-
摘要:
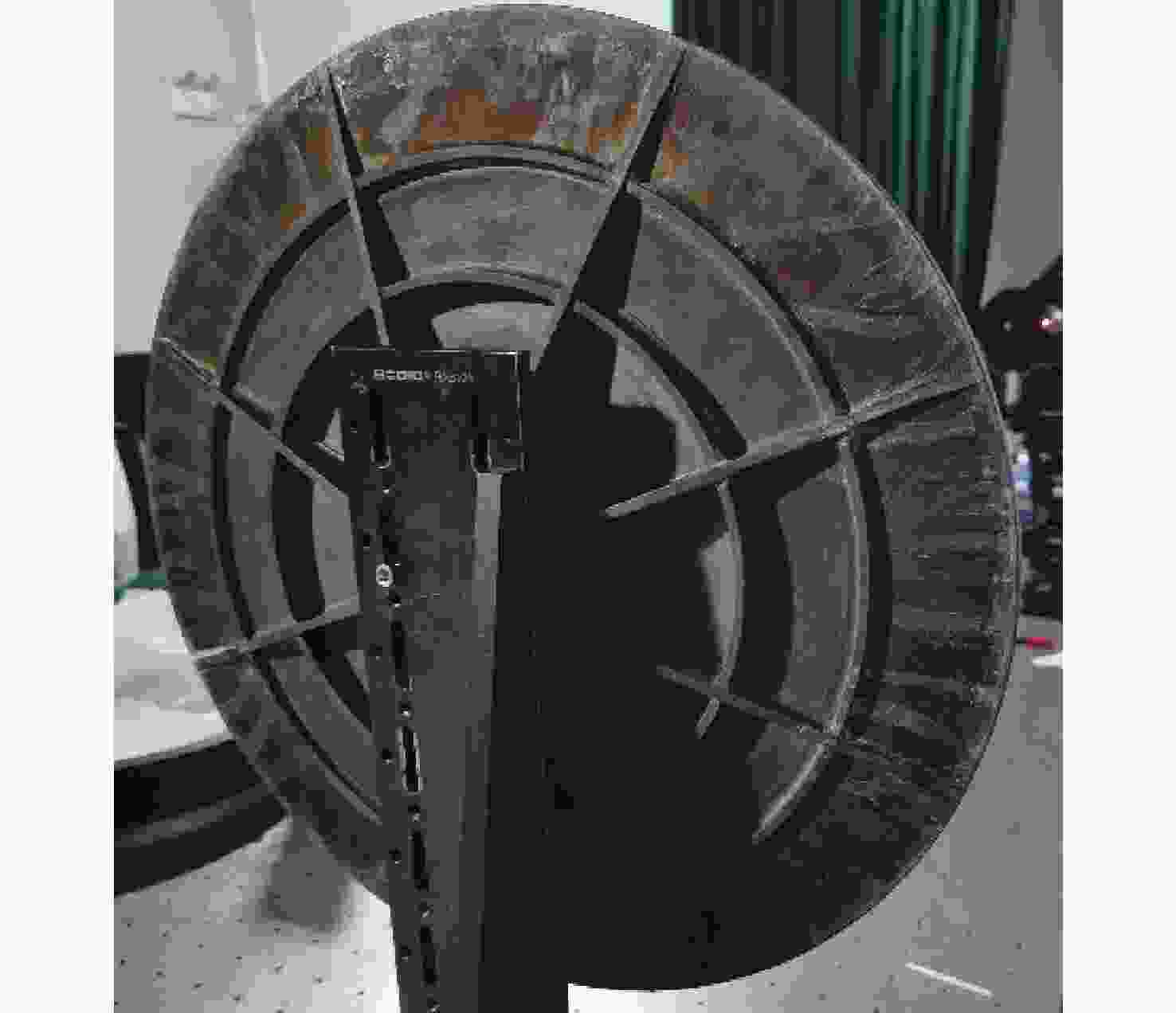
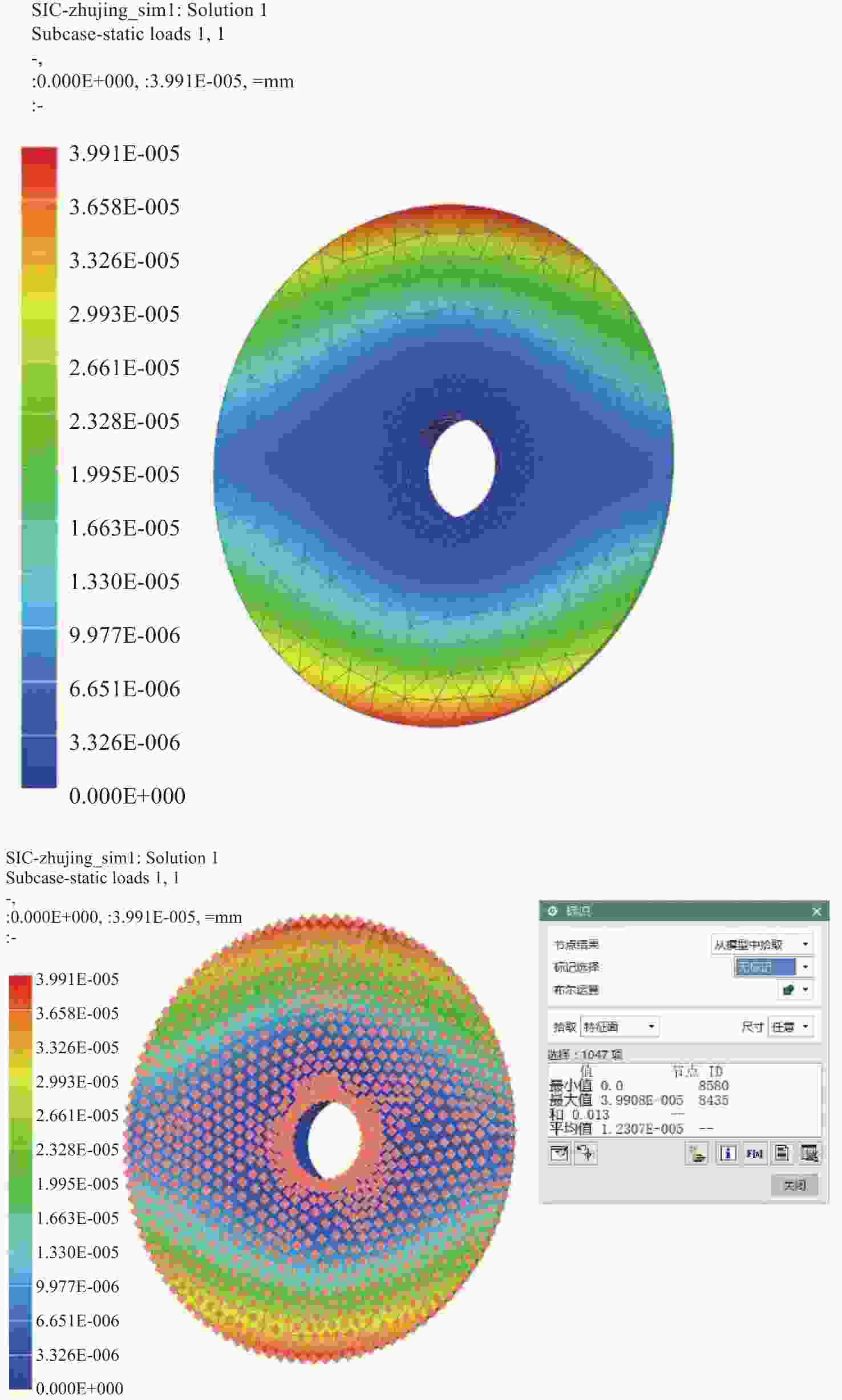
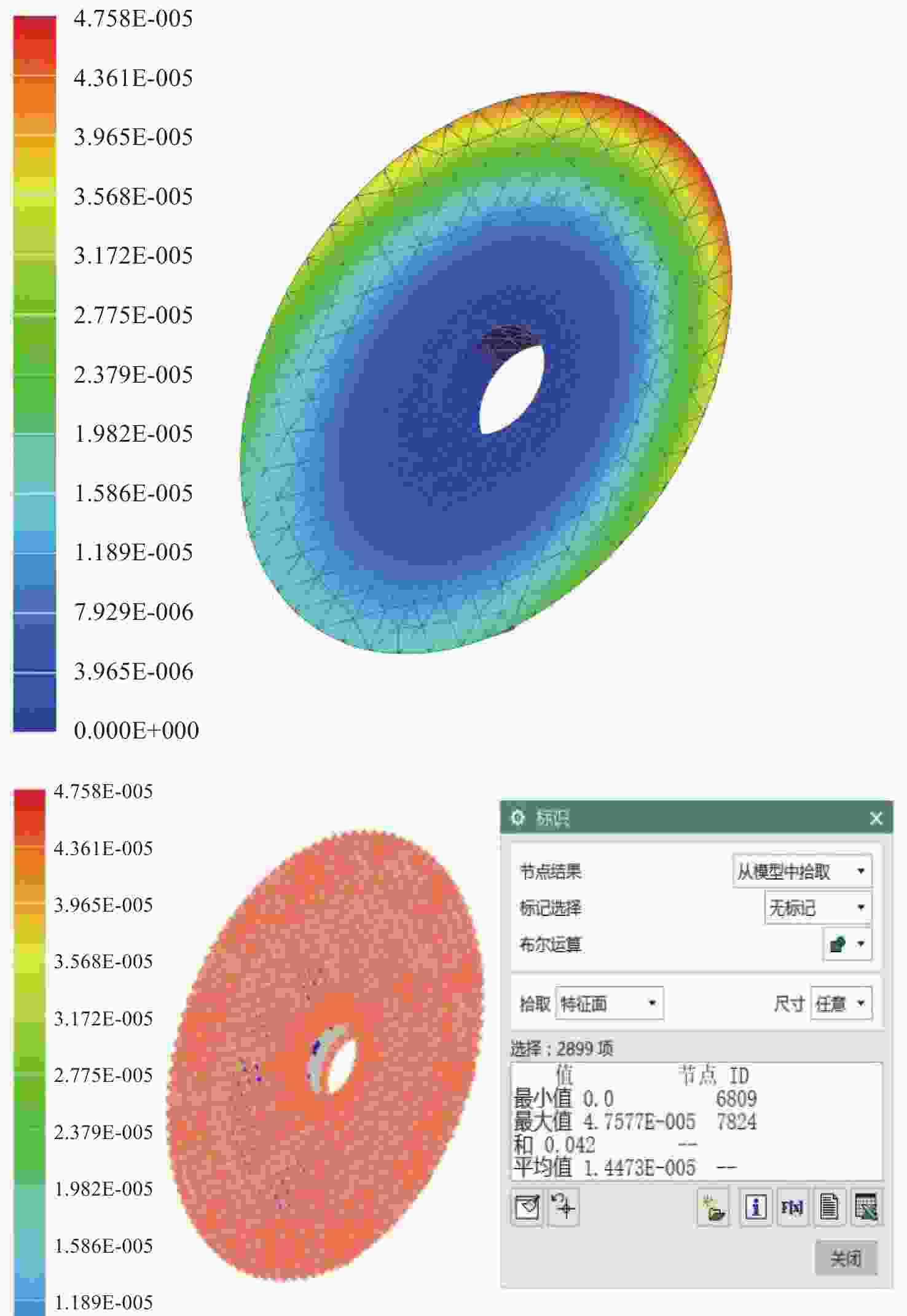
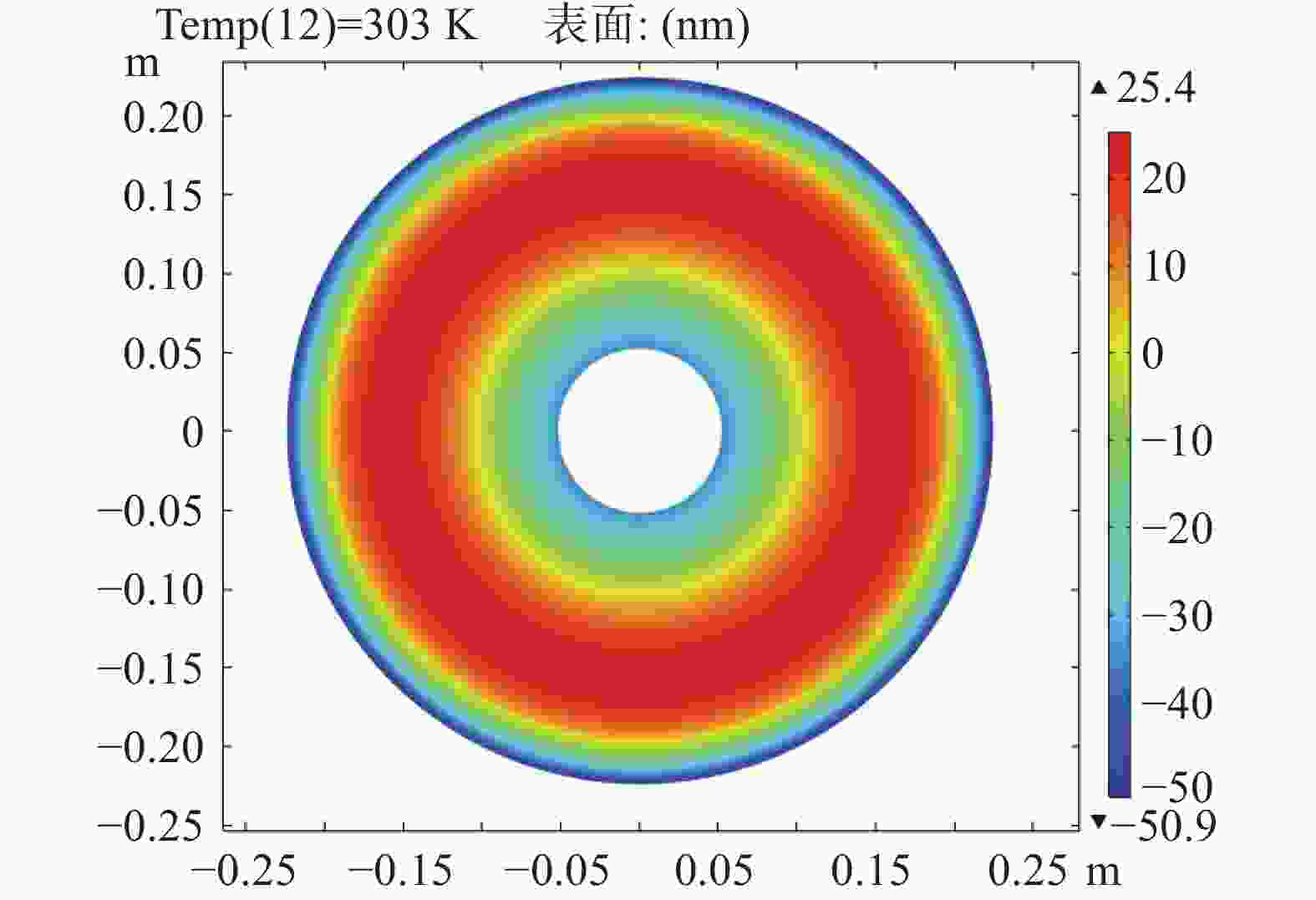
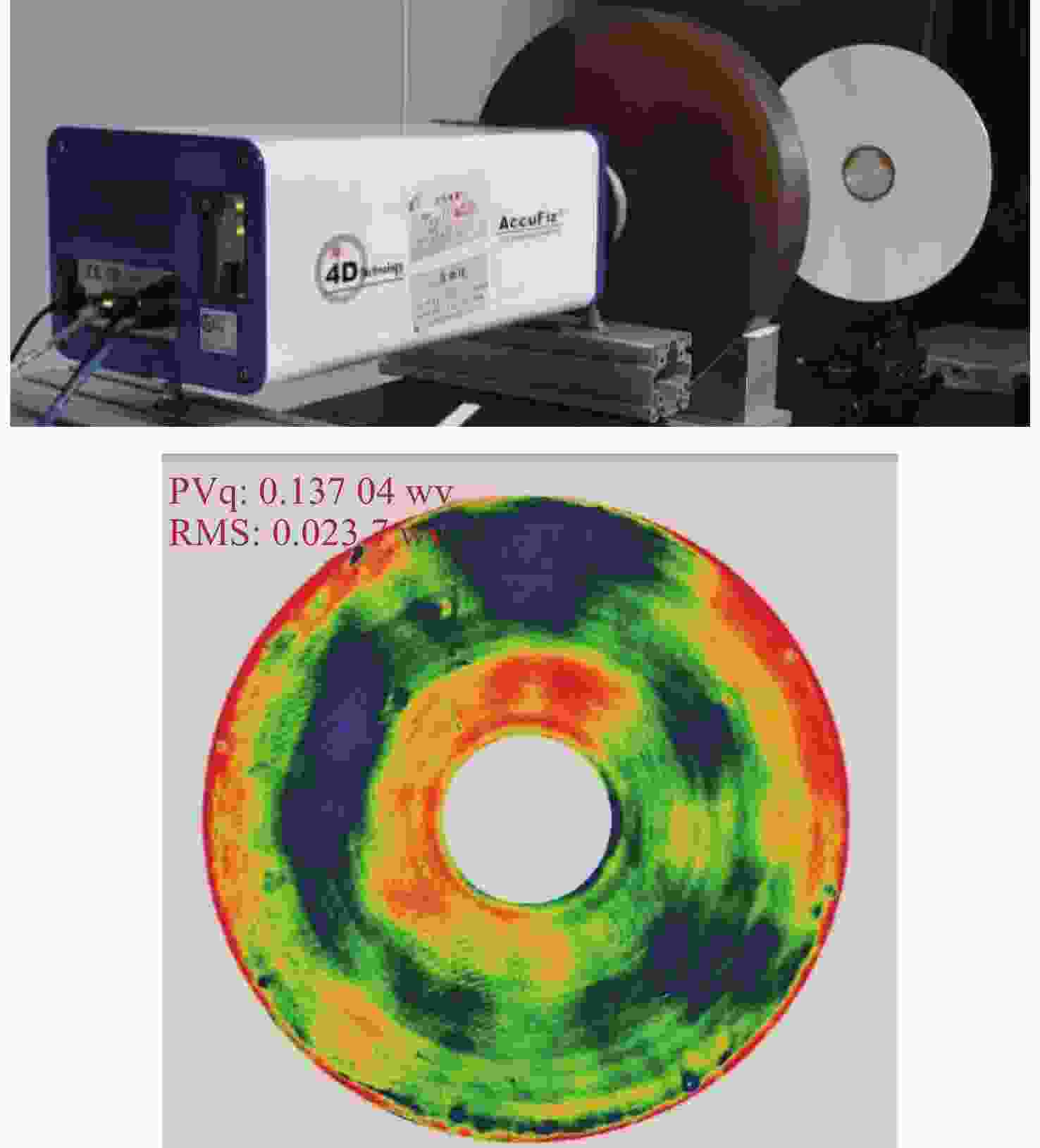
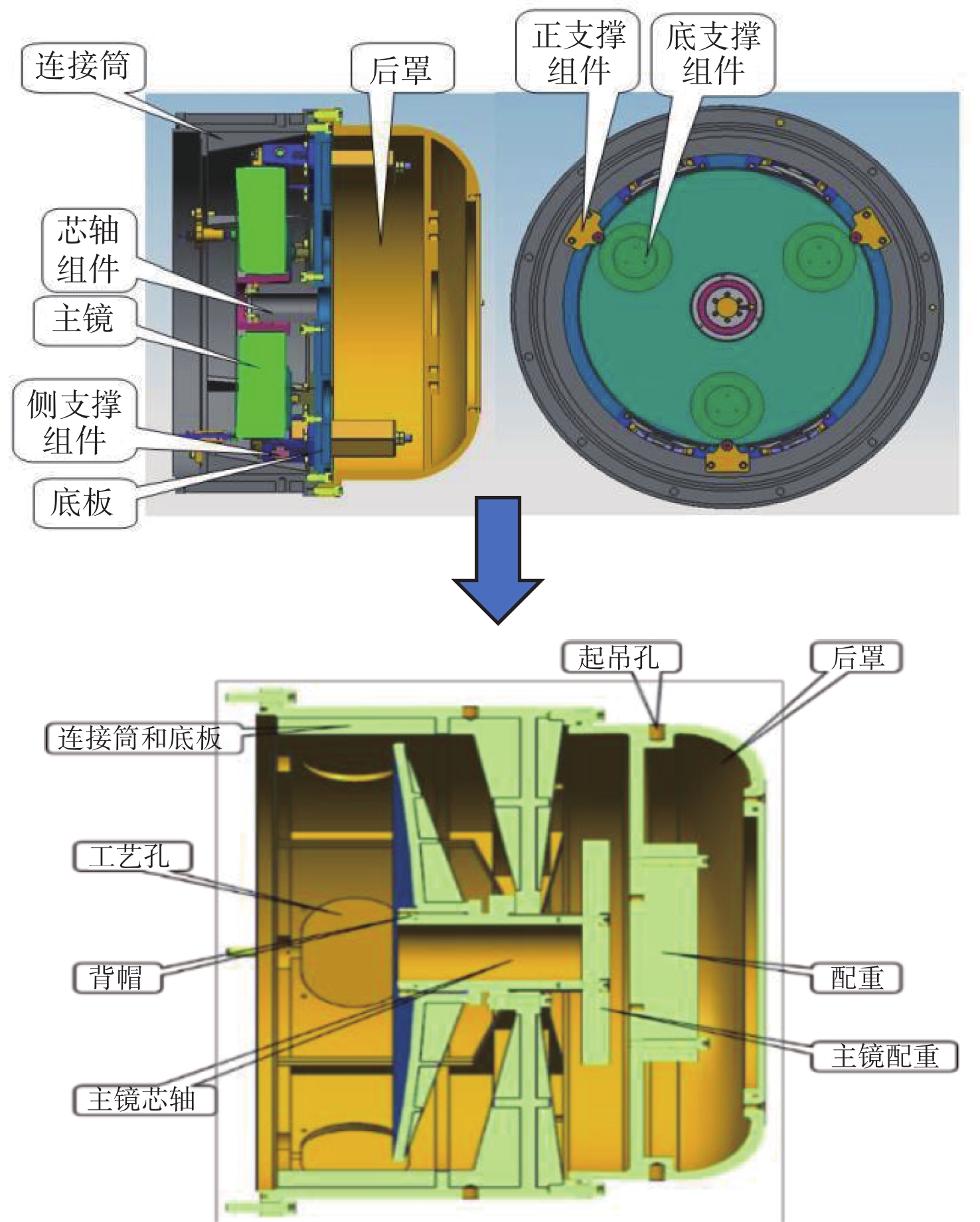
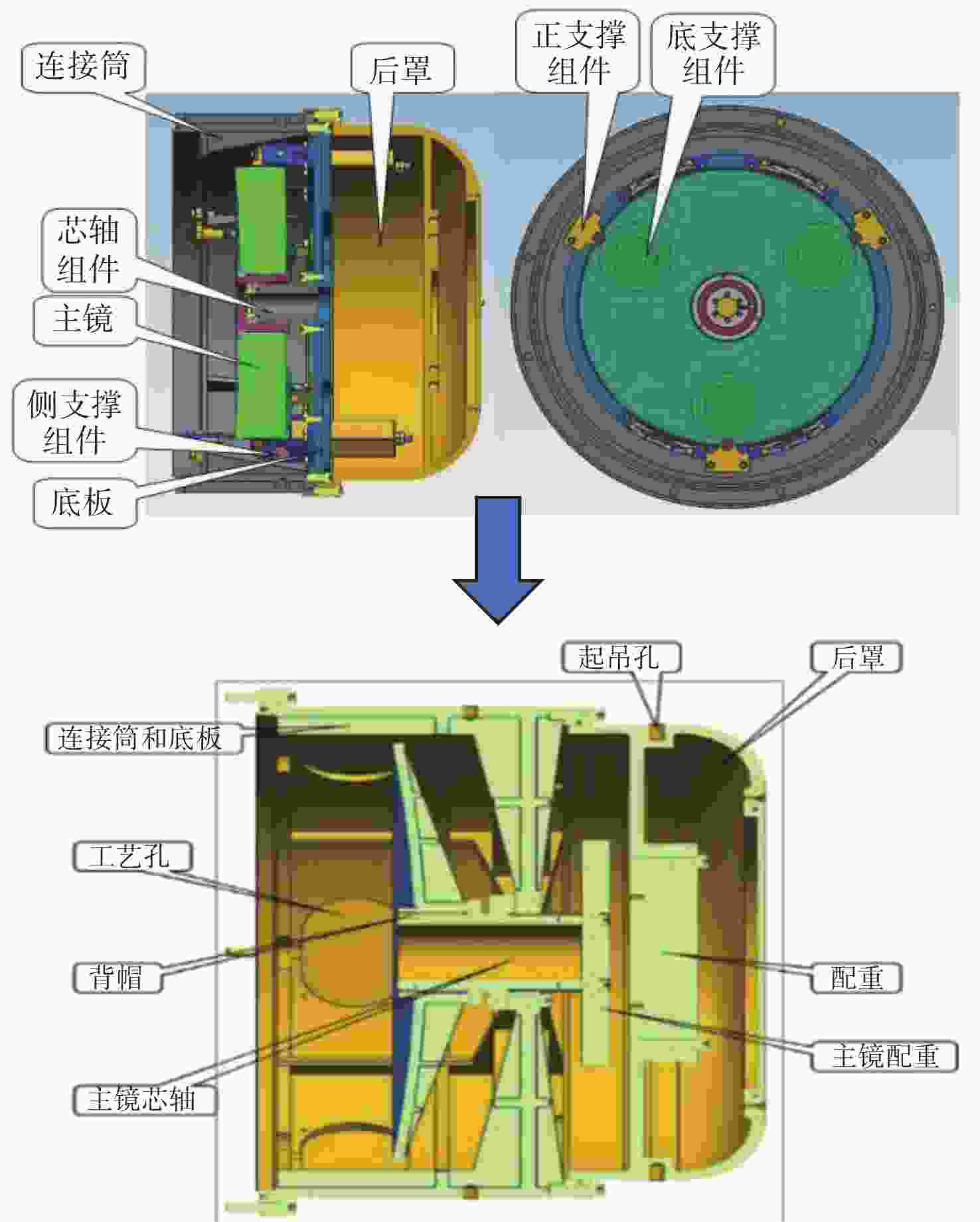
为简化某地基望远镜主镜的支撑方式,兼顾保障望远镜成像质量和精度,研究了460 mm口径单轴支撑碳化硅主镜的优化设计。首先,确定了相近线胀系数材料的单轴支撑方案和扇形的主镜背部结构,针对支撑结构和材料特性,利用先进的碳化硅烧结技术可制备异性结构的特性,结合优化设计理论,在满足主镜面型精度的前提下,对主镜进行了轻量化设计。优化后的主镜质量仅为4.82 kg,主镜水平状态下面型仿真分析RMS为λ/51.4。经实际工程验证,主镜支撑后水平状态下面型精度检测结果优于λ/42,轻量化效果显著并满足实际使用要求。本研究为工程项目提供了理论基础和技术储备。
Abstract:In order to simplify the support method of the mirror of a ground-based telescope and ensure the imaging quality and accuracy of the telescope, the optimization design of a uniaxial supported SiC mirror with 460 mm aperture was studied. First, a uniaxial support scheme for materials with similar linear expansion coefficients and a fan-shaped mirror back structure were determined. Advanced SiC sintering technology was used to prepare anisotropic structures according to the support structure and the material characteristics. Combined with optimization design theory, the mirror was designed to be lightweight while meeting the required accuracy. The optimized mirror weighs only 4.82 kg, and the RMS of the horizontal simulation analysis of the mirror is λ/51.4. After actual engineering verification, the accuracy detection results of the horizontal state under the mirror support are found to be better than λ/42. The lightweight effect is significant and meets the requirements of practical use. This research provides a theoretical foundation and technical reserve for engineering projects.
-
Key words:
- SiC mirror /
- lightweight /
- finite element analysis /
- optimization
-
表 1 常用主镜材料参数
Table 1. Properties of mirror’s materials commonly used
ρ(g/cm3) E(GPa) υ α(10−6/K) K(W/m•K) E/ρ(GPa•cm3/g) Zerodur 2.53 93 0.24 0.01 1.46 36.8 ULE 2.21 67 0.17 0.015 1.3 30.3 Fused
silica2.02 74.6 0.167 0.56 36.9 SiC 2.7 390 0.14 2.4 185 111.8 K9 2.52 81.3 0.25 7.8 1.207 32.1 Be 1.85 280 0.25 11.4 160 151 表 2 碳化硅主镜特点分析
Table 2. Analysis of SiC mirror characteristics
优点 缺点 重量 合理设计结构形式和先进的烧结
工艺,可达到较高的轻量化程度。弹性
模量高弹性模量使得同等应力作用
下,材料的弹性变形更小。刚度高导致加工难度
大、增加加工成本。热膨胀
系数可选择热膨胀系数接近的金属
材料作为支撑,降低环境温度
变化导致的局部应力。热膨胀会导致镜面曲率
半径变化,可通过温度
调焦解决。导热率 高导热率可缩短热平衡时间,降低
环境温度变化导致的局部应力。表 3 优化设计结果
Table 3. Optimized design results
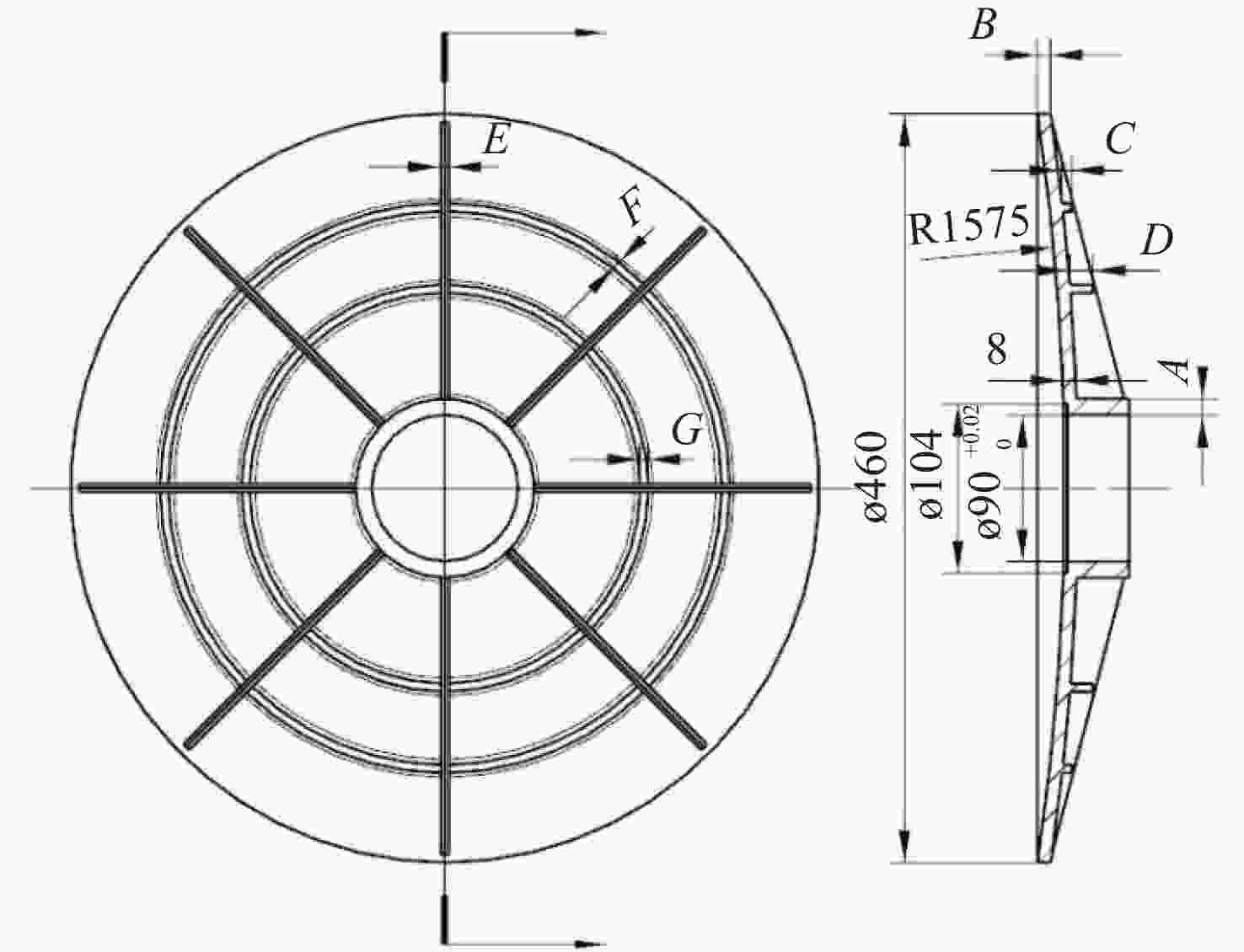
(mm) 设计变量 初始值 优化值 A 8 10.24 B 8 5.9 C 5 6.1 D 15 13.9 E 6 4.42 F 6 5.84 G 8 6.42 -
[1] 王克军, 董吉洪. 空间遥感器Ф2 m量级大口径SiC反射镜镜坯结构设计[J]. 红外与激光工程,2017,46(7):0718005. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201746.0718005WANG K J, DONG J H. Structural design of Ф2 m-level large-diameter SiC reflector used in space remote sensor[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46(7): 0718005. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA201746.0718005 [2] 郭疆, 朱磊, 赵继, 等. 大口径空间反射镜大容差支撑结构设计与优化[J]. 光学 精密工程,2019,27(5):1138-1147. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192705.1138GUO J, ZHU L, ZHAO J, et al. Design and optimize of high tolerance support structure for large aperture space mirror[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(5): 1138-1147. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192705.1138 [3] 王洪浩, 王建立, 陈涛, 等. 地基大口径望远镜重力弯曲引起的指向变化检测与修正[J]. 光学 精密工程,2022,30(23):3021-3030. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223023.3021WANG H H, WANG J L, CHEN T, et al. Measurement and calibration of optical axis changes caused by gravity for ground-based large-aperture telescope[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(23): 3021-3030. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223023.3021 [4] 张景旭. 地基大口径望远镜系统结构技术综述[J]. 中国光学,2012,5(4):327-336.ZHANG J X. Overview of structure technologies of large aperture ground-based telescope[J]. Chinese Optics, 2012, 5(4): 327-336. (in Chinese). [5] 董斌超, 张舸. 超轻量化SiC反射镜的制备及性能[J]. 光学 精密工程,2015,23(8):2185-2491. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152308.2185DONG B CH, ZHANG G. Fabrication and properties of ultra-lightweight SiC mirror[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(8): 2185-2491. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152308.2185 [6] 马昕, 刘海韬, 孙逊. 连续纤维增强陶瓷基复合材料连接件的研究进展[J]. 材料工程,2023,51(8):1-11. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2023.000138MA X, LIU H T, SUN X. Research progress in continuous fiber reinforced ceramic matrix composite joints[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2023, 51(8): 1-11. (in Chinese). doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2023.000138 [7] 康健, 宣斌, 谢京江. 表面改性碳化硅基底反射镜加工技术现状[J]. 中国光学,2013,6(6):824-833.KANG J, XUAN B, XIE J J. Manufacture technology status of surface modified silicon carbide mirrors[J]. Chinese Optics, 2013, 6(6): 824-833. (in Chinese). [8] 邢邵美, 马建平. 碳化硅铝基复合材料的应用与加工[J]. 航天返回与遥感,1998,19(2):45-49.XING SH M, MA J P. The application and process of SiC/Al composite materials[J]. Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 1998, 19(2): 45-49. (in Chinese). [9] 祝汉旺, 薛向尧, 邵明振, 等. 地基光电成像系统中单芯轴的设计与优化[J]. 红外与激光工程,2024,53(3):20230629. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20230629ZHU H W, XUE X Y, SHAO M ZH, et al. Design and optimization of a single-core axis in a ground-based photoelectric imaging system[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2024, 53(3): 20230629. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20230629 [10] 高世林, 魏梦琦, 张赛, 等. 一种卡塞格林反射系统的光机结构设计与分析[J]. 激光与红外,2024,54(7):1136-1140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2024.07.021GAO SH L, WEI M Q, ZHANG S, et al. The optical-mechanical structure design and analysis of a Cassegrain reflection system[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2024, 54(7): 1136-1140. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2024.07.021 [11] 魏钰轩, 王振宇, 李治国, 等. 星载二维转台U型架结构轻量化与优化设计[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(4):896-908. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0227WEI Y X, WANG ZH Y, LI ZH G, et al. Lightweight and optimized U-frame design for space-borne two-dimensional turntable[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(4): 896-908. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0227 [12] VUKOBRATOVICH D. Introduction to Optomechanical Design[M]. US: SPIE Short Course SC014, 2003. [13] 孙景旭, 谢虹波, 李淑贤, 等. 轻小型全铝高分相机[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(6):1450-1462. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0062SUN J X, XIE H B, LI SH X, et al. All-aluminum high-resolution camera with lightweight and compact size[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(6): 1450-1462. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0062 -





 下载:
下载: