Research on high-precision registration methods for GM-APD LiDAR point clouds in dynamic scanning scenarios
-
摘要:
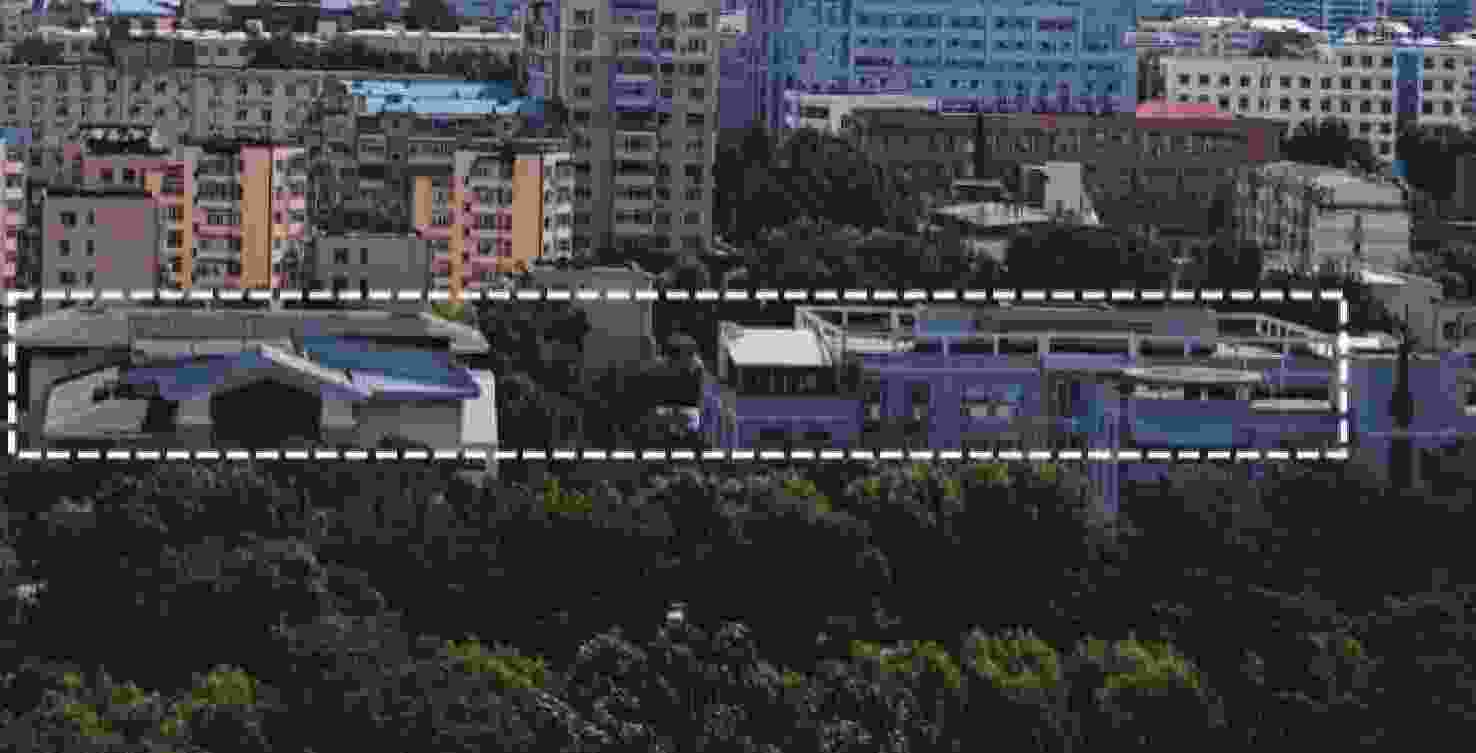
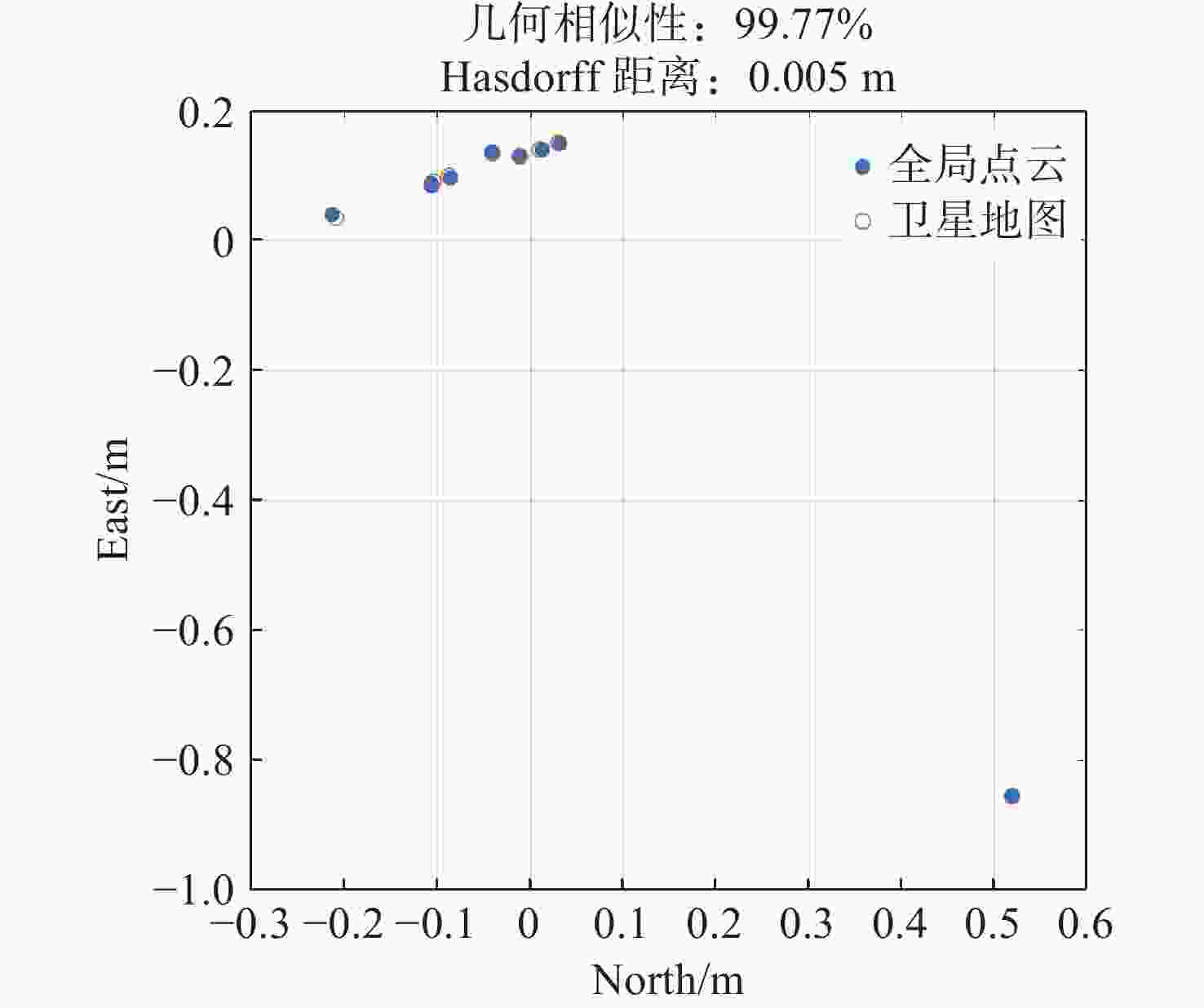
本研究针对盖革雪崩光电二极管(Geiger-mode avalanche photodiode,GM-APD)激光雷达在动态扫描场景下相邻帧点云重叠率低、易强制配准非匹配点对的问题,提出了一种基于双向匹配机制和多分辨率邻域扩展的改进ICP算法,以提高点云配准精度和鲁棒性。首先,通过基于K-D tree的双向匹配机制提取相邻帧点云的重叠区域,利用重叠区域信息建立初始配准模型,解决了低重叠率场景下配准精度下降的问题。其次,采用多分辨率邻域扩展技术,结合局部曲率相似性加权求解变换矩阵,避免了动态配准中强制对齐非匹配点对的现象。最后,通过级联补偿机制实现全局点云的精确配准。实验结果表明,在2 km和400 m扫描成像中,平均距离误差分别为0.21 m和0.10 m。该方案有效解决了动态扫描场景下的点云配准难题,为三维重构提供了高精度数据支持,具有重要应用价值。
Abstract:This paper addresses the challenges of low overlap and mismatched point pairs in Geiger-mode avalanche photodiode (GM-APD) LiDAR point clouds under dynamic scanning conditions. To improve registration accuracy and robustness, an enhanced Iterative Closest Point (ICP) algorithm is proposed, integrating a bidirectional matching scheme and multi-resolution neighborhood expansion. First, a K-D tree-based bidirectional search identifies overlapping regions between consecutive frames, enabling accurate initial alignment. Then, a high-resolution neighborhood expansion approach, weighted by local curvature similarity, is applied to refine the transformation matrix and suppress mismatched correspondences. Finally, a cascaded compensation mechanism ensures global consistency across frames. Experiments demonstrate that our method achieves average distance errors of 0.21 m (2 km scene) and 0.10 m (400 m scene), effectively improving registration precision in dynamic scenarios and offering valuable support for 3D reconstruction.
-
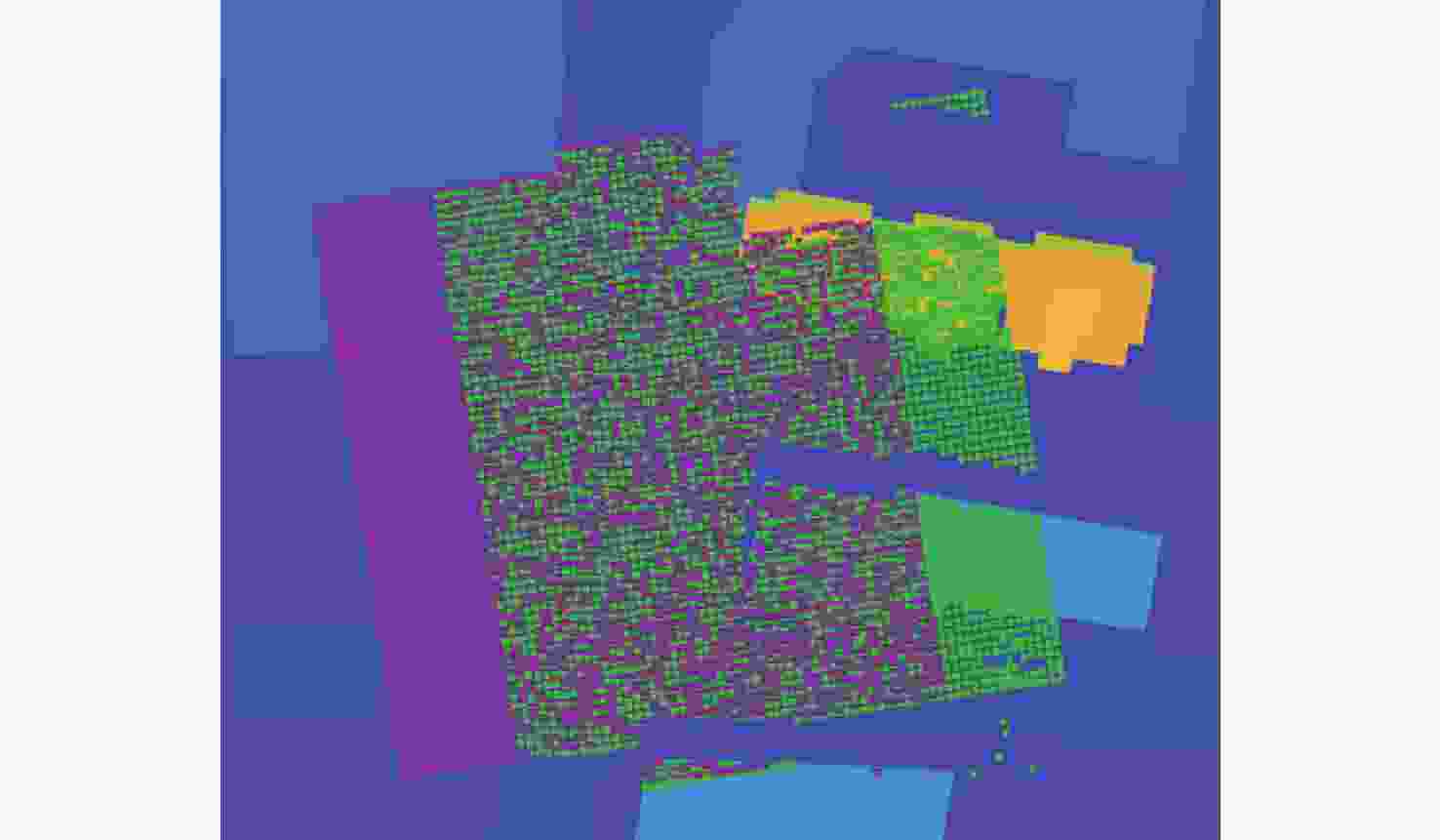
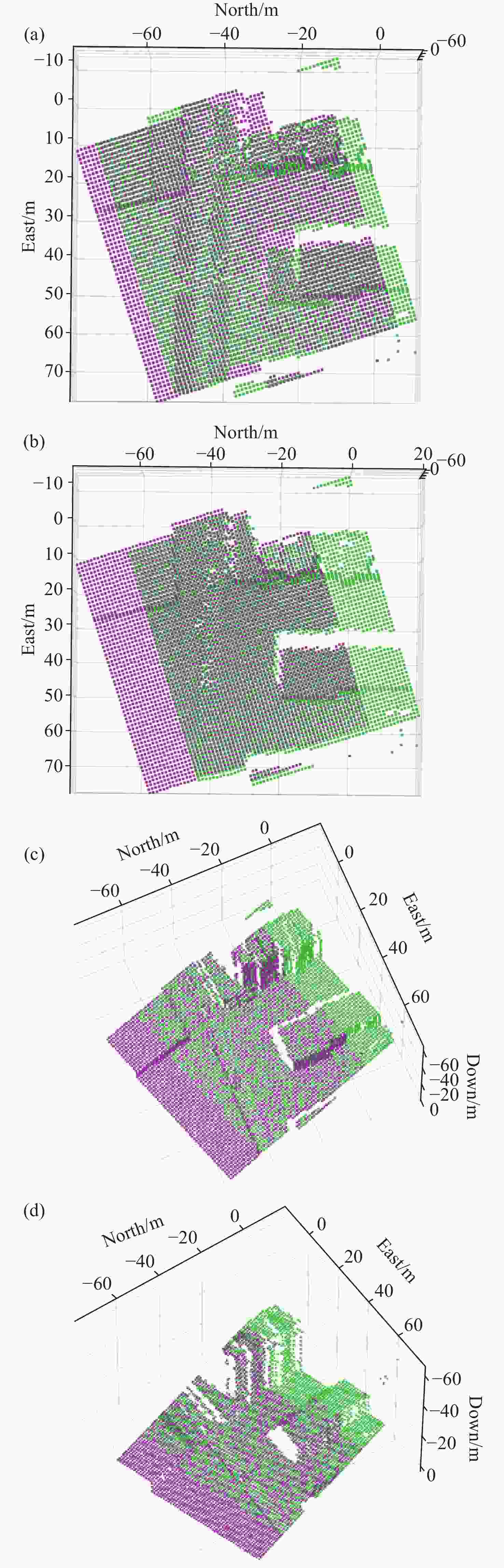
图 6 仿真场景局部配准结果对比。(a)传统ICP;(b)改进ICP;(c)重叠点云提取结合传统ICP;(d)重叠点云提取结合改进ICP
Figure 6. Comparison of local registration results in simulation scenarios.(a) Conventional ICP; (b) Improved ICP; (c) Conventional ICP with Overlapping Point Cloud Extraction; (d) Improved ICP with Overlapping Point Cloud Extraction
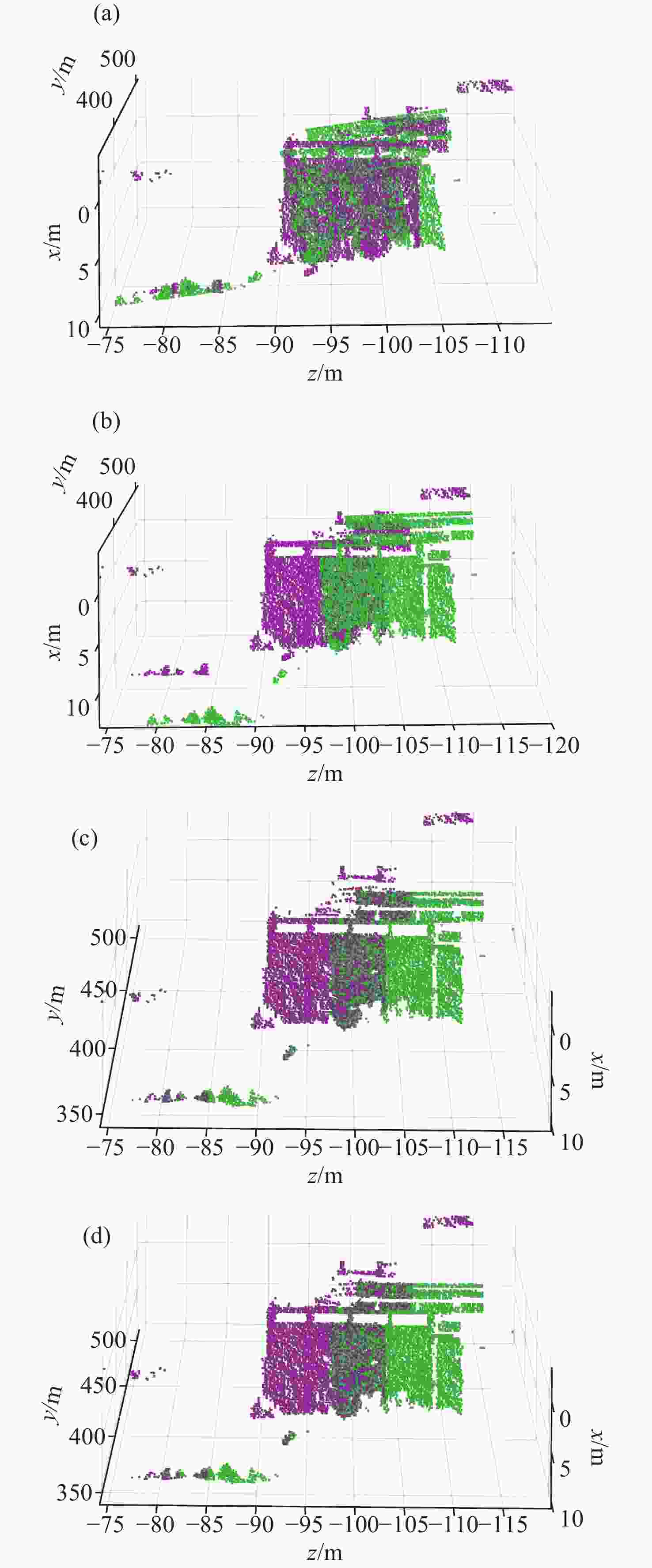
图 10 真实场景局部配准结果对比。(a)传统ICP;(b)改进ICP;(c)重叠点云提取结合传统ICP;(d)重叠点云提取结合改进ICP
Figure 10. Comparison of local registration results in real-world scenes.(a) Conventional ICP; (b) Improved ICP; (c) Conventional ICP with overlapping point cloud extraction; (d) Improved ICP with overlapping point cloud extraction
表 1 仿真场景局部精配准客观评价
Table 1. Local fine registration objective evaluation of simulation scene
传统ICP 改进ICP 提取重叠区域+
传统ICP提取重叠区域+
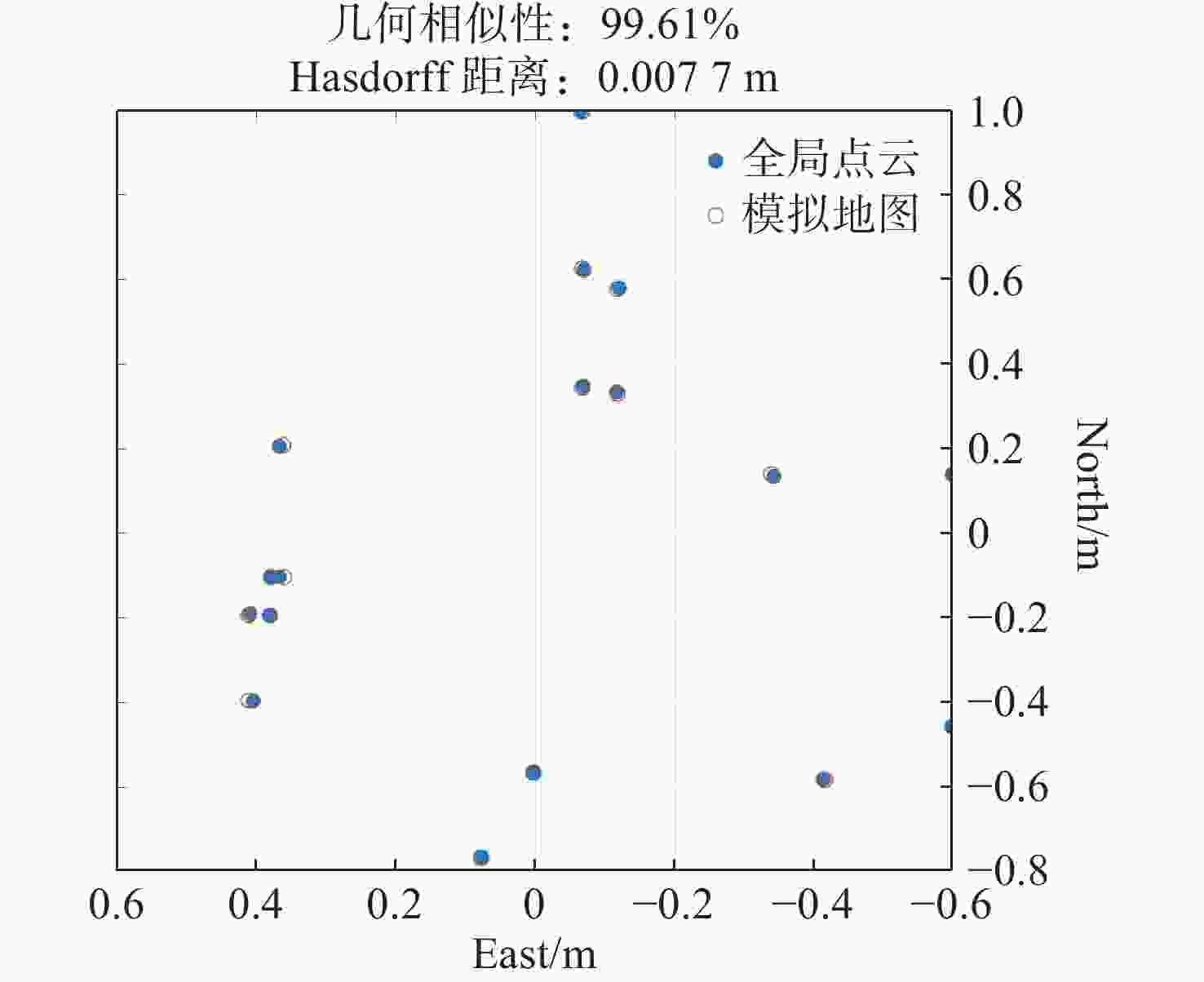
改进ICP平均值 9.03 m 3.67 m 0.26 m 0.21 m 最大值 9.36 m 5.97 m 4.52 m 0.80 m 最小值 8.20 m 2.69 m 0.04 m 0.04 m 标准差 0.34 m 0.58 m 0.77 m 0.16 m 耗时 0.094 s 0.172 s 0.110 s 0.186 s 表 2 仿真场景全局精配准绝对空间一致性分析
Table 2. Absolute spatial consistency analysis for global fine registration in simulated scenarios
平均值 最大值 最小值 标准差 距离误差 0.47 m 0.80 m 0.22 m 0.50 m 表 3 真实场景局部配准精度
Table 3. Local registration accuracy in real-world scenes
传统ICP 改进ICP 提取重叠区域+
传统ICP提取重叠区域+
改进ICP平均值 7.23 m 1.96 m 0.28 m 0.10 m 最大值 7.66 m 2.94 m 0.78 m 0.13 m 最小值 6.79 m 1.29 m 0.09 m 0.05 m 标准差 0.33 m 0.69 m 0.29 m 0.02 m 耗时 0.078 s 0.125 s 0.094 s 0.140 s -
[1] LESLIE M. On-chip LiDAR technology advances for cars, cell phones[J]. Engineering, 2022, 18: 3-5. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2022.09.003 [2] GUO M, SUN M X, ZHOU T F, et al. Novel trajectory optimization algorithm of vehicle-borne LiDAR mobile measurement system[J]. Sensors and Materials, 2020, 32(11): 3935-3953. doi: 10.18494/SAM.2020.3052 [3] 桑洋, 纪新春, 魏东岩, 等. 基于测速测距激光雷达的飞行器地形匹配导航方法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报,2024,32(1):8-15.SANG Y, JI X CH, WEI D Y, et al. Terrain matching navigation method for air vehicle based on FMCW LiDAR[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2024, 32(1): 8-15. [4] 孙国祥, 黄银锋, 汪小旵, 等. 基于LIO-SAM建图和激光视觉融合定位的温室自主行走系统[J]. 农业工程学报,2024,40(3):227-239. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202311146SUN G X, HUANG Y F, WANG X CH, et al. Autonomous navigation system in a greenhouse using LIO-SAM mapping and laser vision fusion localization[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2024, 40(3): 227-239. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202311146 [5] 郭明, 齐慧慧, 郭可才, 等. 融合北斗/GNSS定位和5G通讯的地基激光雷达测量系统[J]. 光学精密工程,2023,31(4):450-458. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20233104.0450GUO M, QI H H, GUO K C, et al. Ground-based LiDAR measurement system integrating BeiDou/GNSS positioning and 5G communication[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2023, 31(4): 450-458. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20233104.0450 [6] GUO M, ZHOU Y Q, ZHAO J H, et al. Urban Geospatial Information Acquisition Mobile Mapping System based on close-range photogrammetry and IGS site calibration[J]. Geo-spatial Information Science, 2021, 24(4): 558-579. doi: 10.1080/10095020.2021.1924084 [7] 王召泽, 韩若愚, 赵智伟, 等. 手持三维激光扫描仪在城市更新立面测量中的应用[J]. 测绘通报,2025(1):133-137.WANG ZH Z, HAN R Y, ZHAO ZH W, et al. The application of handheld 3D laser scanner in urban renewal facade measurement[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2025(1): 133-137. [8] 潘斌, 蔡志刚, 刘微微, 等. 机载激光雷达点云的城市建筑物直线特征提取方法[J]. 测绘工程,2022,31(5):16-23.PAN B, CAI ZH G, LIU W W, et al. Straight line feature extraction method of city airborne LiDAR point clouds[J]. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping, 2022, 31(5): 16-23. [9] MARINO R M, DAVIS W R. Jigsaw: a foliage-penetrating 3D imaging laser radar system[J]. Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 2005, 15(1): 23-36. [10] MARINO R M, STEPHENS T, HATCH R E, et al. A compact 3D imaging laser radar system using Geiger-mode APD arrays: system and measurements[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 5086: 1-15. doi: 10.1117/12.501581 [11] MARINO R M, DAVIS W R, RICH G C, et al. High-resolution 3D imaging laser radar flight test experiments[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2005, 9591: 138-151. [12] ALBOTA M A, AULL B F, FOUCHE D G, et al. Three-dimensional imaging laser radars with Geiger-mode avalanche photodiode arrays[J]. Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 2002, 13(2): 351-370. [13] ALBOTA M, GURJAR R, MANGOGNIA A, et al. The airborne optical systems testbed (AOSTB)[R]. Lexington: MIT Lincoln Laboratory Lexington United States, 2017. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献信息, 请确认). [14] KNOWLTON R. Airborne ladar imaging research testbed[R]. Lexington: MIT Lincoln Laboratory, 2011: 1. [15] PAWLIKOWSKA A M, HALIMI A, LAMB R A, et al. Single-photon three-dimensional imaging at up to 10 kilometers range[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(10): 11919-11931. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.011919 [16] ZHANG Y F, HE Y, YANG F, et al. Three-dimensional imaging lidar system based on high speed pseudorandom modulation and photon counting[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2016, 14(11): 111101-111105. doi: 10.3788/COL201614.111101 [17] ZHANG Z J, XU Y N, WU L, et al. Photon counting range-intensity image strategy in low-light level environments[J]. Optics Letters, 2014, 39(8): 2467-2470. doi: 10.1364/OL.39.002467 [18] 陈勇强, 贺岩, 罗远, 等. 基于盖革APD阵列脉冲式三维成像激光雷达系统[J]. 中国激光,2023,50(2):0210001. doi: 10.3788/CJL220683CHEN Y Q, HE Y, LUO Y, et al. Pulsed three-dimensional imaging lidar system based on Geiger-mode APD array[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2023, 50(2): 0210001. doi: 10.3788/CJL220683 [19] 韩超, 刘志勇, 刘德伟, 等. 单光子激光雷达中时间走时时差校准算法研究[J]. 中国光学,2023,16(2):271-280.HAN CH, LIU ZH Y, LIU D W, et al. Time walk correction algorithm for single-photon LiDAR systems[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(2): 271-280. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献信息, 请确认). [20] 高翔, 马玉波, 王晨, 等. 高精度激光雷达点云配准算法综述[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(3):495-509.GAO X, MA Y B, WANG CH, et al. Review of high-precision point cloud registration algorithms for LiDAR[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(3): 495-509. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献信息, 请确认). -





 下载:
下载: