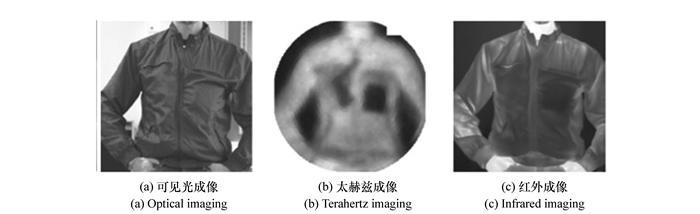
-
摘要: 太赫兹波由于其极低的光子能量和对非极性物质较强的穿透特性已成为人体隐匿物检测应用的热点。本文以室内人体隐匿物品探测为主要应用背景,简要介绍了太赫兹波段的大气传播特性;重点分析了基于辐射检测的室内被动太赫兹成像原理和系统的关键技术,包括辐射计和阵列扫描方式等;回顾了国内外被动太赫兹成像技术在人体安检领域的研究现状。综合考虑系统成本和成像时间,一定数量的高灵敏度辐射计加上扫描机构成像的方式在未来很长一段时间里将是被动太赫兹成像系统的主流方式。Abstract: Terahertz wave has become a hot research point for body hidden objects detection applications due to its extremely low photon energy and the strong penetration properties to non-polar material. In this paper, taking indoor body concealed detection as the main background, we briefly introduce the atmospheric propagation characteristics of THz waveband. Then we focus on the analysis of the indoor passive terahertz imaging principle and the key technology of imaging system based on radiation detection, including radiometer and scanning array mode, and review the research status of passive terahertz imaging technology in the field of human body security inspection at home and abroad. Considering system cost and imaging time, passive terahertz imaging system consisting of a certain number of high sensitivity radiation meters and scanning imaging mechanism will be the mainstream in the future for a long time.
-
Key words:
- Terahertz wave /
- passive imaging /
- radiometer /
- personnel security screening
-
表 1 国外太赫兹被动成像系统
Table 1. Terahertz passive imaging system at abroad
国别 公司 中心频率/GHz 帧速率/Hz 温度分辨率/K 阵元数/个 空间分辨率 美国 NGC 89 17 2 1 040 2.1 cm@5 m Millivision Vela 125 94 10 3 64 5 cm@1.6 m Millitech 94 30 / 64 3 cm@5 m Brijot BIS-WDS? GEN2 90 4-12 1 16 6 cm@(3~5 m) Thruvision T4000 250 / >1 / 3 cm@3 m 英国 QinetiQ iSPO-30 94 15 5 64 2.5 cm@5 m 德国 Jena/IPHT Safe-visitor 350 10 / 10~20 1 cm@1 m 芬兰 VTT/NIST 640 7-10 0.5 64 4 cm@5 m -
[1] GOLDSMITH P F, HSIEH C T, HUGUENIN G R, et al.. Focal plane imaging systems for millimeter wavelengths[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 1993, 41(10):1664-1675. doi: 10.1109/22.247910 [2] YUJIRI L. Passive millimeter wave imaging[J]. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 2006, 4(3):39-50. [3] WILLIAMS T D, VAIDYA N M. A compact, low-cost, passive MMW security scanner[J]. Defense and Security International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2005:109-116. doi: 10.1117/12.603662 [4] GARY V T. Millimeter wave case study of operational deployments:retail, airport, military, courthouse, and customs[J]. SPIE, 2008, 6948:694802-16. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2008SPIE.6948E..02T [5] ANDERTON R N, APPLEBY R, BEALE J E, et al.. Security scanning at 94 GHz[J]. SPIE, 2006, 6211:6211C-8. [6] WIKNER D A. Progress in millimeter-wave imaging[J]. SPIE, 2011, 7936:1392-1398. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/241398300_Progress_in_Millimeter-Wave_Imaging [7] MANN C. A compact real time passive terahertz imager[J]. SPIE, 2006:6211:62110E-5. [8] MAY T, ZIEGER G, ANDERS S, et al.. Safe VISITOR:visible, infrared, and terahertz object recognition for security screening application[J]. SPIE, 2009, 7309:73090E-8. http://spiedigitallibrary.org/data/Conferences/SPIEP/10717/73090E_1.pdf [9] LUUKANEN A A, GRONBERG L, GRONHOLM M, et al.. Real-time passive terahertz imaging system for standoff concealed weapons imaging[J]. SPIE, 2010, 7670:767004-8. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Charles_Dietlein/publication/44788181_Real-time_passive_terahertz_imaging_system_for_standoff_concealed_weapons_imaging/links/0deec5286a047ade69000000.pdf?inViewer=true&pdfJsDownload=true&disableCoverPage=true&origin=publication_detail [10] LUUKANEN A, APPLEBY R, KEMP M, et al.. Millimeter-wave and terahertz imaging in security applications[J]. Terahertz Spectroscopy and Imaging, 2012:491-520. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-29564-5_19/fulltext.html [11] PREISSNER J. The influence of the atmosphere on passive radiometric measurements[J]. In AGARD Millimeter and Submillimeter Wave Propagation and Circuits, 1979. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1979mswp.agarS....P [12] SKOUM N. Microwave radiometer systems:design and analysis[J]. Norwood Ma Artech House P, 1989, 1(2):250-252. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/234373963_Microwave_Radiometer_Systems_Design_and_Analysis [13] 金伟其, 田莉, 王宏臣, 等.THz焦平面探测器及其成像技术发展综述[J].红外技术, 2013, 4:187-194. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWJS201304003.htmJIN W Q, TIAN L, WANG H CH, et al.. Review of THz focal plane detector and the development of its imaging technology[J]. Infrared Technology, 2013, 4:187-194.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWJS201304003.htm [14] 张坤.噪声照射下毫米波辐射测量的实验研究[D].南京:南京理工大学, 2010. http://www.docin.com/p-299149999.htmlZHANG K. Experiment on millimeter wave radiometric measurement under noise illumination[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2010.(in Chinese) http://www.docin.com/p-299149999.html [15] 曾文辉.W波段测量辐射计接收机设计[D].南京:南京理工大学, 2008.ZENG W H. Design of W-band radiometer-measuring receiver[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2008.(in Chinese) [16] 张光锋.毫米波辐射特性及成像研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学, 2005.ZHANG G F. Research on millimeter wave radiometric characteristic and imaging[D]. Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science & Technology, 2005.(in Chinese) [17] 郎量, 张祖荫, 郭伟, 等.毫米波超综合孔径辐射计成像技术[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2009, 31(7):1623-1626. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYD200907024.htmLANG L, ZHANG Z Y, GUO W. Imaging by millimeter wave super-synthesis radiometer[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31(7):1623-1626.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYD200907024.htm [18] 邓小丹, 潘君骅, 窦文斌.毫米波焦面阵成像视场扩大分析[J].电子学报, 2003, 31(12A):2012-2014. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXU2003S1014.htmDENG X D, PAN J H, DOU W B. Analysis of extending the field-of-view of focal-plane imaging system at millimeter-wavelengths[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2003, 31(12A):2012-2014.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXU2003S1014.htm [19] 陈昊, 窦文斌.用于毫米波焦面成像阵的介质加载波导阵元分析[J].红外与毫米波学报, 2003, 22(5):398-400. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYH200305017.htmCHEN H, DOU W B. Analysis of waveguide loaded with dielectric used as millimeter wave focal imaging array elements[J]. J. Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2003, 22(5).398-400.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYH200305017.htm [20] QIU J H, WANG N N, YU F, DENG W B. Design of wide-band monopole antenna with parasitic elements[C]. 2008 Asia-Pacific Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility and 19th International Zurich Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, Singapore, 2008:411-414. [21] 王楠楠, 邱景辉, 张鹏宇, 等.被动毫米波焦面阵成像技术[J].红外与毫米波学报, 2011, 30(5):419-424. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYH201105009.htmWANG N N, QIU J H, ZHANG P Y, et al.. Passive millimeter wave focal plane array imaging technology[J]. J. Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2011, 30(5):419-424.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYH201105009.htm [22] YANG J Y, TAN R J, XIONG J T, LI L C. Frequency domain estimation and correction algorithm of row displacement for scanning PMMW imaging[J]. J. Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves, 2013, 34(2):205-216. doi: 10.1007/s10762-013-9961-y [23] CHEN Q K, FAN Y, LI L C, et al.. Design of W-band 16 elements full sampling focal plane linear array[J]. J. Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2013, 32(1):23-27. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1010.2013.00023 [24] ZANG X F, LI Z, SHI C, et al.. Rotatable illusion media for manipulating terahertz electromagnetic waves[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(21):25565-72. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.025565 [25] ZANG X F, SHI C, CHEN L, et al.. Ultra-broadband terahertz absorption by exciting the orthogonal diffraction in dumbbell-shaped gratings[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5:8901. doi: 10.1038/srep08901 [26] 高春梅, 陈麟, 谢乐, 等.不同周期数牛眼结构对基于伪表面等离子激发的太赫兹透射的影响[J].光子学报, 2012, 41(10):1156-1160. doi: 10.3788/gzxbGAO CH M, CHEN L, XIE L, et al.. Comparison on terahertz transmission based on spoof surface plasmon polaritons between bull's eye structures with different ring grooves[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2012, 41(10):1156-1160.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/gzxb -






 下载:
下载: