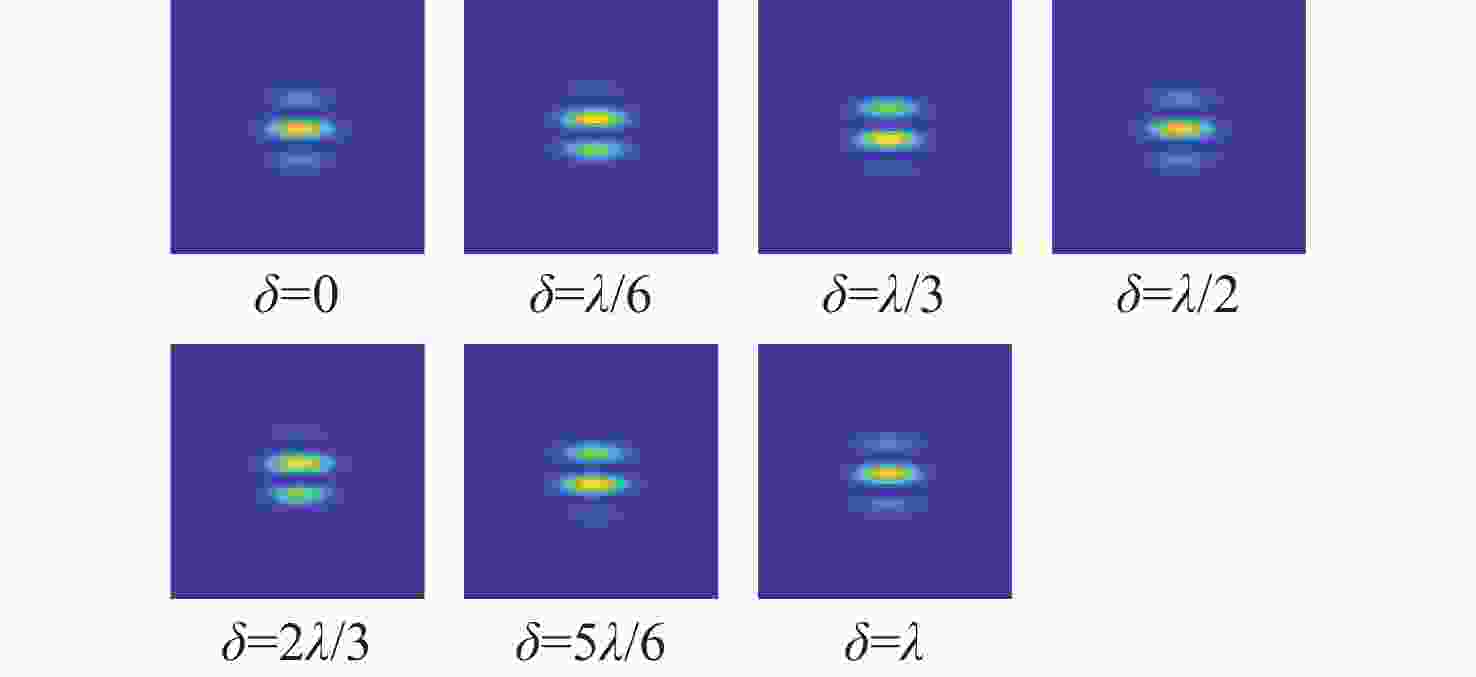
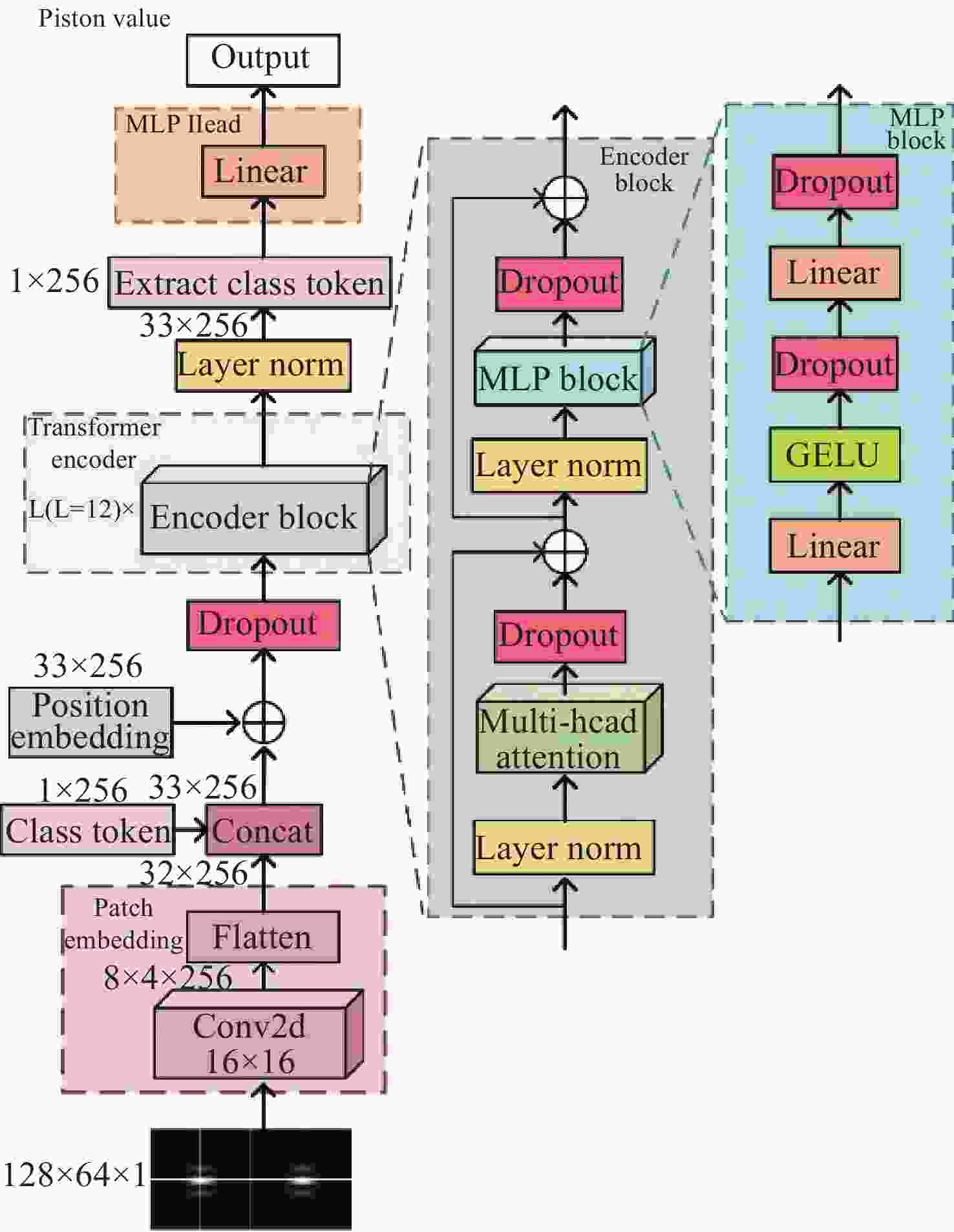
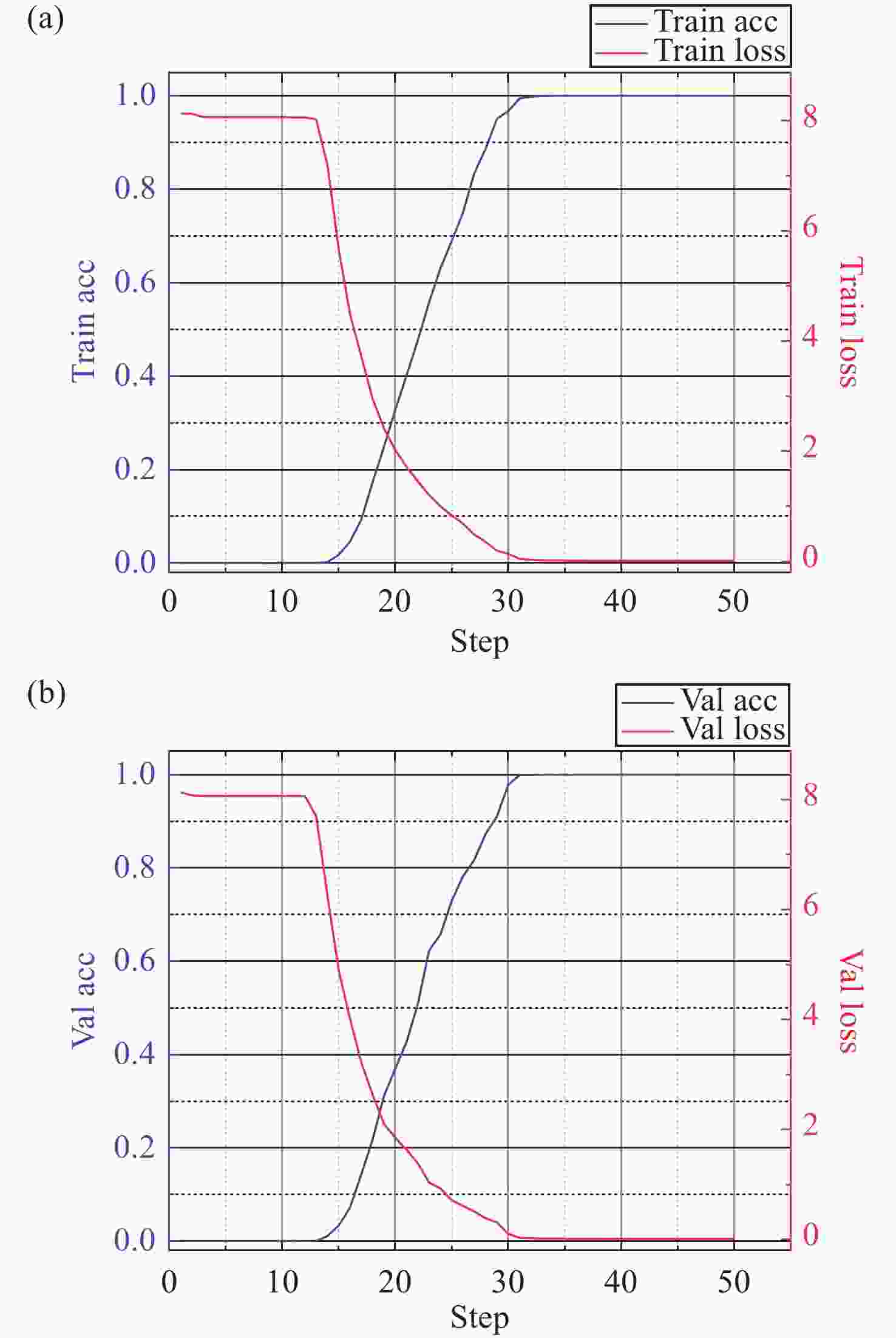
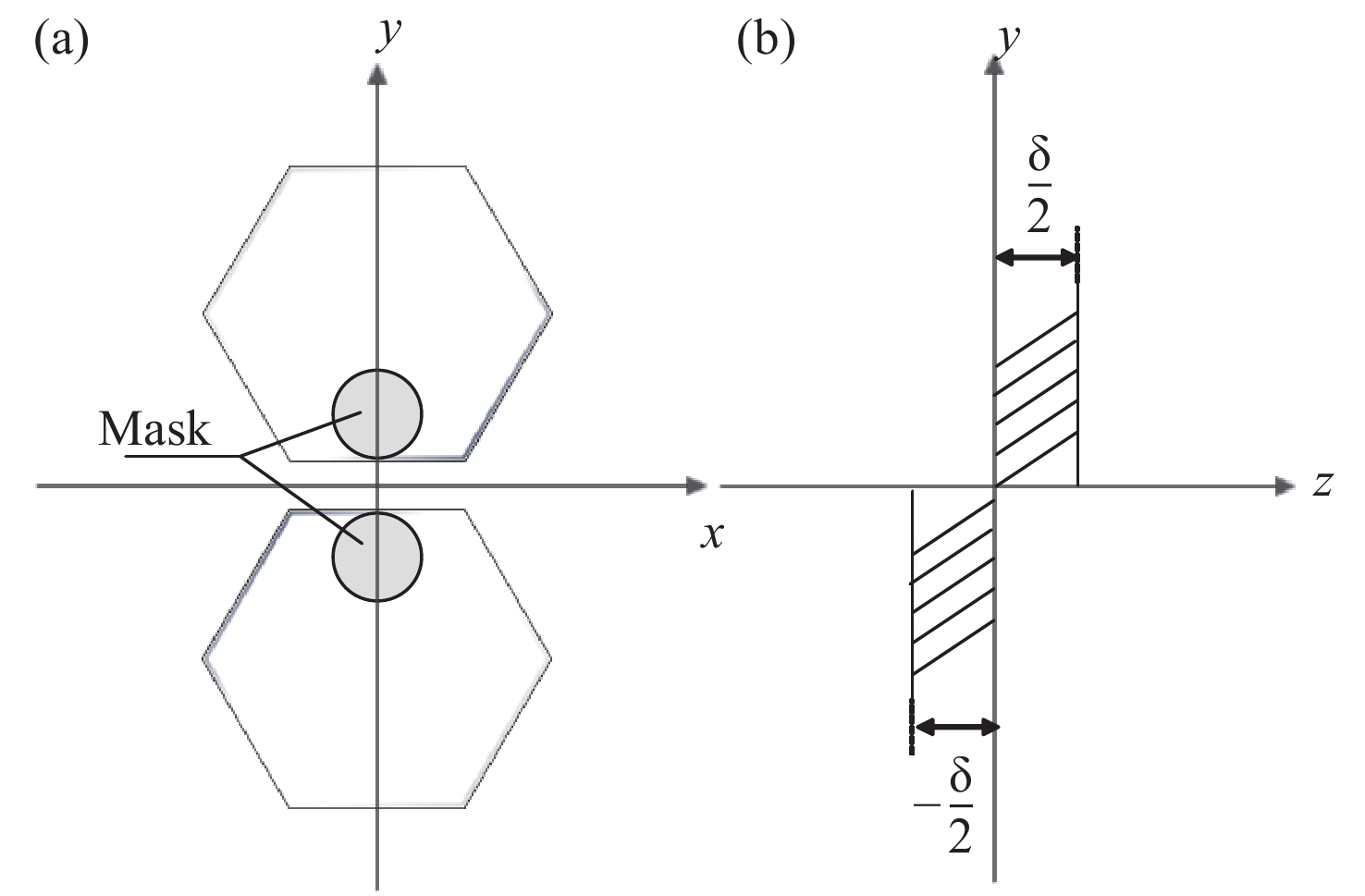
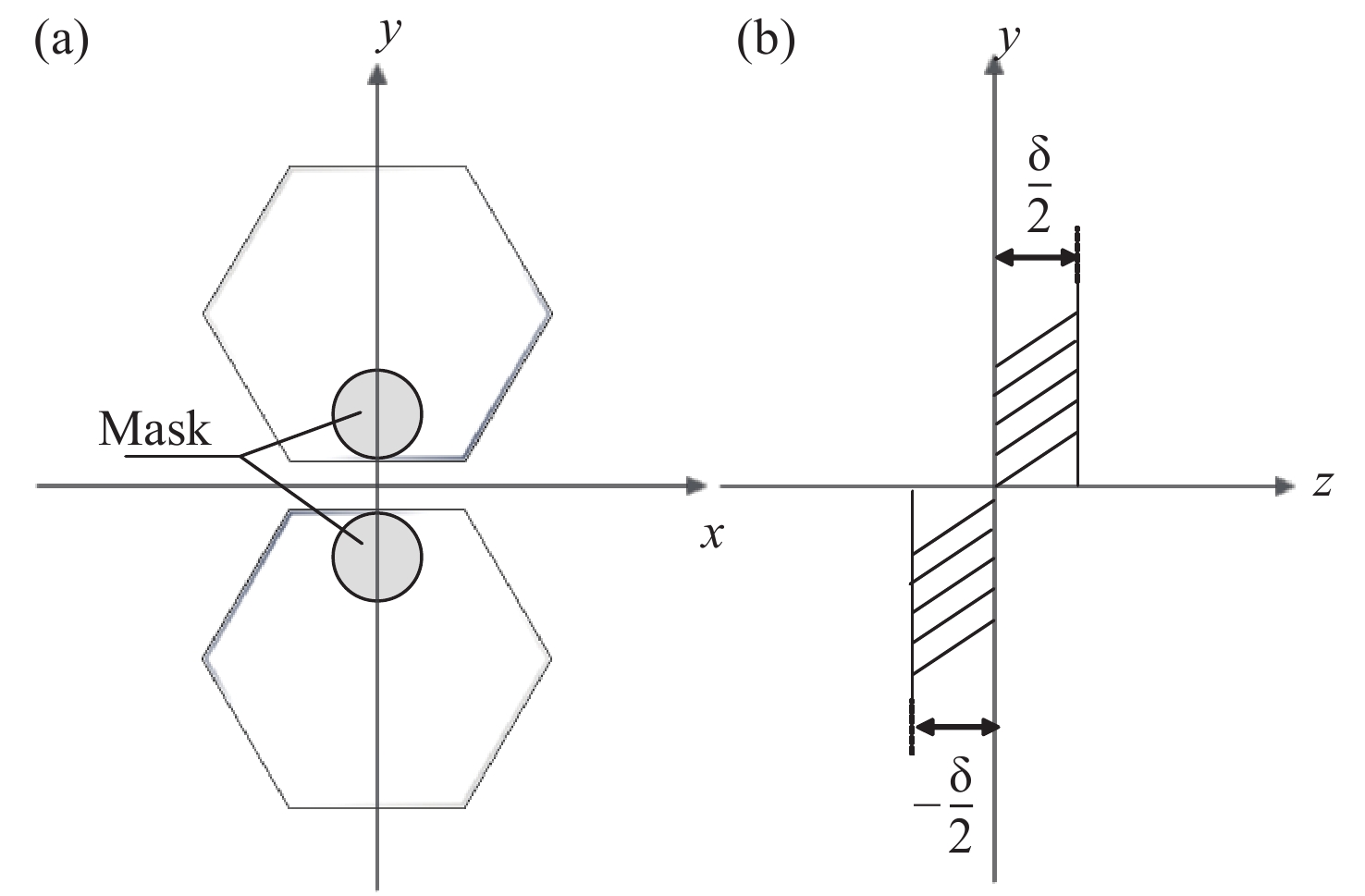
Detection of co-phasing error in segmented mirror based on extended Young’s interferometry combined with Vision Transformer
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2025-0030
-
摘要:
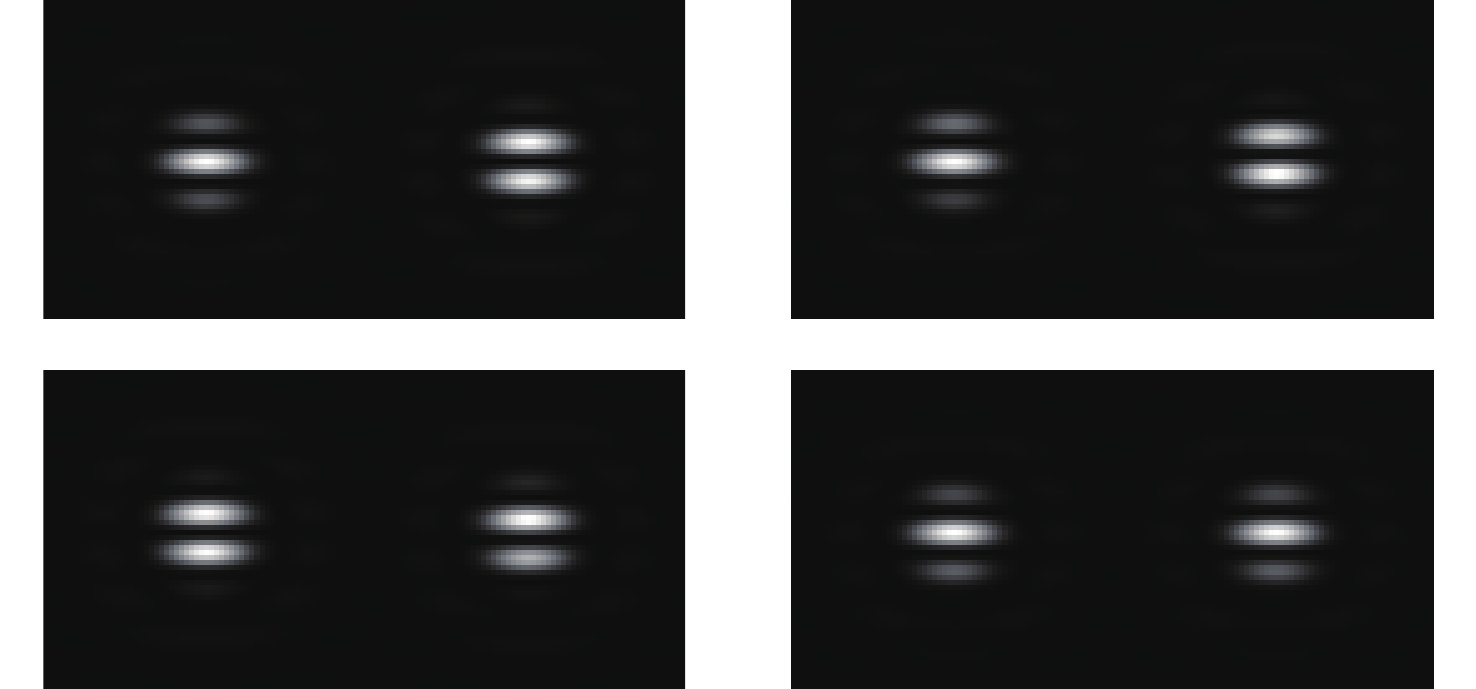
由于单块镜难以达到10 m级水平,拼接镜已成为现代天文研究中不可或缺的工具。然而,为了达到单块镜的成像能力,拼接子镜之间必须保持高度共相,piston误差作为影响分段镜成像质量的关键因素,亟需进行高效、精确的检测。针对目前圆孔衍射结合双波长算法易受偏心误差干扰,传统卷积神经网络(CNN)局部感受野难以捕捉大量程误差下全局特征的问题,本文提出了一种融合扩展杨氏干涉原理与Vision Transformer(ViT)的平移误差检测新方法。通过双孔对称布局抑制偏心误差的干扰,结合589nm和600nm的双波长消模糊算法将检测量程扩展至±7.95 μm,并基于ViT的自注意力机制建模干涉条纹的全局特征,相较于CNN依赖局部卷积核的局限性,ViT 显著提高了对干涉图中周期性变化的灵敏度。仿真结果表明,该方法在高斯噪声(SNR≥15 dB)、泊松噪声(
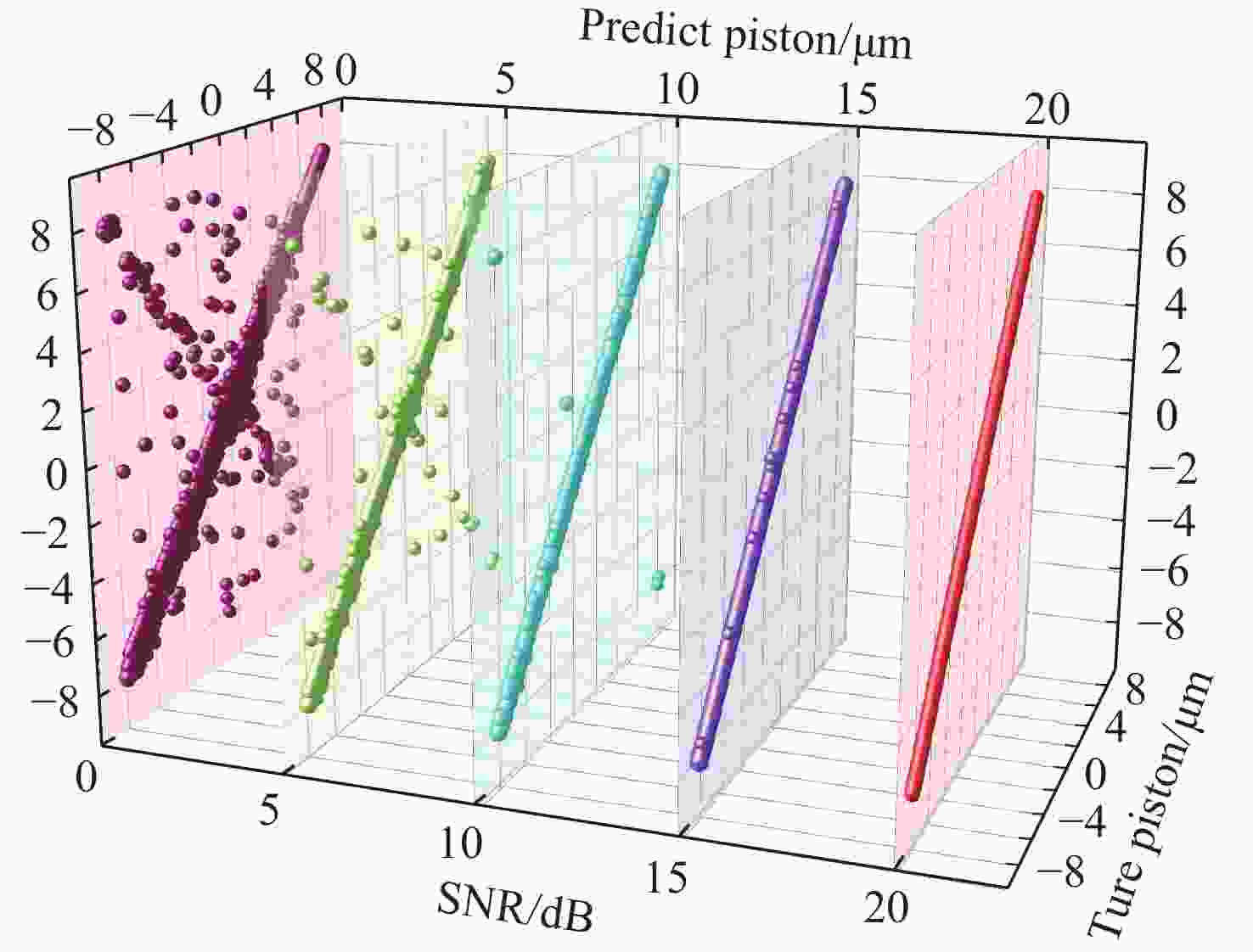
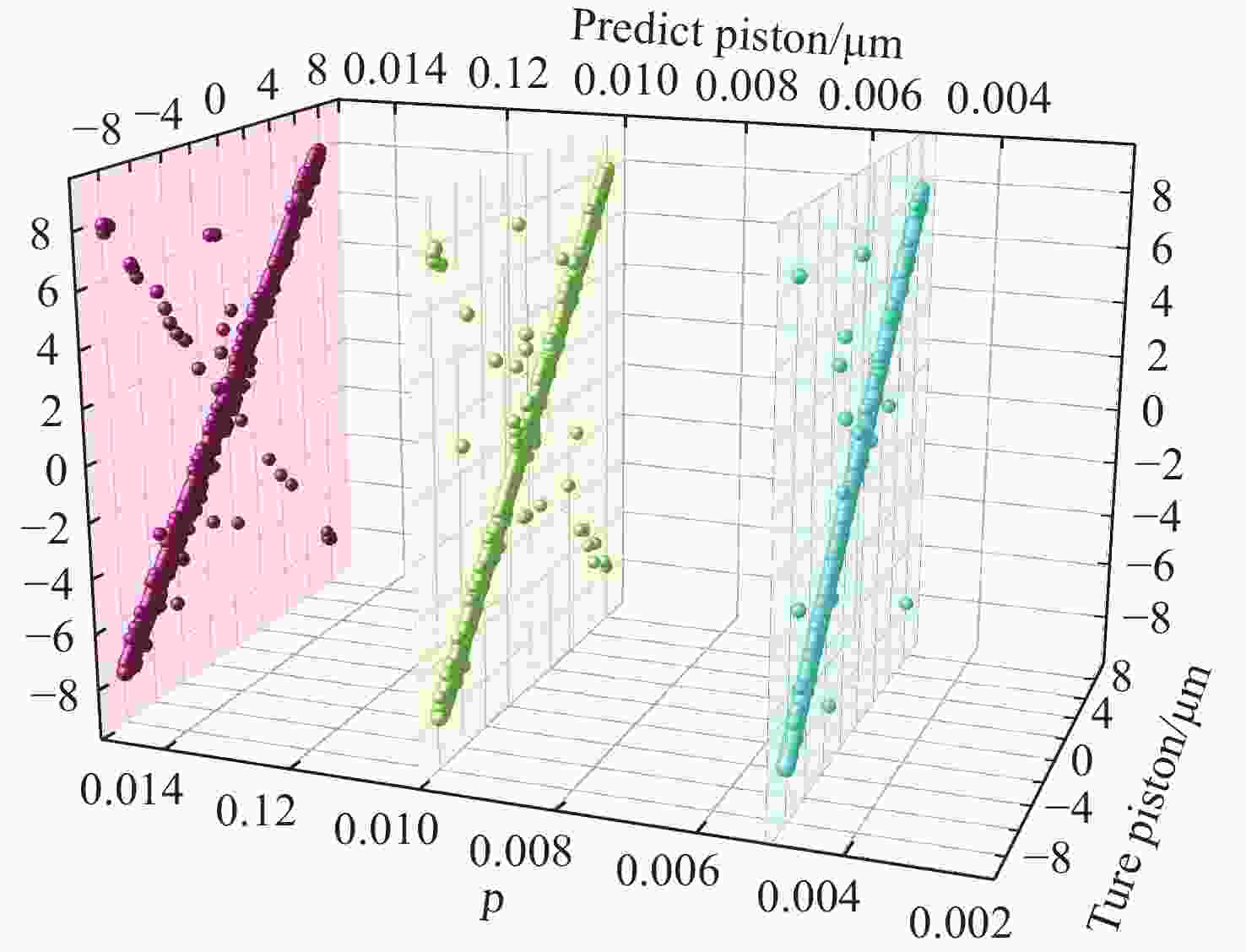
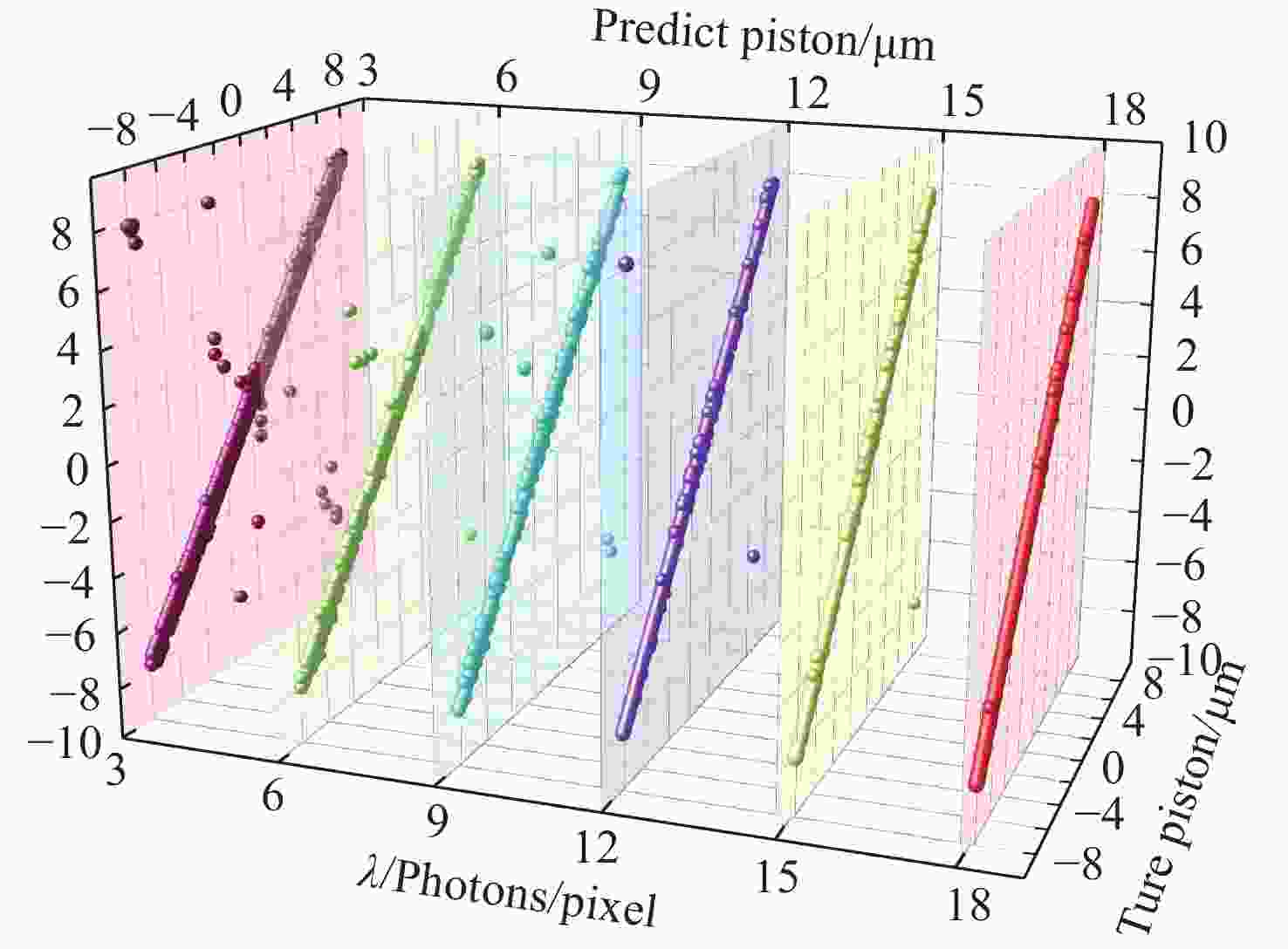
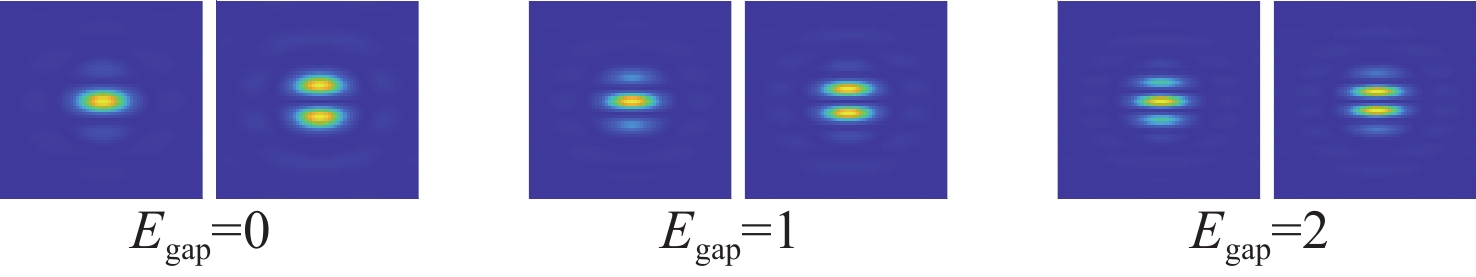
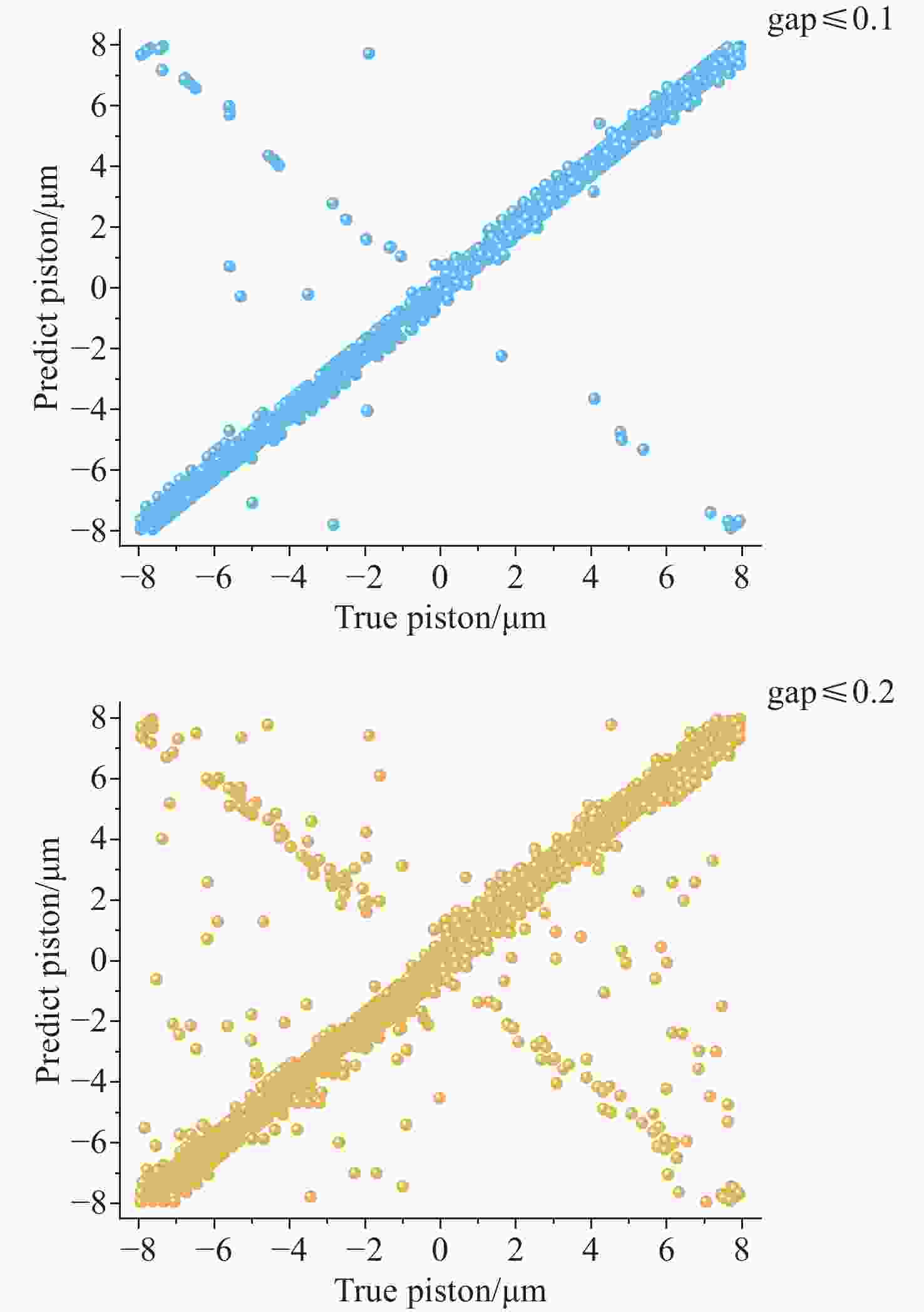
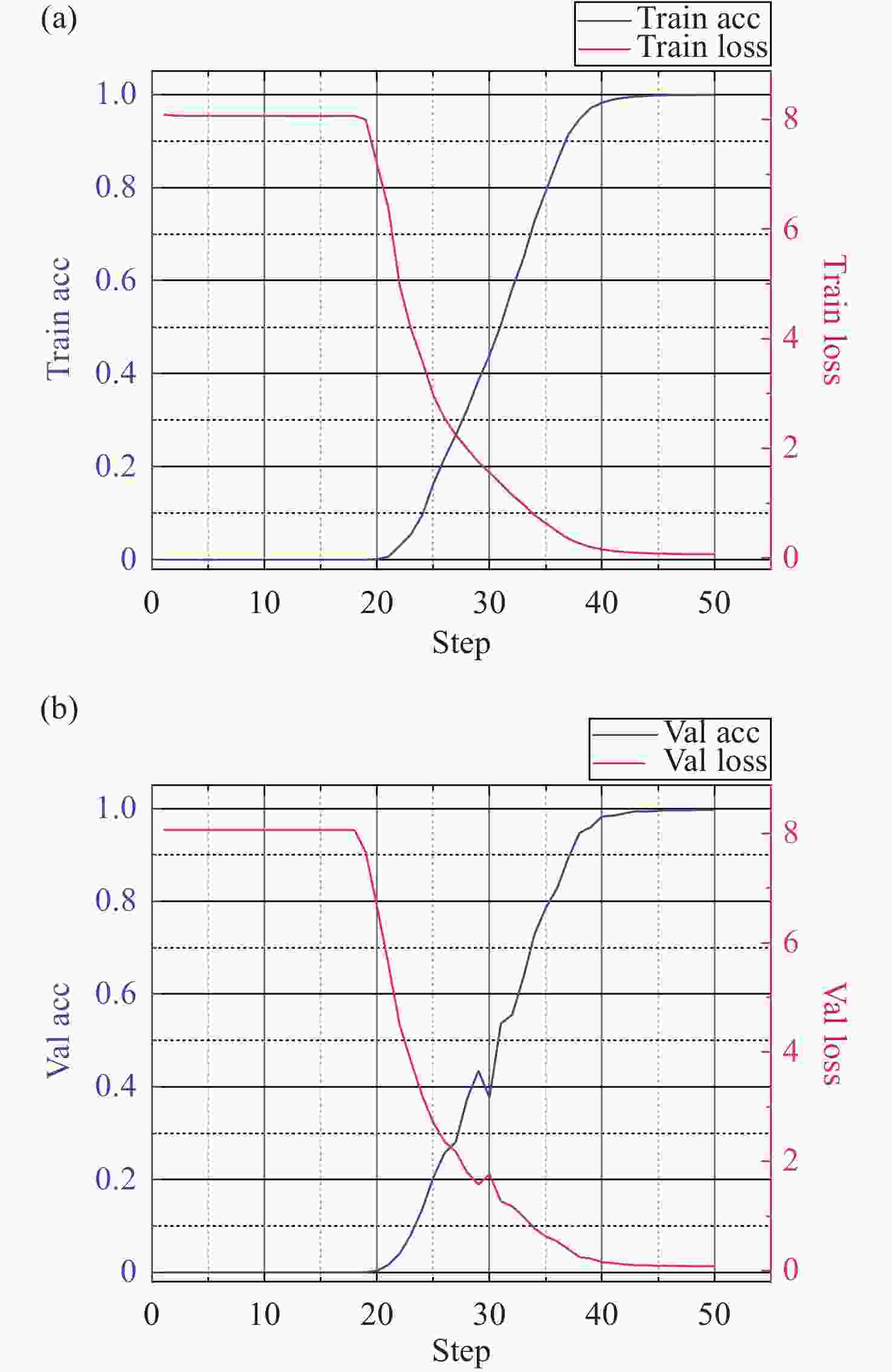
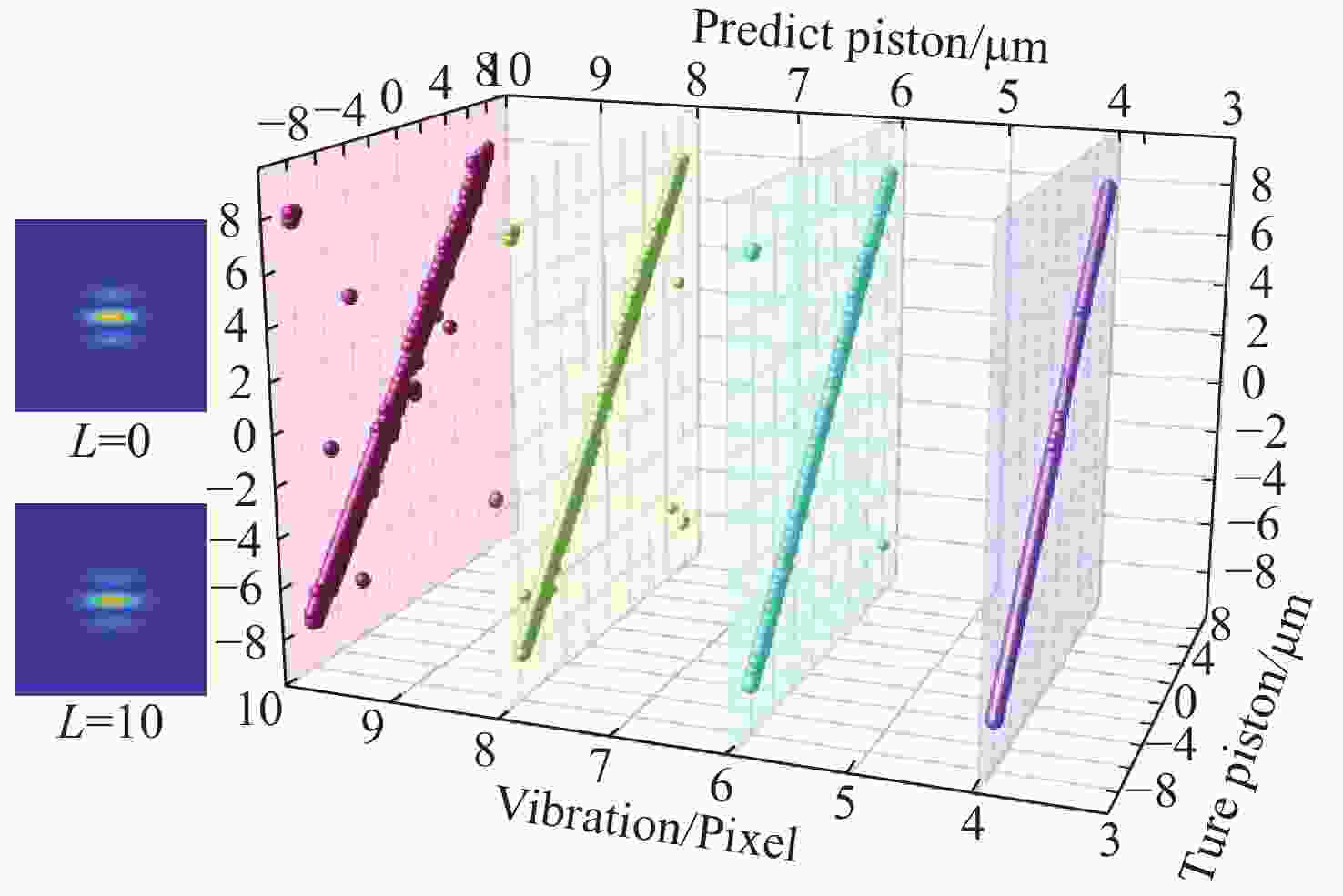
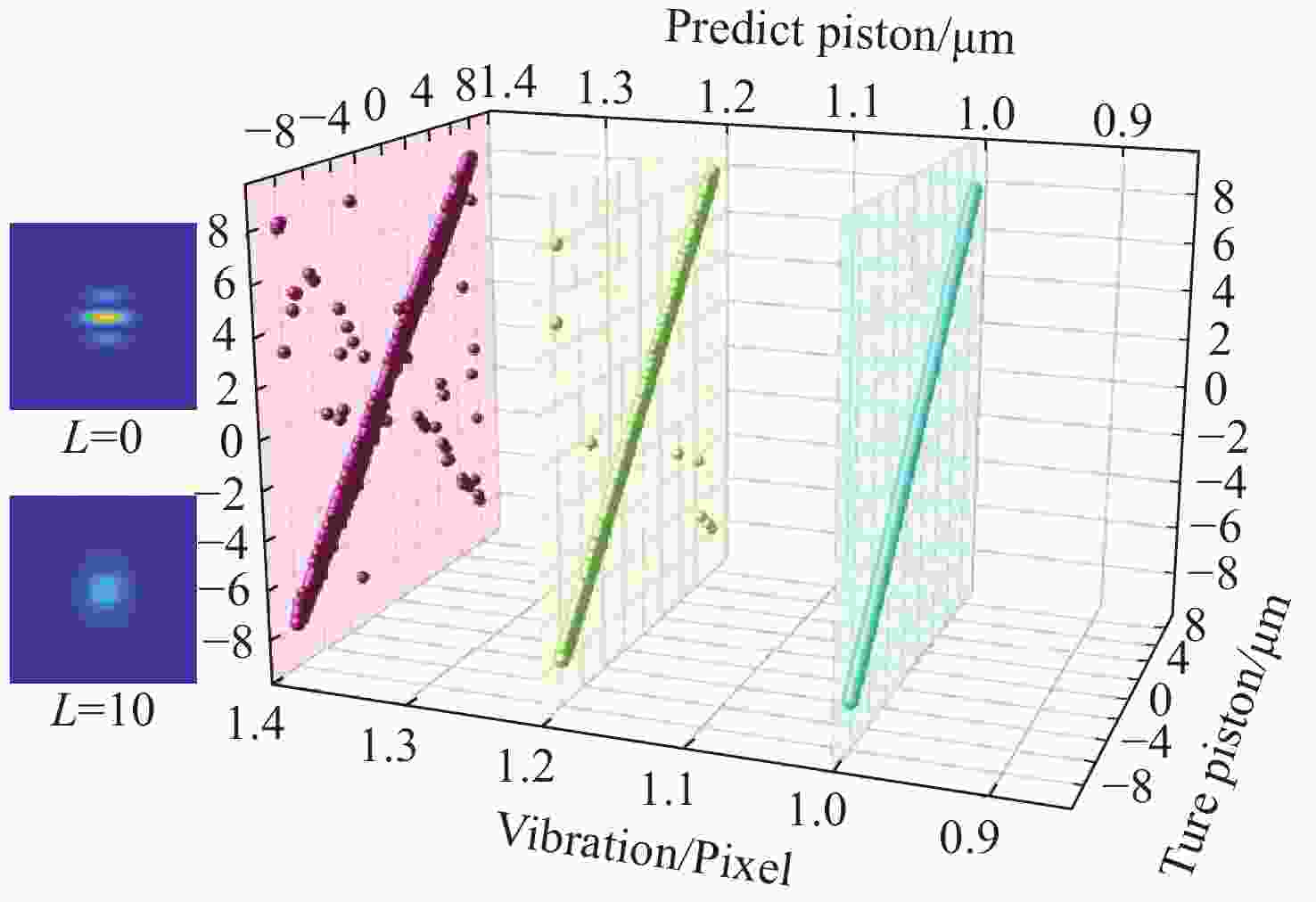
λ ≥9 photons/pixel)及子镜间隙误差(E gap≤ 0.2)干扰下能够在[−7.95 μm, 7.95 μm]范围内实现5 nm的检测精度,同时保持95%以上的准确率,相较于互相关算法检测速度有较大提升。本研究为拼接镜误差检测提供了一种高精度、高鲁棒性的创新技术路线,为高精度天文观测提供了理论支持。Abstract:Due to the inability of manufacturing a single monolithic mirror at the 10-meter scales, segmented mirrors have become indispensable tools in modern astronomical research. However, to match the imaging performance of the monolithic counterpart, the sub-mirrors must maintain precise co-phasing. Piston error critically degrades segmented mirror imaging quality, necessitating efficient and precise detection. To address the limitations that the conventional circular-aperture diffraction with two-wavelength algorithm is susceptible to decentration errors, and the traditional convolutional neural networks (CNNs) struggle to capture global features under large-range piston errors due to their restricted local receptive fields, this paper proposes a method that integrate enhanced Young’s interference principles with a Vision Transformer (ViT) to detect piston error. By suppressing decentration error interference through two symmetrically arranged apertures and extending the measurement range to ± 7.95 μm via a two-wavelength (589 nm/600 nm) algorithm, this approach exploits ViT’s self-attention mechanism to model global characteristics of interference fringes. Unlike CNNs constrained by local convolutional kernels, the ViT significantly improves sensitivity to interferogram periodicity. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves a measurement accuracy of 5 nm (
0.0083 λ 0) across the range of ± 7.95 μm, while maintaining an accuracy exceeding 95% in the presence of Gaussian noise (SNR ≥ 15 dB), Poisson noise (λ ≥ 9 photons/pixel), and sub-mirror gap error (E gap ≤ 0.2) interference. Moreover, the detection speed shows significant improvement compared to the cross-correlation algorithm. This study establishes an accurate, robust framework for segmented mirror error detection, advancing high-precision astronomical observation.-
Key words:
- segmented mirror /
- Co-phasing /
- piston errors /
- ViT /
- Young’s interference principles
-
Table 1. Composition of the dataset containing gap error
Piston tip\tilt gap Train
datasetsValid
datasets[−7.95, 7.95] [−0.03λ, 0.03λ] [0.8r, 1.2r] 47715 15905 Table 2. Comparison with other algorithms
Literature Operating
wavelengthDetection
rangeDetection
accuracyAnti- Decentration
Errorgeneralization
capabilityresponse
timeB. Li,2019 580 nm, 650 nm 2.9 μm 32 nm weak weak 942s Guerra-Ramos
D, 2018λ0=700 nm,
0.930λ0±11λ0 ± 0.0087 λ0-- medium -- X.-F. Ma, 2020 500-600 nm
(λ0=600 nm)(0, 10λ) 0.02λ0 -- medium -- Y.-R. Wang, 2021 632 nm (−0.5λ, 0.5λ) 0.0065 λ-- medium -- A.-K. Yang, 2023 737 nm, 750 nm (−14λ, 14λ) 0.0083 λ0weak medium 75s ViT 589 nm, 600 nm (−13.25λ, 13.25λ) 0.0083 λ0strong strong 26.8s -
[1] AN Q C, LIU X Y, LI H W, et al. Sparse aperture testing method for large-aperture segmented telescopes (invited)[J]. Acta Optica Sinica (Online), 2025, 2(6): 0614001. (in Chinese). [2] VAN DAM M A, LE MIGNANT D, MACINTOSH B A. Performance of the Keck Observatory adaptive-optics system[J]. Applied Optics, 2004, 43(29): 5458-5467. doi: 10.1364/AO.43.005458 [3] PADOVANI P, CIRASUOLO M. The extremely large telescope[J]. Contemporary Physics, 2023, 64(1): 47-64. doi: 10.1080/00107514.2023.2266921 [4] RIEKE G H, WRIGHT G S, BÖKER T, et al. The mid-infrared instrument for the James Webb space telescope, I: introduction[J]. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 2015, 127(953): 584-594. doi: 10.1086/682252 [5] KIM D, CHOI H, BRENDEL T, et al. Advances in optical engineering for future telescopes[J]. Opto-Electronic Advances, 2021, 4(6): 210040. doi: 10.29026/oea.2021.210040 [6] XIE Z L, MA H T, QI B, et al. Experimental demonstration of enhanced resolution of a Golay3 sparse-aperture telescope[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2017, 15(4): 041101. doi: 10.3788/COL201715.041101 [7] LI Y, WANG S Q, RAO C H. Dispersed-fringe-accumulation-based left-subtract-right method for fine co-phasing of a dispersed fringe sensor[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(15): 4267-4273. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.004267 [8] ZHANG Y F, XIAN H. Piston sensing via a dispersed fringe sensor with a merit-function-based active scanning algorithm at low light levels[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2019, 17(12): 121101. doi: 10.3788/COL201917.121101 [9] WANG X H, FU Q, HUANG L H, et al. Experimental research on application of Hartmann micro-lens array in coherent beam combination of two-dimensional laser array[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2012, 10(8): 081402. doi: 10.3788/COL201210.081402 [10] ZHANG D, ZHANG X B, XU S Y, et al. Simplified Phase Diversity algorithm based on a first-order Taylor expansion[J]. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(28): 7872-7877. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.007872 [11] LI B, LIU Y L, YANG A K, et al. Study on the co-phasing simulation and experimental of segmented mirror based on broadband light[J]. Journal of Modern Optics, 2024, 71(1-3): 42-51. doi: 10.1080/09500340.2024.2394954 [12] DUMONT M, CORREIA C M, SAUVAGE J F, et al. Phasing segmented telescopes via deep learning methods: application to a deployable CubeSat[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2024, 41(3): 489-499. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.506182 [13] GUERRA-RAMOS D, DÍAZ-GARCÍA L, TRUJILLO-SEVILLA J, et al. Piston alignment of segmented optical mirrors via convolutional neural networks[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(17): 4264-4267. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.004264 [14] GUERRA-RAMOS D, TRUJILLO-SEVILLA J, RODRÍGUEZ-RAMOS J M. Global piston restoration of segmented mirrors with recurrent neural networks[J]. OSA Continuum, 2020, 3(5): 1355-1363. doi: 10.1364/OSAC.387358 [15] LI D Q, XU S Y, WANG D, et al. Large-scale piston error detection technology for segmented optical mirrors via convolutional neural networks[J]. Optics Letters, 2019, 44(5): 1170-1173. doi: 10.1364/OL.44.001170 [16] LI D Q, WANG D, LI J Q. Large range of a high-precision, independent, sub-mirror three-dimensional co-phase error sensing and correction method via a mask and population algorithm[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24(1): 279. doi: 10.3390/s24010279 [17] LI D Q, WANG D, YAN D J. Piston error automatic correction for segmented mirrors via deep reinforcement learning[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24(13): 4236. doi: 10.3390/s24134236 [18] MA X F, XIE Z L, MA H T, et al. Piston sensing of sparse aperture systems with a single broadband image via deep learning[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(11): 16058-16070. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.016058 [19] MA X F, XIE Z L, MA H T, et al. Piston sensing for sparse aperture systems with broadband extended objects via a single convolutional neural network[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 128: 106005. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2020.106005 [20] HUI M, LI W Q, LIU M, et al. Object-independent piston diagnosing approach for segmented optical mirrors via deep convolutional neural network[J]. Applied Optics, 2020, 59(3): 771-778. doi: 10.1364/AO.379194 [21] HUI M, LI W Q, WU Y, et al. Breadth-first piston diagnosing approach for segmented mirrors through supervised learning of multiple-wavelength images[J]. Applied Optics, 2020, 59(32): 9963-9970. doi: 10.1364/AO.402943 [22] WANG Y R, ZHANG C Y, GUO L, et al. Decoupled object-independent image features for fine phasing of segmented mirrors using deep learning[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(18): 4681. doi: 10.3390/rs14184681 [23] LI B, YANG A K, LI Y B, et al. Research on co-phasing detection of segmented mirror based on convolutioned neural networks[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2023, 167: 109737. [24] CHENG K K, WANG S Q, LIU X S, et al. Co-phase error detection for segmented mirrors based on far-field information and transfer learning[J]. Photonics, 2024, 11(11): 1064. doi: 10.3390/photonics11111064 -





 下载:
下载: