m optical/infrared telescopes[J]. Progress in Astronomy, 2001, 19(2):336-345.(in Chinese) [8] 朱永田, 胡中文, 王磊, 等.LAMOST多目标光纤光谱仪的研制及试运行[J].中国科学:物理学力学天文学, 2011, 41(11):1337-1341. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGXK201111013.htmZHU Y T, HU ZH W, WANG L, et al.. Construction and commissioning of LAMOST low resolution spectrographs[J]. Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron, 2011, 41(11):1337-1341.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGXK201111013.htm [9] 张天一, 季杭馨, 侯永辉, 等.像切割器技术积分视场三维光谱仪[J].应用光学, 2015, 36(4):531-536. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yygx201504007ZHANG T Y, JI H X, HOU Y H, et al.. Integral field spectroscopy imaging technology[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2015, 36(4):531-536.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yygx201504007 [10] NICODEMUS F E, RICHMOND J C, HSIA J J. Geometrical Considerations and Nomendature for Reflectance[M]. Unite States, US Department of Commerce, National Bureau of Standards, 1977. [11] 宋延嵩, 安岩, 李欣航, 等.激光准直系统中的杂散光分析与抑制[J].中国光学, 2016, 9(6):663-670. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9509.shtmlSONG Y S, AN Y, LI X H, et al.. Analyzing and suppressing of stray light in laser collimating system[J]. Chine Optics, 2016, 9(6):663-670.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9509.shtml [12] 葛城显, 吴振森, 白靖, 等.微粗糙光学表面与多个镶嵌粒子差值散射场特性[J].光学精密工程, 2018, 26(2):268-275. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201802003GE CH X, WY ZH S, BAI J, et al.. Difference field scattering properties between multiple inlaid redundant particles and slightly rough optical surface[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2018, 26(2):268-275.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201802003 [13] 谭乃悦, 许中杰, 韦可, 等.透射光学系统像平面一阶散射光照度分布规律研究[J].物理学报, 2017, 66(4):78-84. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wlxb201704010TAN N Y, XU ZH J, WEI K, et al.. The research on the illumination distribution law of the first-order scattered light in the focal plane of transmission optical system[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66(4):78-84.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wlxb201704010 [14] 宋延松, 杨建峰, 李福, 等.基于杂散光抑制要求的光学表面粗糙度控制方法研究[J].物理学报, 2017, 66(19):69-77. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wlxb201719009SONG Y S, YANG J F, LI F, et al.. Method of controlling optical surface roughness based on stray light requirements[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66(19):69-77.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wlxb201719009 [15] HOU Y H, WANG L, HU Z, et al.. The LAMOST low resolution spectrograph stability performance[C]. Ground-based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy IV, 2012: 60. -






 下载:
下载: