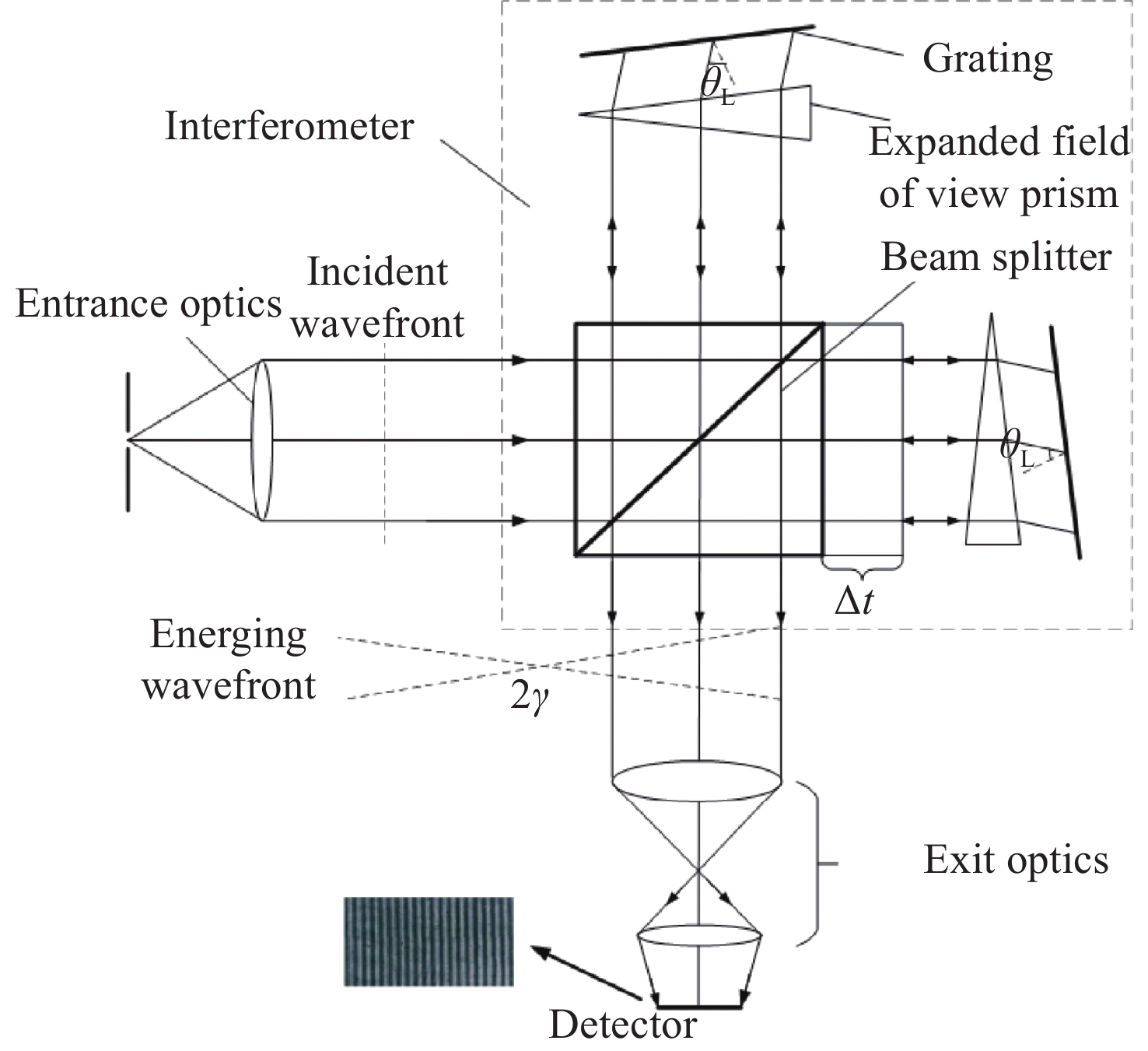
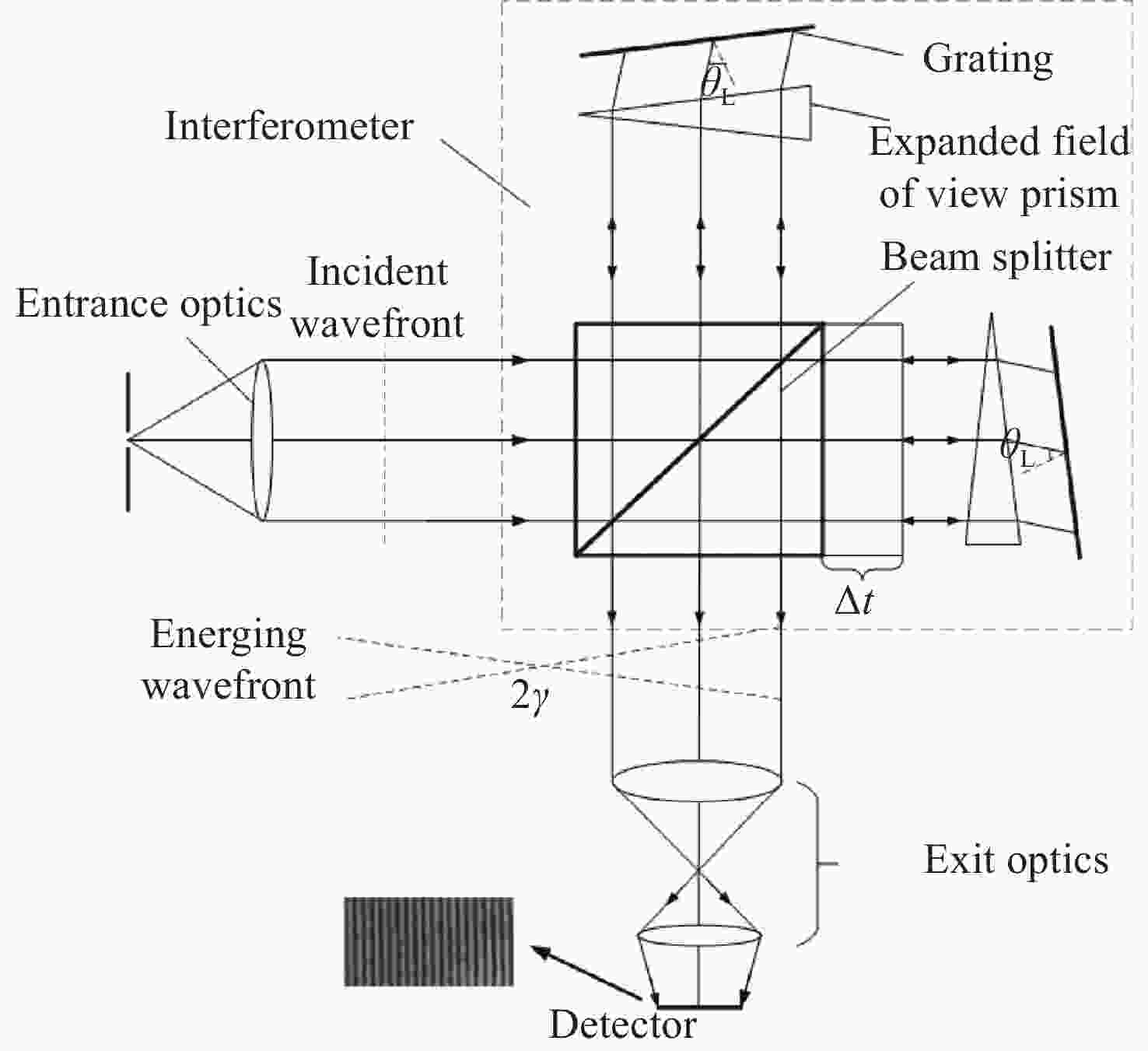
Development of a doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne interferometer for ground-based wind field detection at the 557.7 nm wavelength
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2022-0018
-
摘要:
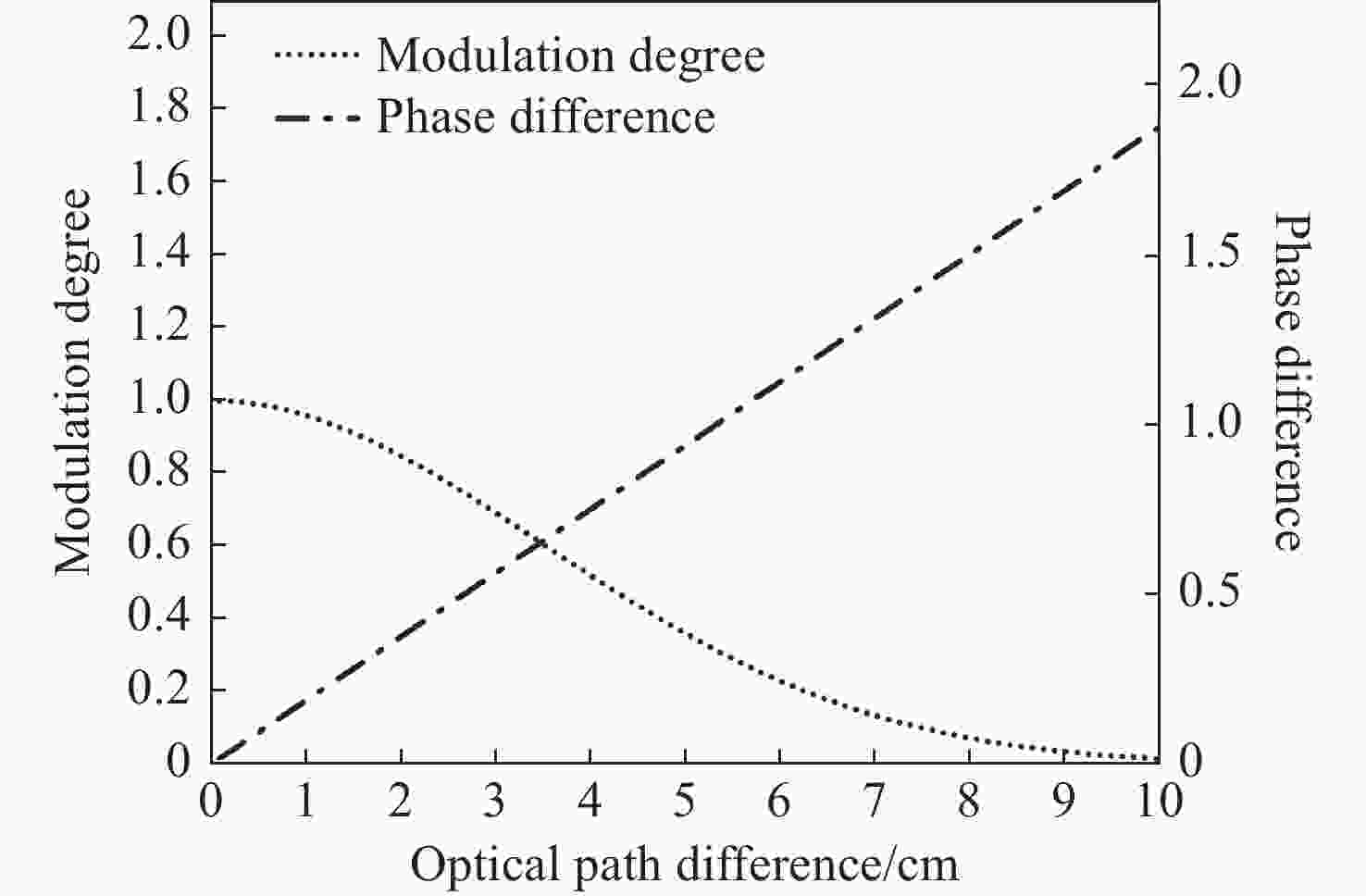
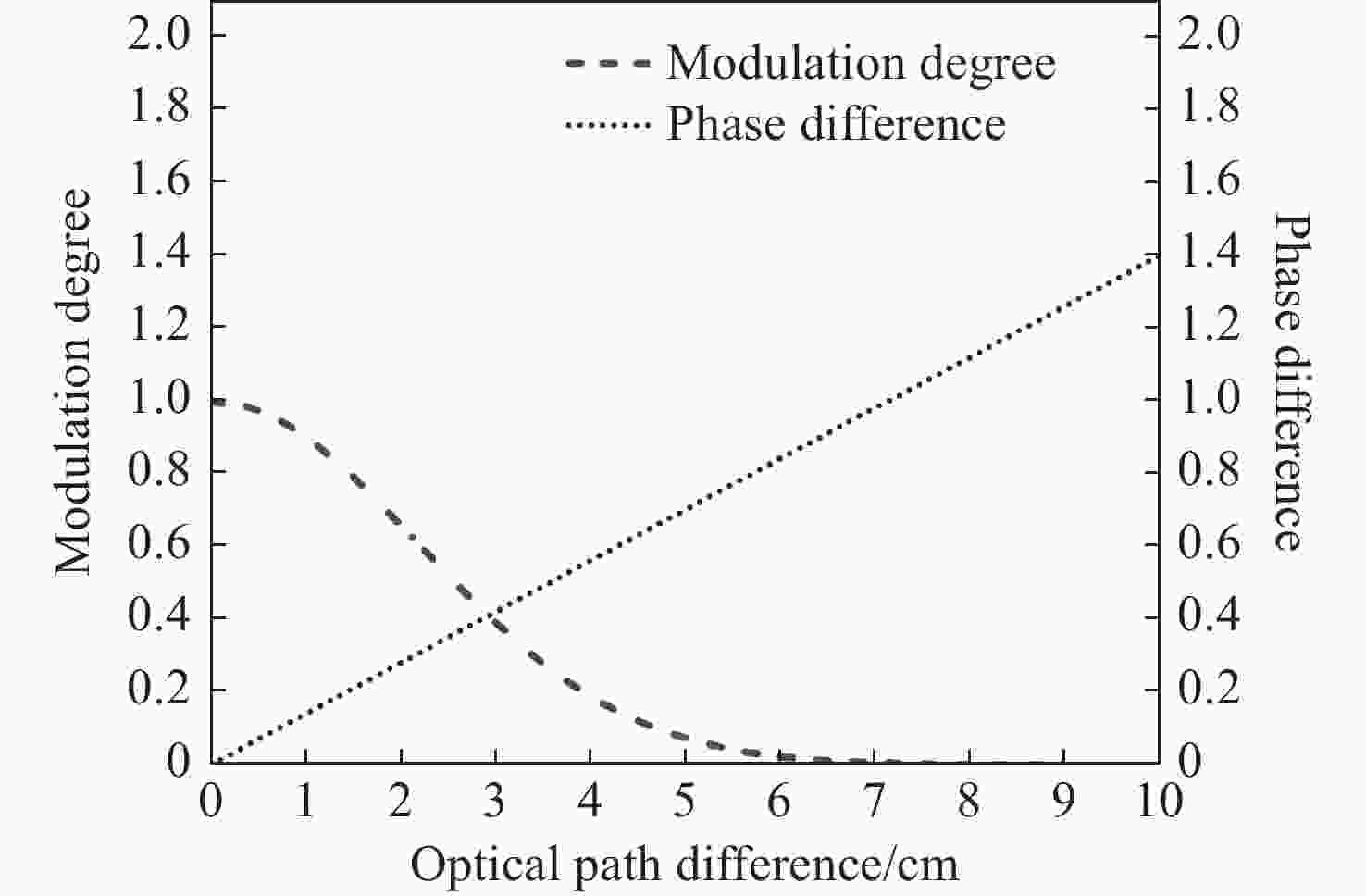
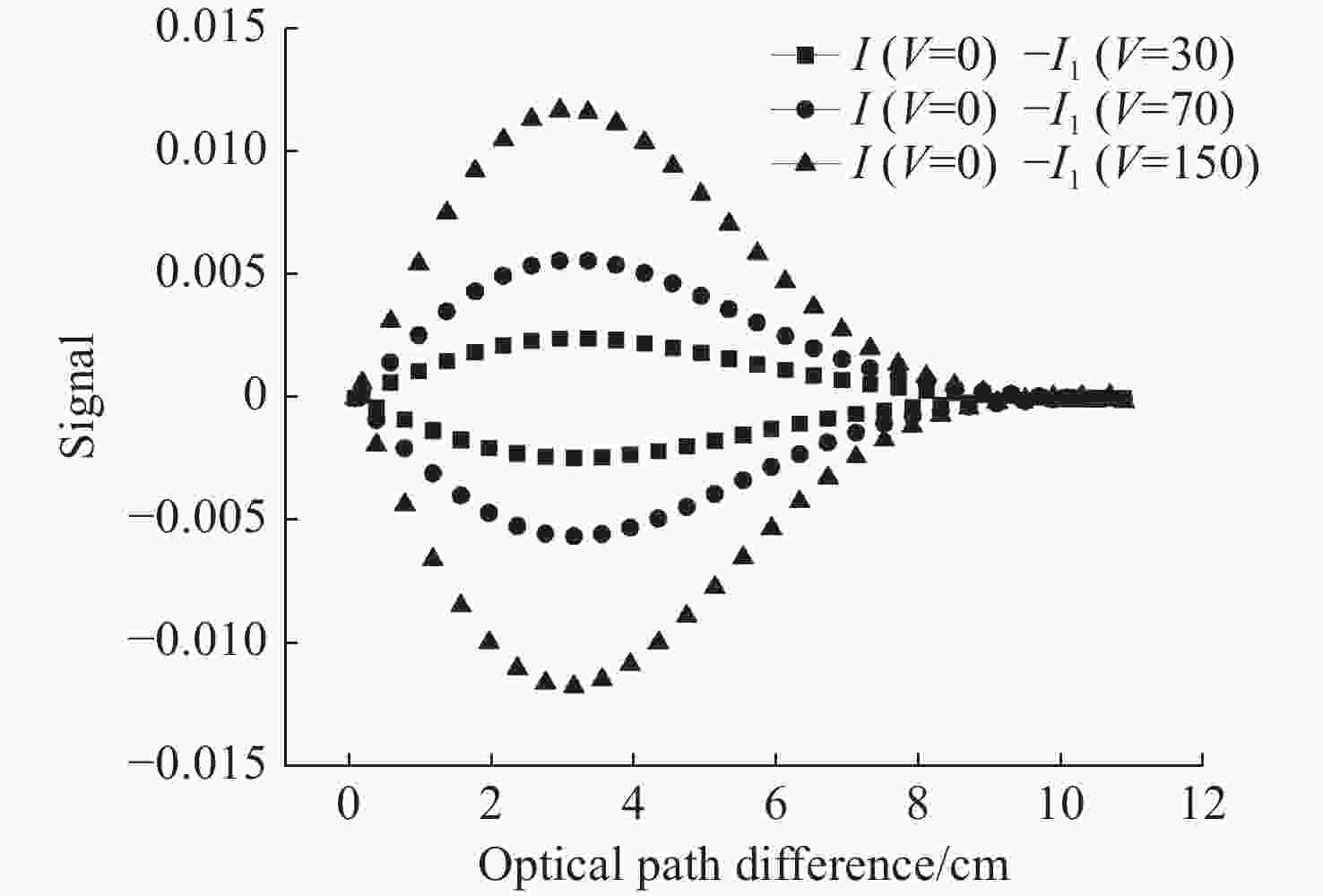
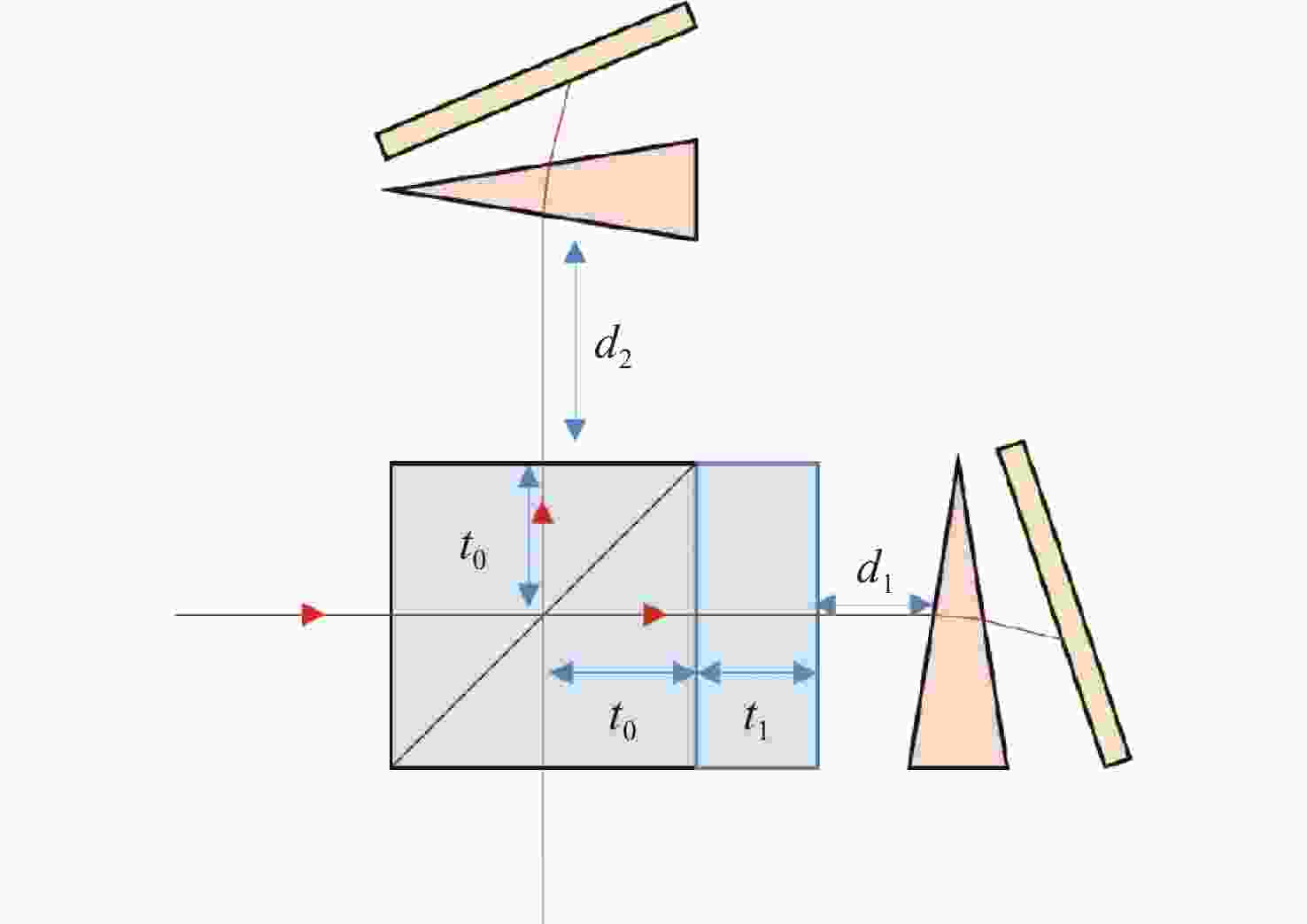
为探测中层大气风场信息,研制了一台具有热补偿特性的大集光率(AΩ)、高信噪比(Signal-to-Noise Ratio, SNR)的地基多普勒非对称空间外差(Doppler Asymmetric Spatial Heterodyne, DASH)干涉仪。针对557.7 nm的氧原子气辉谱线,制定了DASH干涉仪的详细参数和指标。系统采用扩视场和消热差设计,半视场角达到2.815°,集光率为0.09525 cm2sr,系统信噪比在113.75左右,经过热补偿设计后,最终光程差随温度变化(
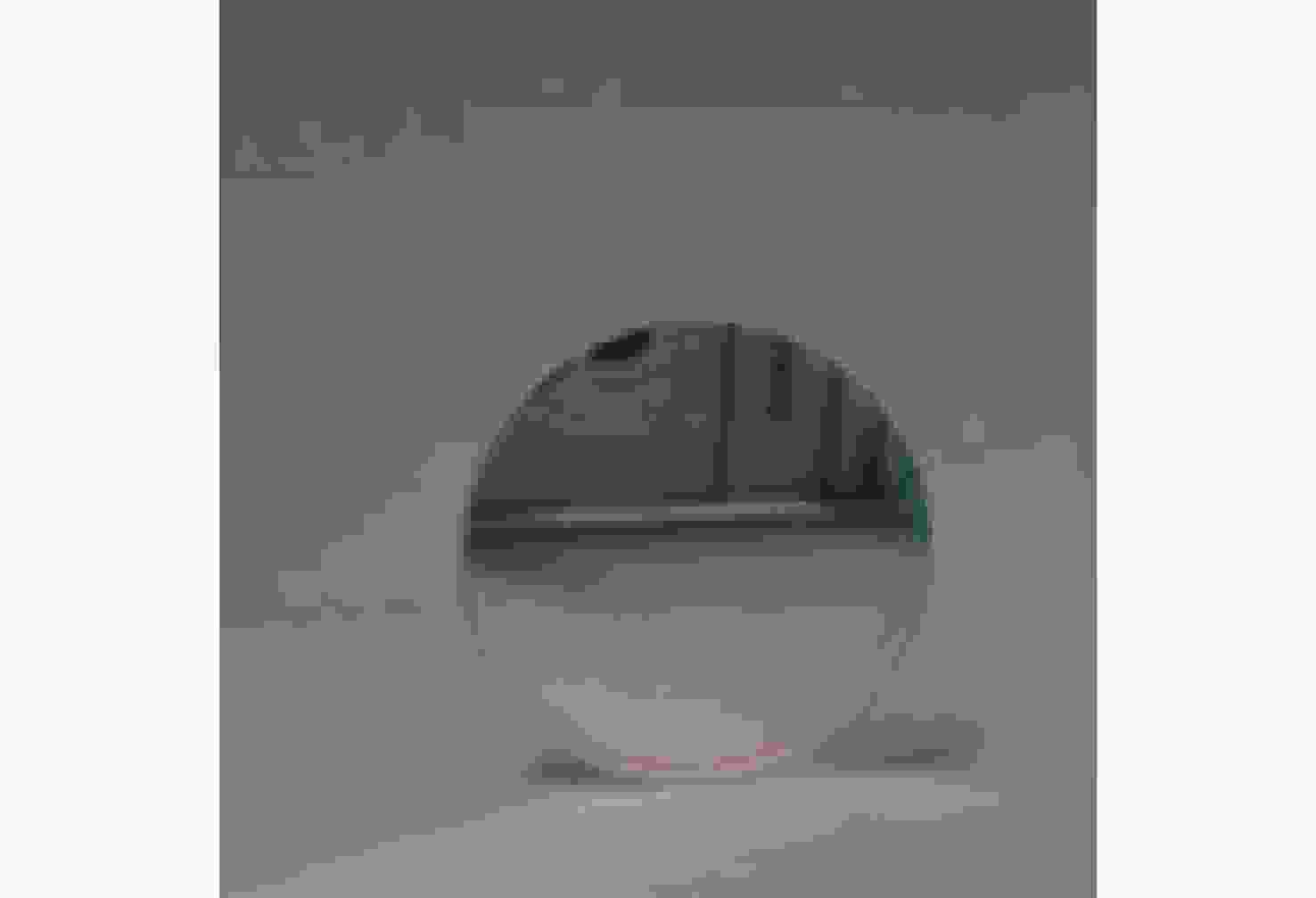
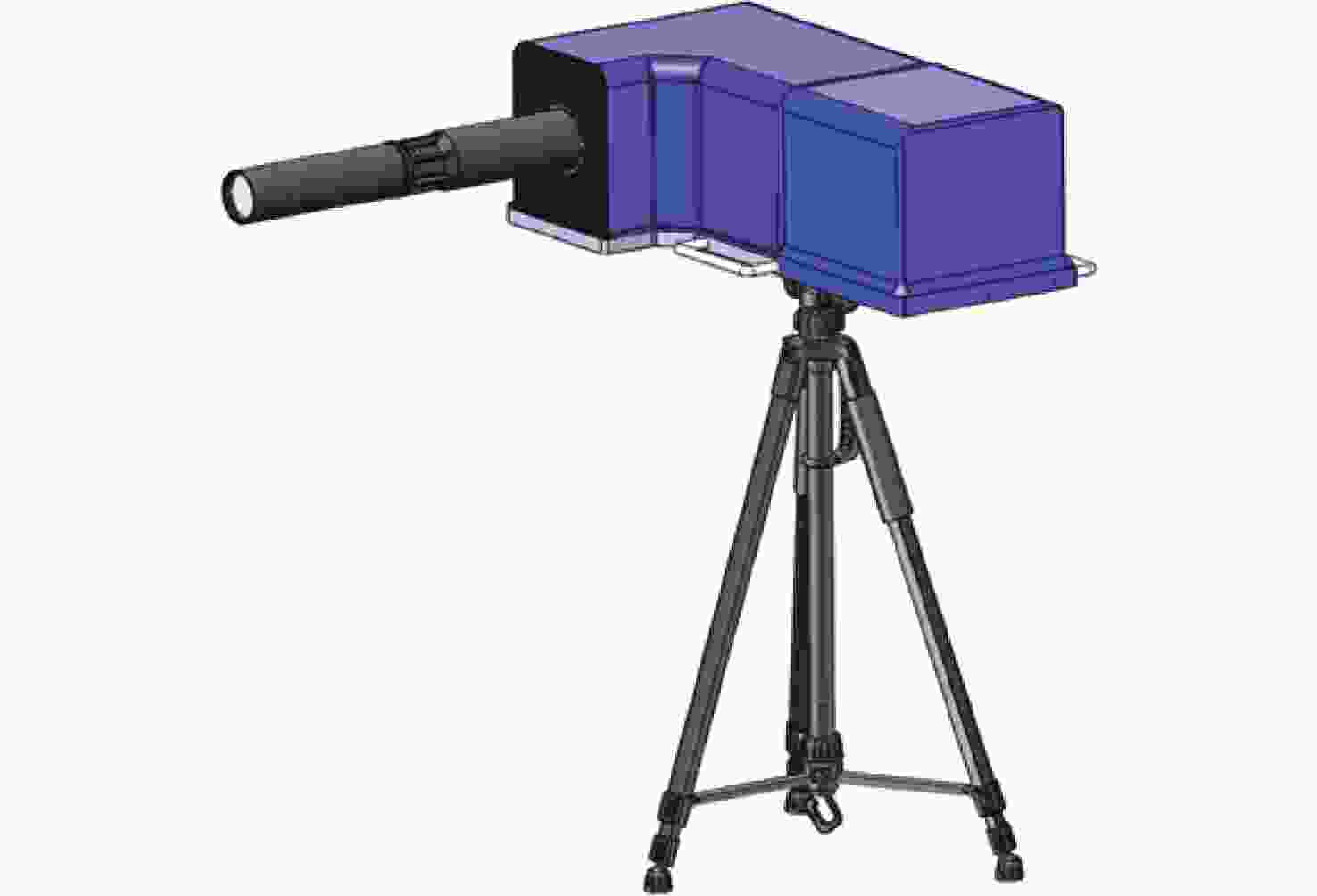
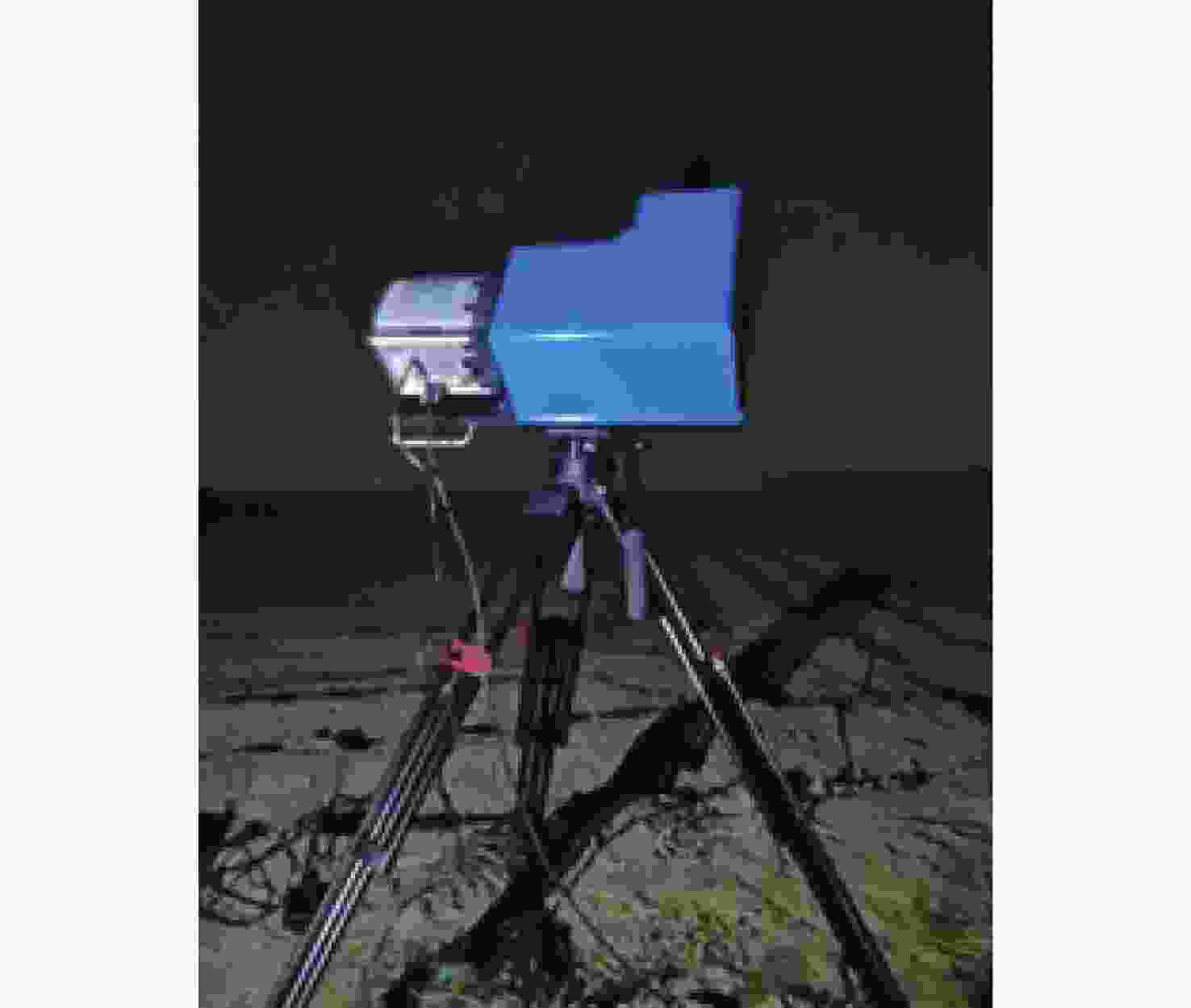
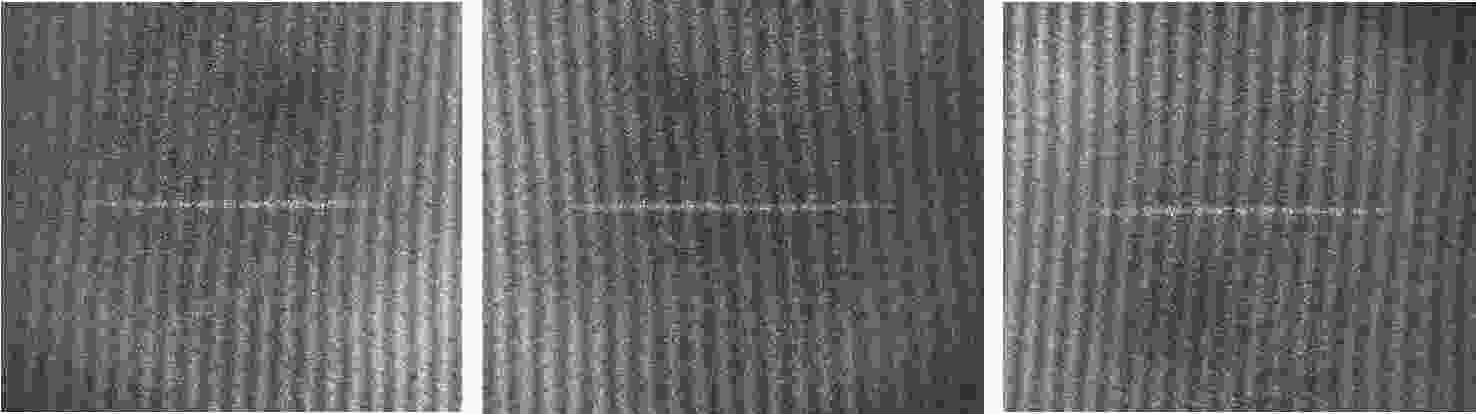
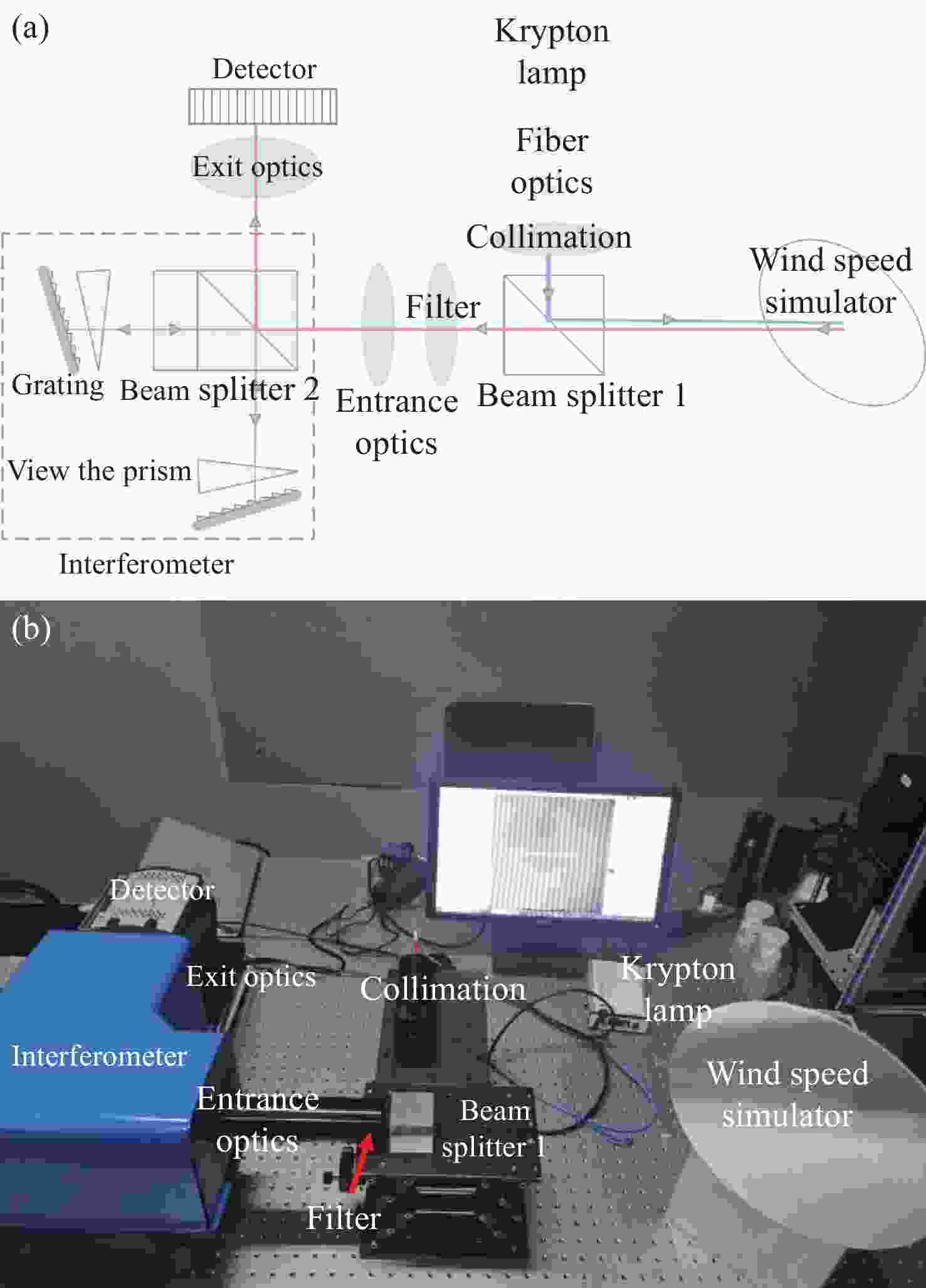
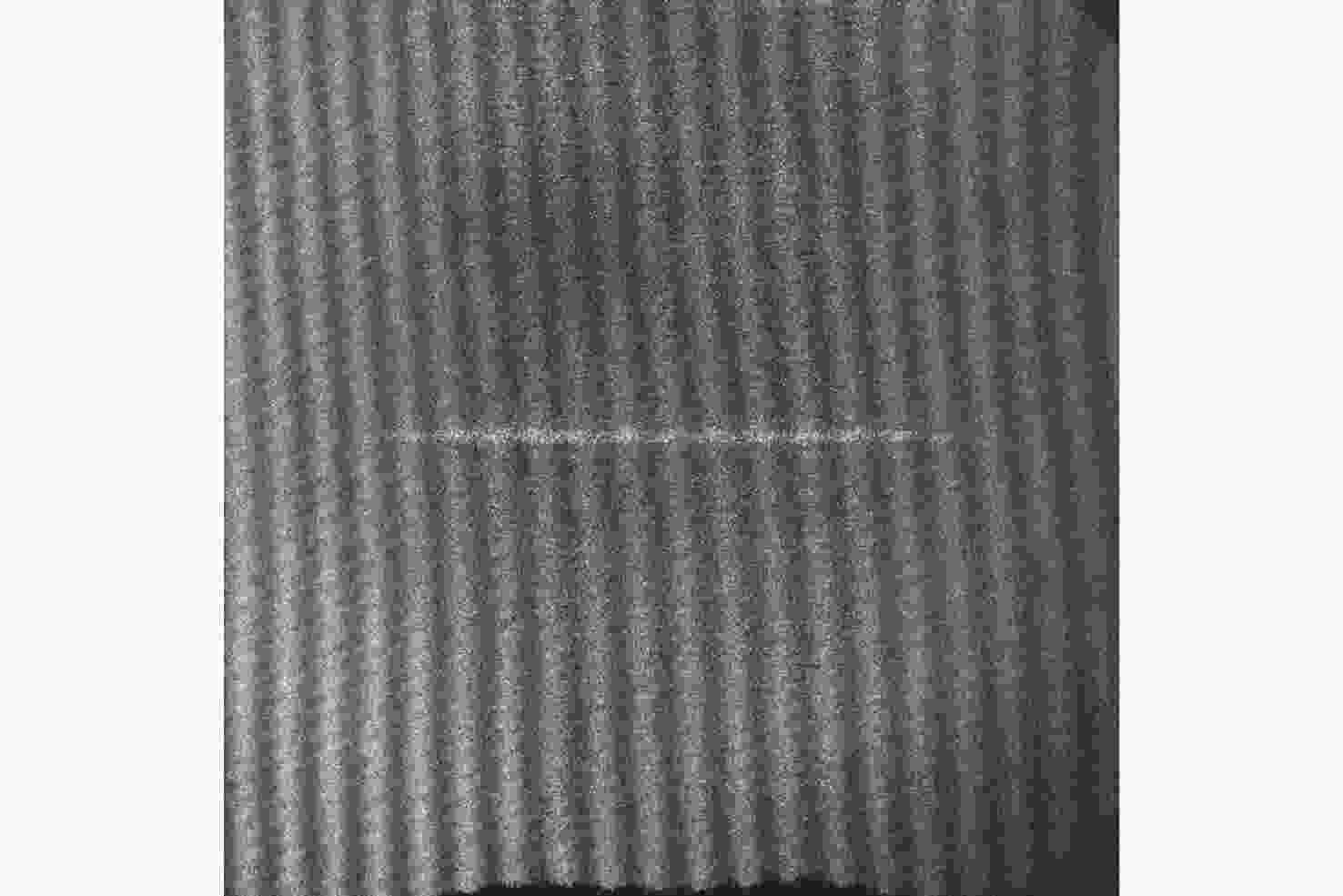
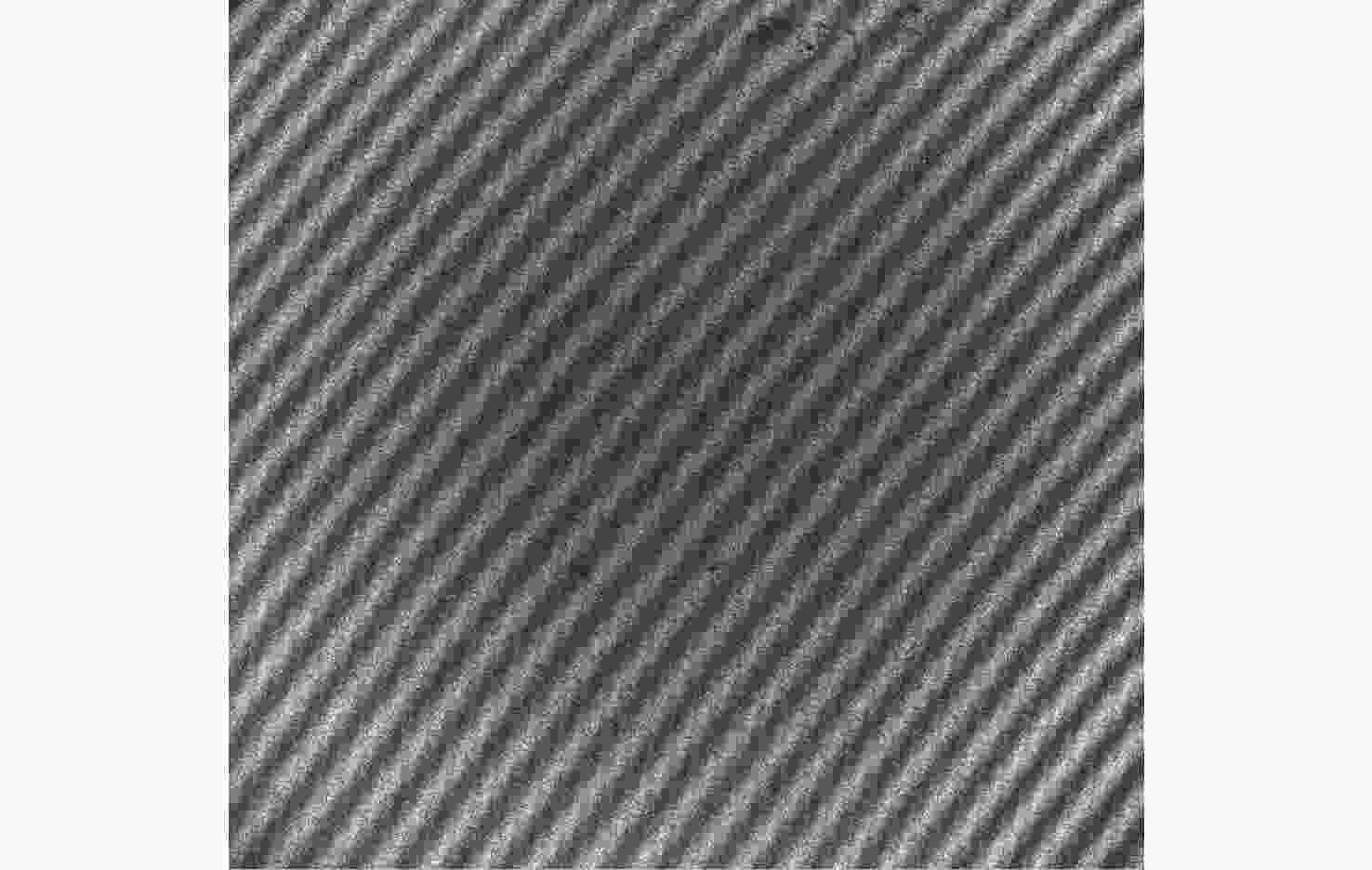
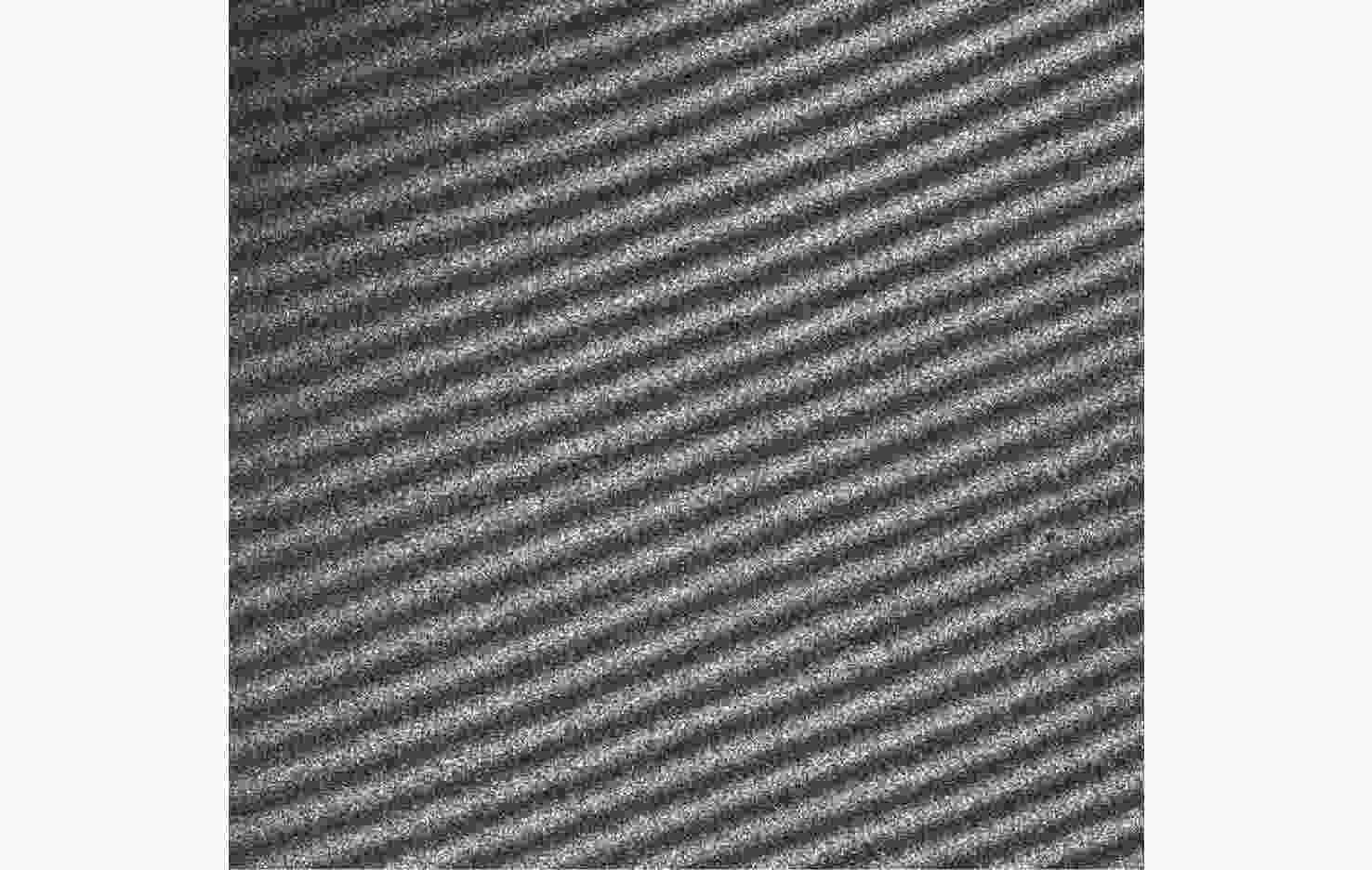
d Δd 0/dT )的数值仅为2.224×10−7 mm/°C。根据相应参数设计优化了光学系统,前置光学系统和探测器光学系统分别采用像方远心和双远心结构,各项指标均满足探测要求。为验证设计结果,搭建了地基DASH干涉仪实验平台,进行室内以及地基室外实验,最终得到了明显的干涉条纹。上述结果证明DASH干涉仪的系统设计是合理的,系统的信噪比和集光率满足检测要求。-
关键词:
- 地基DASH干涉仪 /
- 557.7 nm氧原子气辉谱线 /
- 光学设计 /
- 信噪比
Abstract:A ground-based Doppler Asymmetric Spatial Heterodyne (DASH) interferometer with a high Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) and large etendue (AΩ) with thermal compensation was developed to detect wind field information in the middle atmosphere. The detailed parameters and index of the DASH interferometer were developed for the 557.7 nm oxygen airglow spectral line. The system was designed with an expanded Field Of View (FOV) and thermal compensation. The half-FOV angle reached 2.815°, the etendue was 0.09525 cm2sr, and the system’s SNR was approximately 113.75. Through the thermal compensation design, the final optical path difference with temperature variation (
d Δd 0/dT ) was only 2.224×10−7mm/°C. The optical system was designed and optimized according to the corresponding parameters. Image-side telecentric and bilateral telecentric optical system structures were used in the entrance optics and exit optics, respectively, and parameters such as telecentricity and distortion met the detection requirements. To verify the design results, a ground-based DASH interferometer experimental platform was constructed, and indoor and outdoor ground-based experiments were conducted. In the final experiment, clear interference fringes were obtained, which proves that the system design results of the DASH interferometer are reasonable, and the system’s SNR and etendue meet the detection requirements. -
Table 3. Basic parameters of DASH interferometer
Parameter System indicators Littrow wavelength 557.7 nm Half of view angle 2.815° Diameter of the pupil 40 mm Field of view
extension prismMaterials H-LAK2A Angulus parietalis 8.7424° Wedged spacers Materials Fused silica (spacers1);
H-FK61 (spacers 2)Thickness Fused silica (spacers1);
H-FK61 (spacers 2)Beam splitter Splitting ratio 1∶1 Asymmetrical 20.363 mm Materials H-K9LAGT Gratings Grating Littrow angle 9.631° Grating diffraction order 1 Grating effective width 13.69 mm Materials Fused silica Lines 600 gr/mm Table 1. DASH system parameter list
System Parameter Value Transmittance of an optical system: τtot(σ). 0.07 Detector quantum efficiency: η(σ) 0.9 Optical system: F # 3.862 Detector pixel size: d 13 μm Dark current ηdark (refrigeration
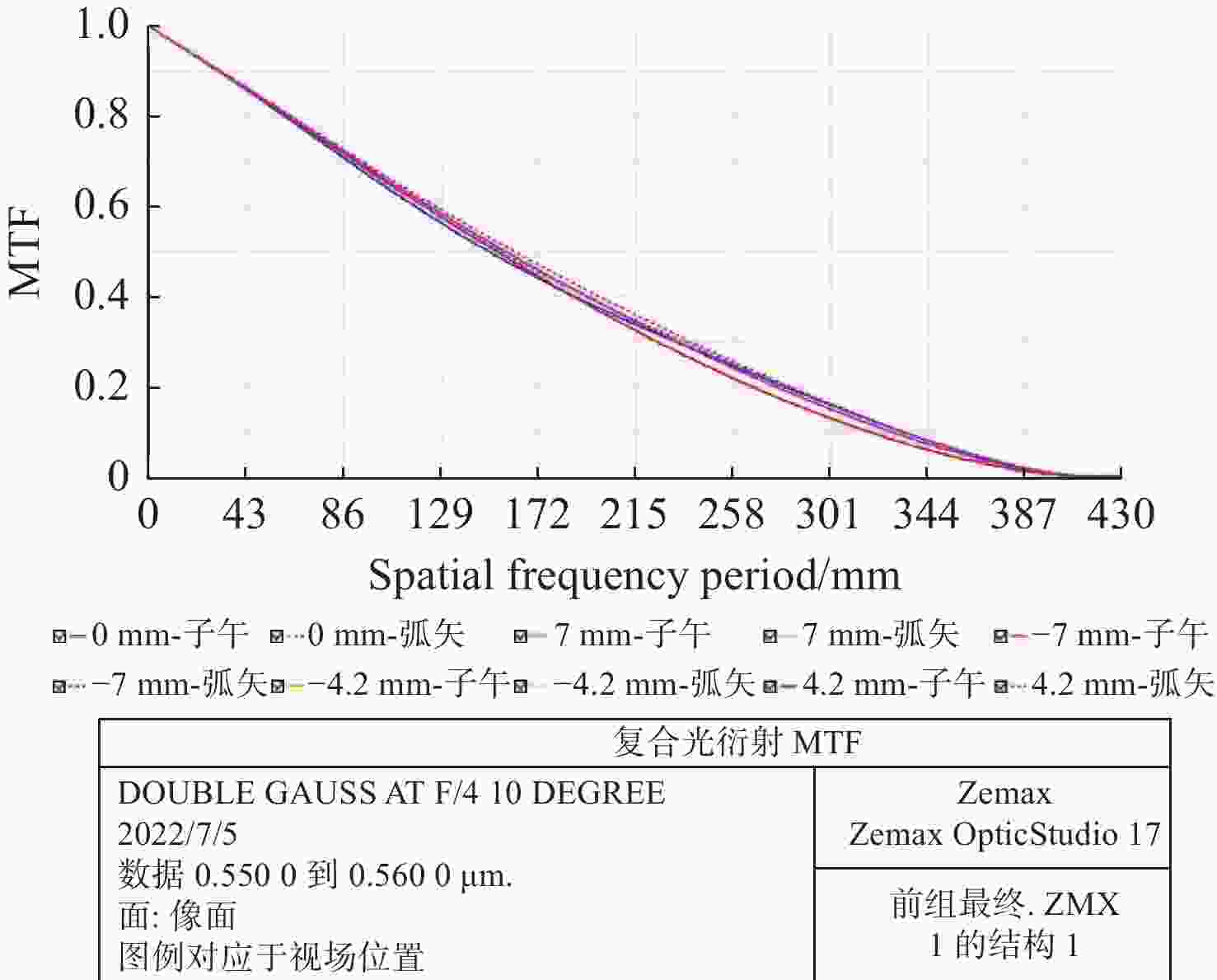
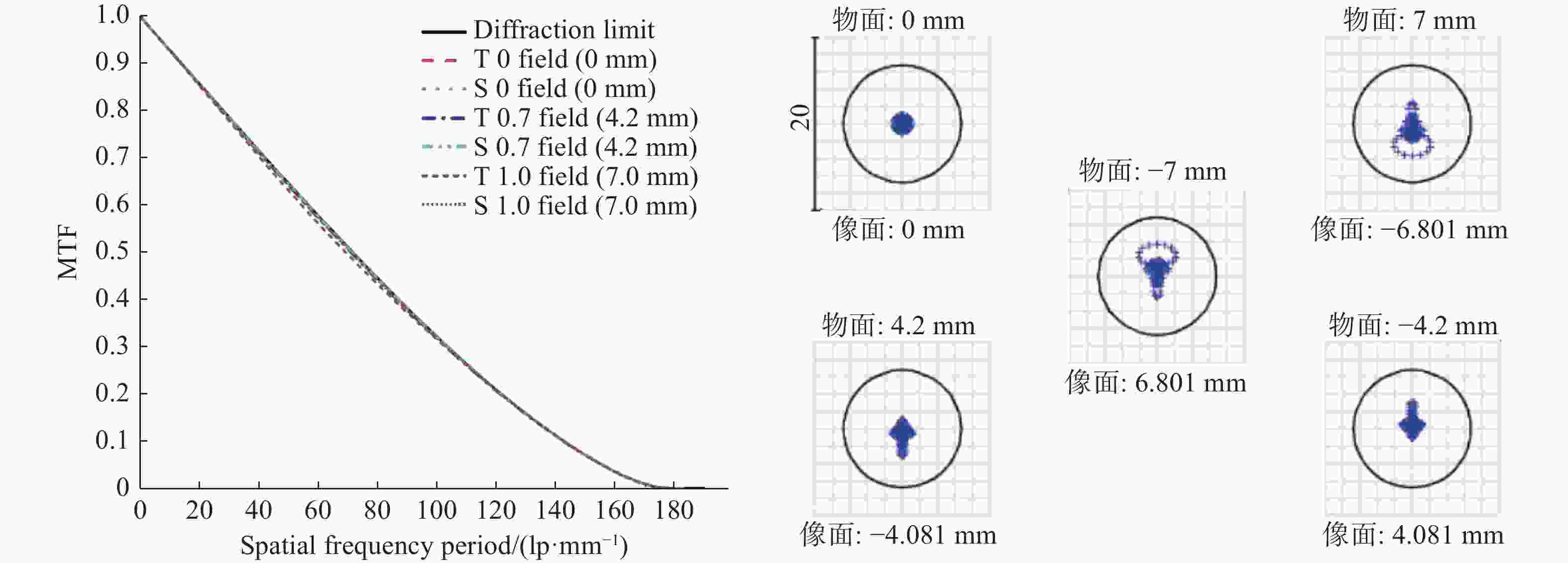
temperature d∆d0/dT:−80 °C)0.00025 Readout noise: σread 1e-/p·s-1 Table 2. Design indices of the dual telecentric optical system
Parameter System indicators Wavelength 557.7 nm Magnification −0.9715 F# 9 Distortion 2.4×10−5 Back focal length 30 mm Telecentricity <7.0×10−3 Table 4. DASH system specifications
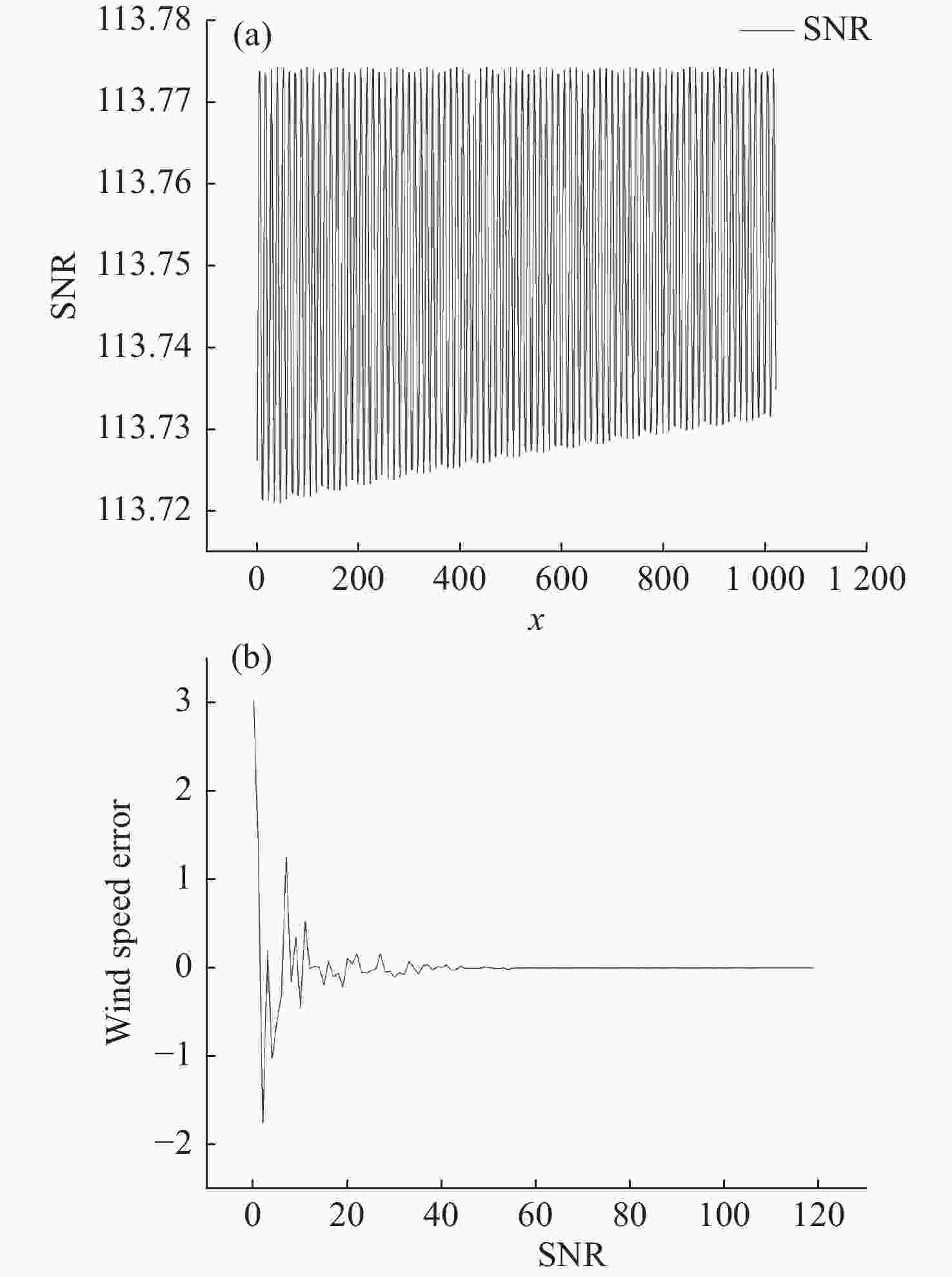
Parameter System indicators Resolving power 16402.941 measuring range 90-110 km (Height of airglow) Resolution of measurement 1.0933 cm−1 (0.034 nm) $\dfrac{ {{\rm{d}}\Delta { d_0} } }{ { {\rm{d} }T} }$ 2.224×10−7 mm/°C Etendue (AΩ) 0.09525 cm2sr SNR 113.75 Decomposition
of precisionTemperature 0.05 rad/°C SNR SNR>60,wind speed error <10−4 m/s Inversion accuracy (Nuttall
window function, FWHM=10)0.00064 m/s -
[1] WANG Y J, WANG Y M, WANG H M. Simulation of ground-based Fabry-Perot interferometer for the measurement of upper atmospheric winds[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2014, 57(6): 1732-1739. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/cjg20140605 [2] SHEPHERD G G, THUILLIER G, GAULT W A, et al. WINDII the wind imaging interferometer on theupper atmosphere research satellite[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 1993, 98(D6): 10725-10750. [3] ENGLERT C R, HARLANDER J M, BABCOCK D D, et al.. Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne spectroscopy (DASH): an innovative concept for measuring winds in planetary atmospheres[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 6303, Atmospheric Optical Modeling, Measurement, and Simulation II, SPIE, 2006: 63030T. [4] ENGLERT C R, BABCOCK D D, HARLANDER J M. Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne spectroscopy (DASH): concept and experimental demonstration[J]. Applied Optics, 2007, 46(29): 7297-7307. doi: 10.1364/AO.46.007297 [5] HARLANDER J M, ENGLERT C R, BABCOCK D D, et al. Design and laboratory tests of a Doppler Asymmetric Spatial Heterodyne (DASH) interferometer for upper atmospheric wind and temperature observations[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(25): 26430-26440. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.026430 [6] BABCOCK D D, HARLANDER J M, ENGLERT C R, et al.. Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne (DASH) interferometer from flight concept to field campaign[C]. Proceedings of the Fourier Transform Spectroscopy 2011, Optica Publishing Group, 2011. [7] HARLANDER J M, ENGLERT C R, BROWN C M, et al.. Design and laboratory tests of the Michelson interferometer for global high-resolution thermospheric imaging (MIGHTI) on the ionospheric connection explorer (ICON) satellite[C]. Proceedings of the Fourier Transform Spectroscopy 2015, Optica Publishing Group, 2015. [8] ENGLERT C R, HARLANDER J M, BROWN C M, et al.. MIGHTI: the spatial heterodyne instrument for thermospheric wind measurements on board the ICON mission[C]. Proceedings of the Fourier Transform Spectroscopy 2015, Optica Publishing Group, 2015. [9] NING T. Doppler wind simulator for spatial heterodyne observations of wind[D]. York: York University, 2012. [10] SOLHEIM B, BROWN S, SIORIS C, et al. SWIFT-DASH: spatial heterodyne spectroscopy approach to stratospheric wind and ozone measurement[J]. Atmosphere—Ocean, 2015, 53(1): 50-57. [11] 沈静. 中高层大气风场探测多普勒非对称空间外差技术研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2017.SHEN J. Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne technique for wind detection in the upper atmosphere[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2017. (in Chinese) [12] 况银丽. 基于非对称空间外差干涉仪的多普勒测速技术研究[D]. 成都: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院光电技术研究所), 2020.KUANG Y L. Research on radial velocity measurement technology based on Doppler asymmetric space heterodyne interferometer[D]. Chengdu: Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020. (in Chinese) [13] FEI X Y, FENG Y T, BAI Q L, et al. Optical system design of a Co-path Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne interferometer with two fields of view[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2015, 35(4): 0422003. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201535.0422003 [14] 陈洁婧. 多普勒差分干涉光谱仪风速反演技术研究[D]. 西安: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所), 2017.CHEN J J. Study on Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne spectrometer in wind velocity retrieval[D]. Xi’an: Xi'an Institute of Optics & Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. (in Chinese) [15] 费小云. 星载测风双视场准共路多普勒外差干涉仪基础问题研究[D]. 西安: 中国科学院研究生院(西安光学精密机械研究所), 2015.FEI X Y. Basic study on a Co-path Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne spectroscopy interferometer with two fields of view for atmospheric wind vector observation form satellite platforms[D]. Xi’an: Xi'an Institute of Optics & Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015. (in Chinese) [16] GAO H, XU J Y, YUAN W. A Method of Inversing the Peak Density of Atomic Oxygen Vertical Distribution in the MLT Region From the OI (557.7nm) Night Airglow Intensity[J]. Space Science Journal, 2005, 25(5): 6. doi: 10.1080/02726340590910084. [17] KHOMICH V Y, SEMENOV A I, SHEFOV N N. Airglow as an Indicator of Upper Atmospheric Structure and Dynamics[M]. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2008. [18] BELL R J. Introductory Fourier Transform Spectroscopy[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1972: 16-32. [19] FU Q, XIANG L B, JING J J. System signal-to-noise ratio analysis based on imaging chain model in multispectral remote sensing[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2012, 32(2): 0211001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201232.0211001 [20] SAPTARI V. Fourier-Transform Spectroscopy Instrumentation Engineering[M]. Bellingham: SPIE, 2003. [21] FENG Y T, BAI Q L, WANG Y M, et al. Theory and method for designing field-widened prism of spatial heterodyne spectrometer[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2012, 32(10): 1030001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201232.1030001 [22] 汪丽. 干涉法大气风场探测技术研究[D]. 西安: 中国科学院研究生院(西安光学精密机械研究所), 2007.WANG L. Study on wind measurement of atmosphere by interferometry technology[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2007. (in Chinese) [23] MARR K D, ENGLERT C R, HARLANDER J M, et al. Thermal sensitivity of DASH interferometers: the role of thermal effects during the calibration of an Echelle DASH interferometer[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(33): 8082-8088. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.008082 [24] XUE Q SH, WANG SH R, LI F T, et al. Analysis and experimental validation of sgnal-to-noise for limb imaging sectrometer[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2010, 30(6): 1697-1701. (in Chinese) [25] CHEN ZH L, LIU Y ZH, FEI M M, et al. Design of industrial double telecentric optical lens with large field of view[J]. Journal of Xi’an Technological University, 2018, 38(5): 444-450. (in Chinese) [26] LI Y T, FU Y G, WANG L J, et al.. Design of full-spectrum imaging optical system for large-aperture space-based platform[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14: 9. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2019-0255 [27] WANG L Y, LI Y Q, CAI R. Noise suppression of laser jitter in space laser interferometer[J]. Chinese Optics (English and Chinese), 2021, 14(6): 1426-1434. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0045 [28] LI X Y, REN G X, LV M R, et al. Spectrometer with high spectral camera model in the laboratory research[J]. Journal of analytical chemistry, 2021. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19756/j.issn.0253-3820.191165 -





 下载:
下载: