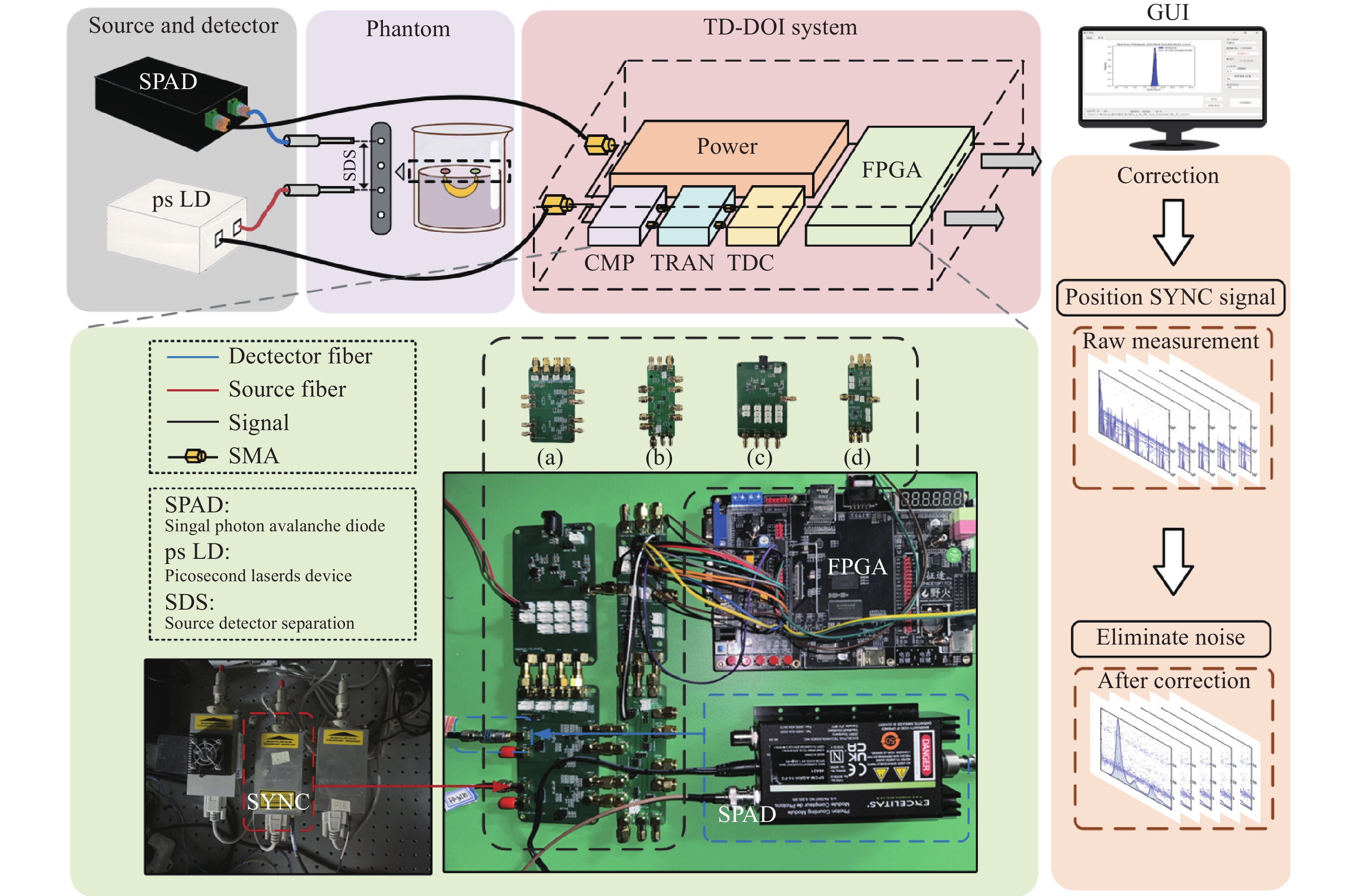
A time-domain diffuse optical imaging system based on differential time-to-digital converter photon-counting technology
-
摘要:
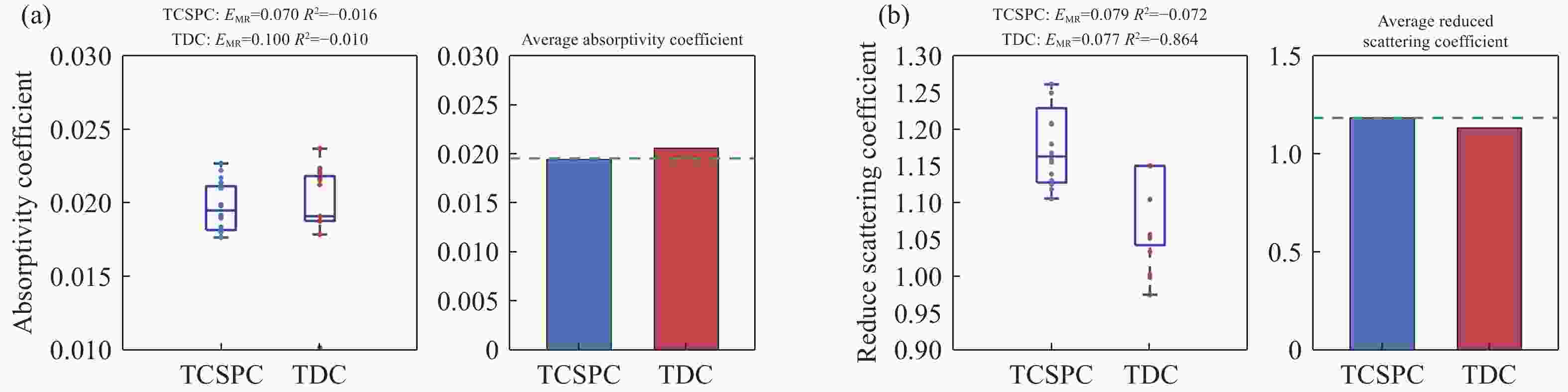
时域扩散光学成像(time domain diffuse optical imaging, TD-DOI)作为一种先进的组织光学成像技术,通过时间相关单光子计数(time-correlated single photon counting, TCSPC)系统可实现生物组织吸收系数与散射系数的定量重建,从而精确评估组织氧代谢、血流灌注等关键生理参数。然而,受限于TCSPC系统固有的硬件复杂性、高成本特性,目前难以实现临床场景下在体多通道动态监测的规模化应用需求。本文发展了一种双通道差分混合触发参考信号策略,通过结合差分时间数字转换(time-to-digital converter, TDC)器件和光子计数技术,构建稳定可靠的时间扩展曲线(time point spread function, TPSF)测量体系,实现了激光同步信号与出射光子信号时间延迟的亚纳秒级精确标定。实验验证数据显示,所发展系统时间分辨率为55 ps,在2.3×104 光子/s计数率条件下,TPSF波动系数可稳定控制在1.35%以内(积分时间1 s)。针对组织仿体的光学参数反演测试表明,组织光学参数反演精度方面,吸收系数与约化散射系数的平均反演误差分别在5.39%和4.34%以内。该技术方案显著提升了TD-DOI多通道并行检测可行性,特别适用于脑皮层血氧饱和度动态监测等生物医学场景,为开发新一代穿戴式光学脑功能成像设备奠定了技术基础。
Abstract:As an advanced tissue optical imaging technology, time-domain diffuse optical imaging (TD-DOI) enables quantitative reconstruction of absorption and reduced scattering coefficients in biological tissues through time-correlated single photon counting (TCSPC) systems, thereby allowing precise assessment of critical physiological parameters such as tissue oxygen metabolism and blood perfusion. However, constrained by the inherent hardware complexity and high cost of TCSPC systems, current implementations face challenges in achieving scalable clinical applications requiring in-vivo multichannel dynamic monitoring. This study innovatively proposes a dual-channel differential hybrid trigger reference signal strategy. By integrating differential time-to-digital converter (TDC) devices with photon counting techniques, we have established a stable and reliable time point spread function (TPSF) measurement system that achieves sub-nanosecond precision (±50 ps) in calibrating the temporal delay between laser synchronization signals and emitted photon events. Experimental validation demonstrates that the developed system attains a temporal resolution of 55 ps. Under photon counting rates of 2.3×104 photons/s, the TPSF fluctuation coefficient remains consistently below 1.35% (1 s integration time). Optical properties inversion on tissue phantoms reveal mean reconstruction errors of 5.39% for absorption coefficient and 4.34% for reduced scattering coefficient. This technological advancement significantly enhances the feasibility of multichannel parallel detection in TD-DOI systems. Particularly suited for biomedical applications, such as dynamic monitoring of cerebral cortical oxygen saturation, it establishes a technical foundation for developing next-generation wearable optical brain function imaging devices.
-
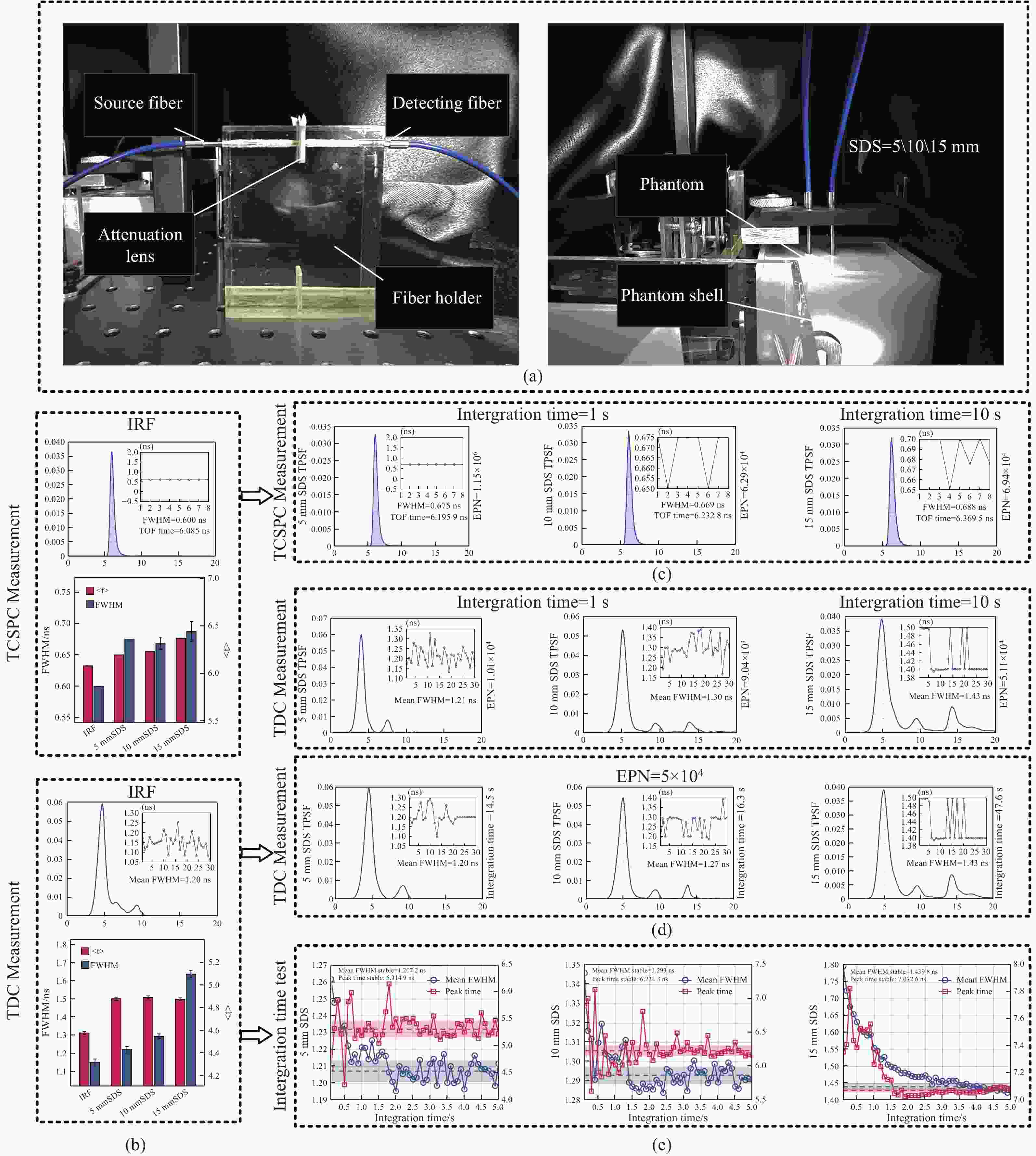
图 6 TPSF曲线稳定性评估实验:(a)实验配置图(仿体尺寸:长85 cm;宽50 cm;高50 cm);(b)TCSPC与TDC系统的IRF曲线特点对比;(c)TCSPC在不同配置下TPSF曲线;(d)TDC在不同配置下TPSF曲线;(e)TDC在不同配置下FHWM变化规律
Figure 6. Results of the evaluation of TPSF stability in the phantom experiment: (a) Experimental configuration diagram (phantom dimensions: 85 cm (L) × 50 cm (W) × 50 cm (H)); (b) Comparison of the of the IRF between TCSPC and the TDC module; (c) TPSF of TCSPC under different configurations; (d) TPSF curves of TDC module under different configurations; (e) Variation of FWHM of TDC module under different configurations.
-
[1] PAPADIMITRIOU K I, DEMPSEY L A, HEBDEN J C, et al. A spread spectrum approach to time-domain near-infrared diffuse optical imaging using inexpensive optical transceiver modules[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2018, 9(6): 2648-2663. doi: 10.1364/BOE.9.002648 [2] DELPY D T, COPE M, VAN DER ZEE P, et al. Estimation of optical pathlength through tissue from direct time of flight measurement[J]. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 1988, 33(12): 1433-1442. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/33/12/008 [3] ALMAJIDY R K, MANKODIYA K, ABTAHI M, et al. A newcomer's guide to functional near infrared spectroscopy experiments[J]. IEEE Reviews in Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 13: 292-308. doi: 10.1109/RBME.2019.2944351 [4] SONG M, ZHANG Y J, CUI Y, et al. Brain network studies in chronic disorders of consciousness: advances and perspectives[J]. Neuroscience Bulletin, 2018, 34(4): 592-604. doi: 10.1007/s12264-018-0243-5 [5] YANG L, WABNITZ H, GLADYTZ T, et al. Spatially-enhanced time-domain NIRS for accurate determination of tissue optical properties[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(19): 26415-26431. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.026415 [6] NABACINO M, AMENDOLA C, CONTINI D, et al. Fast multi-distance time-domain NIRS and DCS system for clinical applications[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24(22): 7375. doi: 10.3390/s24227375 [7] ORTEGA-MARTINEZ A, ROGERS D J, ANDERSON J, et al. How much do time-domain functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) moments improve estimation of brain activity over traditional fNIRS?[J]. Neurophotonics, 2023, 10(1): 013504. [8] WEI L P, TIAN Y, YAN W R, et al. Liquid-core waveguide TCSPC sensor for high-accuracy fluorescence lifetime analysis[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2019, 411(16): 3641-3652. doi: 10.1007/s00216-019-01847-6 [9] FARINA S, LABANCA I, ACCONCIA G, et al. A 4.5 Ps precision TCSPC system: design principles and characterization[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2024, 30(1): 3800611. [10] CHEKIN Y, DECKER D, DEHGHANI H, et al. Time-domain diffuse optical tomography for precision neuroscience[J]. bioRxiv, 2024: 2024. 04. 30. 591765. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献卷期页码信息, 请确认). [11] CHEN H CH. Design and implementation of high linearity FPGA-TDCs and an integrated large scale TCSPC system for time-resolved applications[D]. Glasgow: University of Strathclyde, 2020. [12] XIAO D, SAPERMSAP N, SAFAR M, et al. On synthetic instrument response functions of time-correlated single-photon counting based fluorescence lifetime imaging analysis[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2021, 9: 635645. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2021.635645 [13] DUBOIS J, DUFFY J G, FIELD R M, et al. A functional neuroimaging biomarker of mild cognitive impairment using TD-fNIRS[J]. npj Dementia, 2025, 1(1): 14. doi: 10.1038/s44400-025-00018-y [14] RE R, PIROVANO I, CONTINI D, et al. Reliable fast (20 Hz) acquisition rate by a TD fNIRS device: brain resting-state oscillation studies[J]. Sensors, 2022, 23(1): 196. doi: 10.3390/s23010196 [15] LI C, LUO Y J, HUANG Y, et al. A low-cost test method for accurate detection of different excited-state species with a lifetime span over 5 orders of magnitude in one time window[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 95(21): 8150-8155. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c00319 [16] DUBOIS J, FIELD R M, JAWHAR S, et al. Reliability of brain metrics derived from a time-domain functional near-infrared spectroscopy system[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1): 17500. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68555-9 [17] BAN H Y, BARRETT G M, Borisevich A, et al. Kernel flow: a high channel count scalable TD-fNIRS system[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2021, 11663: 116630B. [18] BOAS D, VON LÜHMANN A, YÜCEL M, et al. Advances in wearable high density fNIRS and utility for BCI[C]. Proceedings of 2024 12th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface (BCI), IEEE, 2024: 1-2. [19] RE R, CONTINI L, CONTINI D, et al. Cerebral resting state oscillations study with TD fNIRS[C]. Proceedings of European Conference on Biomedical Optics, Optica Publishing Group, 2023: 126280I. [20] ZALKE J B, PANDEY S R, NARKHEDE N P. An ultrasonic time-of-flight sensing system based on custom hardware of Time to Digital Converter (TDC) for measurement of glucose concentration[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(7): 11136-11143. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3363763 [21] MACLEAN J I, STEWART B D, GYONGY I. TDC-less direct time-of-flight imaging using spiking neural networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(20): 33838-33846. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3454974 [22] ARREDONDO-VELÁZQUEZ M, REBOLLEDO-HERRERA L, ZEPEDA-FERNÁNDEZ H, et al. Trimmed-TDL-based TDC architecture for time-of-flight measurements tested on a cyclone V FPGA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: 2003309. [23] WU J Y, SHI Z H. The 10-ps wave union TDC: improving FPGA TDC resolution beyond its cell delay[C]. Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record, IEEE, 2008: 3440-3446. [24] ADAMIČ M, TROST A. A fast high-resolution time-to-digital converter implemented in a Zynq 7010 SoC[C]. Proceedings of 2019 Austrochip Workshop on Microelectronics (Austrochip), IEEE, 2019: 29-34. [25] KIM E J, PARK H S, CHOI W Y, et al. Direct time-of-flight sensor system based on SPAD IC[C]. Proceedings of 2024 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Asia (ICCE-Asia), IEEE, 2024: 1-4. -





 下载:
下载: