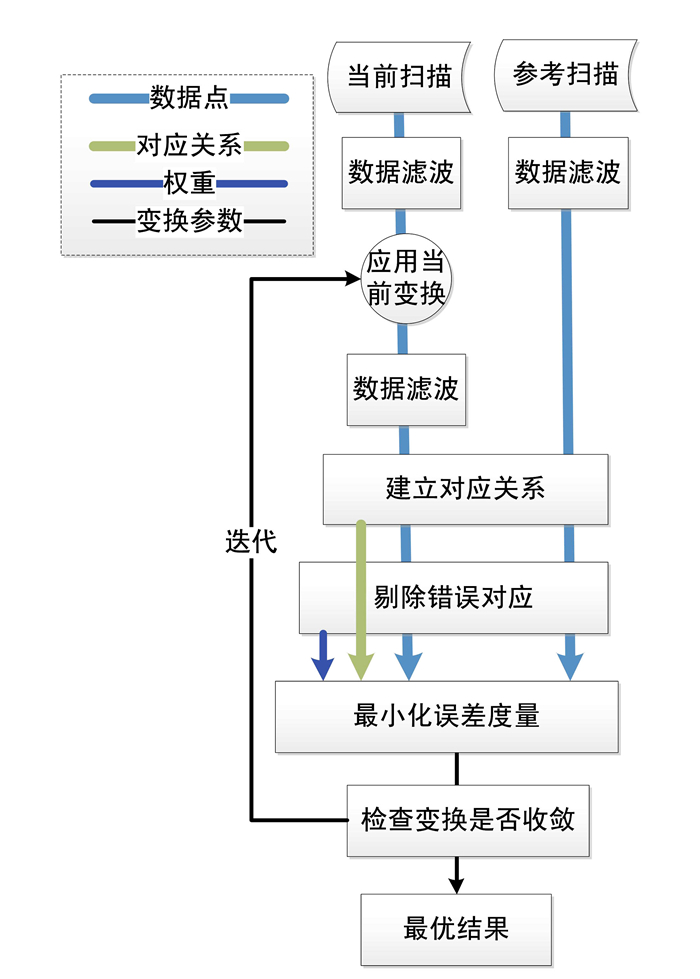
-
摘要: 激光扫描匹配是利用激光雷达进行导航、定位与地图构建的基础,本文对各类激光扫描匹配方法进行了综述。将现有方法归纳为基于点的扫描匹配方法、基于特征的扫描匹配方法和基于数学特性的扫描匹配方法3类,系统总结了相应类型的常见方法;对典型的算法及其改进算法进行了梳理,并指出了存在的主要问题和发展趋势;介绍了激光扫描匹配方法性能评价和对比的最新研究进展,最后,展望了激光扫描匹配技术未来的研究方向。Abstract: Laser scan matching is a foundation for navigation, localization and mapping using Light Detection and Ranging(LiDAR). Various laser scan matching methods are reviewed in detail in this paper. The existing methods are divided into three categories:point-based scan matching method, feature-based scan matching method and mathematical property-based scan matching method, and the common algorithms of corresponding categories are summarized systematically. The typical algorithms and their improved algorithms are outlined, the main issues and development trends are discussed. Then, the latest research progress of performance evaluation and comparison of laser scan matching methods is introduced. Finally, the future research directions of laser scan matching technology are prospected.
-
Key words:
- laser scan matching /
- point cloud registration /
- SLAM /
- LiDAR
-
表 1 典型扫描匹配方法的特点
Table 1. Features of typical scan matching methods
特点 ICP类方法 基于特征的方法 NDT类方法 是否需要迭代 需要 非必须 需要 是否需要初值 需要 不需要 需要 收敛域 小 / 大 运行速度 慢 快 较快 能否辅助闭环检测 不能 能 能 鲁棒性 较差 较好 好 精度 高,受离群点和噪声影响较大 低,与特征提取精度有关 较高,与体素尺寸密切相关 适用范围 广 结构化场景 广 -
[1] CADENA C, CARLONE L, CARRILLO H, et al.. Past, present, and future of simultaneous localization and mapping:towards the robust-perception age[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2016, 32(6):1309-1332. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2016.2624754 [2] 林辉灿, 吕强, 张洋, 等.稀疏和稠密的VSLAM的研究进展[J].机器人, 2016, 38(5):621-631. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jqr201605014LIN H C, LV Q, ZHANG Y, et al.. The sparse and dense VSLAM:a survey[J]. ROBOT, 2016, 38(5):621-631.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jqr201605014 [3] 梁明杰, 闵华清, 罗荣华.基于图优化的同时定位与地图创建综述[J].机器人, 2013, 35(4):500-512. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jqr201304016LIANG M J, MIN H Q, LUO R H. Graph-based SLAM:a survey[J]. ROBOT, 2013, 35(4):500-512.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jqr201304016 [4] CENSI A. Scan matching in a probabilistic framework[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2006: 2291-2296. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=1642044 [5] PARK, KIM D H, PARK M, et al.. Spectral scan matching for robot pose estimation[J]. Electronics Letters, 2009, 45(21):1076-1077. doi: 10.1049/el.2009.1355 [6] RÖWEKÄMPER J, SPRUNK C, TIPALDI G D, et al.. On the position accuracy of mobile robot localization based on particle filters combined with scan matching[C]. IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2012: 3158-3164. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=6385988 [7] HOUSHIAR H, ELSEBERG J, BORRMANN D, et al.. A study of projections for key point based registration of panoramic terrestrial 3D laser scan[J]. Geo-spatial Information Science, 2015, 18(1):11-31. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkjxxkxxb-e201501002 [8] PARK S, PARK S K. Spectral scan matching and its application to global localization for mobile robots[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2010: 1361-1366. [9] LEHTOLA V V, KAARTINEN H, NÜCHTER A, et al.. Comparison of the selected state-of-the-art 3D indoor scanning and point cloud generation methods[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(8):796. doi: 10.3390/rs9080796 [10] FURUKAWA T, DANTANARAYANA L, ZIGLAR J, et al.. Fast global scan matching for high-speed vehicle navigation[C]. IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems, 2015: 37-42. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=7295742 [11] YOSHITAKA H, HIROHIKO K, AKIHISA O, et al.. Mobile Robot localization and mapping by scan matching using laser reflection intensity of the SOKUIKI sensor[C]. IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics, 2007: 3018-3023. [12] BORRMANN D, ELSEBERG J, KAI L, et al.. Globally consistent 3D mapping with scan matching[J]. Robotics & Autonomous Systems, 2008, 56(2):130-142. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921889007000863 [13] MARTINEZ J L, GONZALEZ J, MORALES J, et al.. Mobile robot motion estimation by 2D scan matching with genetic and iterative closest point algorithms[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2006, 23(1):21-34. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=450127f45c33d0ef5a2f8cd257b2c91b [14] GAO Y, LIU S, ATIA M M, et al.. INS/GPS/LiDAR integrated navigation system for urban and indoor environments using hybrid scan matching algorithm[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(9):23286-23302. doi: 10.3390/s150923286 [15] CHEN Y, MEDIONI G. Object modeling by registration of multiple range images[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 1991: 145-155. [16] BESL P J, MCKAY H D. A method for registration of 3-D shapes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1992, 14(2):239-256. doi: 10.1109/34.121791 [17] LU F, MILIOS E E. Robot Pose Estimation in unknown environments by matching 2D range scans[J]. Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems, 1997, 18(3):249-275. doi: 10.1023/A:1007957421070 [18] GUTMANN J S, SCHLEGEL C. AMOS: comparison of scan matching approaches for self-localization in indoor environments[C]. Proceedings of the First Euromicro Workshop on Advanced Mobile Robot, 1996: 61-67. [19] COX I J. Blanche-an experiment in guidance and navigation of an autonomous robot vehicle[C]. International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 1991, 7(2): 193-204. http://doi.ieeecomputersociety.org/resolve?ref_id=doi:10.1109/70.75902&rfr_id=trans/tp/2002/02/ttp2002020237.htm [20] MINGUEZ J, MONTESANO L, LAMIRAUX F. Metric-based iterative closest point scan matching for sensor displacement estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2006, 22(5):1047-1054. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2006.878961 [21] CAMPBELL D, WHITTY M, LIM S. Mobile 3D indoor mapping using the continuous normal distributions transform[C]. IEEE International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, 2012: 1-9. [22] BOSSE M C. ATLAS: a framework for large scale automated mapping and localization[D]. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2004. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1023391 [23] CENSI A. An ICP variant using a point-to-line metric[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2008: 19-25. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4543181/ [24] BOSSE M, ZLOT R. Continuous 3D scan-matching with a spinning 2D laser[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2009: 4244-4251. [25] 李明磊, 李广云, 王力, 等.采用八叉树体素生长的点云平面提取[J].光学精密工程, 2018, 26(1):172-183. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201801021LI M L, LI G Y, WANG L, et al.. Planar feature extraction from unorganized point clouds using octree voxel-based region growing[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2018, 26(1):172-183.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201801021 [26] SEGAL A, HAEHNEL D, THRUN S. Generalized-ICP[C]. Robotics: Science and Systems, 2009, 2(4): 435. [27] SERAFIN J, GRISETTI G. Using augmented measurements to improve the convergence of icp[C]. International Conference on Simulation, Modeling, and Programming for Autonomous Robots. Springer, Cham, 2014: 566-577. Using augmented measurements to improve the convergence of icp [28] SERAFIN J, GRISETTI G. NICP: dense normal based point cloud registration[C]. IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2015: 742-749. [29] LV J, YUKINORI K, RAVANKAR A A, et al.. A solution to estimate robot motion with large rotation by matching laser scans[C]. IEEE Society of Instrument and Control Engineers of Japan, 2015: 1083-1088. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7285356/ [30] YANG J, LI H, JIA Y. Go-ICP: solving 3D registration efficiently and globally optimally[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE Computer Society, 2013: 1457-1464. [31] HAN J D, YIN P, HE Y Q, et al.. Enhanced ICP for the registration of large-scale 3D environment models:an experimental study[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(2):228. doi: 10.3390/s16020228 [32] HONG S, KO H, KIM J. VICP: velocity updating iterative closest point algorithm[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2012: 1893-1898. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=5509312 [33] ALISMAIL H, BAKER L D, BROWNING B. Continuous trajectory estimation for 3D SLAM from actuated lidar[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2014: 6096-6101. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=6907757 [34] RUSINKIEWICZ S, LEVOY M. Efficient variants of the ICP algorithm[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on 3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling, 2001: 145-152. [35] POMERLEAU F, COLAS F, SIEGWART R, et al.. Comparing ICP variants on real-world data sets[J]. Autonomous Robots, 2013, 34(3):133-148. doi: 10.1007/s10514-013-9327-2 [36] GELFAND N, IKEMOTO L, RUSINKIEWICZ S, et al.. Geometrically stable sampling for the ICP algorithm[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on 3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling, 2003: 260-267. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=1240258 [37] MONTESANO L, MINGUEZ J, MONTANO L. Probabilistic scan matching for motion estimation in unstructured environments[C]. IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2005: 3499-3504. [38] DIOSI A, KLEEMAN L. Laser scan matching in polar coordinates with application to SLAM[C]. IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2005: 3317-3322. [39] DIOSI A, KLEEMAN L. Fast laser scan matching using polar coordinates[J]. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2007, 26(10):1125-1153. doi: 10.1177/0278364907082042 [40] CAI Z S, HONG B R, LI H. An improved polar scan matching using genetic algorithm[J]. Information Technology Journal, 2007, 6(1):89-95. doi: 10.3923/itj.2007.89.95 [41] CHEN F, CHOPRA I, RAND O. Perimeter-based polar scan matching(PB-PSM) for 2D laser odometry[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2015, 80(2):231-254. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=25d5e73393dd6ea35dfdb9dab8853a36 [42] TSARDOULIAS E, PETROU L. Critical rays scan match SLAM[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2013, 72(3-4):441-462. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0231654603/ [43] BONNABEL S, BARCZYK M, GOULETTE F, et al.. On the covariance of ICP-based scan-matching techniques[C]. American Control Conference(ACC), 2016: 5498-5503. [44] CENSI A. On achievable accuracy for range-finder localization[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2007: 4170-4175. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=4209738 [45] OLSON E B. Real-time correlative scan matching[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2009: 1233-1239. [46] ELSEBERG J, MAGNENAT S, SIEGWART R, et al.. Comparison on nearest-neigbour-search strategies and implementations for efficient shape registration[J]. Annual Report of Natural Science & Home Economics Kinjo Gakuin College, 2012, 22(3):268-269. [47] NÜCHTER A, KAI L, HERTZBERG J, et al.. 6D SLAM-3D mapping outdoor environments[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2007, 24(8-9):699-722. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1556-4967 [48] VERDOJA F, THOMAS D, SUGIMOTO A. Fast 3D point cloud segmentation using supervoxels with geometry and color for 3D scene understanding[C]. IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo. IEEE Computer Society, 2017: 1285-1290. [49] JENSFELT P, KRISTENSEN S. Active global localization for a mobile robot using multiple hypothesis tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics & Automation, 2001, 17(5):748-760. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1f0043a8e72e54b429b6fe8810a8e555 [50] NAKAMURA T, TASHITA Y. Congruence transformation invariant feature descriptor for robust 2D scan matching[C]. IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 2014: 1648-1653. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2571272.2572330&coll=DL&dl=GUIDE&CFID=420369950&CFTOKEN=21427784 [51] NAKAMURA T, WAKITA S. Robust global scan matching method using congruence transformation invariant feature descriptors and a geometric constraint between keypoints[J]. Transactions of the Society of Instrument & Control Engineers, 2015, 51(5):309-318. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/5610708 [52] TALEGHANI S, SHARBAFI M A, HAGHIGHAT A T, et al.. ICE matching, a robust mobile robot localization with application to SLAM[C]. IEEE International Conference on TOOLS with Artificial Intelligence. IEEE Computer Society, 2010: 186-192. [53] MOHAMED H A, MOUSSA A M, ELHABIBY M M, et al.. Improved real-time scan matching using corner features[C]. ISPRS International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2016, XLI-B5: 533-539. [54] TIPALDI G D, BRAUN M, ARRAS K O. FLIRT: Interest regions for 2D range data with applications to robot navigation[C]. Experimental Robotics. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2014: 695-710. [55] TOMBARI F, SALTI S, STEFANO L D. Performance evaluation of 3D keypoint detectors[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2013, 102(1-3):198-220. doi: 10.1007/s11263-012-0545-4 [56] GUO Y, BENNAMOUN M, SOHEL F, et al.. A comprehensive performance evaluation of 3D local feature descriptors[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2016, 116(1):66-89. doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0824-y [57] LIU S, ATIA M M, GAO Y, et al.. Adaptive covariance estimation method for LiDAR-aided multi-sensor integrated navigation systems[J]. Micromachines, 2015, 6(2):196-215. doi: 10.3390/mi6020196 [58] SIADAT A, KASKE A, KLAUSMANN S, et al.. An optimized segmentation method for a 2D laser-scanner applied to mobile robot navigation[C]. IFAC Proceedings, 1997, 30(7): 149-154. [59] GRISETTI G, IOCCHI L, NARDI D. Global Hough localization for mobile robots in polygonal environments[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2002(1): 353-358. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=1013386 [60] CENSI A, IOCCHI L, GRISETTI G. Scan matching in the Hough domain[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2006: 2739-2744 [61] ZEZHONG X, JILIN L, ZHIYU X. Scan matching based on CLS relationships[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics, Intelligent Systems and Signal Processing, 2003, 1: 99-104. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=conference&id=WFHYXW83869 [62] MAZURAN M, AMIGONI F. Matching line segment scans with mutual compatibility constraints[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation(ICRA 2014), 2014: 4298-4303. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=6907484 [63] NUÑEZ P, VÁZQUEZ-MART N R, TORO J C D, et al.. Natural landmark extraction for mobile robot navigation based on an adaptive curvature estimation[J]. Robotics & Autonomous Systems, 2008, 56(3):247-264. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=41e84f4c7adaf4845fbec6a90c6e2beb [64] YUAN X, ZHAO C, TANG Z, et al.. Lidar scan-matching for mobile robot localization[J]. Information Technology Journal, 2010, 9(1):27-33. doi: 10.3923/itj.2010.27.33 [65] LI J, ZHONG R, HU Q, et al.. Feature-based laser scan matching and its application for indoor mapping[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(8):1265. doi: 10.3390/s16081265 [66] TOMONO M. A scan matching method using Euclidean invariant signature for global localization and map building[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2004. ICRA. IEEE, 2004: 866-871 Vol.1. [67] NOBILI S, SCONA R, CARAVAGNA M, et al.. Overlap-based ICP tuning for robust localization of a humanoid robot[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2017: 4721-4728. [68] SERAFIN J, OLSON E, GRISETTI G. Fast and robust 3D feature extraction from sparse point clouds[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2016: 4105-4112. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7759604/ [69] ZHANG J, SINGH S. Low-drift and real-time lidar odometry and mapping[J]. Autonomous Robots, 2017, 41(2):401-416. doi: 10.1007/s10514-016-9548-2 [70] RUSU R B, BLODOW N, MARTON Z, et al.. Aligning point cloud views using persistent feature histograms[C]. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems(IROS 2008), Sep.2008: 3384-3391. [71] RUSU R B, BLODOW N, BEETZ M. Fast point feature histograms(FPFH) for 3D registration[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2009: 1848-1853. [72] JIANG J, CHENG J, CHEN X. Registration for 3-D point cloud using angular-invariant feature[J]. Neurocomputing, 2009, 72(16):3839-3844. doi: 10.1016-j.neucom.2009.05.013/ [73] NUÑEZ P, VÁZQUEZMART N R, BANDERA A, et al.. Fast laser scan matching approach based on adaptive curvature estimation for mobile robots[J]. Robotica, 2009, 27(3):469-479. http://journals.cambridge.org/abstract_S0263574708004840 [74] CHONG Z J, QIN B, BANDYOPADHYAY T, et al.. Synthetic 2D LIDAR for precise vehicle localization in 3D urban environment[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2013: 1554-1559. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=6630777 [75] SHU L, XU H, HUANG M. High-speed and accurate laser scan matching using classified features[C]. IEEE International Symposium on Robotic and Sensors Environments, 2014: 61-66. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6698419/ [76] RAMOS F T, FOX D, DURRANT-WHYTE H F. CRF-matching: conditional random fields for feature-based scan matching[C]. Robotics: Science and Systems, 2007. [77] RYU H, WAN K C. Efficient scan matching method using direction distribution[J]. Electronics Letters, 2015, 51(9):686-688. doi: 10.1049/el.2014.4034 [78] SEHGAL A, CERNEA D, MAKAVEEVA M. Real-time scale invariant 3d range point cloud registration[C]. International Conference on Image Analysis and Recognition. Springer-Verlag, 2010: 220-229. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2176924.2176951 [79] STEDER B, RUSU R B, KONOLIGE K, et al.. NARF: 3D range image features for object recognition[C]. Workshop on Defining and Solving Realistic Perception Problems in Personal Robotics at the IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems(IROS), 2010: 44. [80] OLSON E. M3RSM: many-to-many multi-resolution scan matching[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation(ICRA 2015), 2015: 5815-5821. [81] RAY R, BANERJI D, NANDY S, et al.. Keypoints based laser scan matching-a robust approach[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, 2012: 741-746. [82] LENAC K, KITANOV A, CUPEC R, et al.. Fast planar surface 3D SLAM using LIDAR[J]. Robotics & Autonomous Systems, 2017, 92:197-220. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1f1613a46b4f8cfd3a3d47ccf6d1d075 [83] MOHAMED H, MOUSSA A, ELHABIBY M, et al.. A novel real-time reference key frame scan matching method[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(5):1060-1088. doi: 10.3390/s17051060 [84] HUANG X, ZHENG B, MASUDA T, et al.. Robust 3D features for matching between distorted range scans captured by moving systems[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE Computer Society, 2014: 2957-2964. [85] BIBER P, STRA ER W. The normal distributions transform: a new approach to laser scan matching[C]. Proceedings of 2003 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems(IROS 2003), 2003, 3: 2743-2748. [86] MAGNUSSON M, LILIENTHAL A, DUCKETT T. Scan registration for autonomous mining vehicles using 3D-NDT[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2007, 24(10):803-827. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1556-4967 [87] BIBER P, FLECK S, STRA ER W. A probabilistic framework for robust and accurate matching of point clouds[C]. Joint Pattern Recognition Symposium. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2004: 480-487. http://www.springerlink.com/content/306ffbk2a4rnyqc8 [88] MAGNUSSON M. The three-dimensional normal-distributions transform: an efficient representation for registration, surface analysis, and loop detection[D]. rebro University, 2009. [89] STOYANOV T D, MAGNUSSON M, ANDREASSON H, et al.. Fast and accurate scan registration through minimization of the distance between compact 3D NDT representations[J]. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2012, 31(12):1377-1393. doi: 10.1177/0278364912460895 [90] MAGNUSSON M, VASKEVICIUS N, STOYANOV T, et al.. Beyond points: Evaluating recent 3D scan-matching algorithms[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2015: 3631-3637. [91] WEI G, PUTTKAMER E. A map based on laser scans without geometric interpretation[C]. Intelligent Autonomous Systems, 1995, 4(2): 403-407. [92] KONECNY J, PRAUZEK M, KROMER P, et al.. Novel point-to-point scan matching algorithm based on cross-correlation[J]. Mobile Information Systems, 2016(15):1-11. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=Doaj000003970137 [93] LEORDEANU M, HEBERT M. A spectral technique for correspondence problems using pairwise constraints[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE Computer Society, 2005: 1482-1489. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=1544893 [94] WANG X, JIA Y, XI N, et al.. Mobile robot pose estimation using laser scan matching based on Fourier transform[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, 2014: 474-479. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=6739504 [95] Kim H, Dugarjav B, Lee K H, et al. A study on scan matching method using procrustes analysis[C]. International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems, 2014: 1027-1030. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=6987941 [96] PEDROSA E, PEREIRA A, LAU N. A scan matching approach to SLAM with a dynamic likelihood field[C]. International Conference on Autonomous Robot Systems and Competitions, 2016: 35-40. [97] BOUGHORBEL F, KOSCHAN A, ABIDI B, et al.. Gaussian fields:a new criterion for 3D rigid registration[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2004, 37(7):1567-1571. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2004.02.005 [98] LENAC K, MUMOLO E, NOLICH M. Fast Genetic Scan Matching in Mobile Robotics[M]. Evolutionary Image Analysis and Signal Processing. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2009: 133-152. [99] KROMER P, KONECNY J, PRAUZEK M. Point-based scan matching by differential evolution[C]. International Conference on Intelligent NETWORKING and Collaborative Systems, 2016: 215-221. [100] WULF O, NÜCHTER A, HERTZBERG J, et al.. Benchmarking urban six-degree-of-freedom simultaneous localization and mapping[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2008, 25(3):148-163. doi: 10.1002/rob.v25:3 [101] DU Q H. Metrics for 3D Rotations:Comparison and Analysis[J]. Journal of Mathematical Imaging & Vision, 2009, 35(2):155-164. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1574531 [102] MAGNUSSON M, NUCHTER A, LORKEN C, et al.. Evaluation of 3D registration reliability and speed-a comparison of ICP and NDT[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2009: 2263-2268. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1703817 [103] PATHAK K, BORRMANN D, ELSEBERG J, et al.. Evaluation of the robustness of planar-patches based 3D-registration using marker-based ground-truth in an outdoor urban scenario[C]. Ieee/rsj International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2010: 5725-5730. [104] PATHAK K, BIRK A, VAŠKEVIČIUS N, et al.. Fast registration based on noisy planes with unknown correspondences for 3-D mapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2010, 26(3):424-441. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2010.2042989 [105] LI Q, M LLER F, WENZEL A, et al.. Simulation-based comparison of 2D scan matching algorithms for different rangefinders[C]. 201621st International Conference on Methods and Models in Automation and Robotics(MMAR), 2016: 924-929. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7575261/ [106] ELBAZ G, AVRAHAM T, FISCHER A. 3D point cloud registration for localization using a deep neural network auto-encoder[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR 2017), 2017: 2472-2481. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8099748/ [107] BEDKOWSKI J M, RÖHLING T. Online 3D LIDAR Monte Carlo localization with GPU acceleration[J]. Industrial Robot, 2017, 44(4). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=36434d2fa5393edb2ff0860e3ce11c3d -






 下载:
下载: