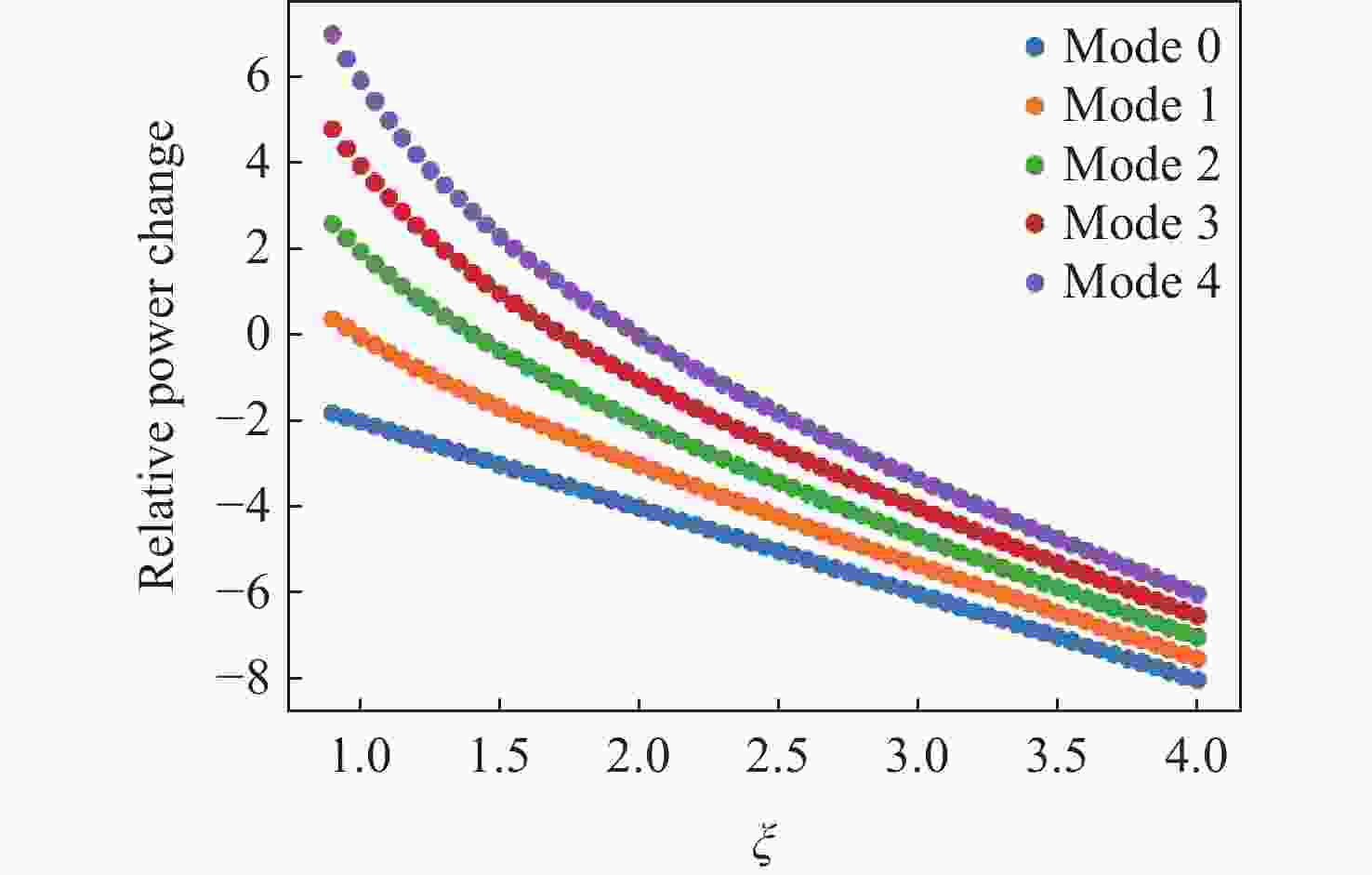
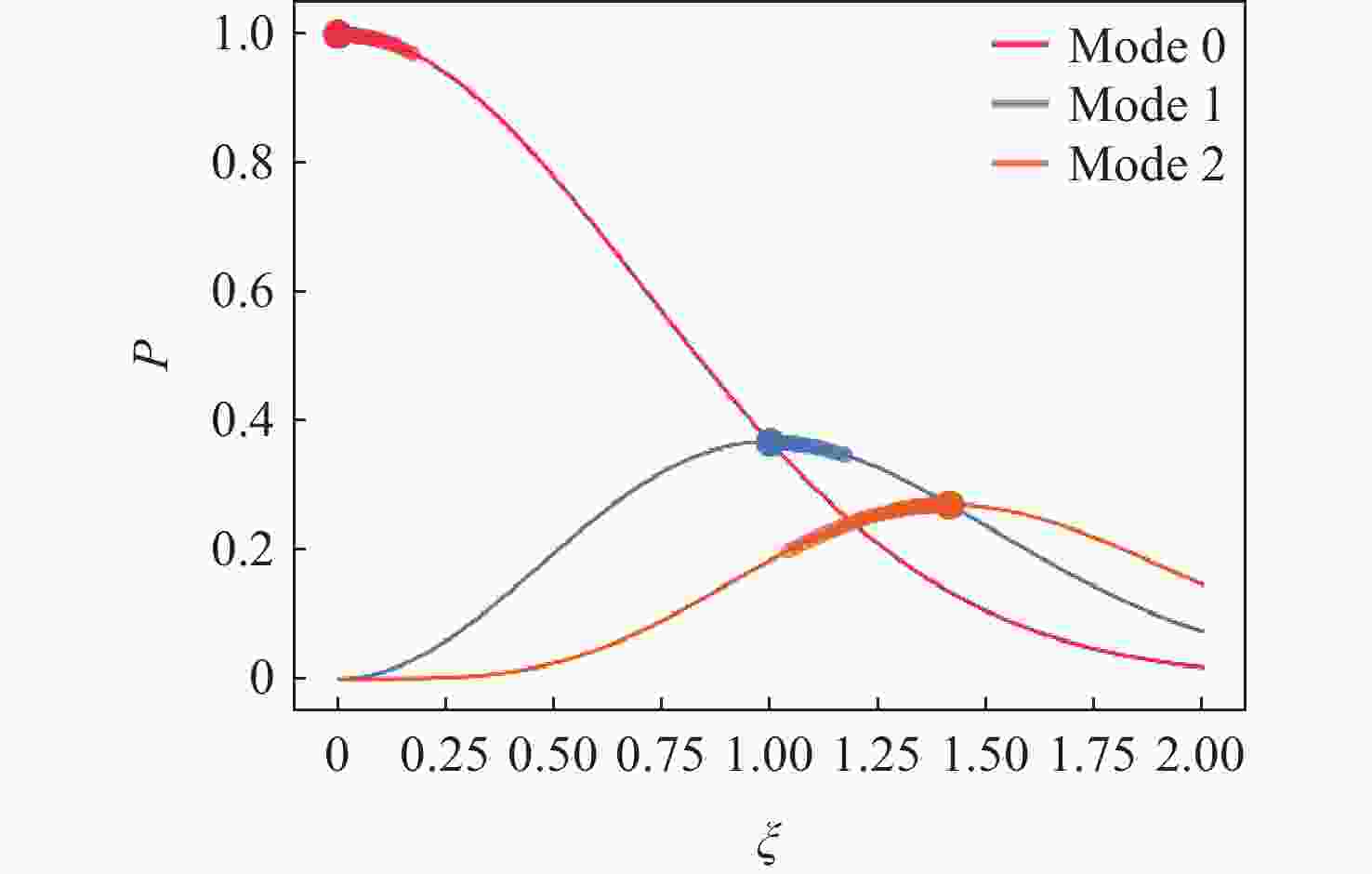
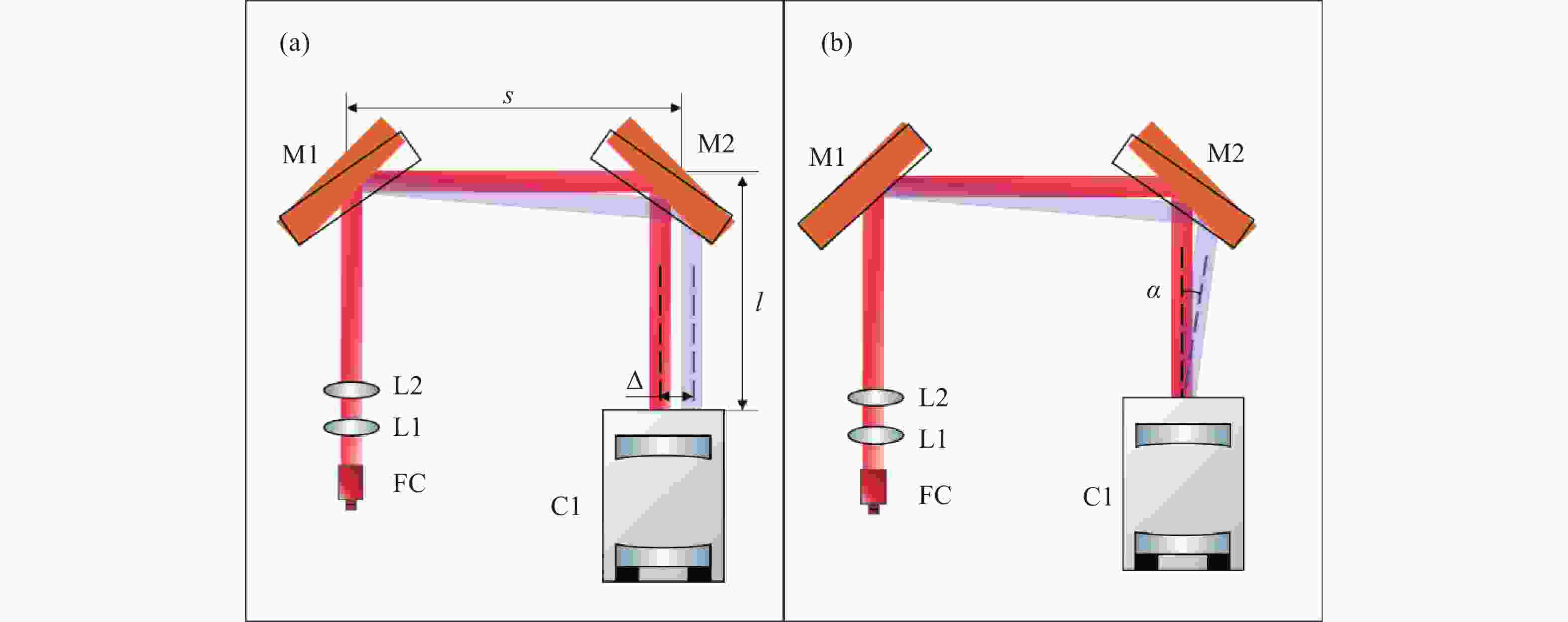
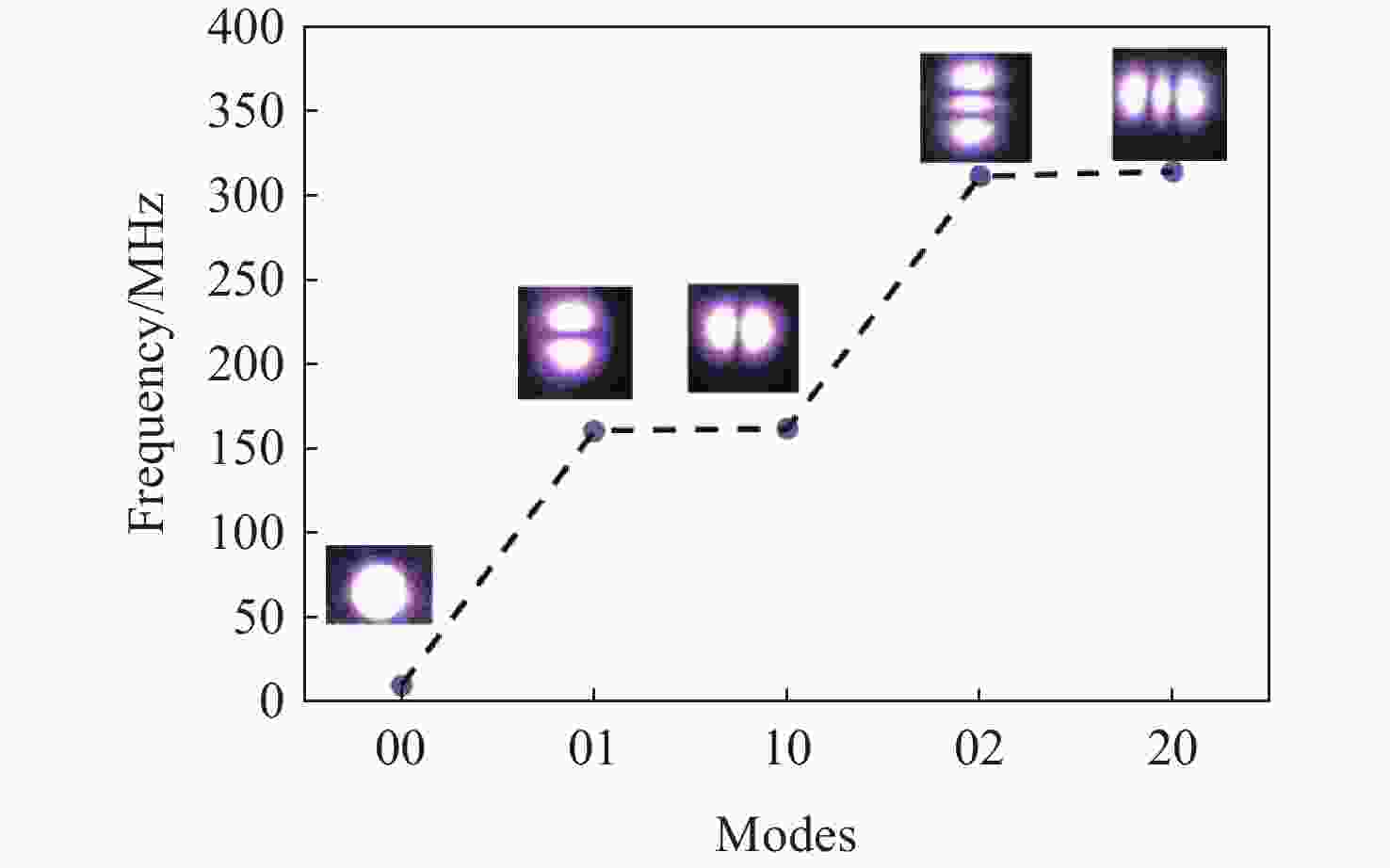
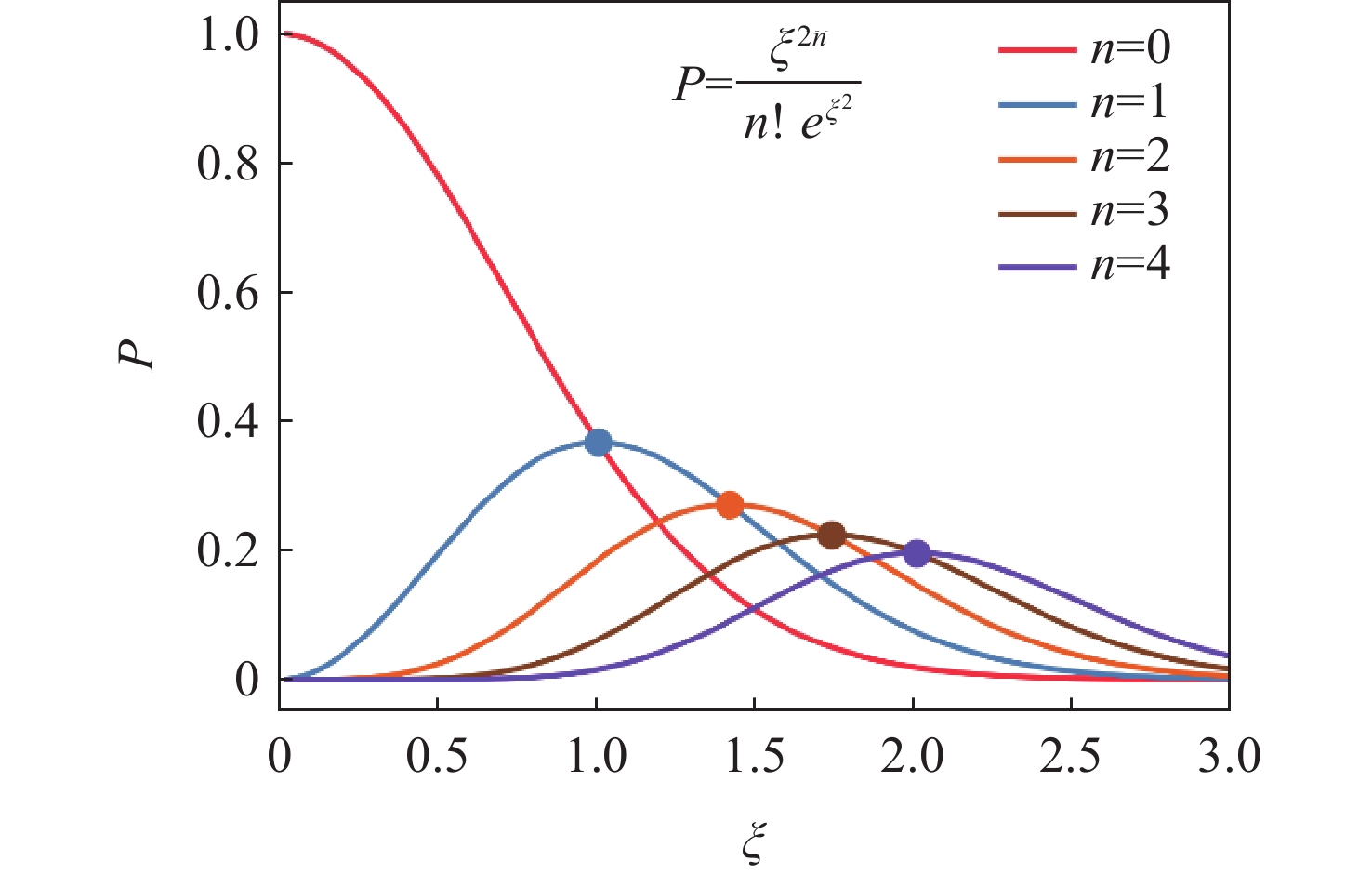
-
摘要:
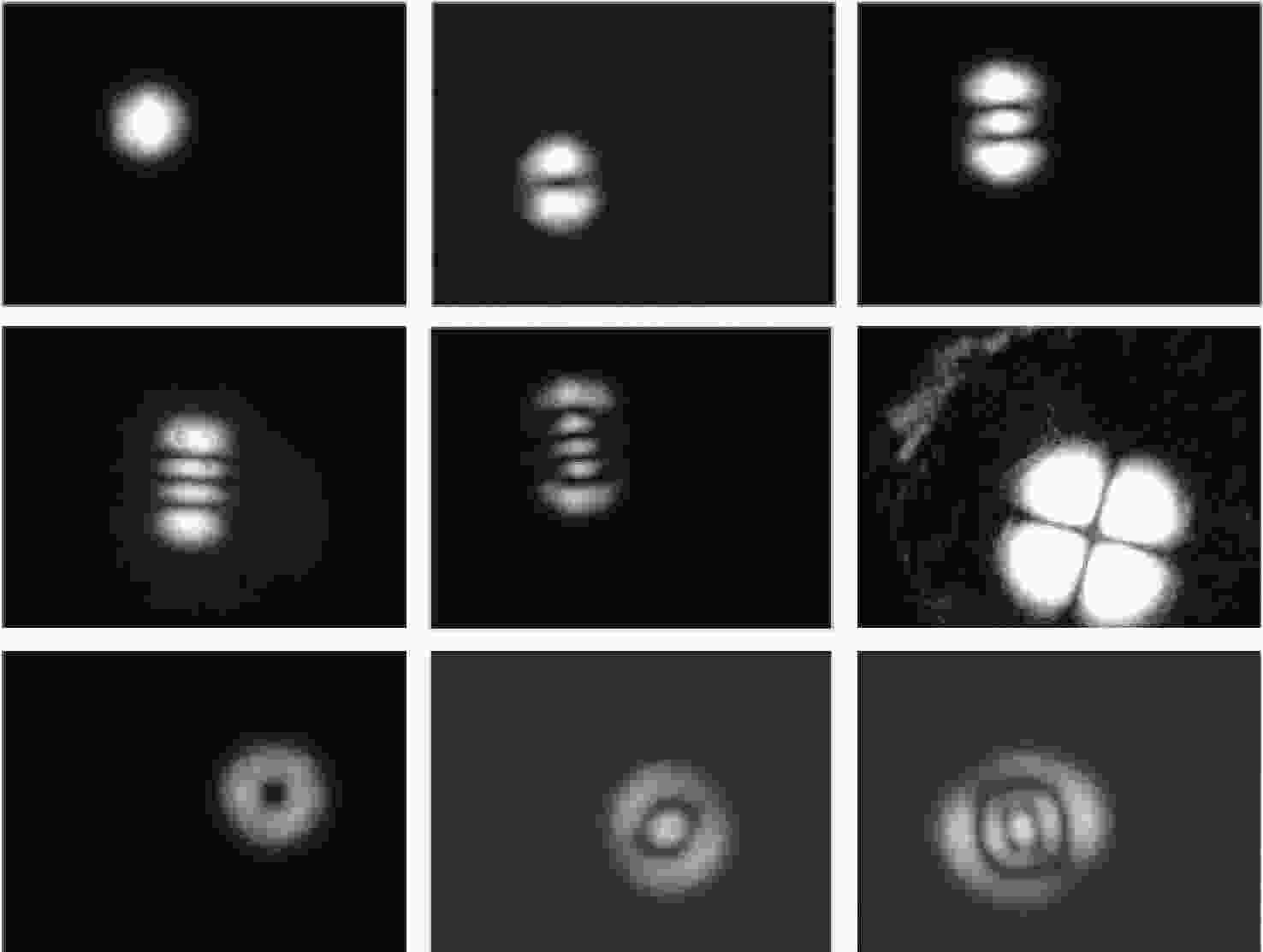
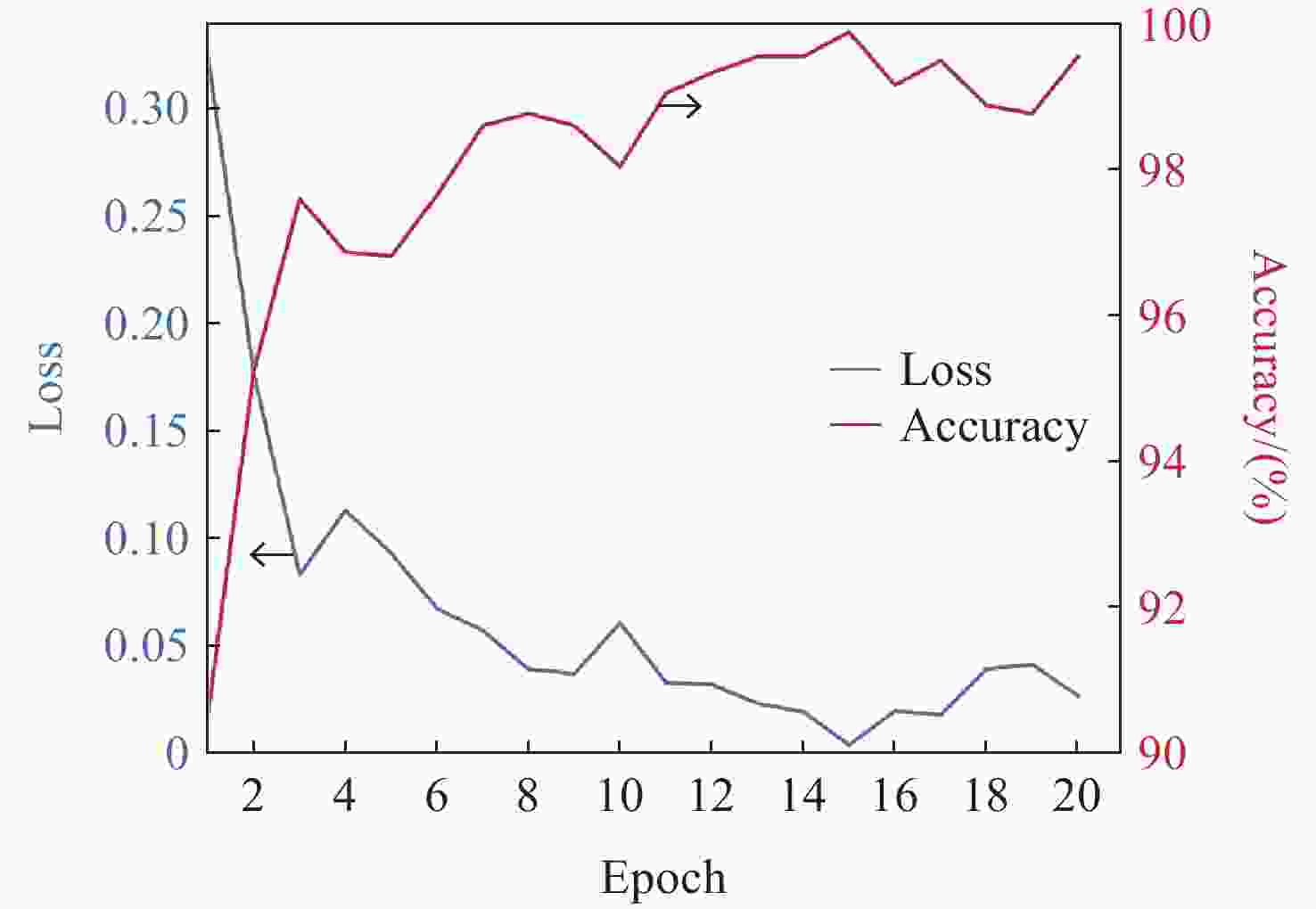
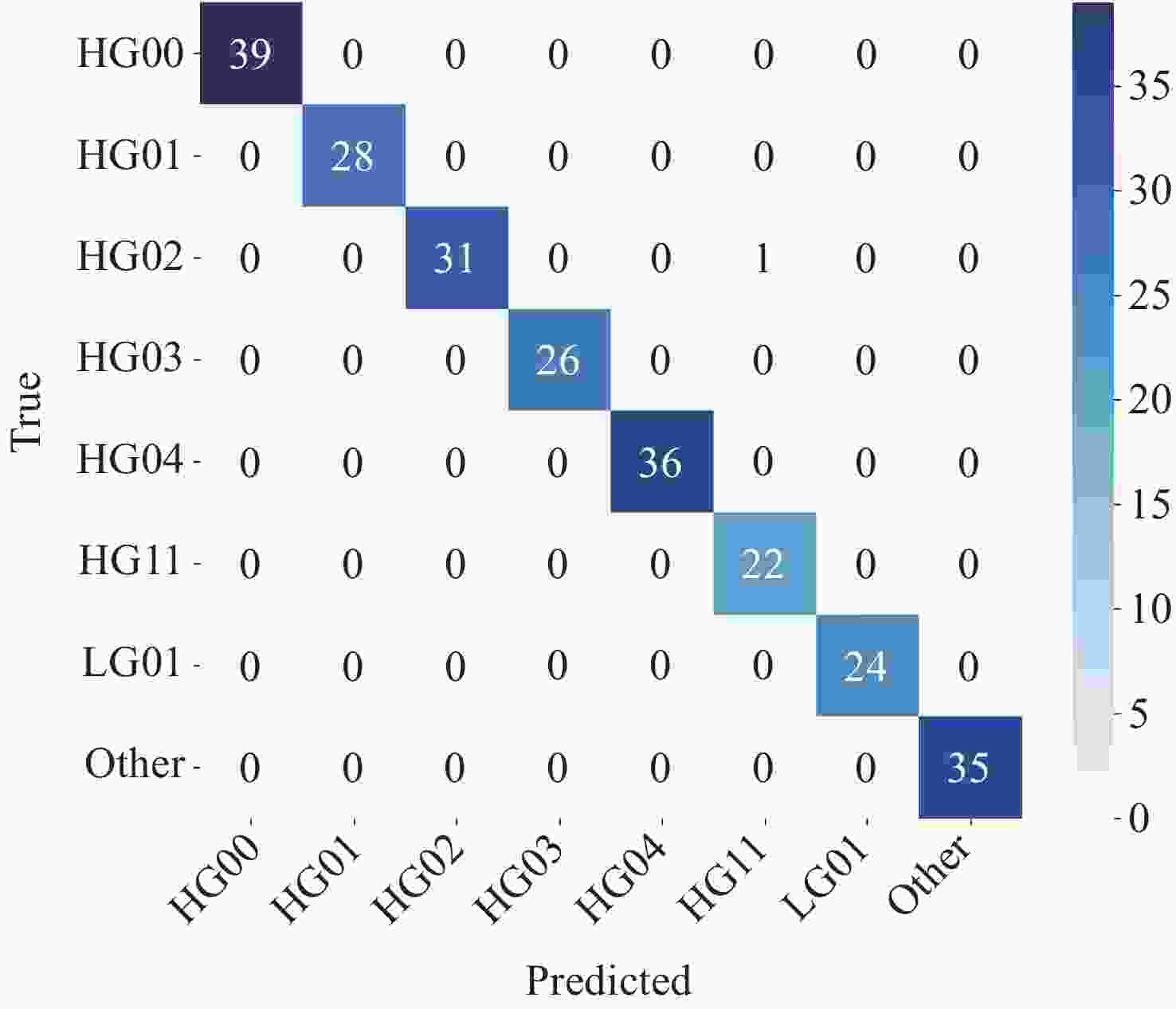
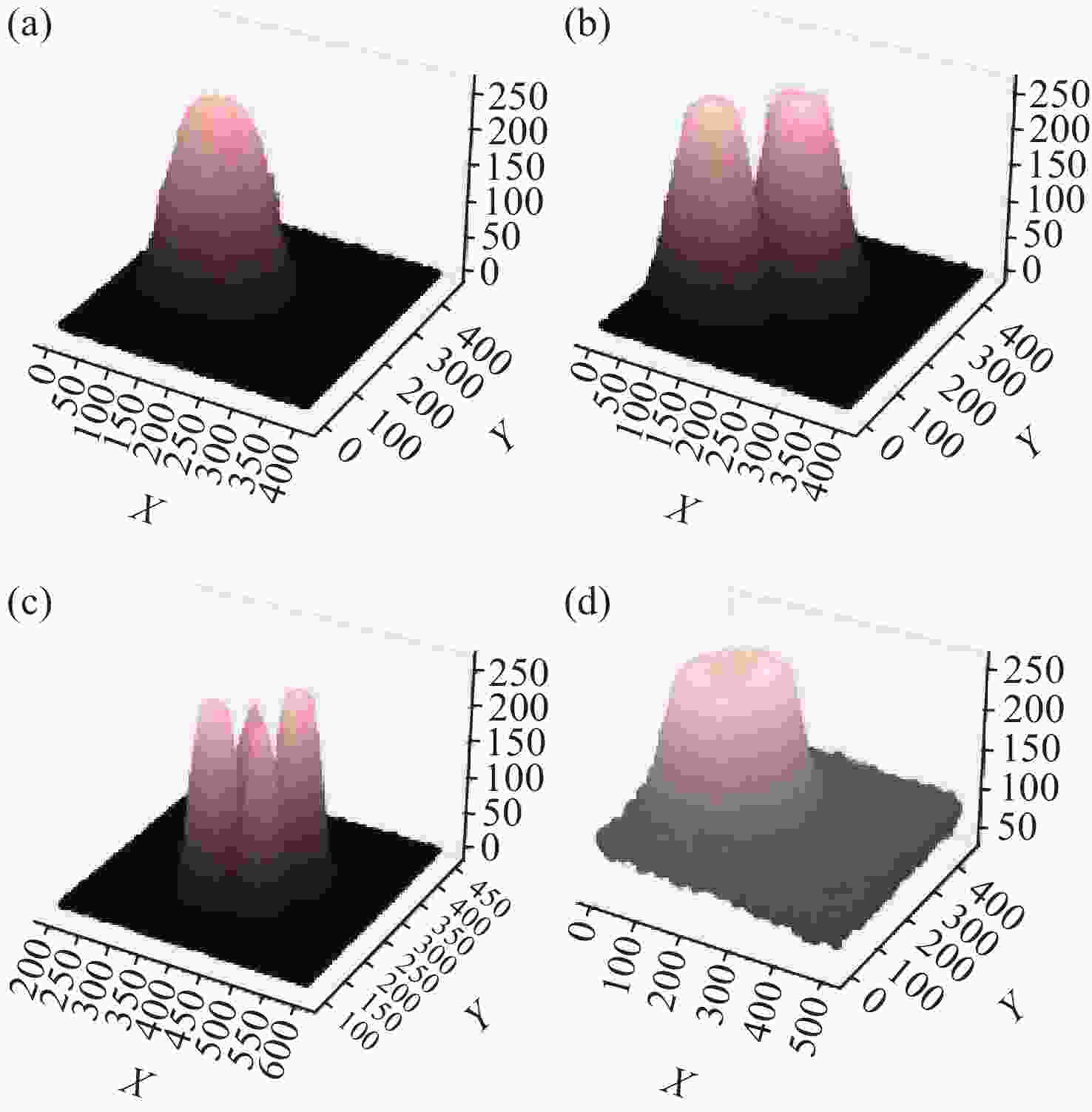
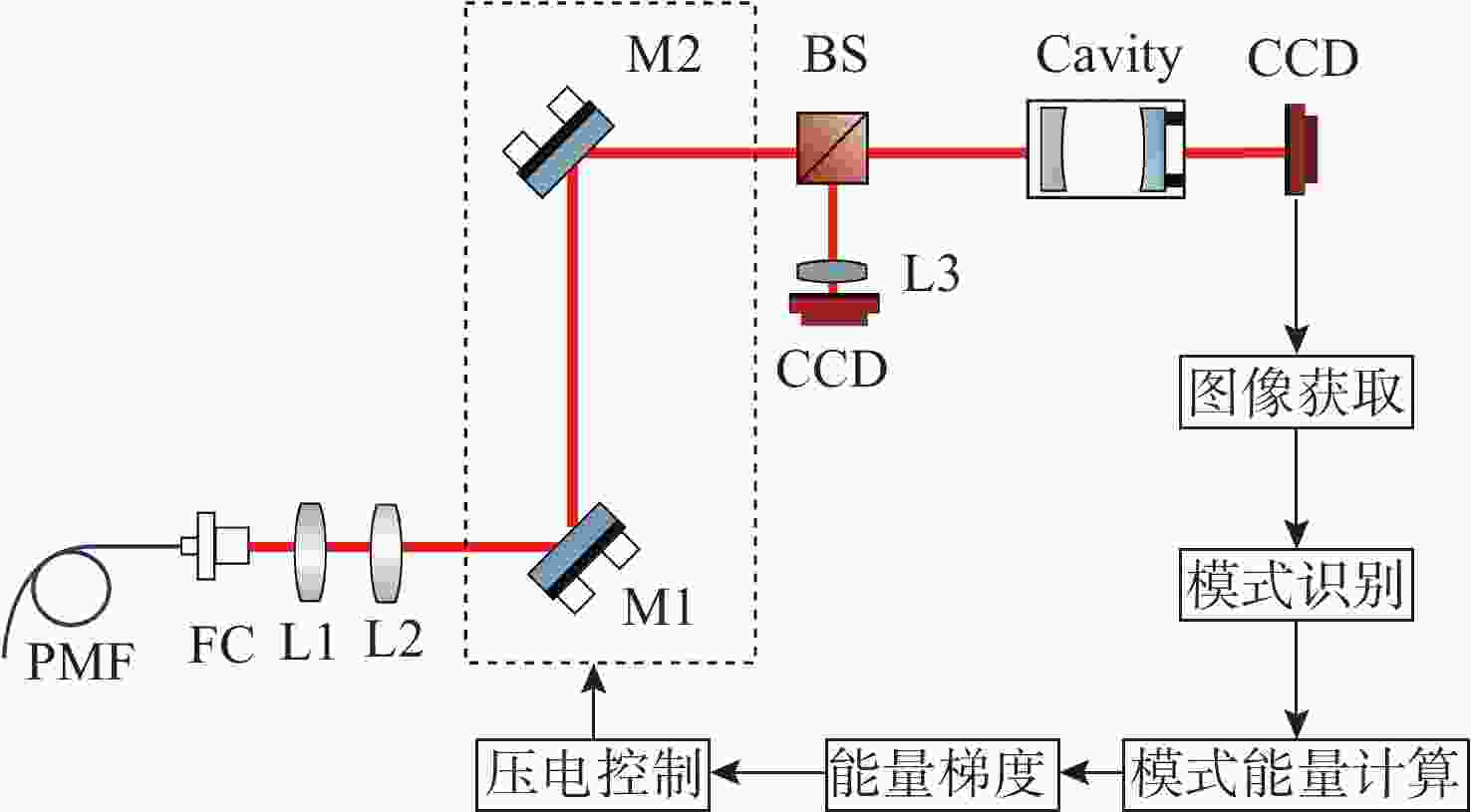
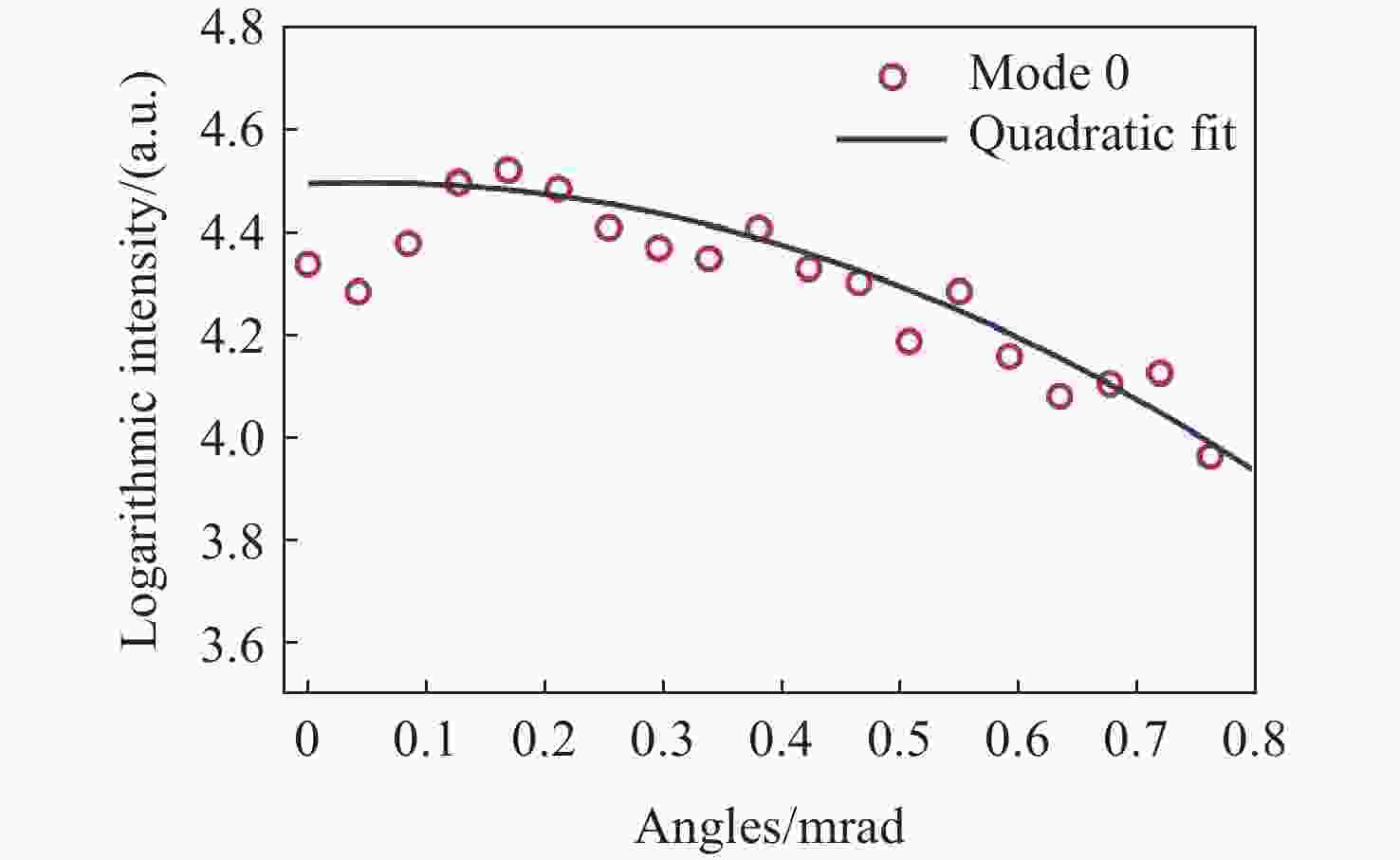
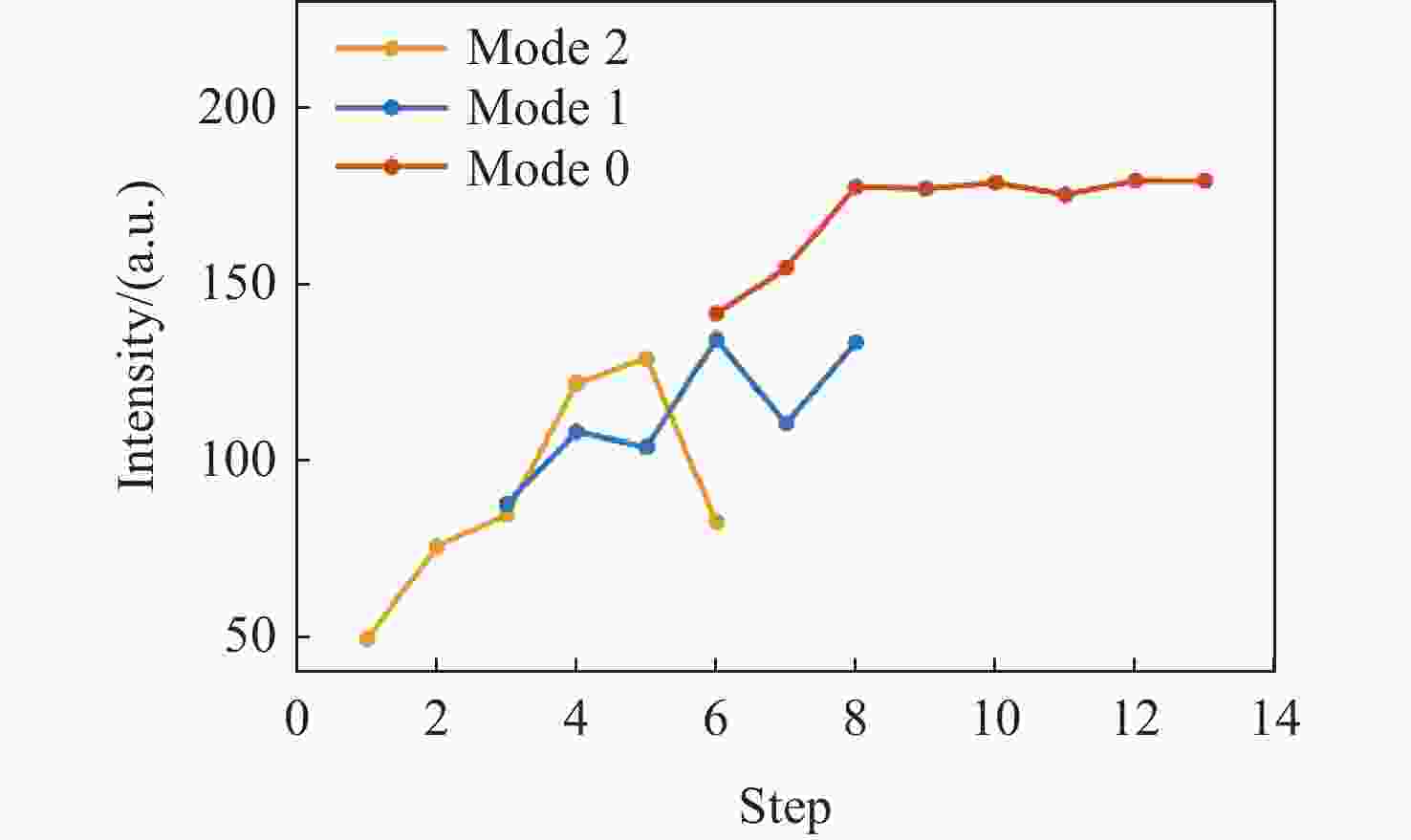
为了解决光束与法布里珀罗腔的入腔失调问题,本文基于谐振模式能量梯度上升自适应调整双反射镜步进,实现所需谐振模式的入腔光束指向。首先,利用双反射镜步进与入腔光束失调的关系,提出分离式入腔光束平移与角度调整方法。其次,利用EfficientNET神经网络对谐振模式图片进行分类,实现不同激光模式的图像识别。最后,利用腔后模式能量梯度调整双反射镜步进,低成本、高效率实现目标谐振模式的入腔耦合。本文的入腔光束指向调整方法为超稳激光器以及引力波探测中法布里珀罗腔的入腔耦合提供了新思路。
Abstract:Addressing the issue of beam alignment with Fabry-Pérot cavities, this paper proposes an adaptive dual-mirror step adjustment method based on the gradient ascent of transmitted resonant mode energy to achieve cavity coupling. First, leveraging the relationship between the reflection angles of the dual mirrors and the beam pointing, independent adjustment of the incident beam position and angle was proposed. Second, the EfficientNet neural network was used to classify resonant mode images, enabling identification of different mode images. Third, the energy gradient of the cavity mode was utilized for adaptively dual mirrors step adjustment, enabling low-cost and efficient cavity coupling of both fundamental and higher-order modes. The beam pointing adjustment method proposed will offer a novel solution for coupling lasers with Fabry-Pérot cavities in ultra-stable lasers and gravitational wave detection.
-
Key words:
- cavity coupling /
- beam pointing /
- Fabry-Pérot cavities /
- dual steering mirrors /
- gradient ascent
-
-
[1] AASI J, ABBOTT B P, ABBOTT R, et al. Advanced LIGO[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2015, 32(7): 074001. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/32/7/074001 [2] AASI J, ABADIE J, ABBOTT B P, et al. Enhanced sensitivity of the LIGO gravitational wave detector by using squeezed states of light[J]. Nature Photonics, 2013, 7(8): 613-619. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.177 [3] DANZMANN K, PRINCE T, BINETRUY P, et al. LISA: unveiling a hidden universe[R]. Paris: European Space Agency, 2011. [4] BLOOM B, NICHOLSON T L, WILLIAMS J R, et al. An optical lattice clock with accuracy and stability at the 10−18 level[J]. Nature, 2014, 506(7486): 71-75. doi: 10.1038/nature12941 [5] DREVER R W P, HALL J L, KOWALSKI F V, et al. Laser phase and frequency stabilization using an optical resonator[J]. Applied Physics B, 1983, 31(2): 97-105. [6] CAHILLANE C, MANSELL G L, SIGG D. Laser frequency noise in next generation gravitational wave detectors[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29: 42144-42161. doi: 10.1364/OE.439253 [7] ROSI G, SORRENTINO F, CACCIAPUOTI L, et al. Precision measurement of the Newtonian gravitational constant using cold atoms[J]. Nature, 2014, 510(7506): 518-521. doi: 10.1038/nature13433 [8] KESSLER T, HAGEMANN C, GREBING C, et al. A sub-40-mHz-linewidth laser based on a silicon single-crystal optical cavity[J]. Nature Photonics, 2012, 6(10): 687-692. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2012.217 [9] ANDERSON D Z. Alignment of resonant optical cavities[J]. Applied Optics, 1984, 23(17): 2944-2949. doi: 10.1364/AO.23.002944 [10] MAVALVALA N. Alignment issues in laser interferometric gravitational-wave detectors[D]. Cambridge: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1997. [11] BOND C, BROWN D, FREISE A, et al. Interferometer techniques for gravitational-wave detection[J]. Living Reviews in Relativity, 2016, 19(1): 3. doi: 10.1007/s41114-016-0002-8 [12] MORRISON E, MEERS B J, ROBERTSON D I, et al. Automatic alignment of optical interferometers[J]. Applied Optics, 1994, 33(22): 5041-5049. doi: 10.1364/AO.33.005041 [13] MORRISON E, MEERS B J, ROBERTSON D I, et al. Experimental demonstration of an automatic alignment system for optical interferometers[J]. Applied Optics, 1994, 33(22): 5037-5040. doi: 10.1364/AO.33.005037 [14] GROTE H, HEINZEL G, FREISE A, et al. The automatic alignment system of GEO 600[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2002, 19(7): 1849-1855. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/19/7/384 [15] SAYEH M R, BILGER H R, HABIB T. Optical resonator with an external source: excitation of the Hermite-Gaussian modes[J]. Applied Optics, 1985, 24(22): 3756-3761. doi: 10.1364/AO.24.003756 [16] TAO L, KELLEY-DERZON J, GREEN A C, et al. Power coupling losses for misaligned and mode-mismatched higher-order Hermite–Gauss modes[J]. Optics Letters, 2021, 46(11): 2694-2697. doi: 10.1364/OL.426999 [17] HOU Y. Control system for mirror tilting by deep learning[D]. Tokyo: Tokyo Institute of Technology, 2023. [18] MENG F CH, LI Z CH, LI J Q, et al. An active method for coupling laser with a high-finesse Fabry–Pérot cavity in ultra-stable lasers[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2024, 171: 110371. [19] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale[C]. Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR, 2021. [20] WANG C Y, BOCHKOVSKIY A, LIAO H Y M. YOLOv7: trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2023: 7464-7475. [21] KIRILLOV A, MINTUN E, RAVI N, et al. Segment anything[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2023: 4015-4026. [22] SOROKIN D, ULANOV A, SAZHINA E, et al. Interferobot: aligning an optical interferometer by a reinforcement learning agent[C]. Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Curran Associates Inc. , 2020: 1110. [23] SHAO R, ZHANG G, GONG X. Generalized robust training scheme using genetic algorithm for optical neural networks with imprecise components[J]. Photonics Research, 2022, 10(8): 1868-1876. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.449570 [24] QIN J Y, KINDER K, JADHAV S, et al. Automated alignment of an optical cavity using machine learning[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2025, 42(4): 045003. doi: 10.1088/1361-6382/ada864 [25] TAN M X, LE Q V. EfficientNet: rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML, 2019: 6105-6114. -





 下载:
下载: