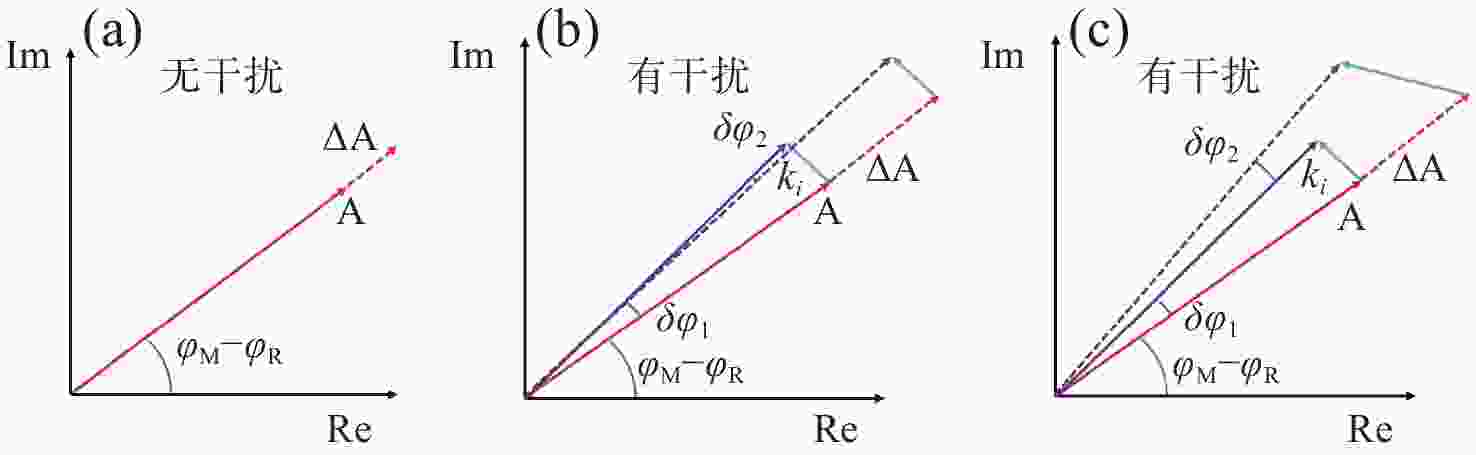
-
摘要:
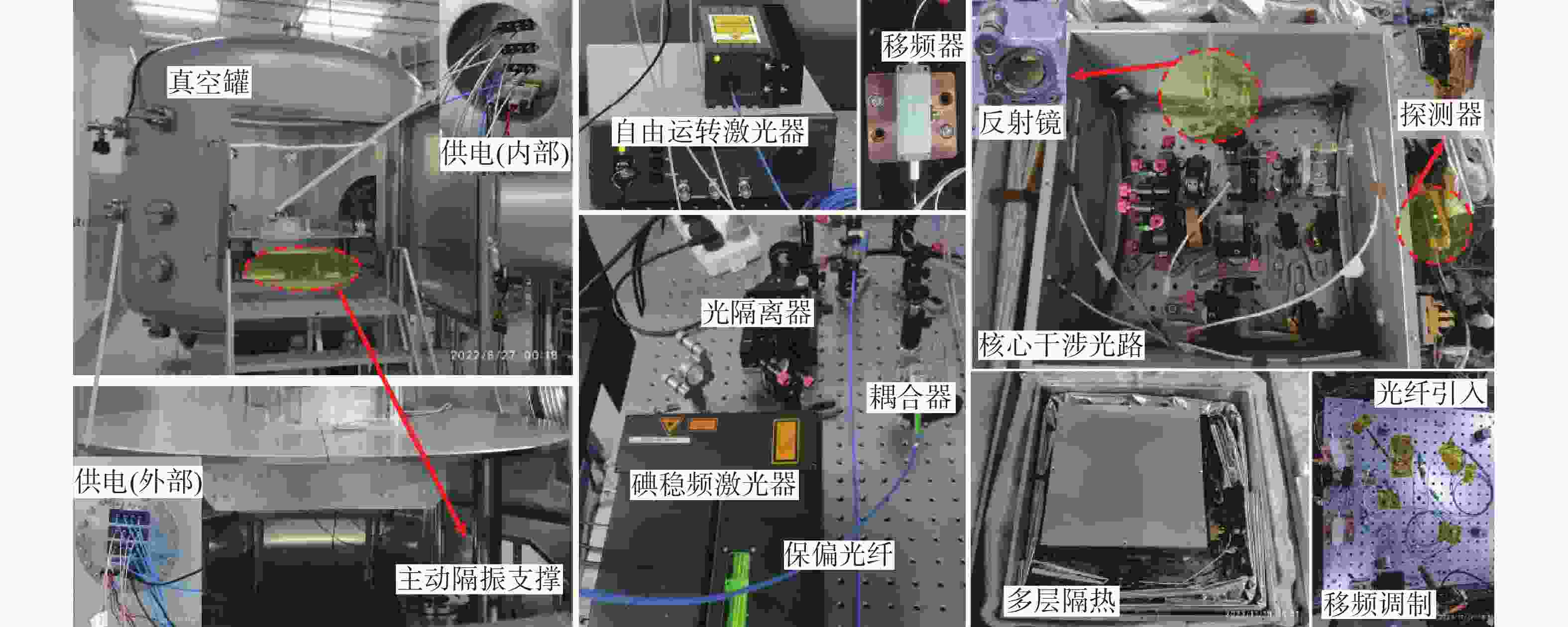
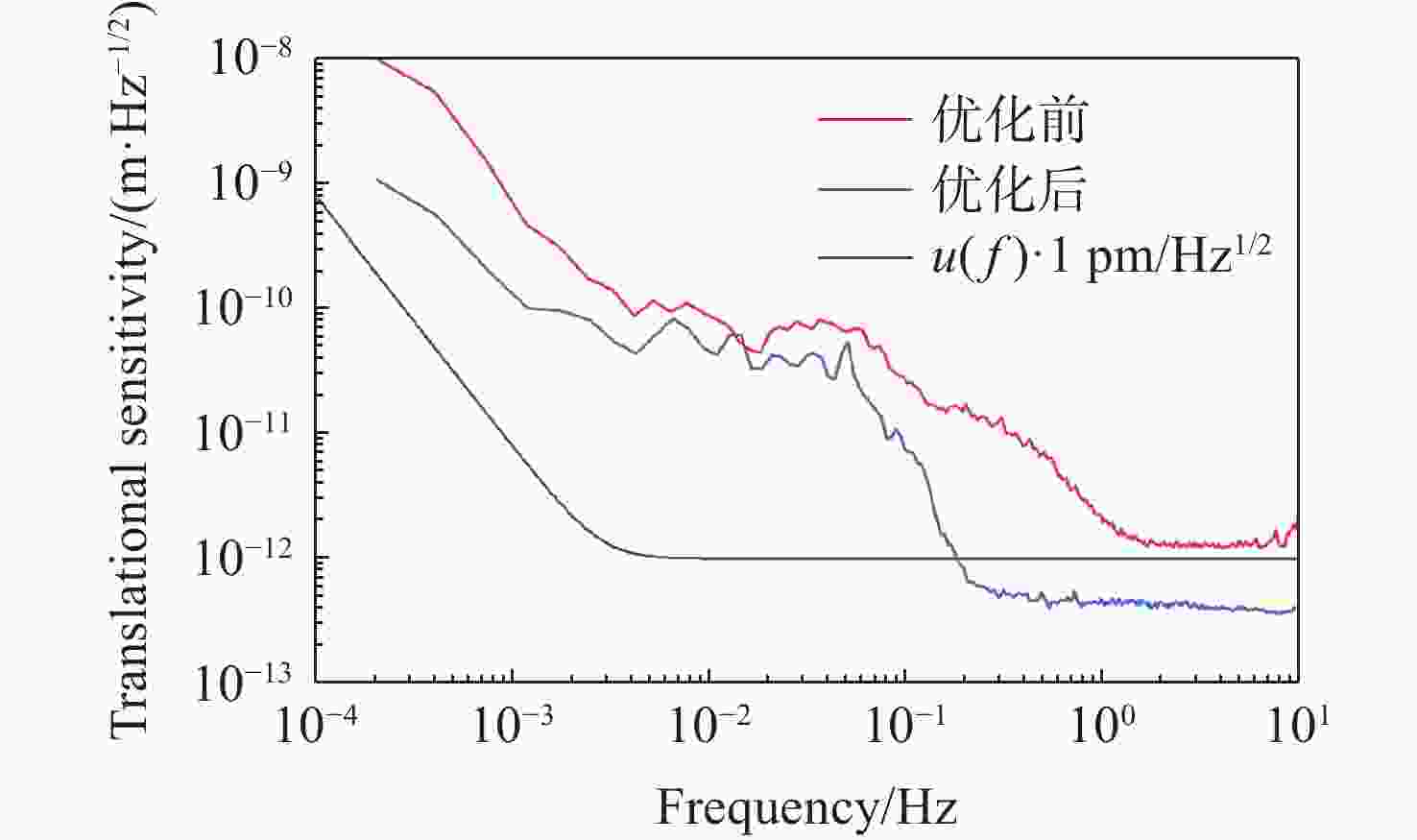
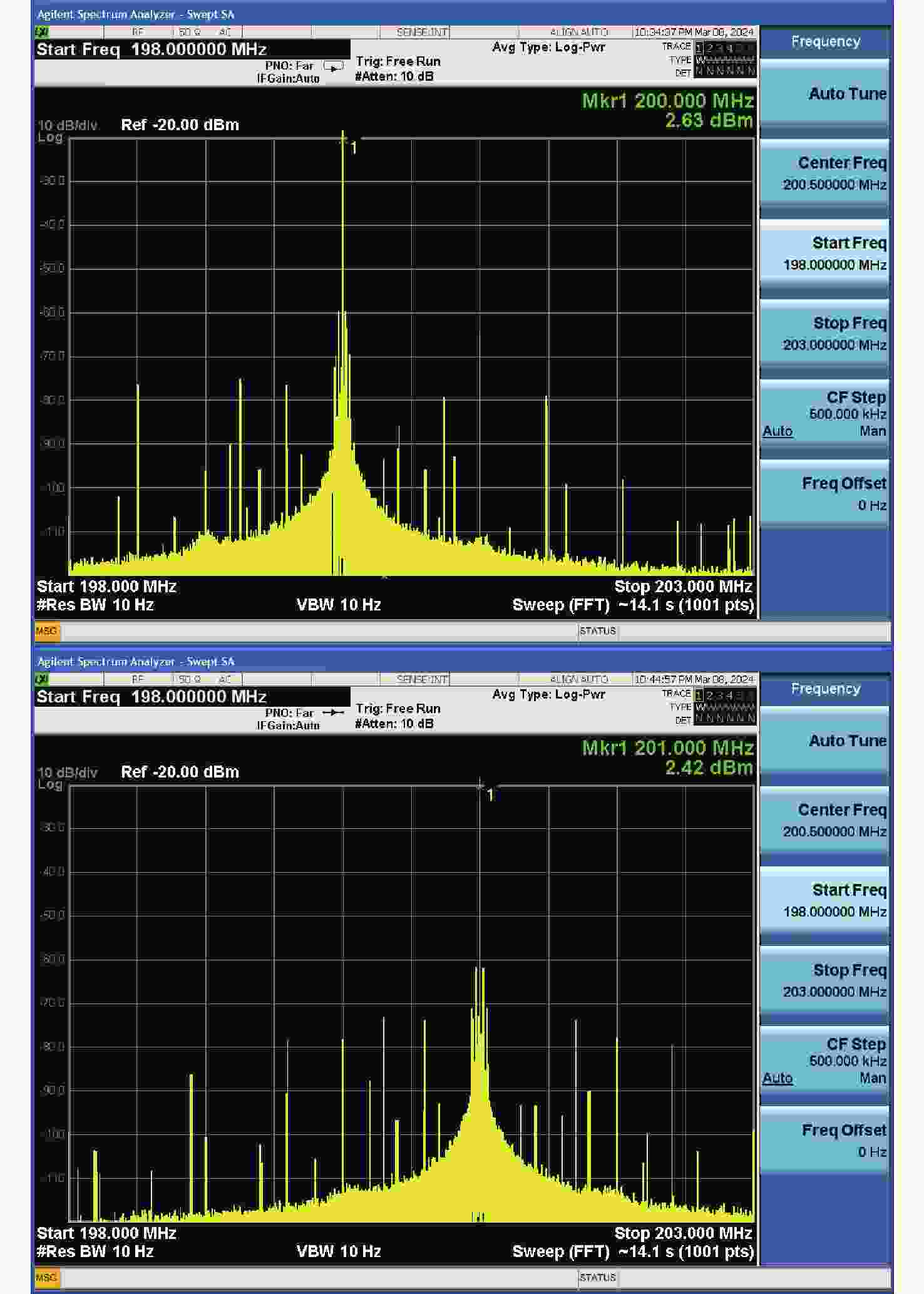
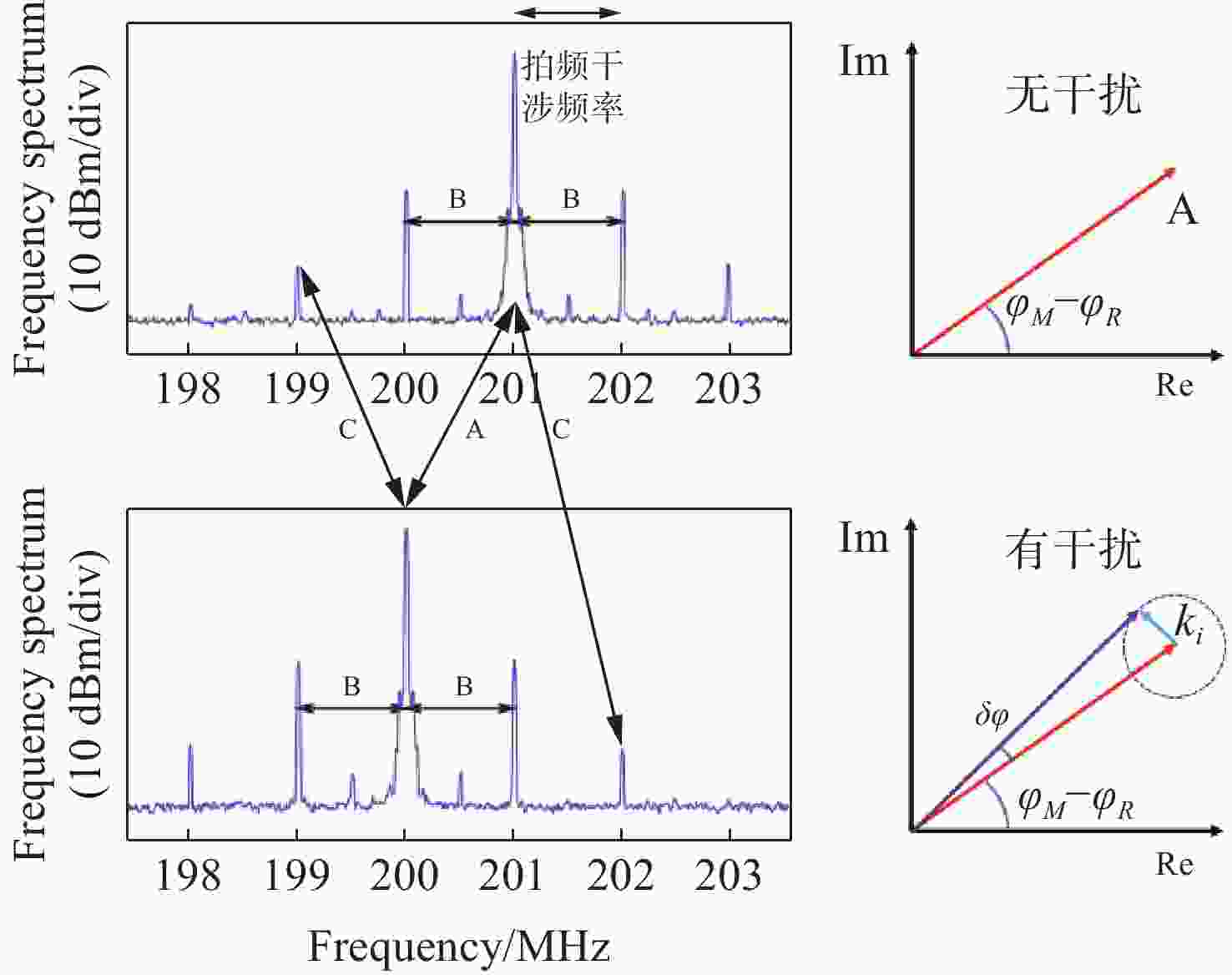
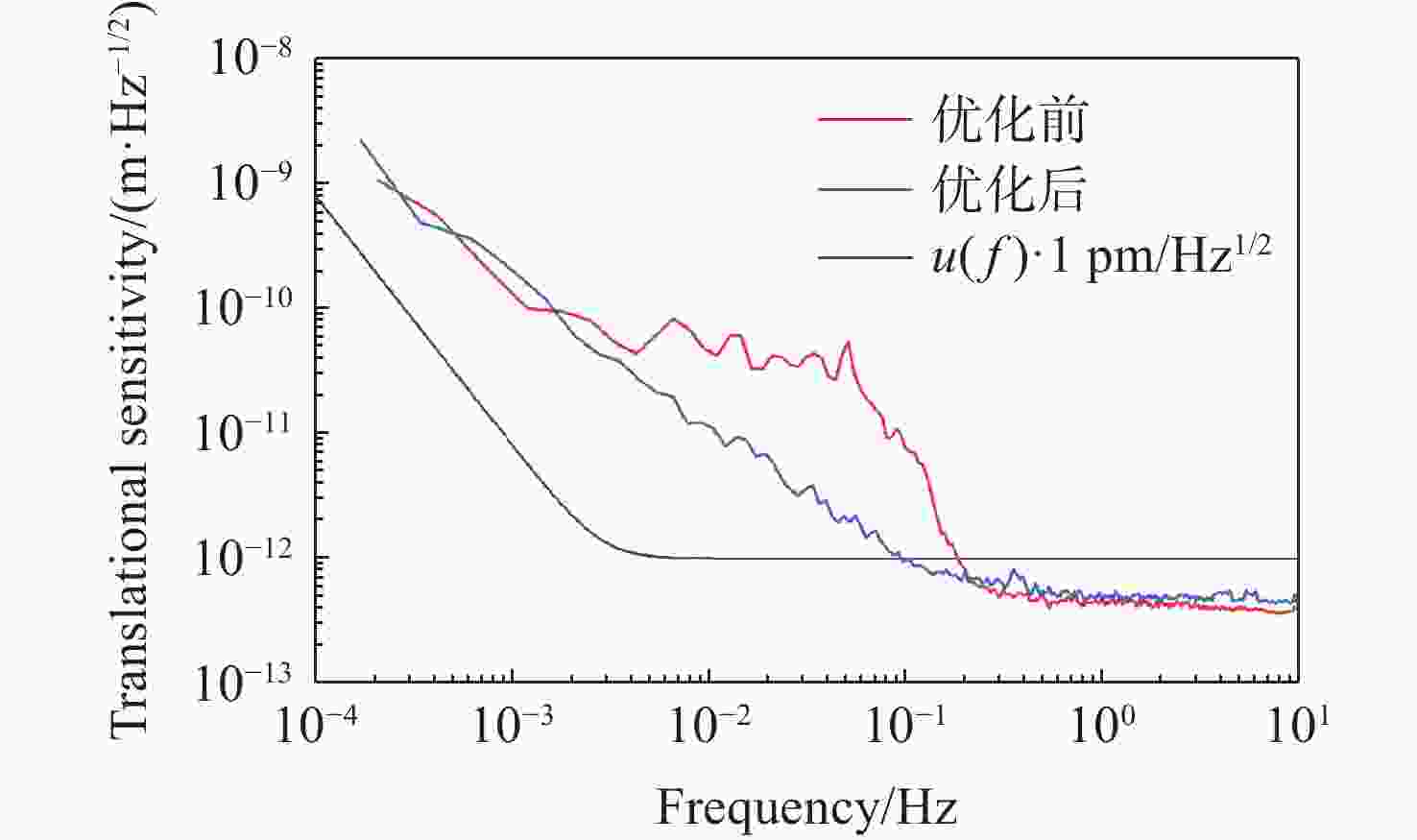
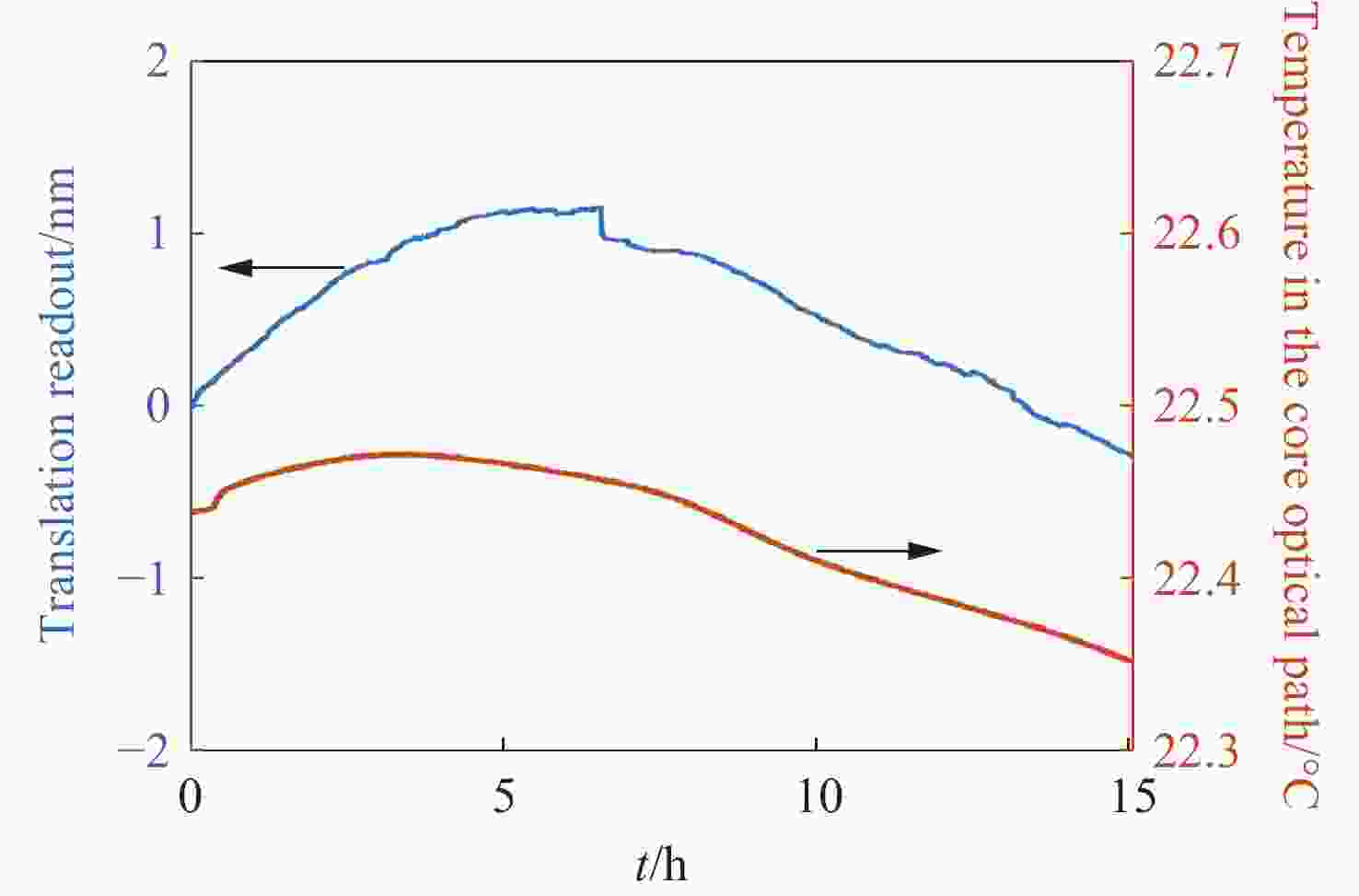
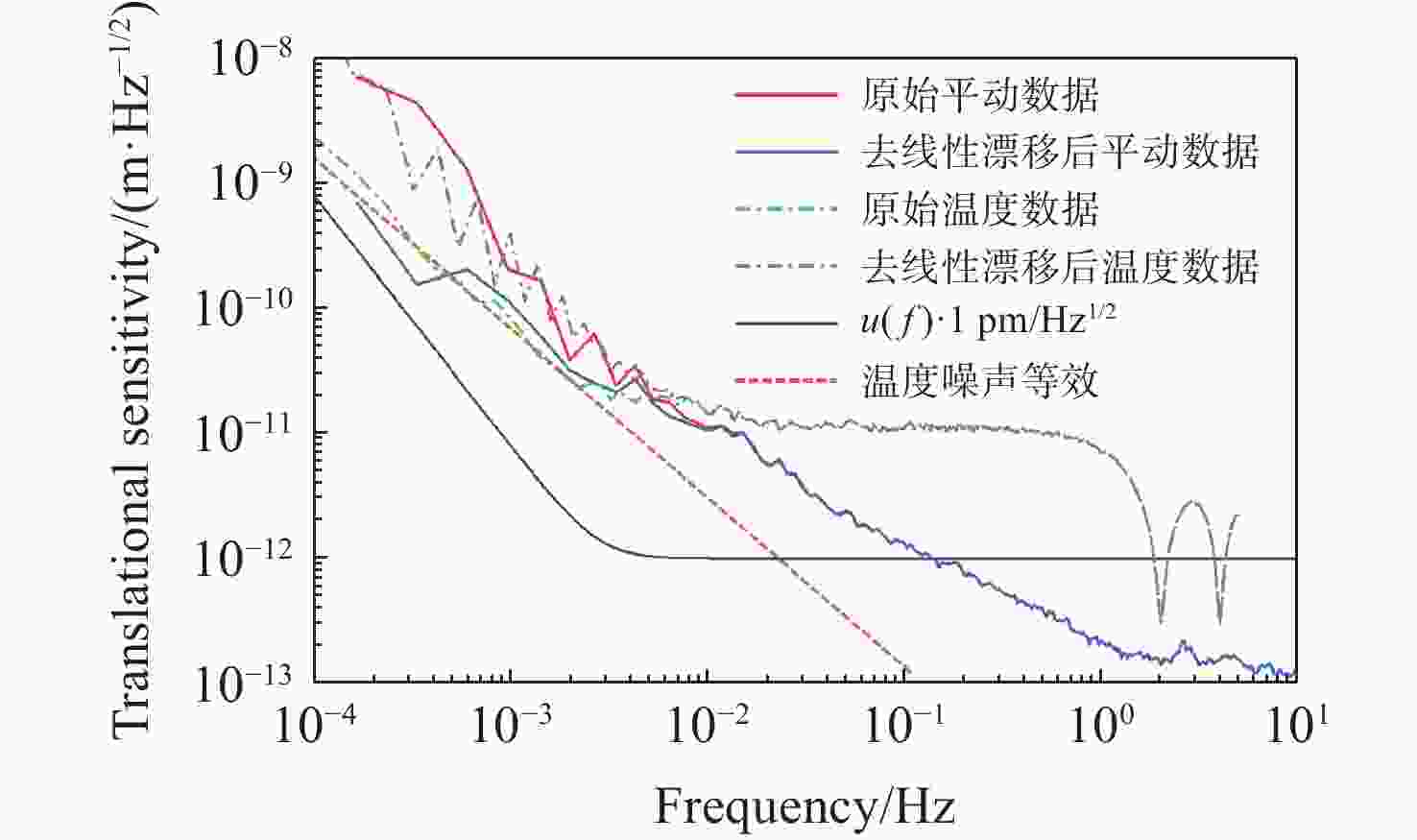
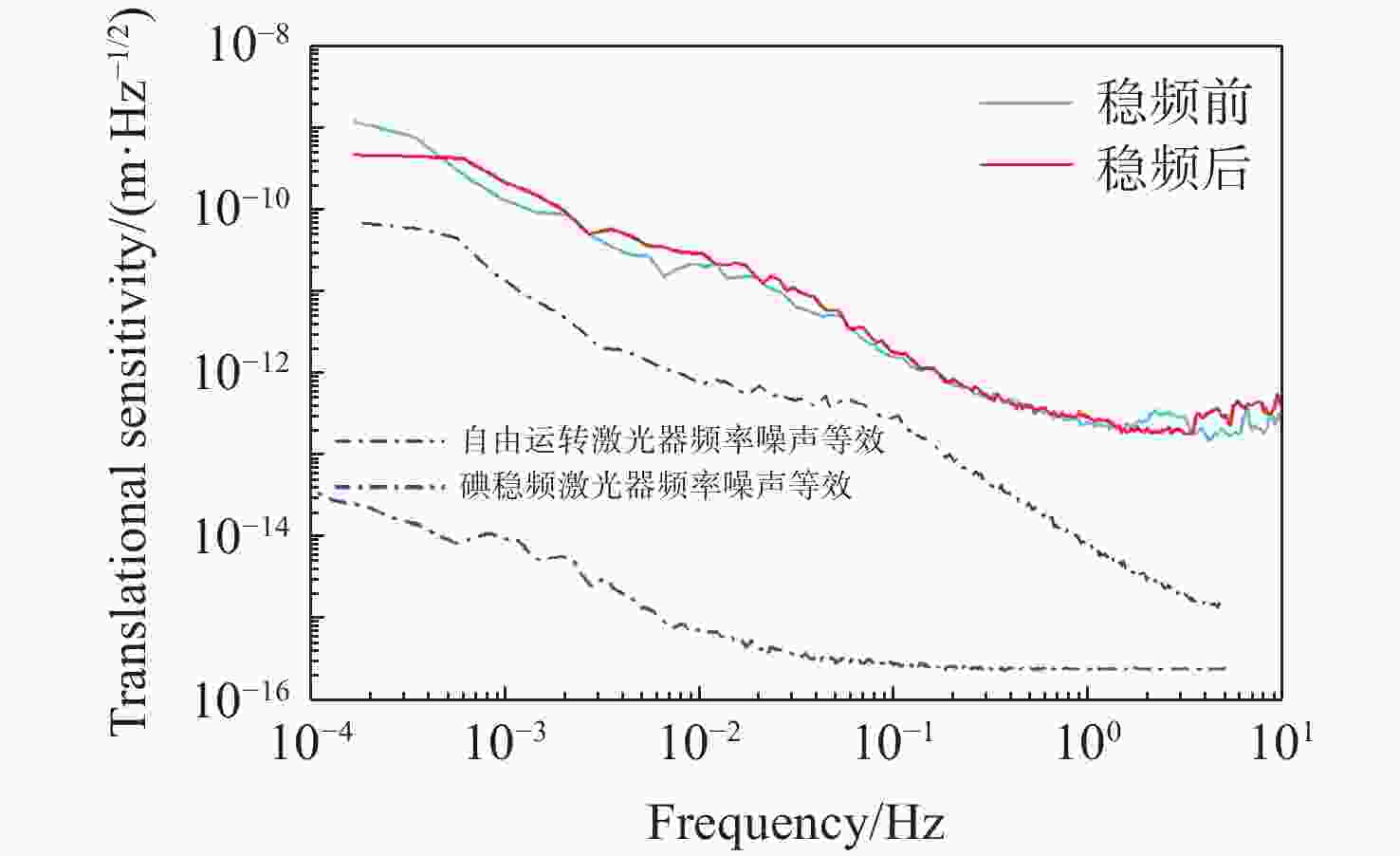
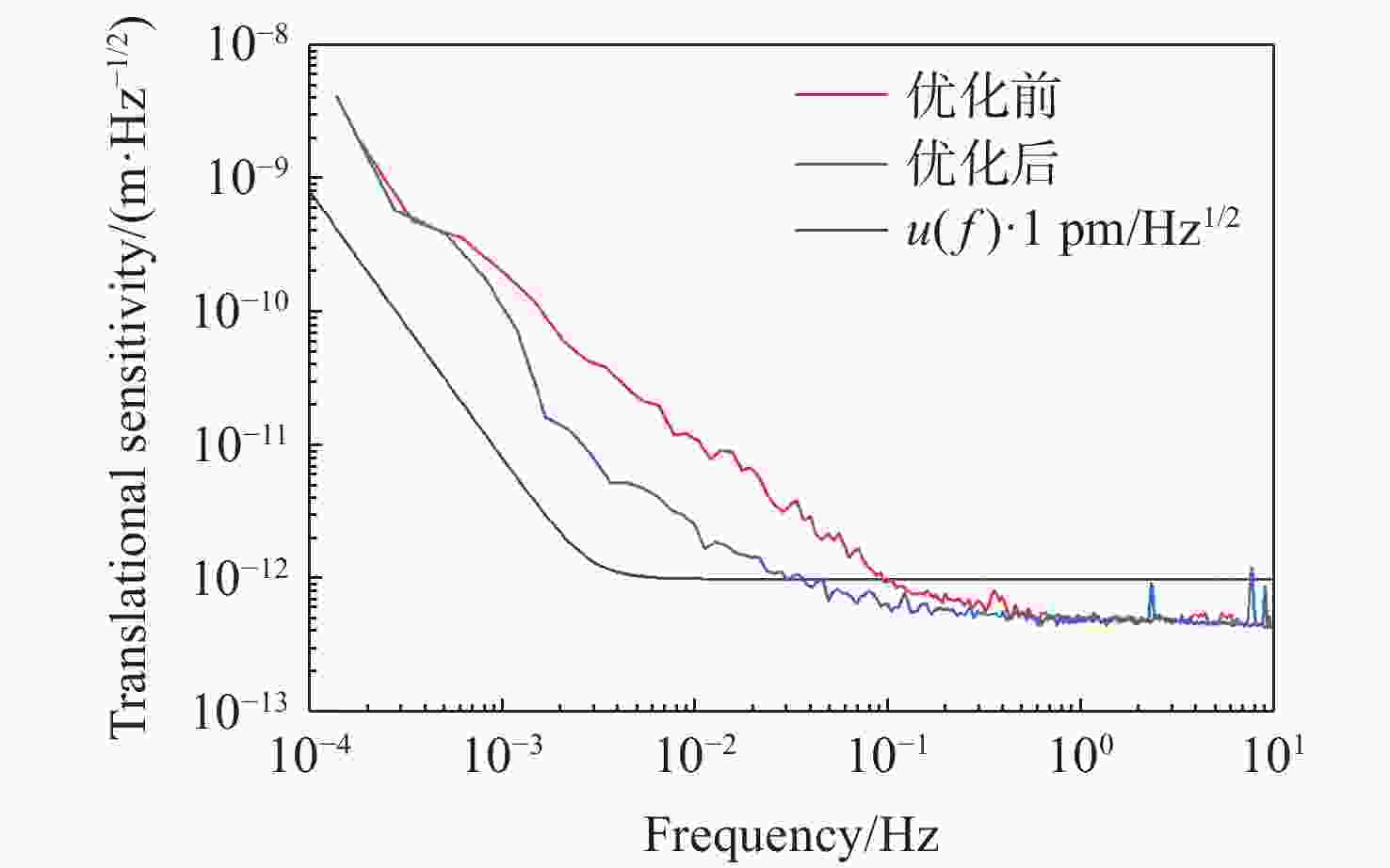
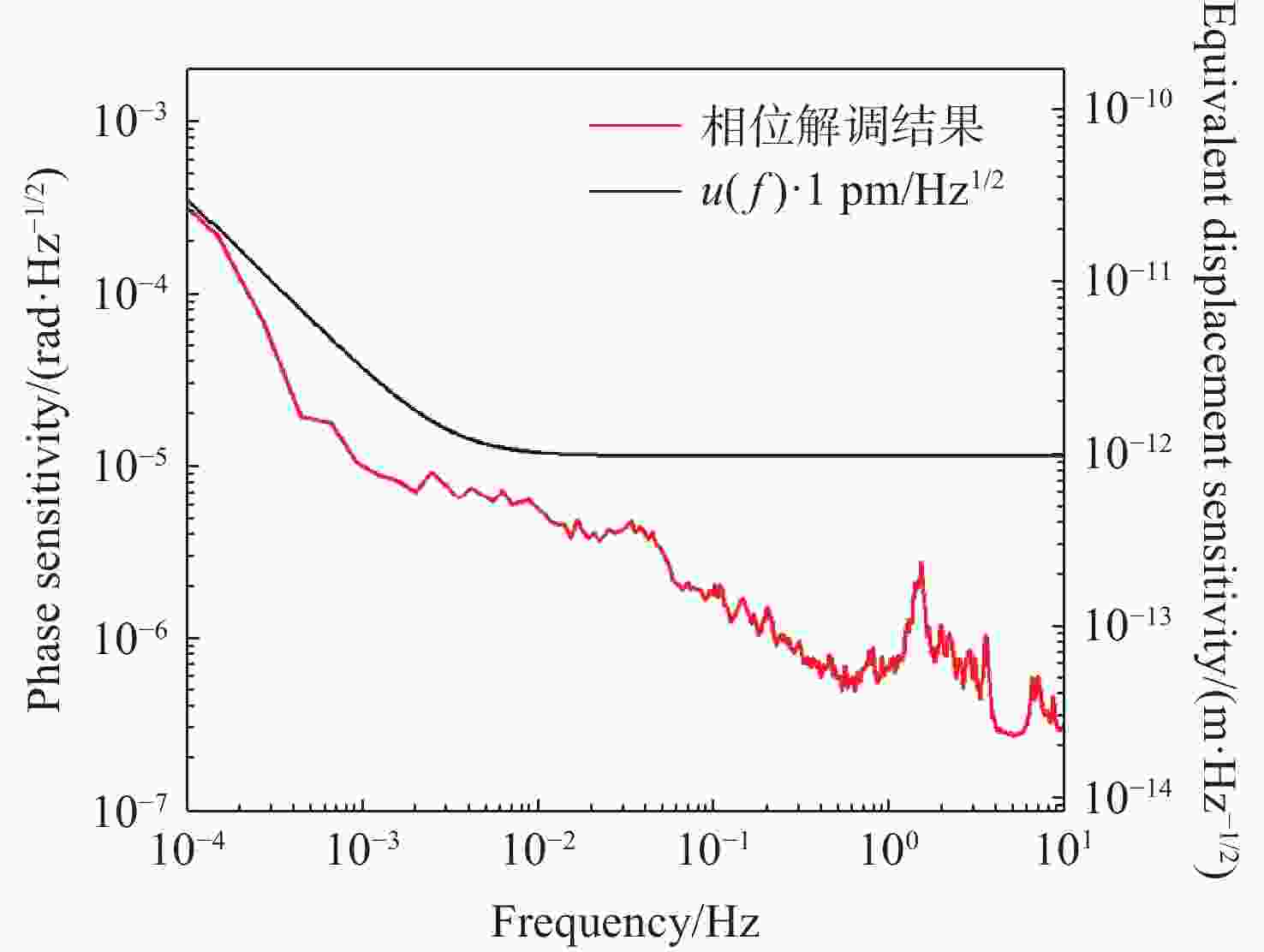
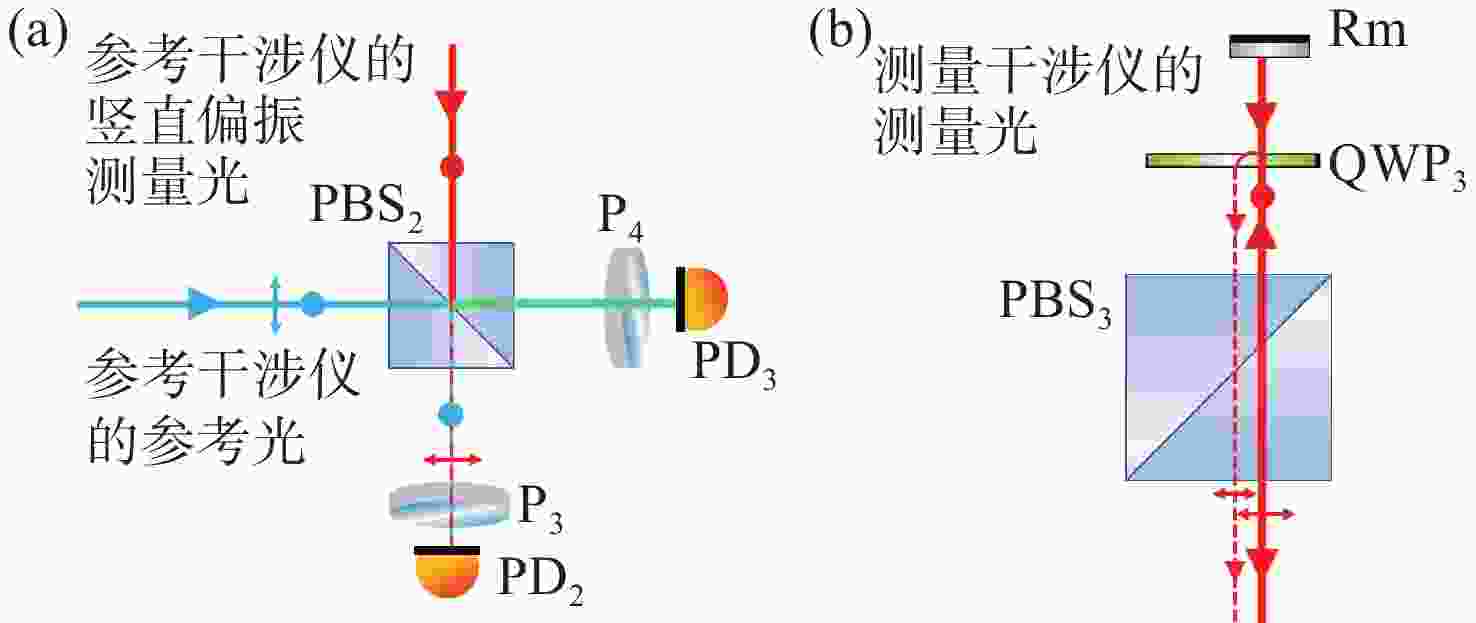
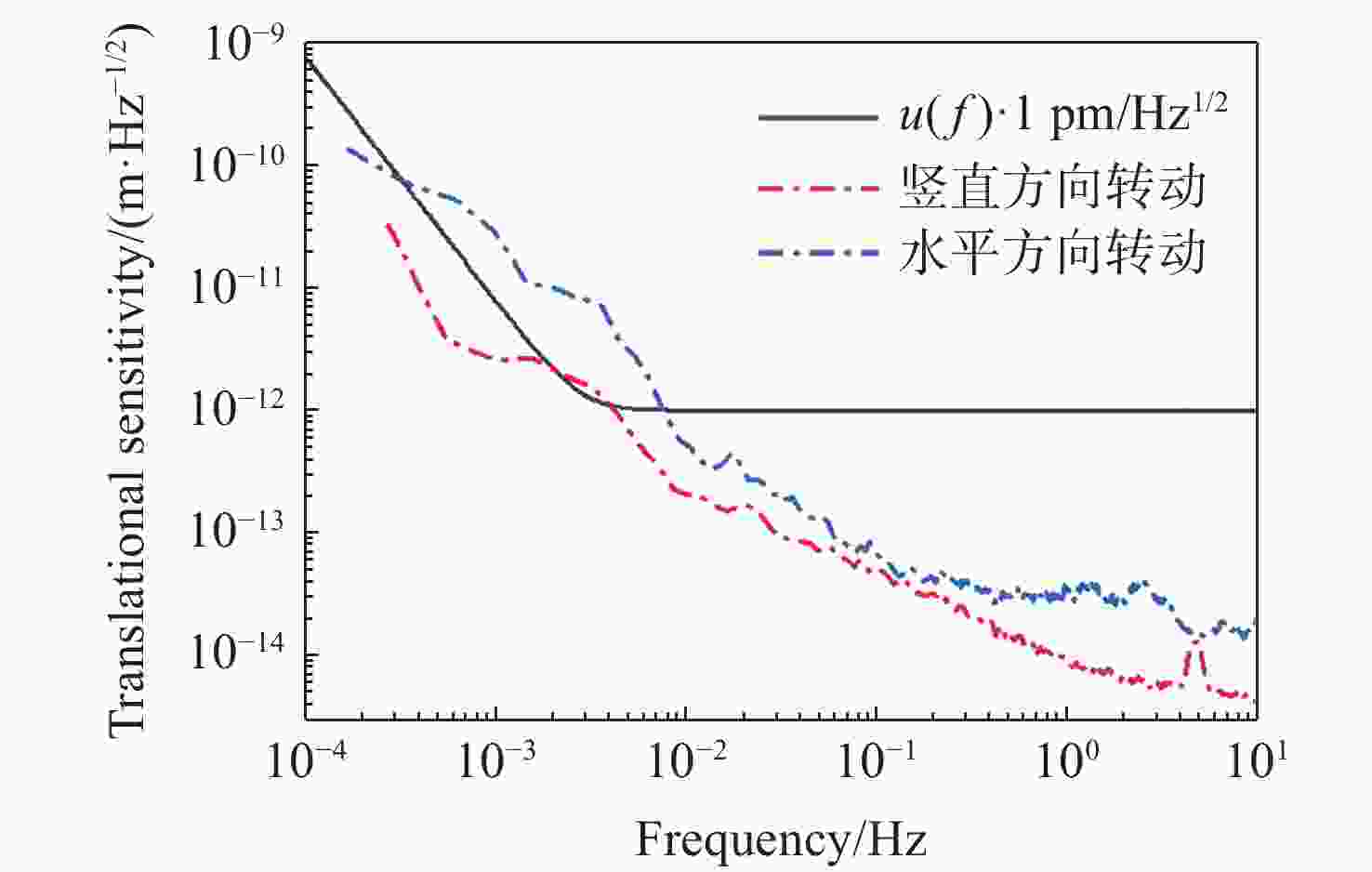
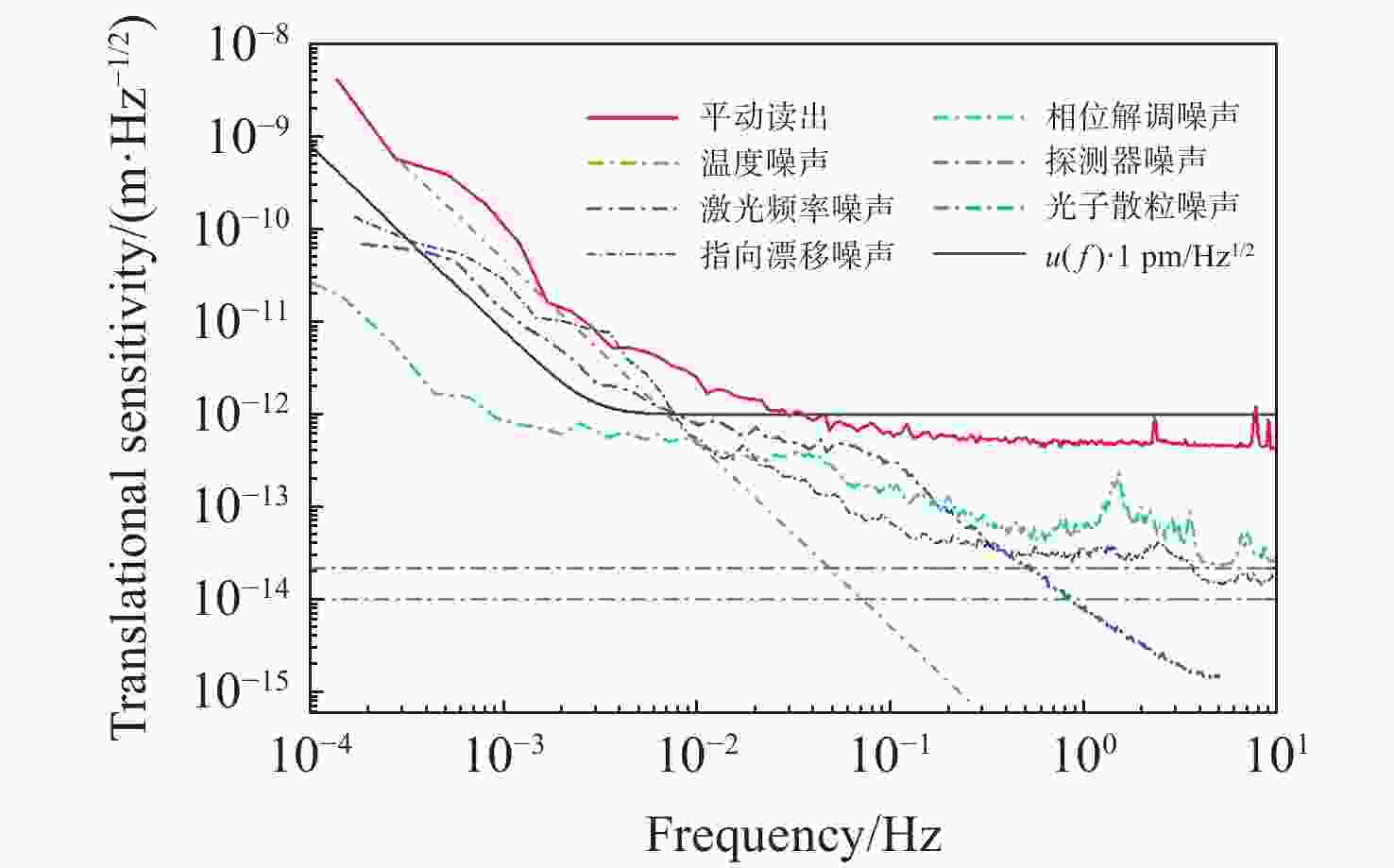
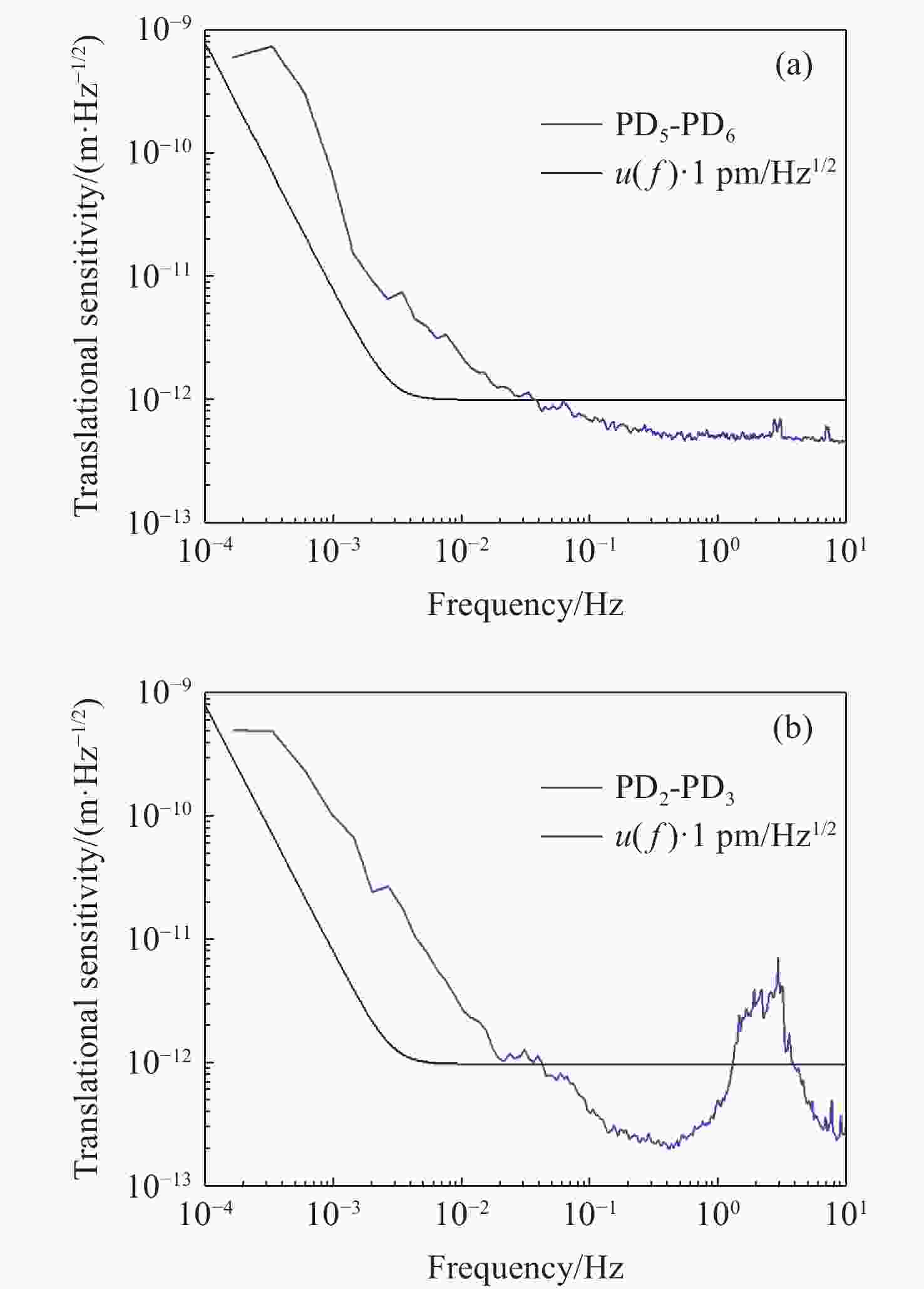
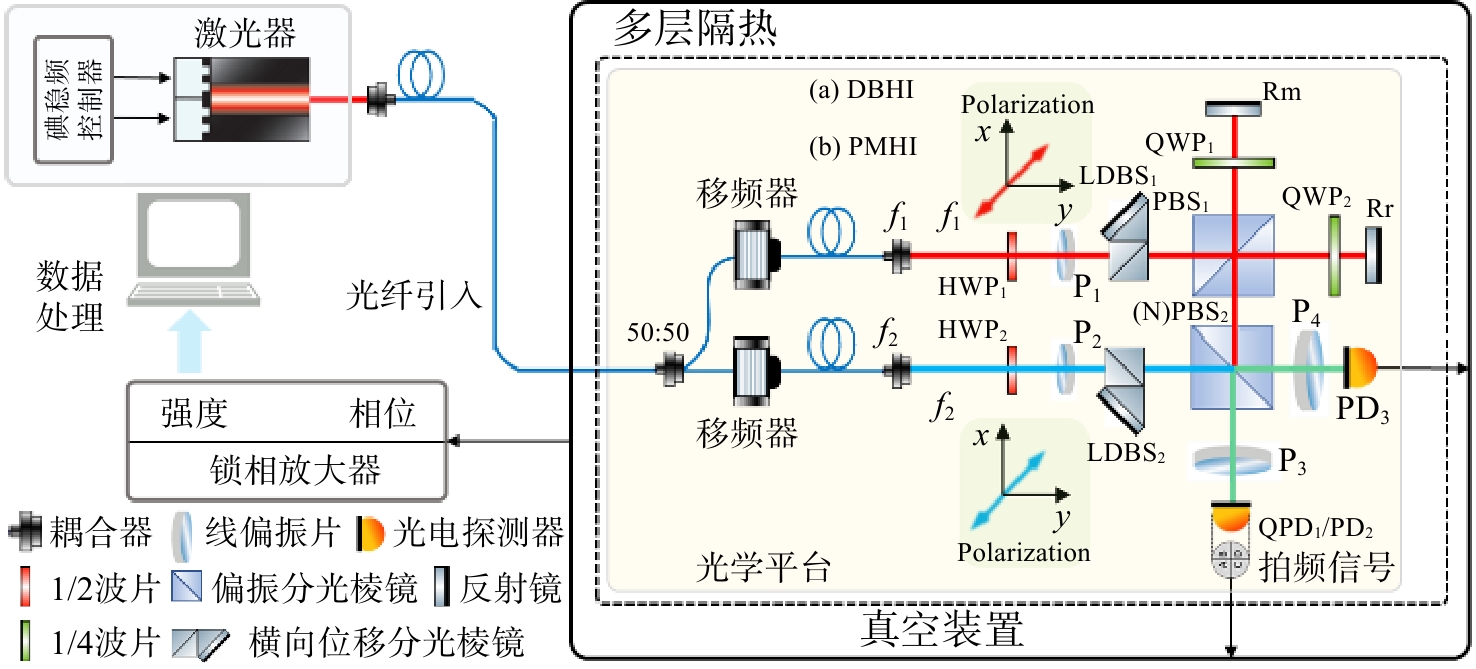
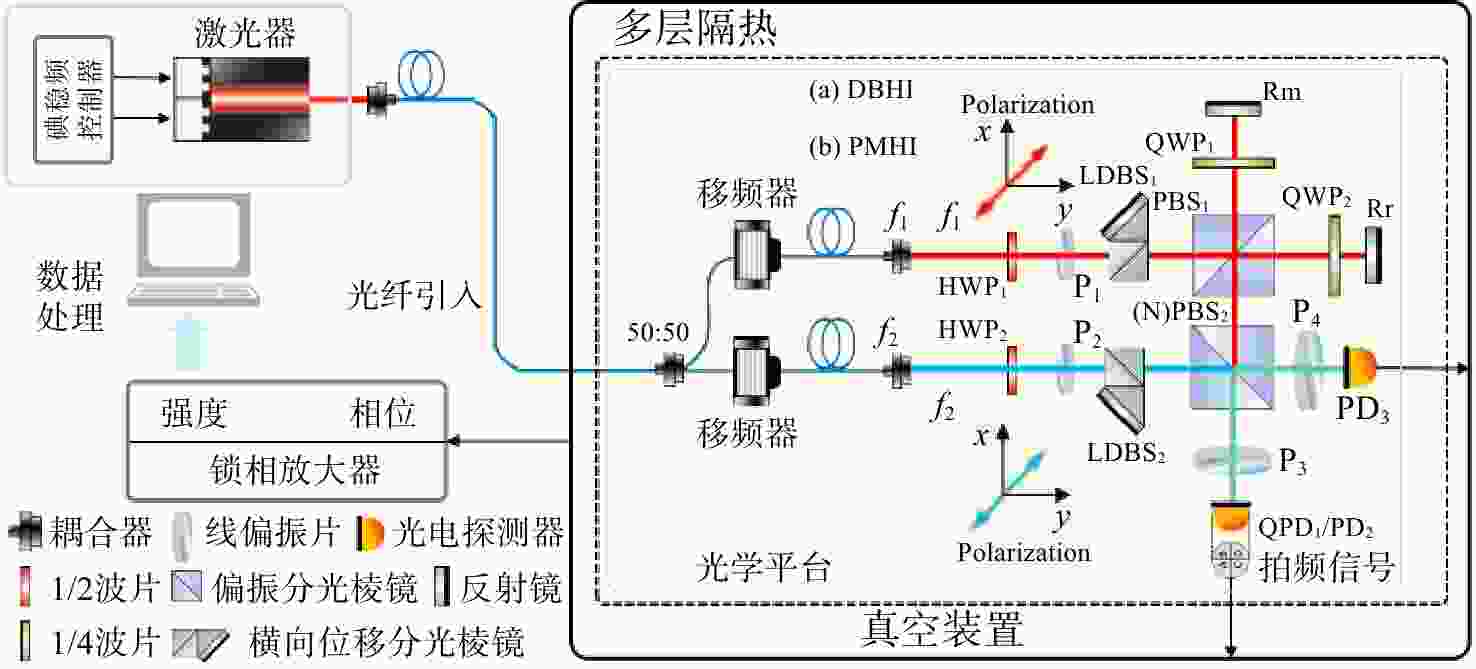
针对空间引力波探测中星内检验质量的高灵敏测量需求,构建了激光外差干涉测量地面模拟系统,开展皮米级平动测量技术研究。首先,开展真空环境下激光外差干涉测量系统的平动灵敏度测试。接着,根据灵敏度结果开展激光外差干涉测量系统噪声溯源研究,分析多种噪声源作用机理、探索主导噪声源消减方案。最后,在噪声溯源分析的基础上完成激光外差干涉测量系统优化。测试结果表明平动测量灵敏度优于1 pm/Hz1/2@30 mHz−1 Hz。该研究有望为空间引力波探测中皮米级激光干涉测量技术的进一步发展提供可靠的噪声溯源地面测试平台。
Abstract:To address the high sensitivity measurement requirement of the test mass’s displacement in spaceborne gravitational wave detection, a ground-based simulation system using laser heterodyne interferometry has been established, initiating research into picometer-level displacement measurement techniques. Initially, the translational sensitivity of the designed laser heterodyne interferometer is tested under vacuum conditions. Subsequently, based on the sensitivity outcomes, noise source tracing research for the laser heterodyne interferometric system is conducted, including the development of a system noise model, analysis of various noise source mechanisms, and investigation of strategies to reduce the predominant noise sources. Ultimately, upon completion of the noise source tracing, the interferometric system is optimized, with tests indicating a displacement measurement sensitivity better than 1 pm/Hz1/2 in the range of 30 mHz to 1 Hz. This paper is expected to provide a reliable ground-based test platform for noise source tracing, facilitating the advancement of picometer-level laser interferometry technologies for spaceborne gravitational wave detection.
-
-
[1] K Danzmann for the LISA Study Team. LISA-an ESA cornerstone mission for a gravitational wave observatory[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 1997, 14(6): 1399-1404. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/14/6/002 [2] LUO Z R, GUO Z K, JIN G, et al. A brief analysis to Taiji: science and technology[J]. Results in Physics, 2020, 16: 102918. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102918 [3] WU Y L. Space gravitational wave detection in China[C]. Presentation on 1st eLISA Consortium Meeting, APC-Paris, 2012. [4] 罗俊, 艾凌皓, 艾艳丽, 等. 天琴计划简介[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版),2021,60(1-2):1-19.LUO J, AI L H, AI Y L, et al. A brief introduction to the TianQin project[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2021, 60(1-2): 1-19. (in Chinese). [5] HECHLER F, FOLKNER W M. Mission analysis for the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) mission[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2003, 32(7): 1277-1282. doi: 10.1016/S0273-1177(03)90332-2 [6] HU W R, WU Y L. The Taiji program in space for gravitational wave physics and the nature of gravity[J]. National Science Review, 2017, 4(5): 685-686. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwx116 [7] LUO J, CHEN L S, DUAN H Z, et al. TianQin: a space-borne gravitational wave detector[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2016, 33(3): 035010. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/33/3/035010 [8] AMARO-SEOANE P, AUDLEY H, BABAK S, et al. Laser interferometer space antenna[J]. arXiv: 1702.00786, 2017. [9] ARMANO M, AUDLEY H, BAIRD J, et al. Sensor noise in LISA pathfinder: in-flight performance of the optical test mass readout[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2021, 126(13): 131103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.131103 [10] ARMANO M, AUDLEY H, BAIRD J, et al. Sensor noise in LISA Pathfinder: an extensive in-flight review of the angular and longitudinal interferometric measurement system[J]. Physical Review D, 2022, 106(8): 082001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.106.082001 [11] LIU H SH, LUO Z R, SHA W, et al. In-orbit performance of the laser interferometer of Taiji-1 experimental satellite[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics A, 2021, 36(11n12): 2140004. doi: 10.1142/S0217751X21400042 [12] LUO J, BAI Y ZH, CAI L, et al. The first round result from the TianQin-1 satellite[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2020, 37(18): 185013. doi: 10.1088/1361-6382/aba66a [13] XU X, LIU H SH, TAN Y D. Verification of laser heterodyne interferometric bench for Chinese spaceborne gravitational wave detection missions[J]. Research, 2024, 7: 0302. doi: 10.34133/research.0302 [14] GARCÍA MARÍN A. Minimisation of optical pathlength noise for the detection of gravitational waves with the spaceborne laser interferometer LISA and LISA Pathfinder[D]. Hannover: Albert Einstein Institute & University of Hannover, 2007. [15] DEHNE M. Construction and noise behaviour of ultra-stable optical systems for space interferometers[D]. Hannover: Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Universität Hannover, 2012. [16] 颜浩. 基于激光干涉的高精度多自由度光学传感研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2019.YAN H. Study on ultra-precision multi-degree-of-freedom optical measurement base on laser interferometry[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2019. (in Chinese). [17] FULDA P, DEROSA R T, DEMARCO E, et al. Multi-axis heterodyne interferometry at MHz frequencies: a short-arm measurement demonstration for LISA with off-the-shelf hardware[J]. Applied Optics, 2019, 58(23): 6346-6356. doi: 10.1364/AO.58.006346 [18] SASSO C P, MANA G, MOTTINI S. The LISA interferometer: Impact of stray light on the phase of the heterodyne signal[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2019, 36(7): 075015. doi: 10.1088/1361-6382/ab0a15 [19] DEHNE M, TRÖBS M, HEINZEL G, et al. Verification of polarising optics for the LISA optical bench[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(25): 27273-27287. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.027273 [20] WITTCHEN A, LPF Collaboration. Coupling of relative intensity noise and pathlength noise to the length measurement in the optical metrology system of LISA Pathfinder[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2017, 840: 012003. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/840/1/012003 [21] WISSEL L, WITTCHEN A, SCHWARZE T S, et al. Relative-intensity-noise coupling in heterodyne interferometers[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2022, 17(2): 024025. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.17.024025 -





 下载:
下载: