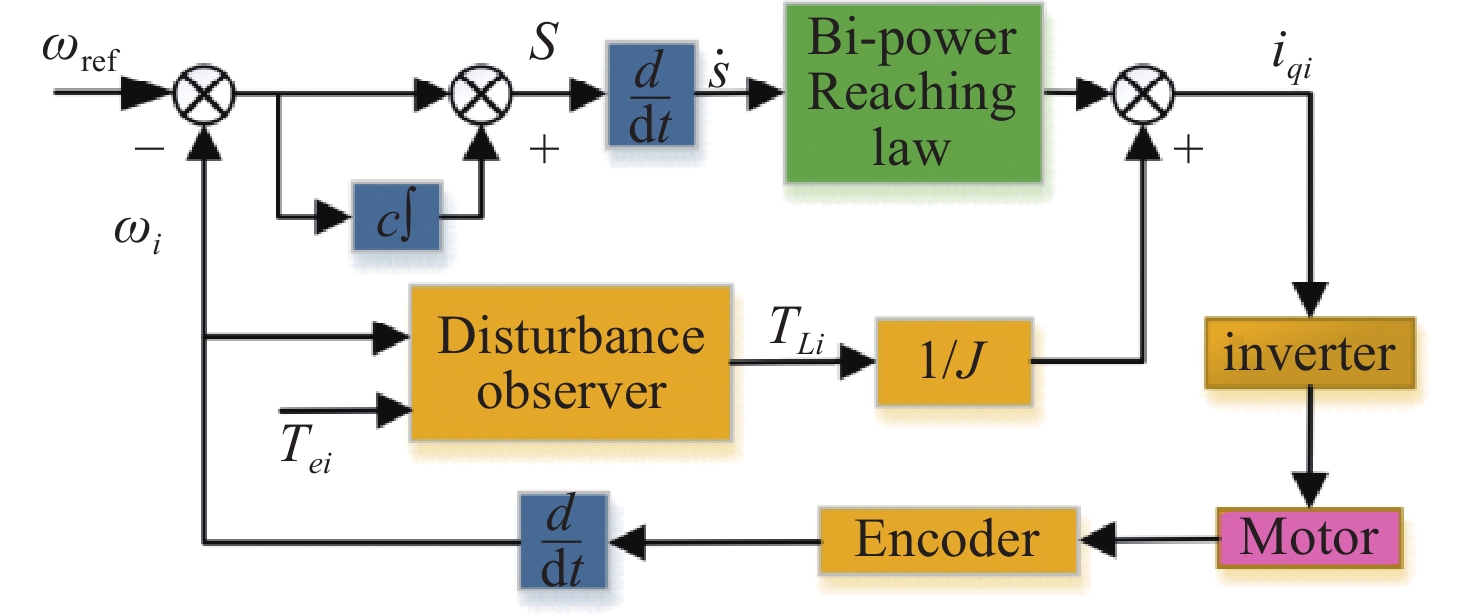
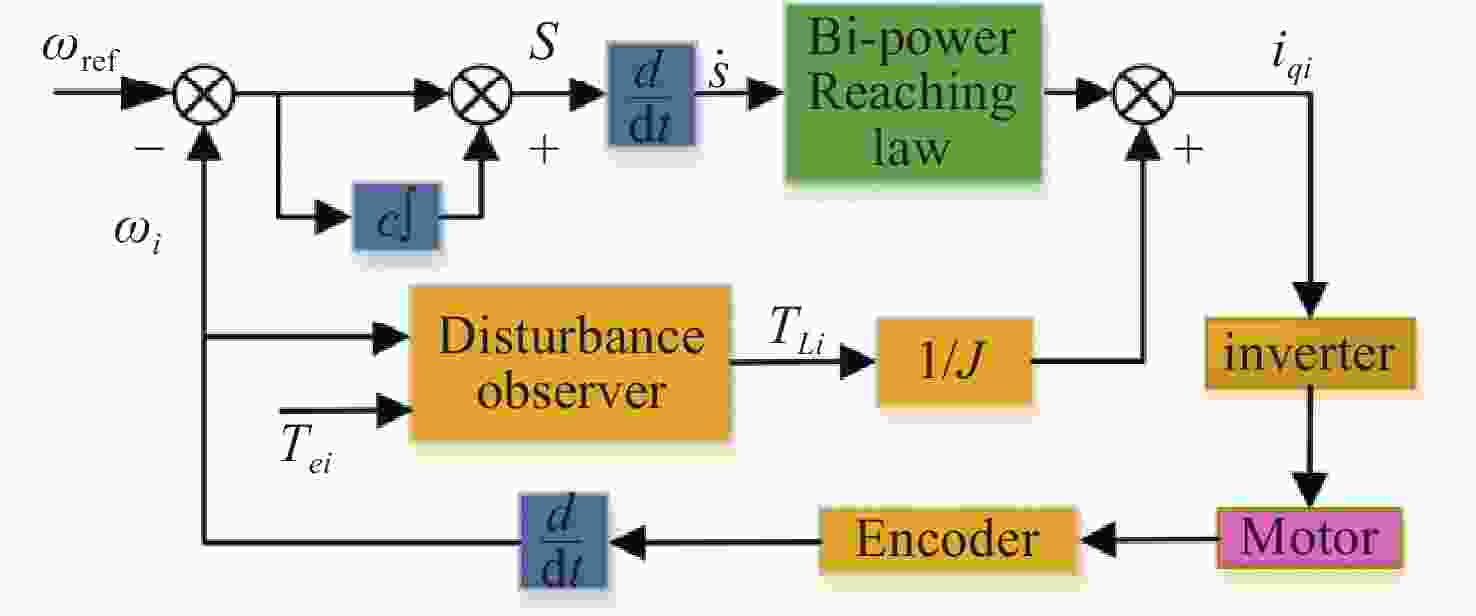
A sliding-mode control of a Dual-PMSMs synchronization driving method
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2022-0026
-
摘要:
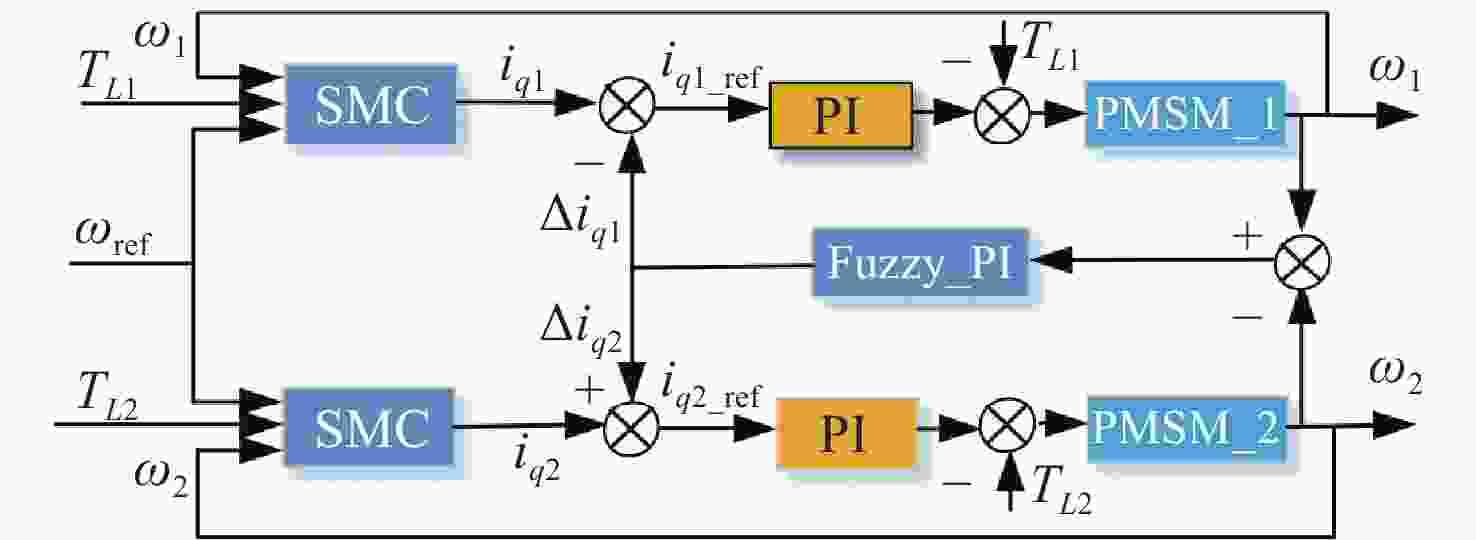
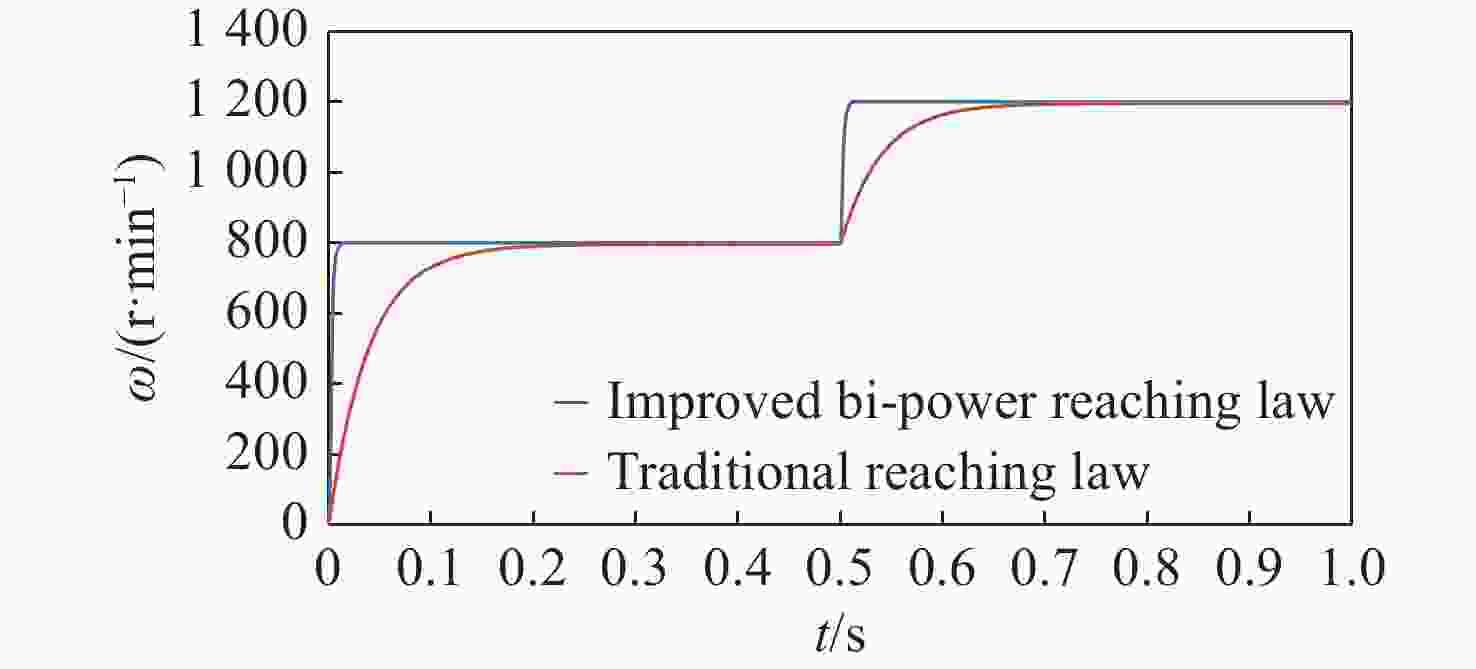
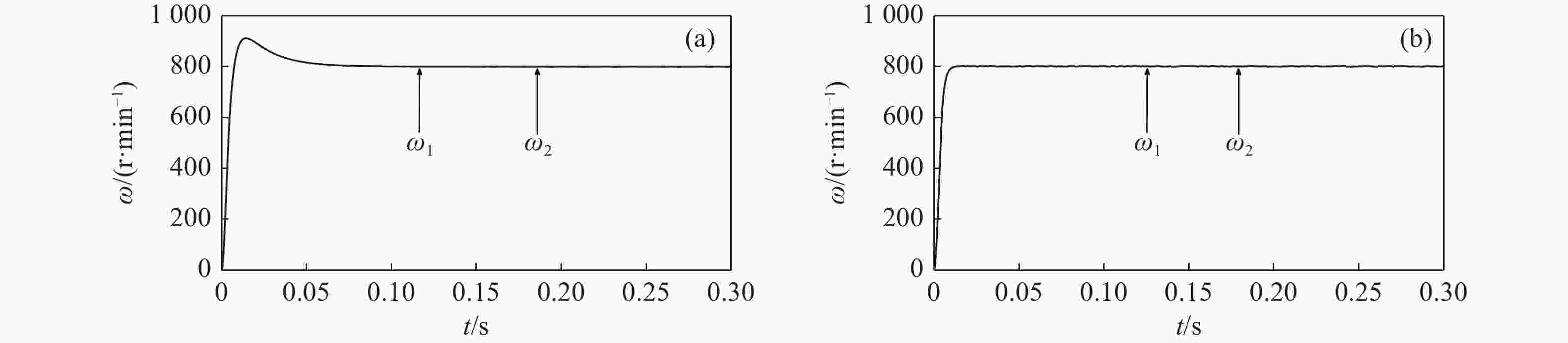
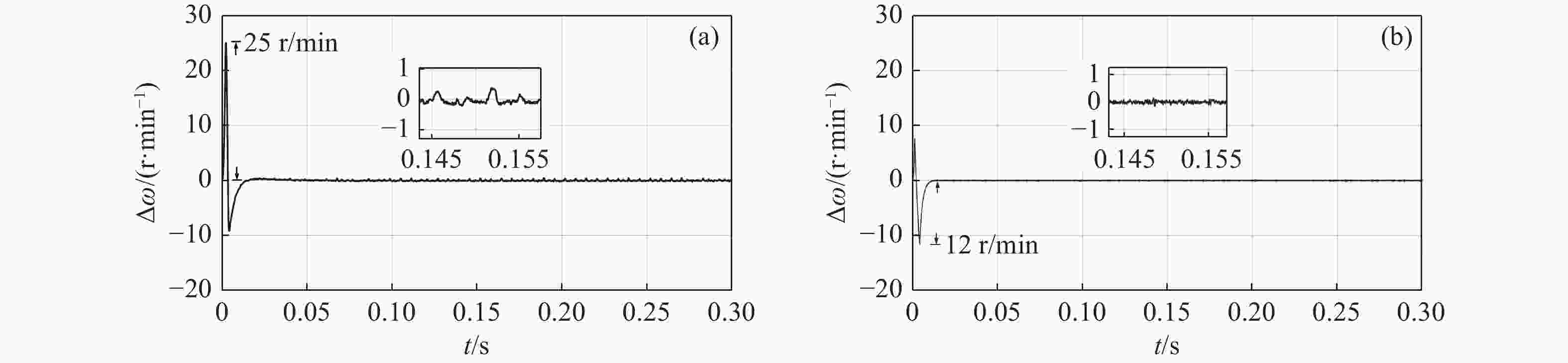
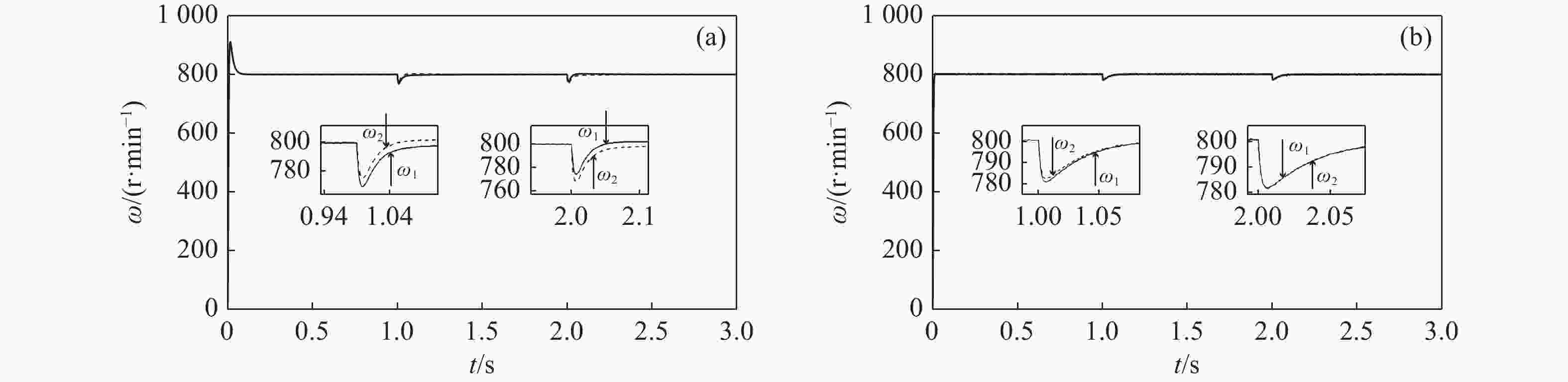
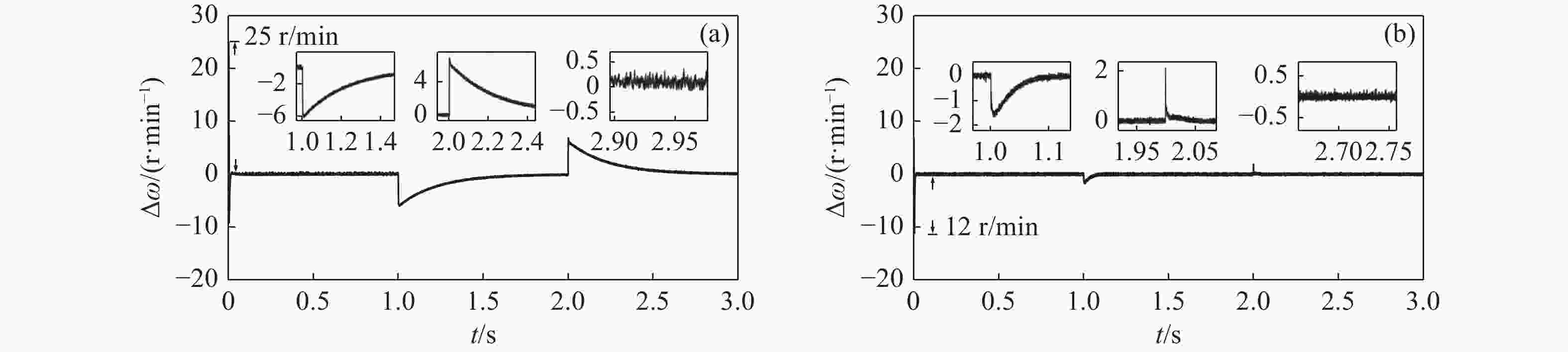
速度同步性能和抗干扰性是影响双永磁同步电机(dual-PMSM)同步运行动态响应和稳态精度的重要因素。通过引入交叉耦合控制作为模型,提出了一种基于改进双功率趋近律的积分滑模速度跟踪控制器,以减小两台电机之间的速度误差。设计了负载转矩观测器,将观测值引入滑模控制(SMC)趋近律,以提高系统的抗干扰性能。同时,采用模糊比例积分微分(FPID)控制设计了同步控制器,以提高双永磁同步电机的同步性。验证结果表明,当目标转速为800 r/min时,与传统的PI算法相比,所提出的控制方法可以在空载启动时将两台电机的速度同步误差从25 r/min降低到12 r/min,在负载突然转矩下将速度同步误差由7 r/min降低至2.2 r/min,从而提高了同步性和抗干扰性。
Abstract:Speed synchronization performance and anti-interference are important factors that affect the synchronous operation dynamic response and steady-state accuracy of dual Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors’ (Dual-PMSMs). By introducing cross-coupling control as the framework, an integral sliding mode speed tracking controller based on an improved bi-power reaching method is proposed to reduce the speed error between two motors. A load torque observer is designed to bring the observed value into the Sliding Mode Control (SMC) reaching method that enhances the anti-disturbance performance of the system. Meanwhile, a synchronous controller is designed using a Fuzzy-Proportional-Integral-Derivative (FPID) control to improve the synchronization of the Dual-PMSMs. The results show that compared with the traditional PI algorithm as the target speed is 800 r/min, the proposed control method can decrease the two motors’ speed synchronization error from 25 r/min to 12 r/min under a no-load startup and reduce the speed synchronization error from 7 r/min to 2.2 r/min with sudden load torque, improving the synchronization and disturbance rejection.
-
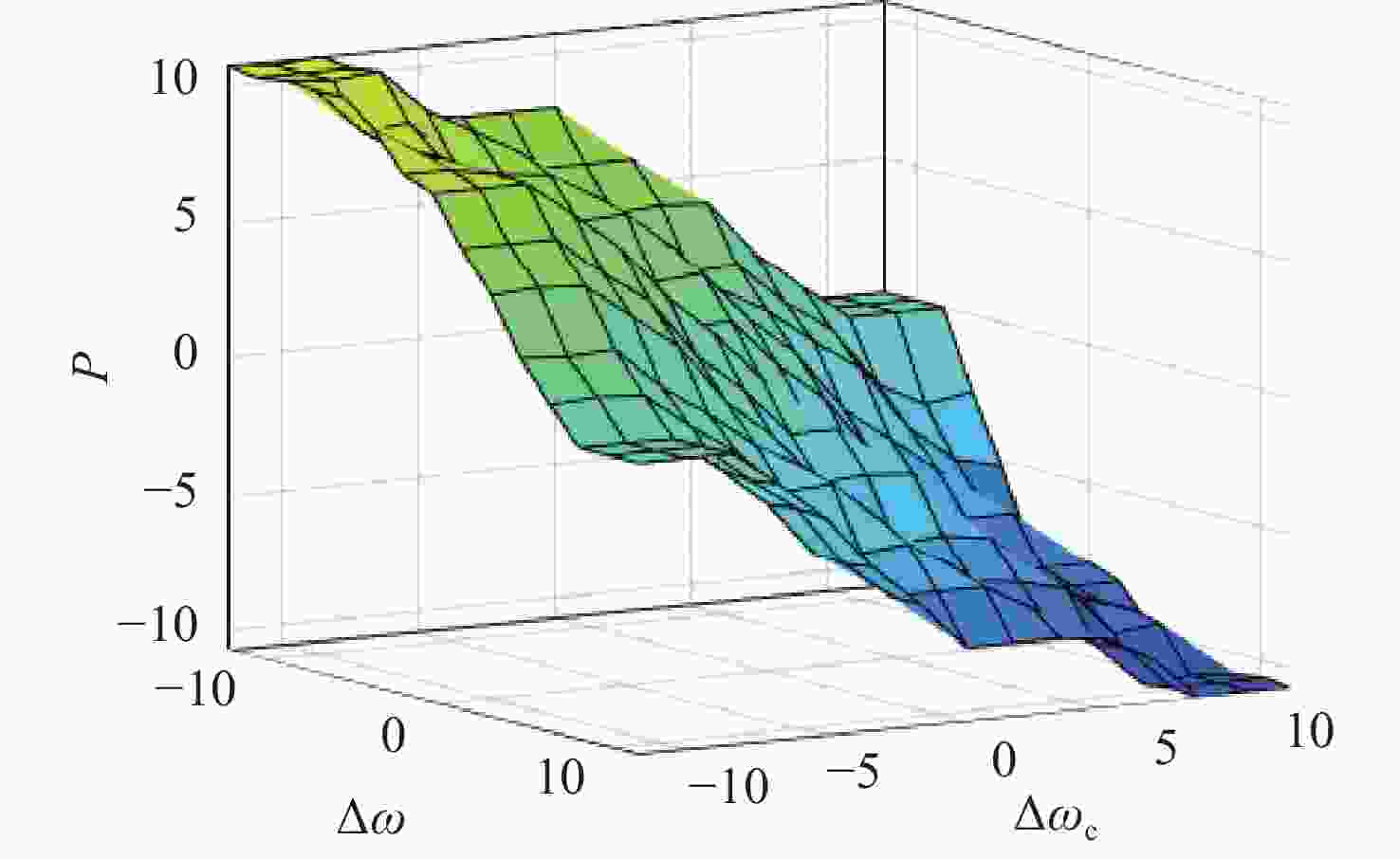
Table 2. ki fuzzy rule table
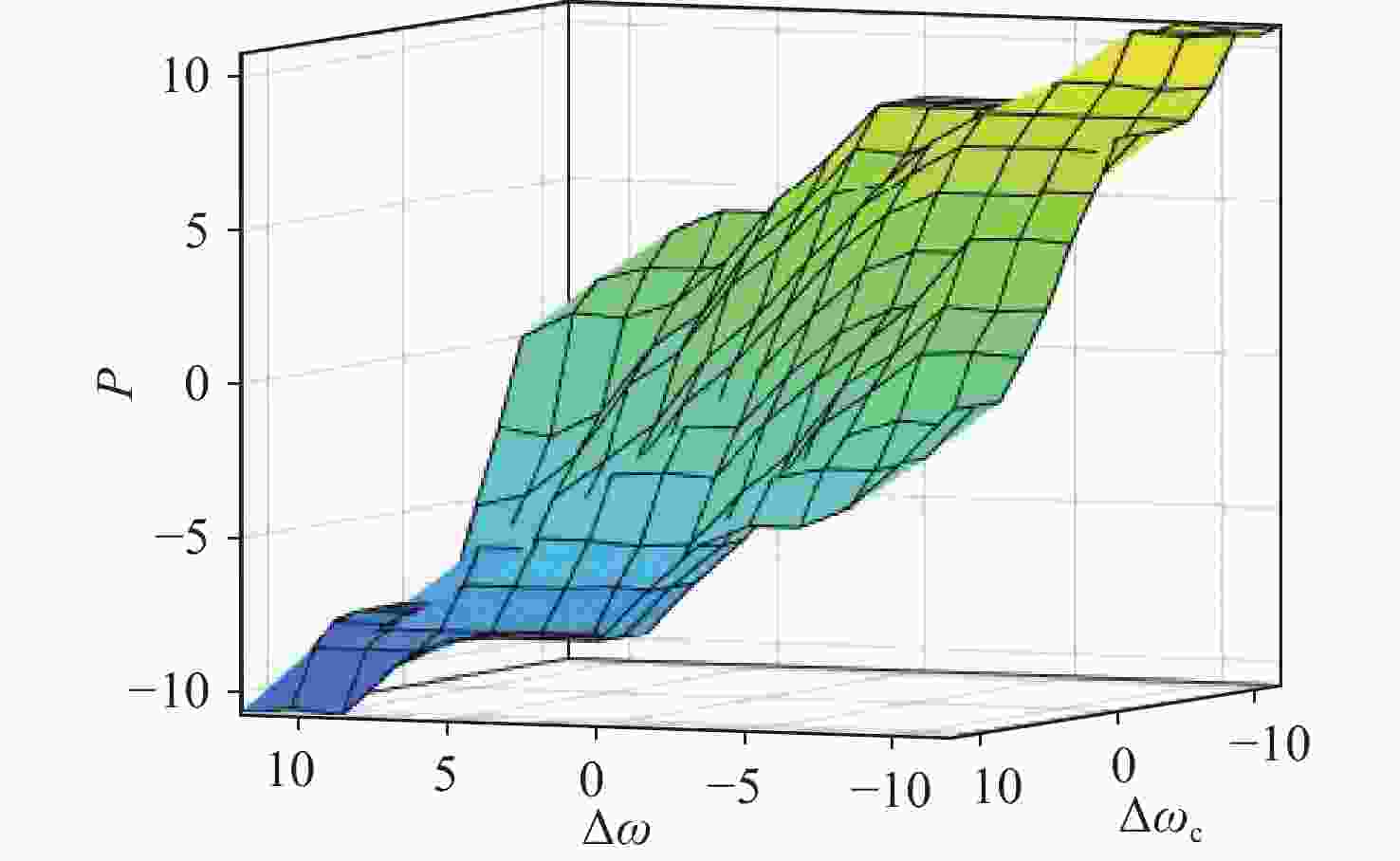
∆$\omega_c $ ∆$\omega $ NB NM NS ZE PS PM PB NB NB NB NB NM NS ZE ZE NM NB NB NM NS NS ZE PS NS NB NM NS NS ZE PS PM ZE NM NM NS ZE PS PM PM PS NM NM NS ZE PS PS PB PM ZE ZE PS PS PM PB PB PB ZE ZE PS PM PM PB PB Table 1. kp fuzzy rule table
∆$\omega_c $ ∆$\omega $ NB NM NS ZE PS PM PB NB PB PB PB PM PS ZE ZE NM PB PB PM PM ZE ZE NS NS PB PM PM PS ZE NS NS ZE PM PM PS ZE NS NM NM PS PM PS ZE NS NS NM NM PM PS ZE NS NM NM NM NB PB ZE ZE NM NM NB NB NB Table 3. Parameters of the motor
Parameters PMSM1 PMSM2 R(Ω) 7.29 12.24 L(mH) 0.14 0.18 P 4 4 J (kg∙m2) 0.000945 0.000885 ωN (r/min) 1500 1500 TN (N∙m) 2 2.5 B(N∙m∙s) 0.0090577 0.0080581 Table 4. SMC controller parameters
k1 k2 k3 c α β η PMSM1 5 3 50 0.2 0.13 2 0.0001 PMSM2 5 3 1200 0.35 0.13 2 0.0001 -
[1] ZHANG X Y, SHI T N, WANG ZH Q, et al. Generalized predictive contour control of the biaxial motion system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(11): 8488-8497. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2808899 [2] JUNG J W, LEU V Q, DO T D, et al. Adaptive PID speed control design for permanent magnet synchronous motor drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2015, 30(2): 900-908. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2014.2311462 [3] WU Y J, CHENG Y B, WANG Y L. Research on a multi-motor coordinated control strategy based on fuzzy ring network control[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 39375-39388. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2974906 [4] LU Y K. Adaptive-fuzzy control compensation design for direct adaptive fuzzy control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(6): 3222-3231. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2815552 [5] HU X L, SUN CH Y, ZHANG B. Design of recurrent neural networks for solving constrained least absolute deviation problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2010, 21(7): 1073-1086. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2010.2048123 [6] LIANG D L, LI J, QU R H, et al. Adaptive second-order sliding-mode observer for PMSM sensorless control considering VSI nonlinearity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2018, 33(10): 8994-9004. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2017.2783920 [7] ZENG T Y, REN X M, ZHANG Y. Fixed-time sliding mode control and high-gain nonlinearity compensation for dual-motor driving system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(6): 4090-4098. doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2950806 [8] ZHANG X G, SUN L ZH, ZHAO K, et al. Nonlinear speed control for PMSM system using sliding-mode control and disturbance compensation techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2013, 28(3): 1358-1365. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2012.2206610 [9] RODRIGUEZ J, KAZMIERKOWSKI M P, ESPINOZA J R, et al. State of the art of finite control set model predictive control in power electronics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2013, 9(2): 1003-1016. doi: 10.1109/TII.2012.2221469 [10] KARAMANAKOS P, GEYER T. Guidelines for the design of finite control set model predictive controllers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, 35(7): 7434-7450. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2019.2954357 [11] WANG H, SHI L H, MAN ZH H, et al. Continuous fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode control of automotive electronic throttle systems using finite-time exact observer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(9): 7160-7172. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2795591 [12] LI SH H, ZHOU M M, YU X H. Design and implementation of terminal sliding mode control method for PMSM speed regulation system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2013, 9(4): 1879-1891. doi: 10.1109/TII.2012.2226896 [13] LI J, FANG Y T, HUANG X Y, et al. Comparison of synchronization control techniques for traction motors of high-speed trains[C]. Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, IEEE, 2014: 2l14-2119. [14] KOREN Y. Cross-coupled biaxial computer control for manufacturing systems[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 1980, 102(4): 265-272. doi: 10.1115/1.3149612 [15] SHIH Y T, CHEN CH SH, LEE A CH. A novel cross-coupling control design for Bi-axis motion[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2002, 42(14): 1539-1548. doi: 10.1016/S0890-6955(02)00109-8 [16] SHI T N, LIU H, GENG Q, et al. Improved relative coupling control structure for multi-motor speed synchronous driving system[J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2016, 10(6): 451-457. doi: 10.1049/iet-epa.2015.0515 [17] LIM CH SH, LEVI E, JONES M, et al. A comparative study of synchronous current control schemes based on FCS-MPC and PI-PWM for a two-motor three-phase drive[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(8): 3867-3878. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2013.2286573 [18] BRANDO G, PIEGARI L, SPINA I. Simplified optimum control method for monoinverter dual parallel PMSM drive[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(5): 3763-3771. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2758751 [19] XU B, SHEN X K, JI W, et al. Adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding model control for permanent magnet synchronous motor based on disturbance observer[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 48913-48920. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2867463 [20] ZHOU X L, LI X F. Trajectory tracking control for electro-optical tracking system using ESO based fractional- order sliding mode control[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 45891-45902. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3067680 [21] GAO W B, HUNG J C. Variable structure control of nonlinear systems: a new approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 1993, 40(1): 45-55. doi: 10.1109/41.184820 [22] BHAT S P, BERNSTEIN D S. Finite-time stability of continuous autonomous systems[J]. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 2000, 38(3): 751-766. doi: 10.1137/S0363012997321358 -





 下载:
下载: