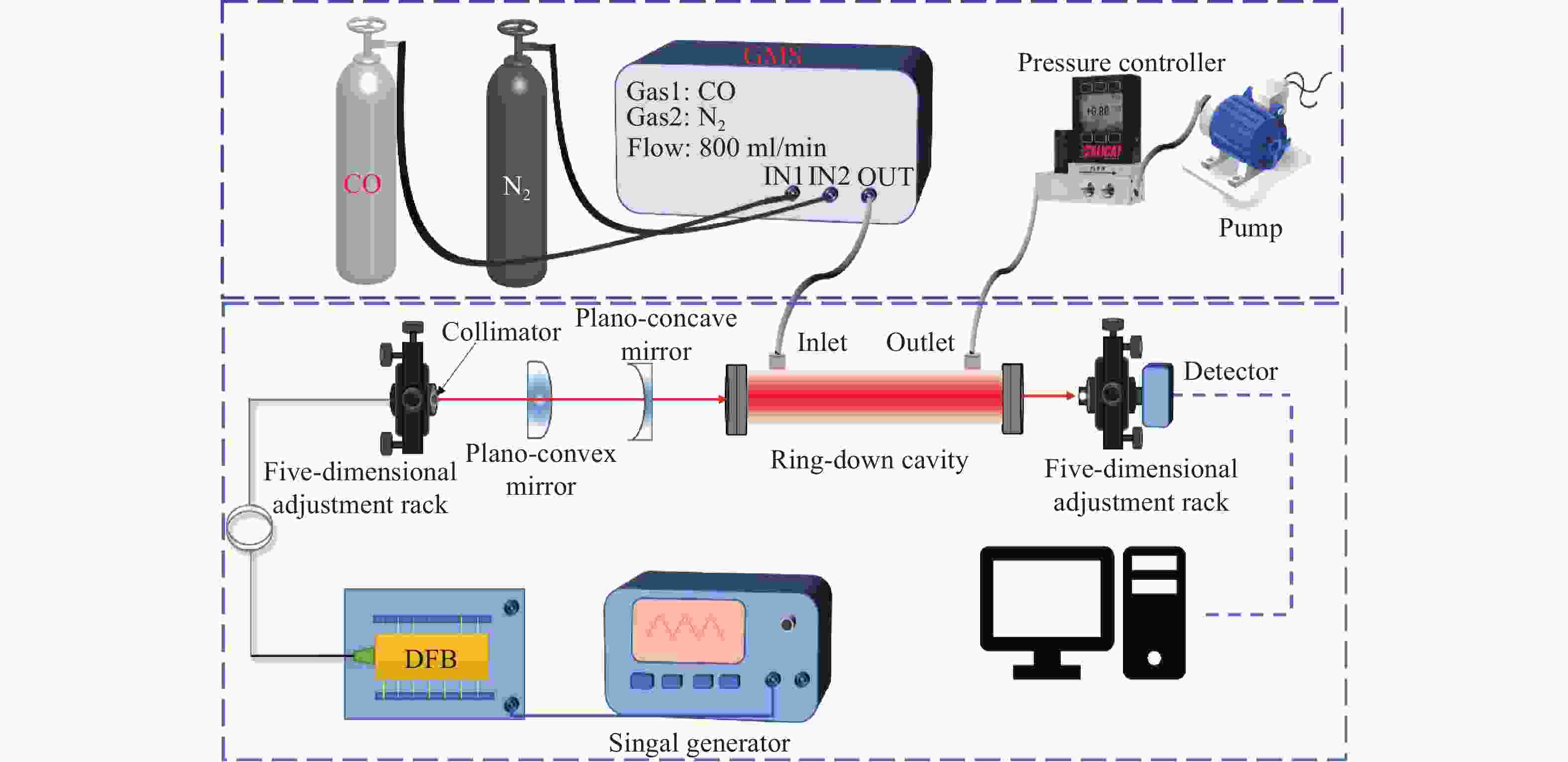
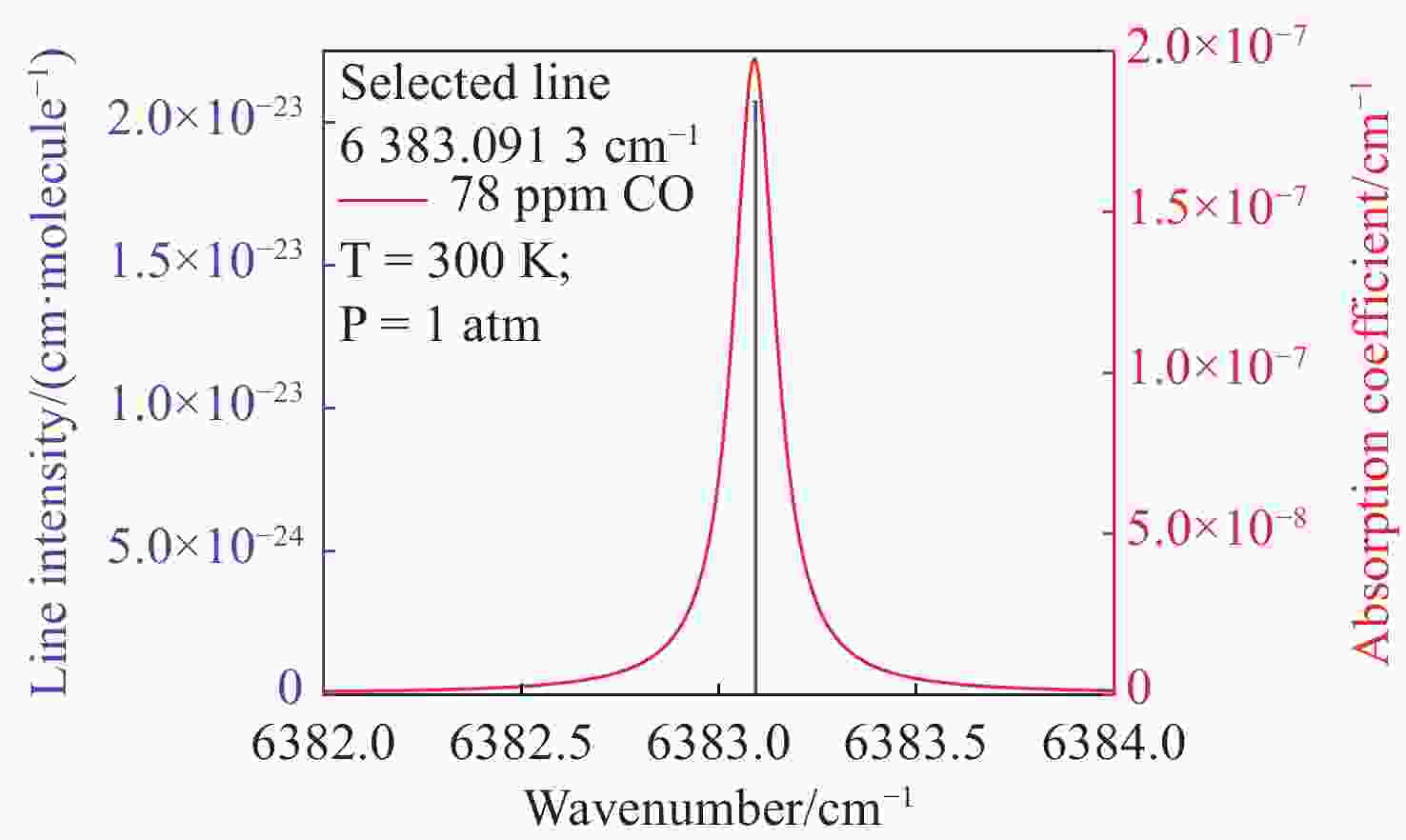
Cavity ring-down spectroscopy CO gas sensor integrating principal component analysis with savitzky-golay filtering
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2025-0032
-
摘要:
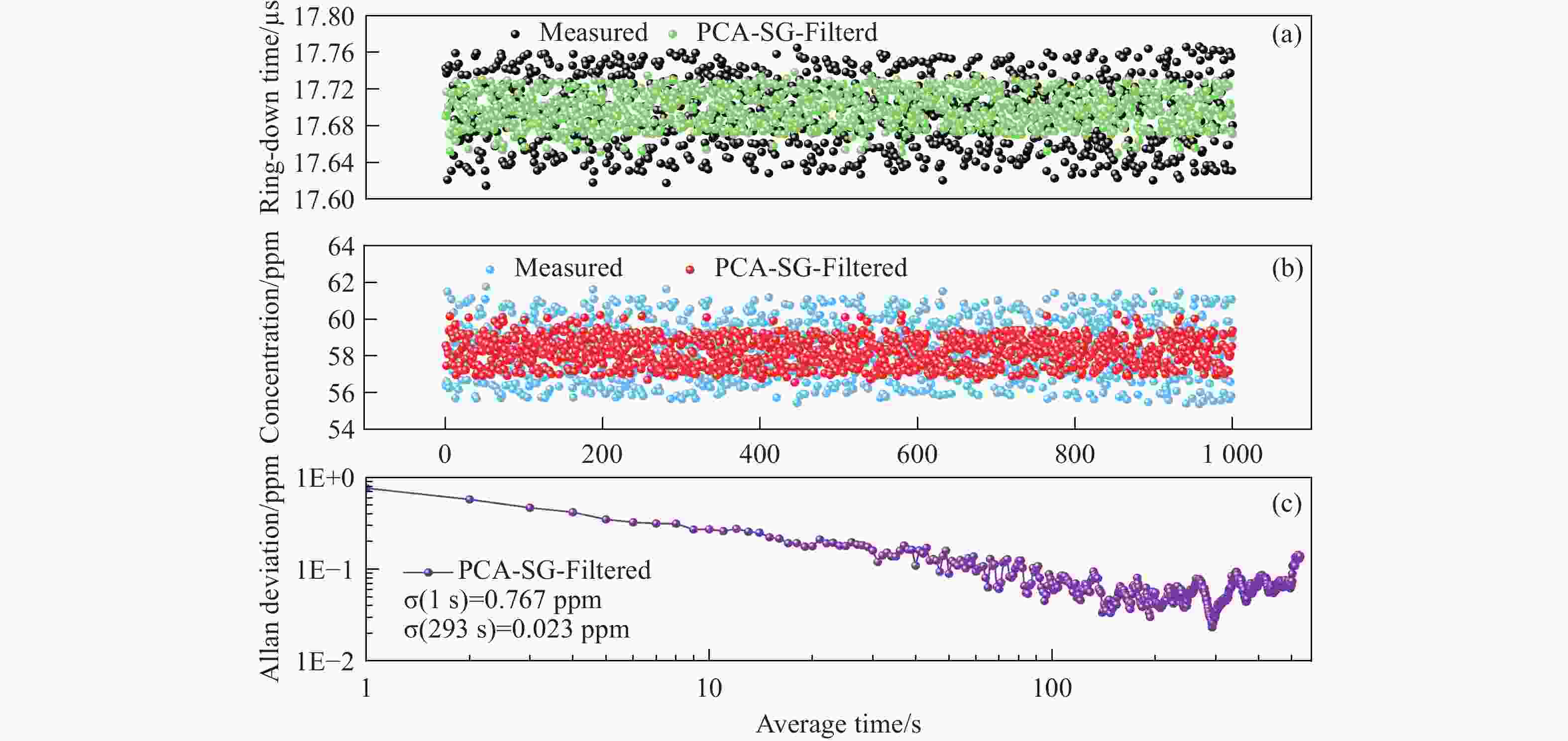
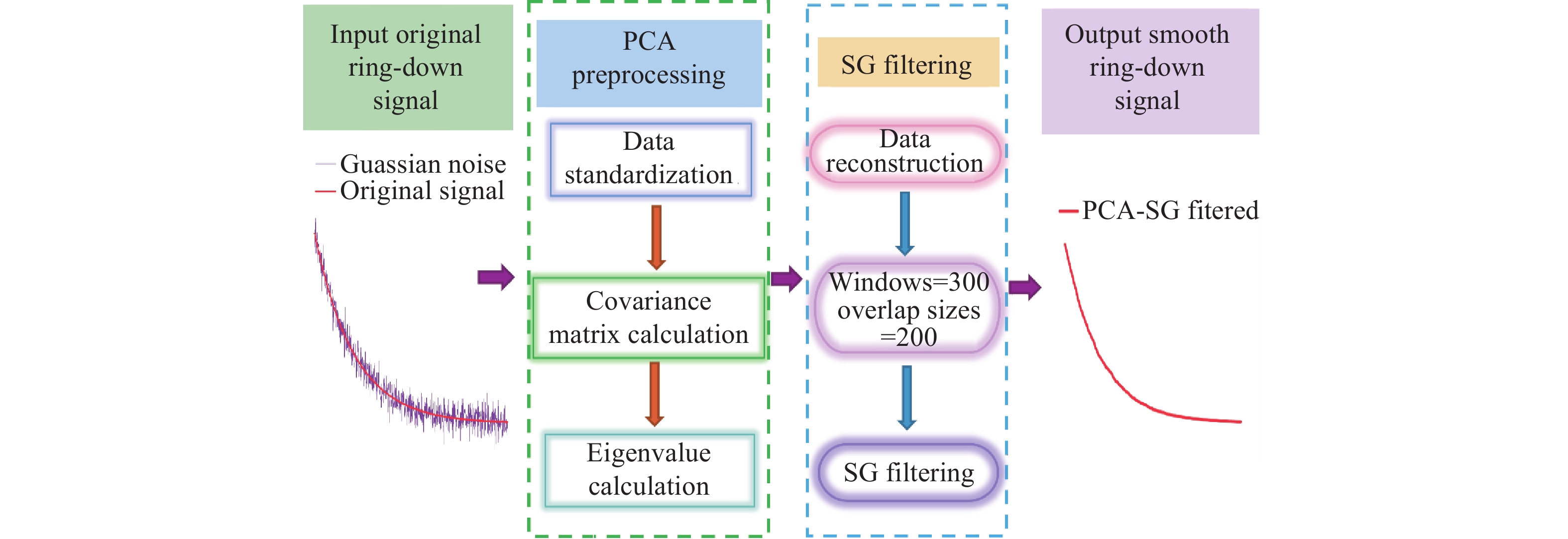
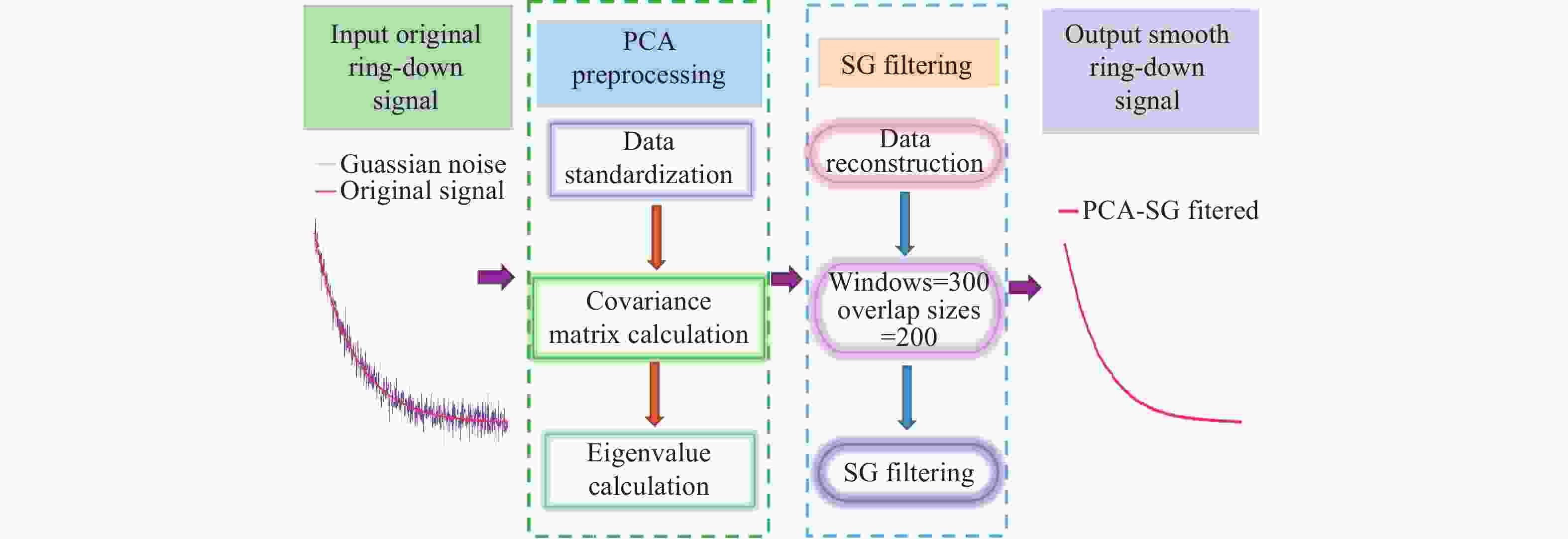
SG滤波器采用多项式最小二乘近似来平滑数据并估计导数,被广泛用于处理含噪声数据。然而,SG滤波器在数据边界和高频段的噪声抑制能力有限,导致信噪比(SNR)明显降低。为解决该问题,本文提出了一种将主成分分析法(PCA)与 SG滤波协同集成的新方法。这种方法避免了SG滤波较大窗口尺寸带来的过度平滑问题。所提出的PCA-SG滤波算法被应用于基于光腔衰荡光谱(CRDS)的CO气体传感系统。通过与移动平均滤波(MAF)、小波变换(WT)、卡尔曼滤波(KF)和SG滤波器进行对比,验证了PCA-SG滤波算法的性能。结果表明,与所评估的其他算法相比,该算法表现出更优异的降噪能力。衰荡信号的信噪比从
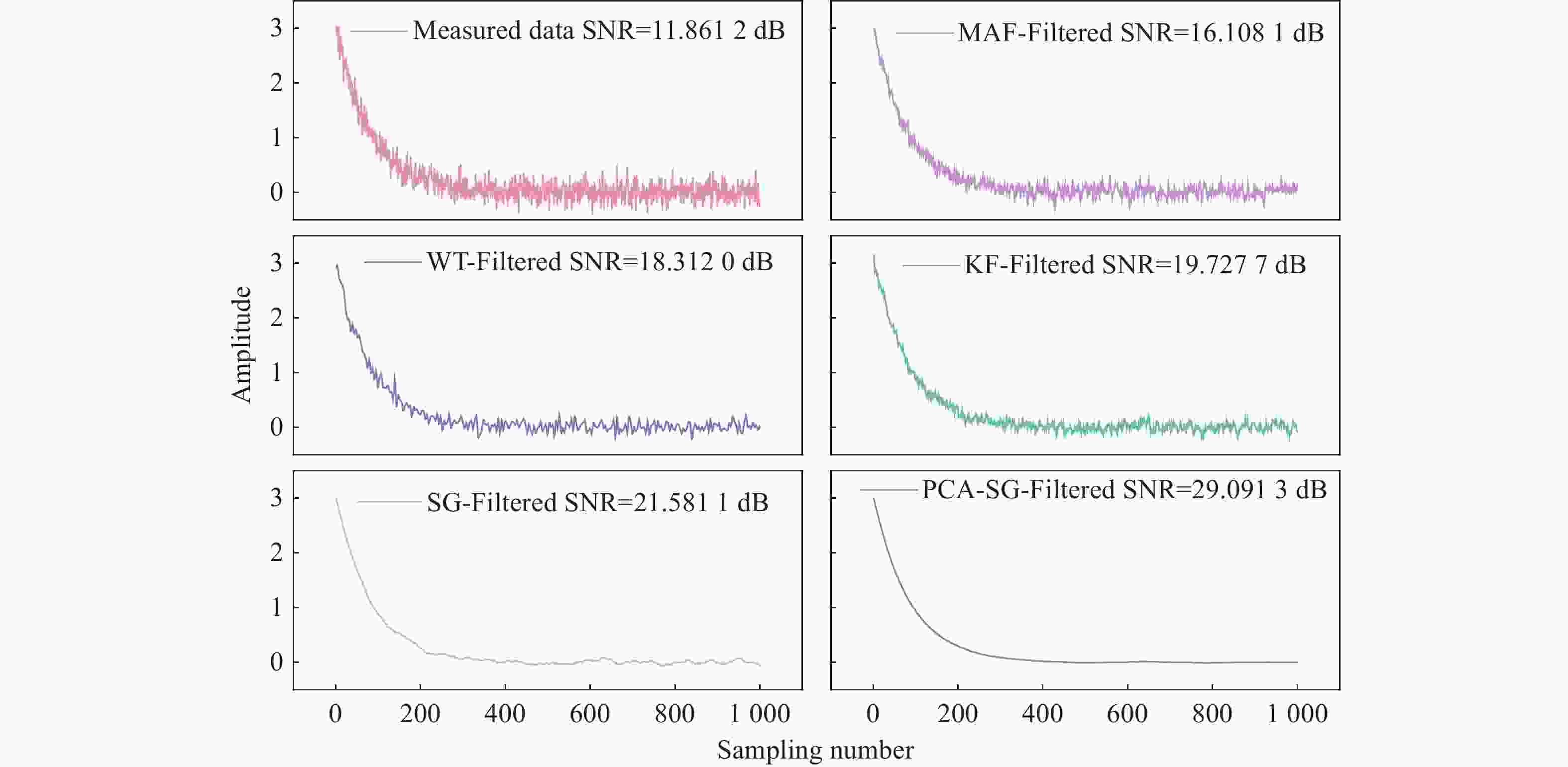
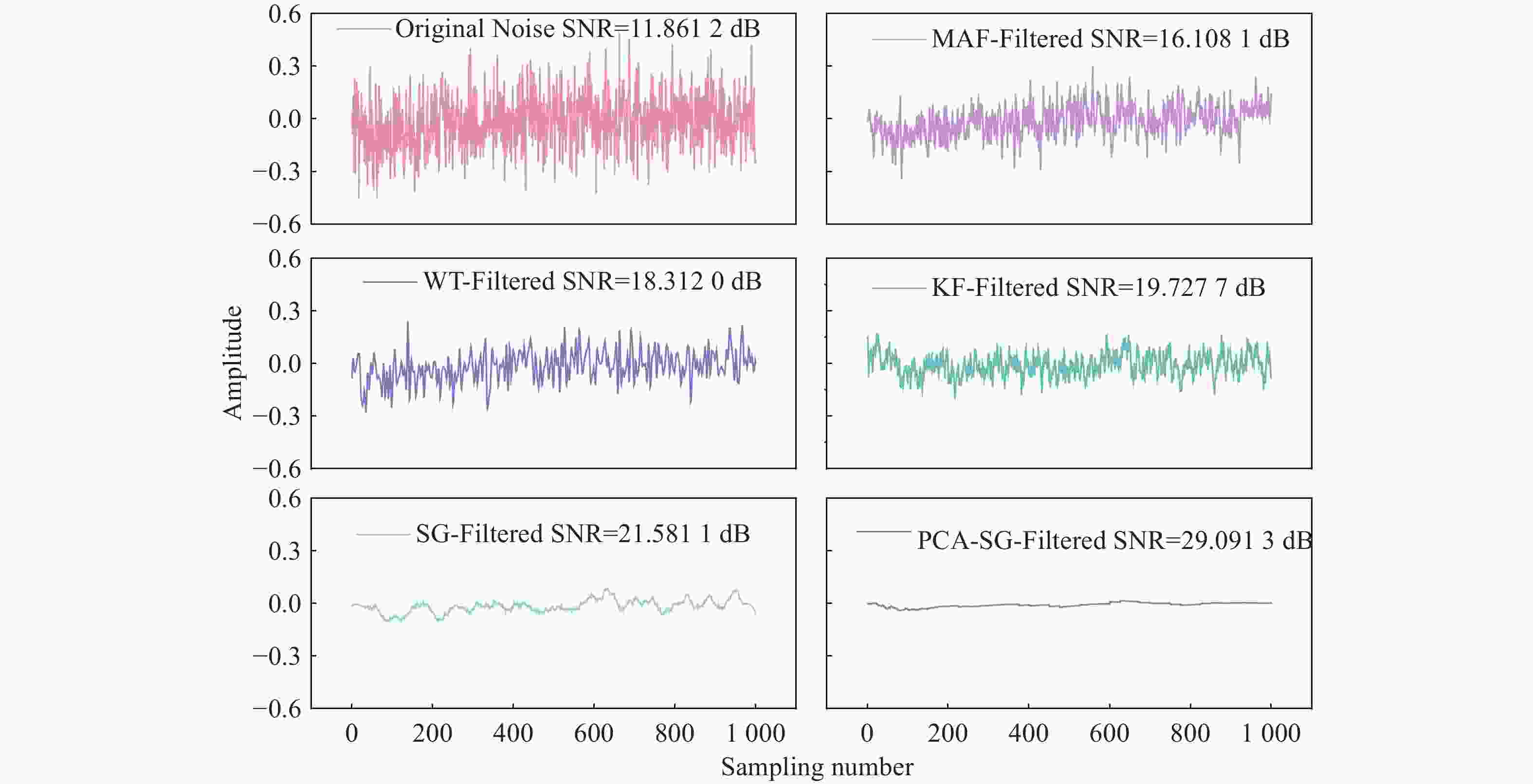
11.8612 dB提升至29.0913 dB,提取的衰荡时间常数的标准差从0.037 µs降低至0.018 µs。这些结果表明,所提出的PCA-SG滤波算法有效提高了衰荡曲线数据的平滑度,证明了其可行性。Abstract:The Savitzky-Golay (SG) filter, which employs polynomial least-squares approximations to smooth data and estimate derivatives, is widely used for processing noisy data. However, noise suppression by the SG filter is recognized to be limited at data boundaries and high frequencies, which can significantly reduce the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). To solve this problem, a novel method synergistically integrating Principal Component Analysis (PCA) with SG filtering is proposed in this paper. This approach avoids the issue of excessive smoothing associated with larger window sizes. The proposed PCA-SG filtering algorithm was applied to a CO gas sensing system based on Cavity Ring-Down Spectroscopy (CRDS). The performance of the PCA-SG filtering algorithm is demonstrated through comparison with Moving Average Filtering (MAF), Wavelet Transformation (WT), Kalman Filtering (KF), and the SG filter. The results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm exhibits superior noise reduction capabilities compared to the other algorithms evaluated. The SNR of the ring-down signal was improved from
11.8612 dB to29.0913 dB, and the standard deviation of the extracted ring-down time constant was reduced from 0.037 µs to 0.018 µs. These results confirm that the proposed PCA-SG filtering algorithm effectively improves the smoothness of the ring-down curve data, demonstrating its feasibility.-
Key words:
- cavity ring-down spectroscopy /
- CO gas sensor /
- PCA /
- SG filter
-
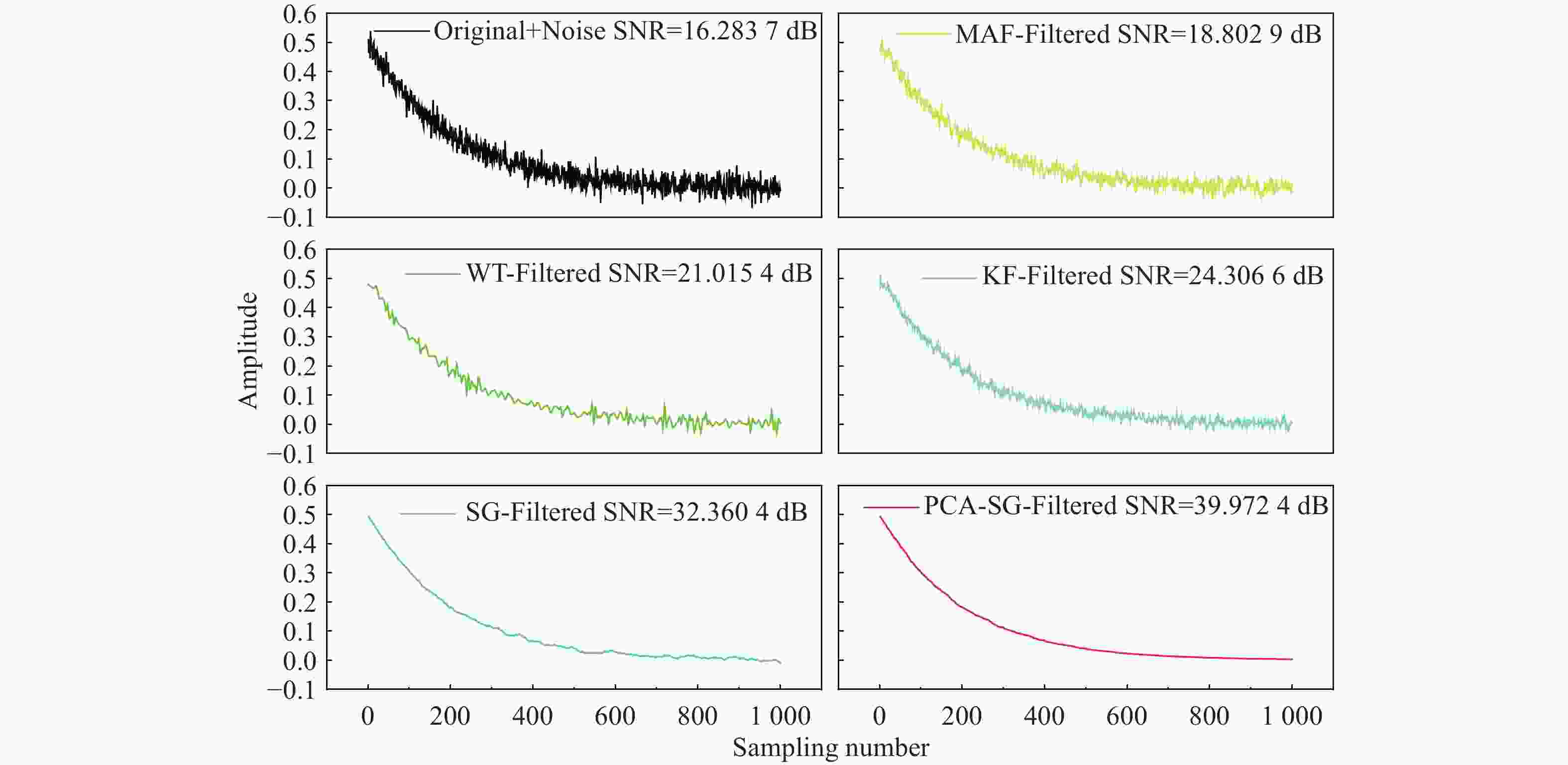
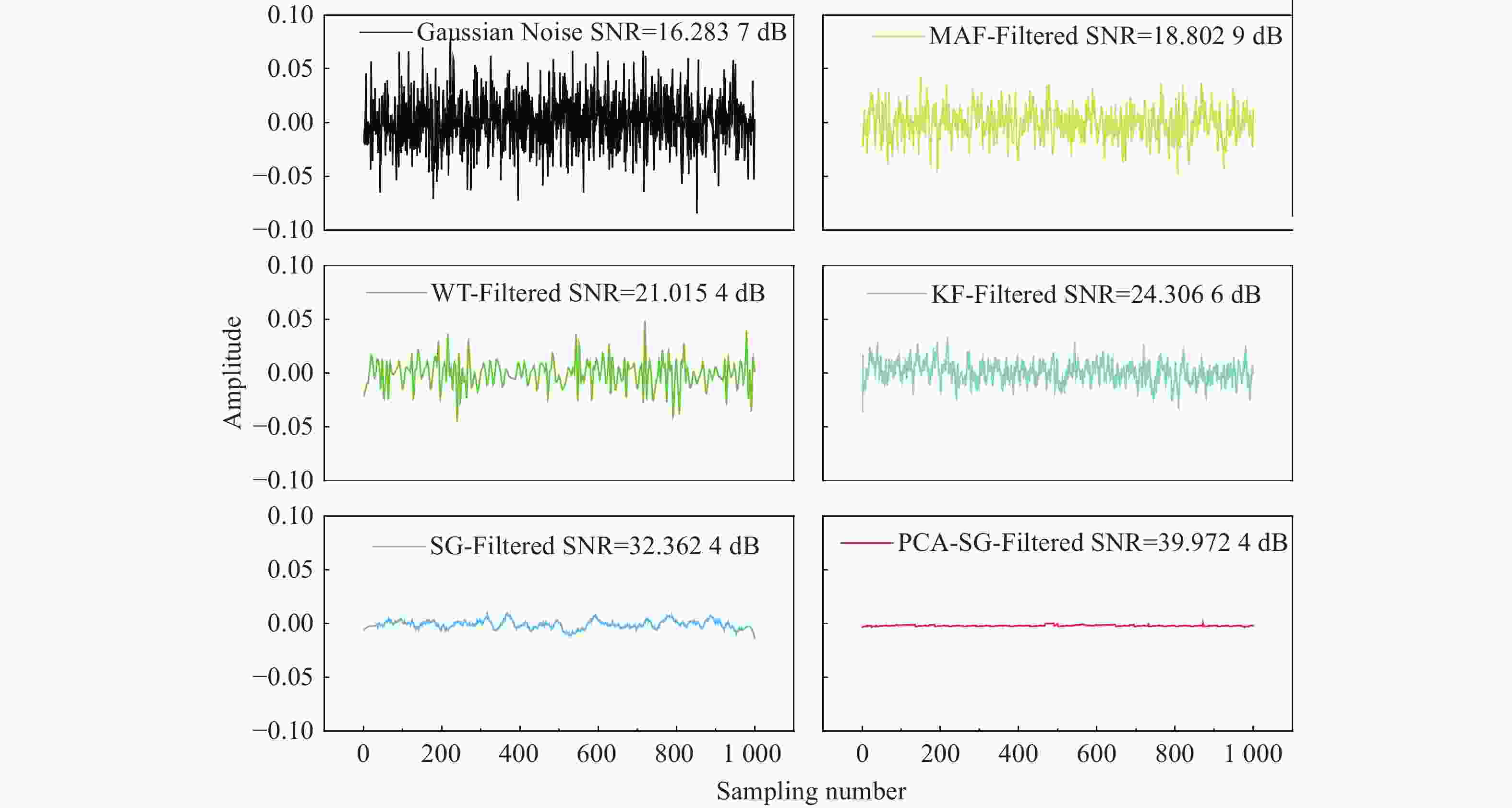
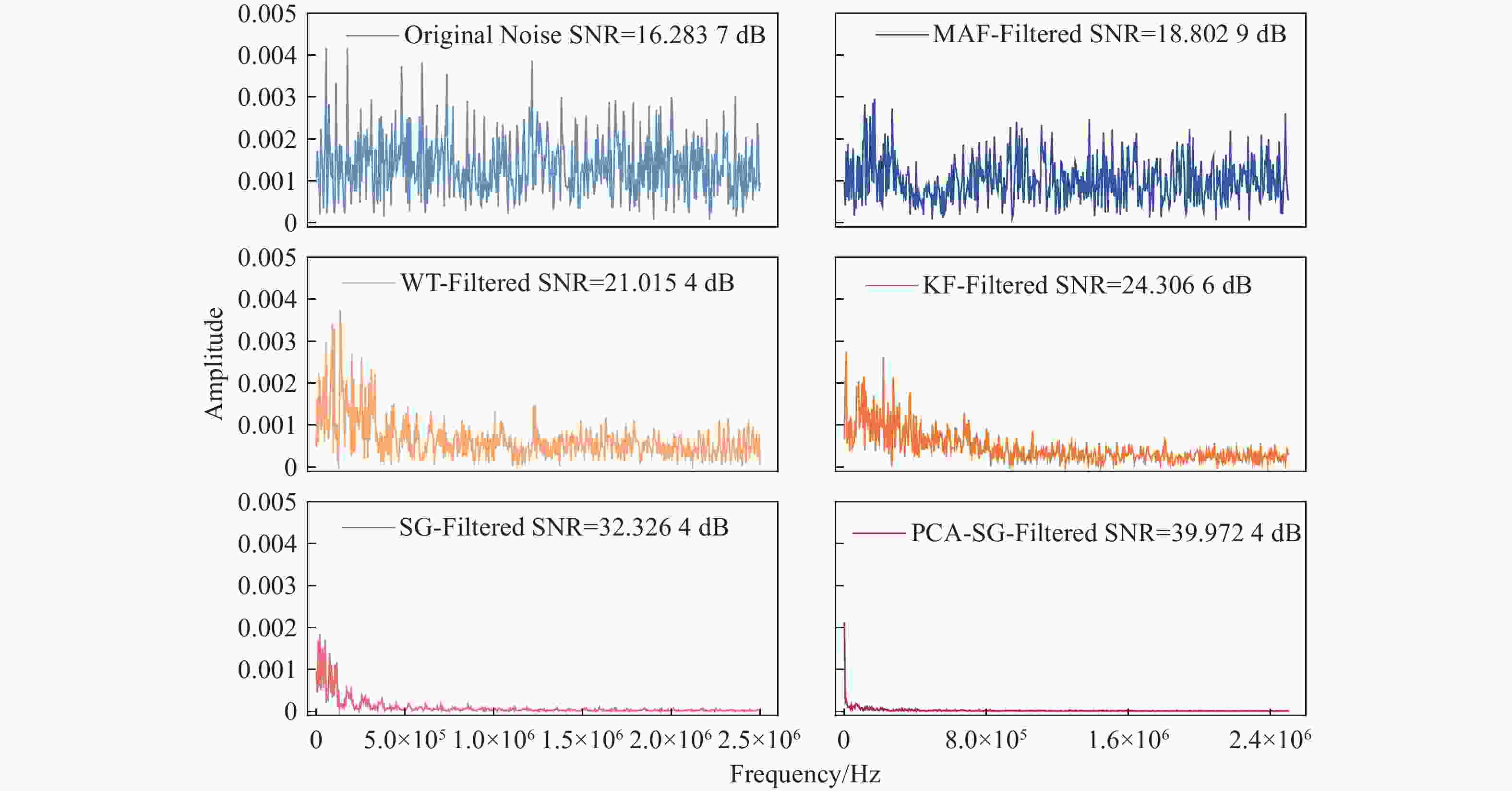
Table 1. Comparison of the SNR、RMSE and R2 for the filtered signal obtained by different filtering algorithms.
Algorithm SNR/dB RMSE R2 Noise signal 16.2837 5.162×10−4 0.96205 MAF(3 times) 18.8029 3.332×10−4 0.97808 WT 21.0154 1.991×10−4 0.98691 KF 24.3066 9.518×10−5 0.99374 SG 32.3624 1.451×10−5 0.99904 PCA-SG 39.9724 2.510×10−6 0.99983 Table 2. Comparison of the SNR、RMSE and R2 for the filtered signal obtained by different filtering algorithms.
Algorithm SNR/dB RMSE R2 Noise signal 11.8612 6.247×10−4 0.96797 MAF(3 times) 16.1081 2.482×10−4 0.97295 WT 18.3120 1.478×10−4 0.98388 KF 19.7277 1.136×10−4 0.98760 SG 21.5811 6.903×10−5 0.99247 PCA-SG 29.0913 1.295×10−5 0.99858 -
[1] BROWN I J, KITIDIS V, REES A P. Simultaneous high-precision, high-frequency measurements of methane and nitrous oxide in surface seawater by cavity ring-down spectroscopy[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2023, 10: 1197727. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1197727 [2] TANG R W, SONG Y SH, ZHANG H D, et al. A wide dynamic range gas analysis model with deep learning based on cavity ring-down spectroscopy[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2025, 433: 137575. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2025.137575 [3] LI Q Y, LI J, WEI X, et al. An exploratory study on online quantification of isoprene in human breath using cavity ringdown spectroscopy in the ultraviolet[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2020, 1131: 18-24. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2020.07.056 [4] AI Y K, LI J, LI Q Y, et al. Cavity ringdown spectroscopy of nitric oxide in the ultraviolet region for human breath test[J]. Journal of Breath Research, 2020, 14(3): 037101. doi: 10.1088/1752-7163/ab8184 [5] XIONG F, PENG ZH M, WANG ZH, et al. Accurate measurement of trace H2S concentration based on cavity ring-down absorption spectroscopy under CO2/CO disturbance[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2023, 72(4): 043302. (in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.72.20221851 [6] LEE J, OH M K. Real-time ultrasensitive detection of ammonia gas using a compact CRDS spectrometer[J]. Applied Optics, 2023, 62(5): 1357-1363. doi: 10.1364/AO.477575 [7] SONG Y SH, ZHAO J L, ZHANG X N, et al. A CNN-assisted mid-infrared high-sensitivity exhaled ammonia sensor based on cavity ring-down spectroscopy[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2024, 401: 135071. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2023.135071 [8] SHEN M H, HWANG C H, WANG W C. Using higher steps phase-shifting algorithms and linear least-squares fitting in white-light scanning interferometry[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2015, 66: 165-173. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2014.09.004 [9] DING F. Least squares parameter estimation and multi-innovation least squares methods for linear fitting problems from noisy data[J]. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2023, 426: 115107. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2023.115107 [10] KALLAPUR A G, BOYSON T K, PETERSEN I R, et al. Nonlinear estimation of ring-down time for a Fabry-Perot optical cavity[J]. Optics Express, 2011, 19(7): 6377-6386. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.006377 [11] ZHENG J Y, DING F. A filtering-based recursive extended least squares algorithm and its convergence for finite impulse response moving average systems[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2024, 34(9): 6063-6082. doi: 10.1002/rnc.7307 [12] GOLESTAN S, RAMEZANI M, GUERRERO J M, et al. Moving average filter based phase-locked loops: performance analysis and design guidelines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2014, 29(6): 2750-2763. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2013.2273461 [13] ZHANG Y J, WU T, ZHANG X ZH, et al. Rayleigh lidar signal denoising method combined with WT, EEMD and LOWESS to improve retrieval accuracy[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(14): 3270. doi: 10.3390/rs14143270 [14] LU X Y, LI Y, CHEN X, et al. Discrete wavelet transform assisted convolutional neural network equalizer for PAM VLC system[J]. Optics Express, 2024, 32(6): 10429-10443. doi: 10.1364/OE.516195 [15] GU L, FEI ZH W, XU X B. Enhancement method of weak Lidar signal based on adaptive variational modal decomposition and wavelet threshold denoising[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2022, 120: 103991. [16] ZHOU SH, SHEN CH Y, ZHANG L, et al. Dual-optimized adaptive Kalman filtering algorithm based on BP neural network and variance compensation for laser absorption spectroscopy[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(22): 31874-31888. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.031874 [17] CHANG R J, CHEN ZH, YIN F L. Distributed kalman filtering for speech dereverberation and noise reduction in acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(24): 31027-31037. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3328610 [18] SCHMID M, RATH D, DIEBOLD U. Why and how savitzky-golay filters should be replaced[J]. ACS Measurement Science Au, 2022, 2(2): 185-196. doi: 10.1021/acsmeasuresciau.1c00054 [19] ZHANG G SH, HAO H, WANG Y CH, et al. Optimized adaptive Savitzky-Golay filtering algorithm based on deep learning network for absorption spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2021, 263: 120187. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2021.120187 [20] LANJEWAR M G, PANCHBHAI K G, PATLE L B. Sugar detection in adulterated honey using hyper-spectral imaging with stacking generalization method[J]. Food Chemistry, 2024, 450: 139322. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.139322 [21] JANA C, BANERJEE S, MAUR S, et al. Mathematical morphology-based sensing of power system disturbances using PCA-aided support vector machine[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(11): 18035-18042. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3389047 [22] CHAKRABORTY S, PATRA I, PAL A, et al. Development of a semi-supervised machine learning based noise filter for quantum cascade laser-coupled mid-infrared spectrometer[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2024, 141: 105452. -





 下载:
下载: