Phase measurement technique based on MHz-lever depth frequency modulated laser interferometry
-
摘要:
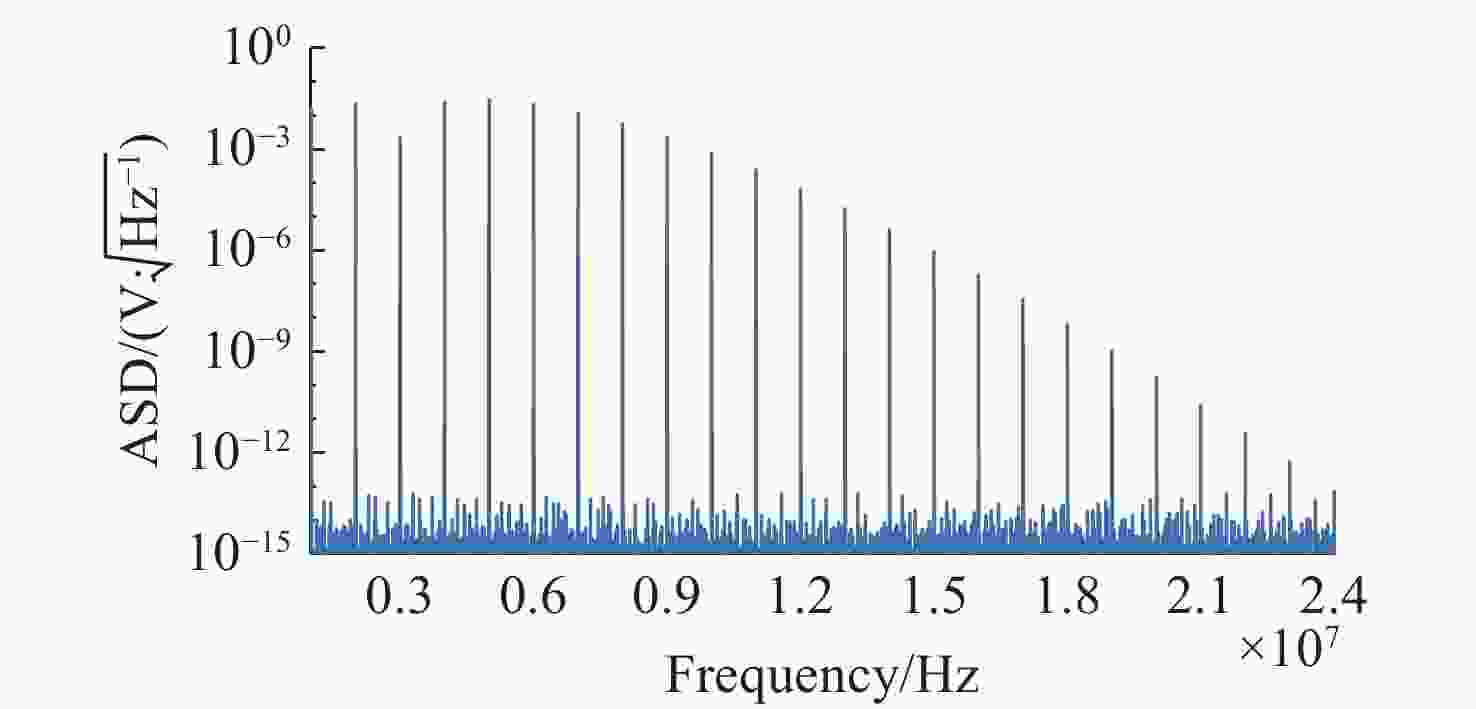
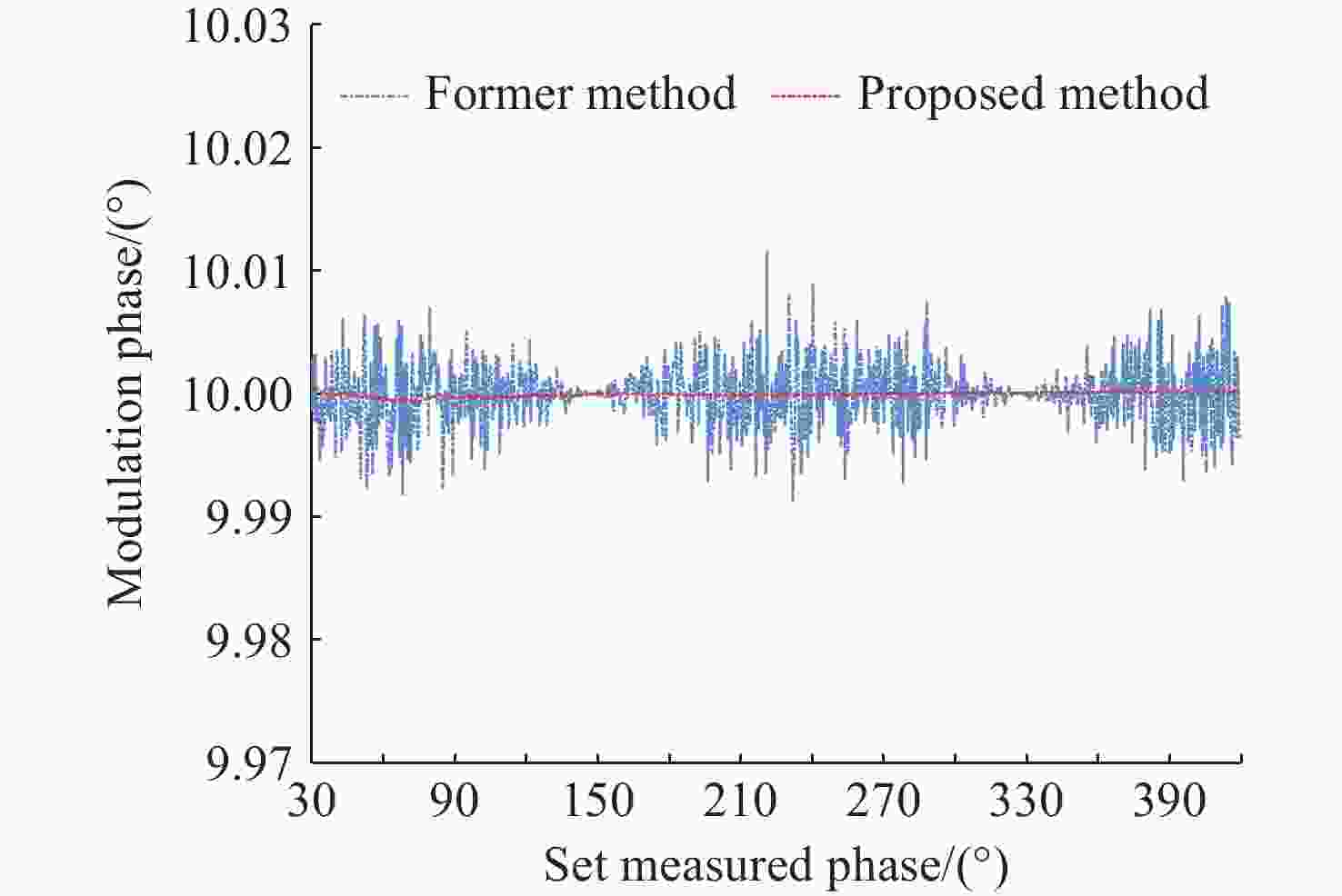
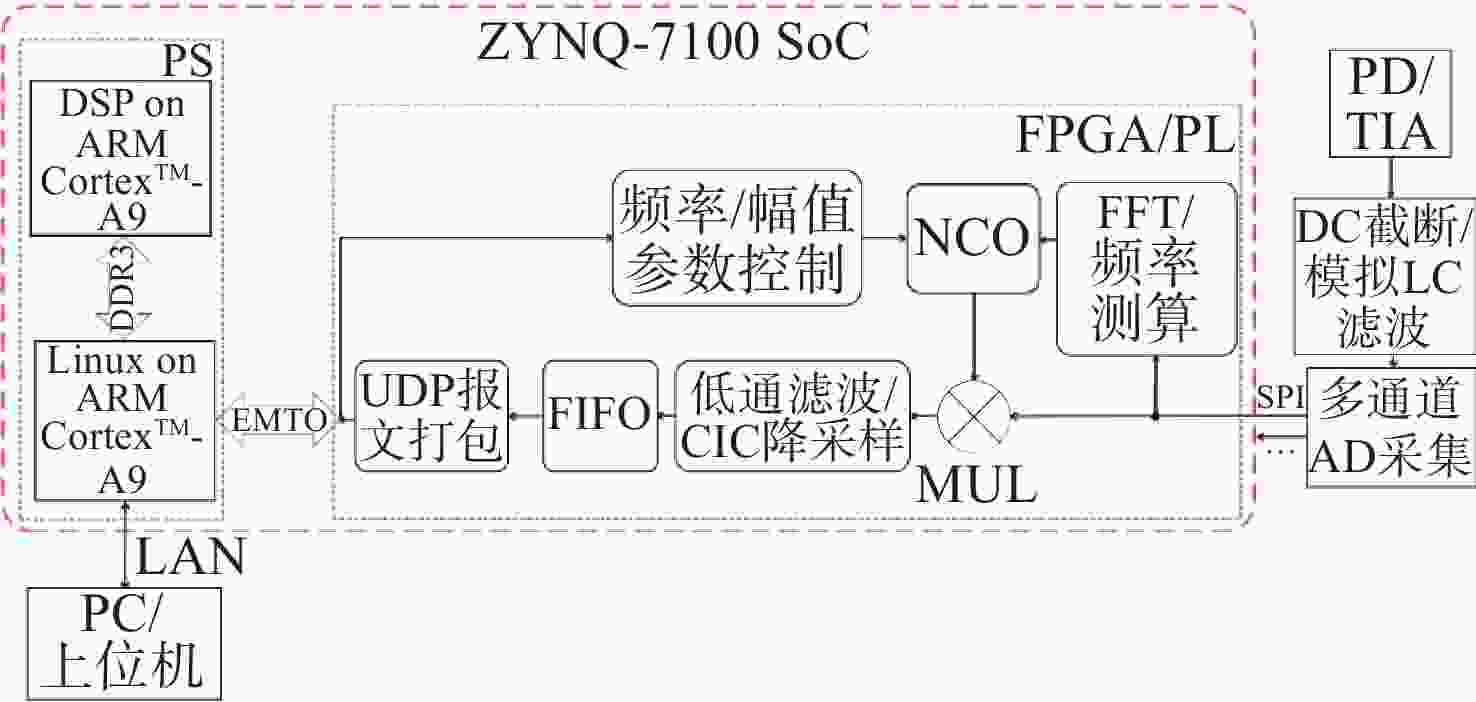
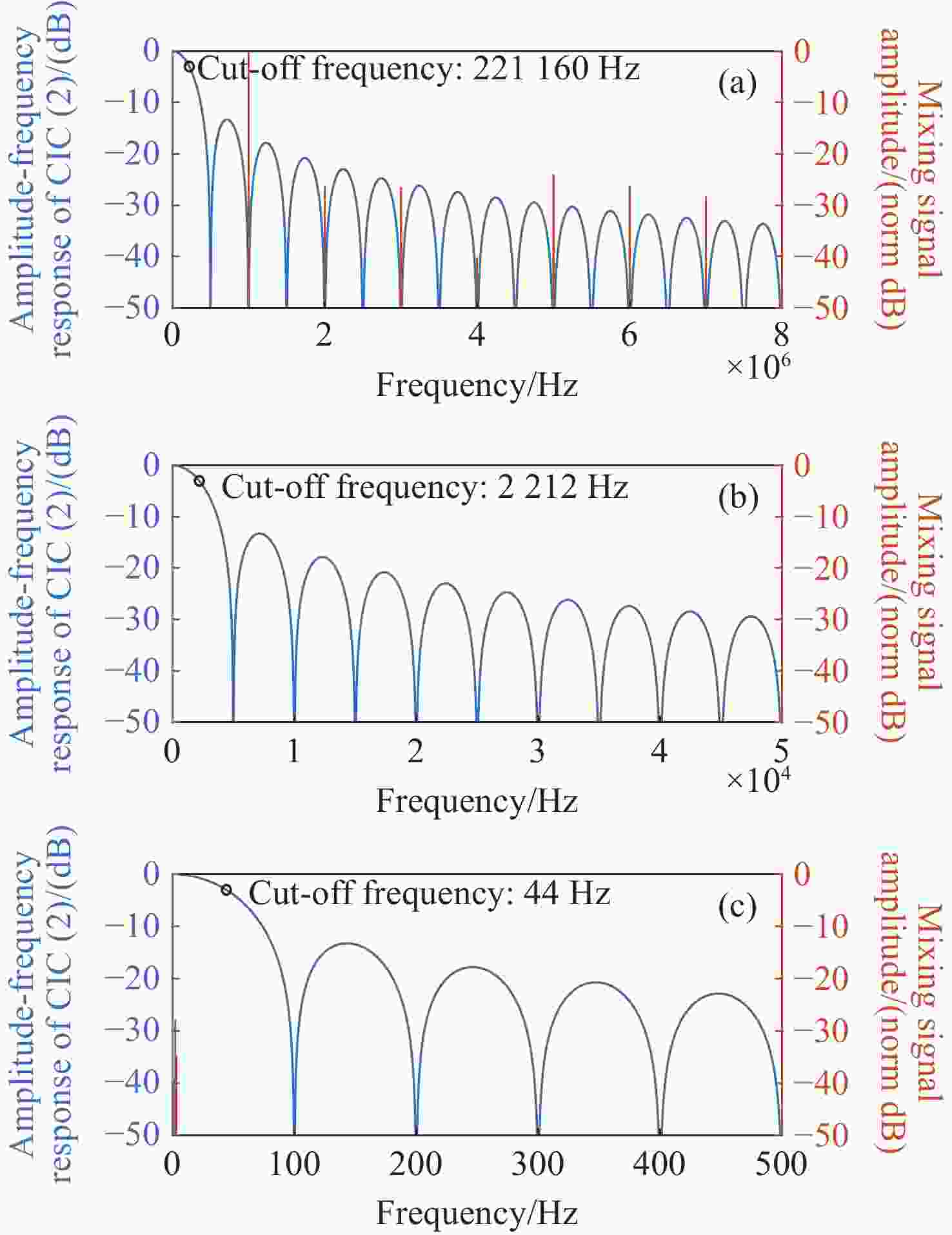
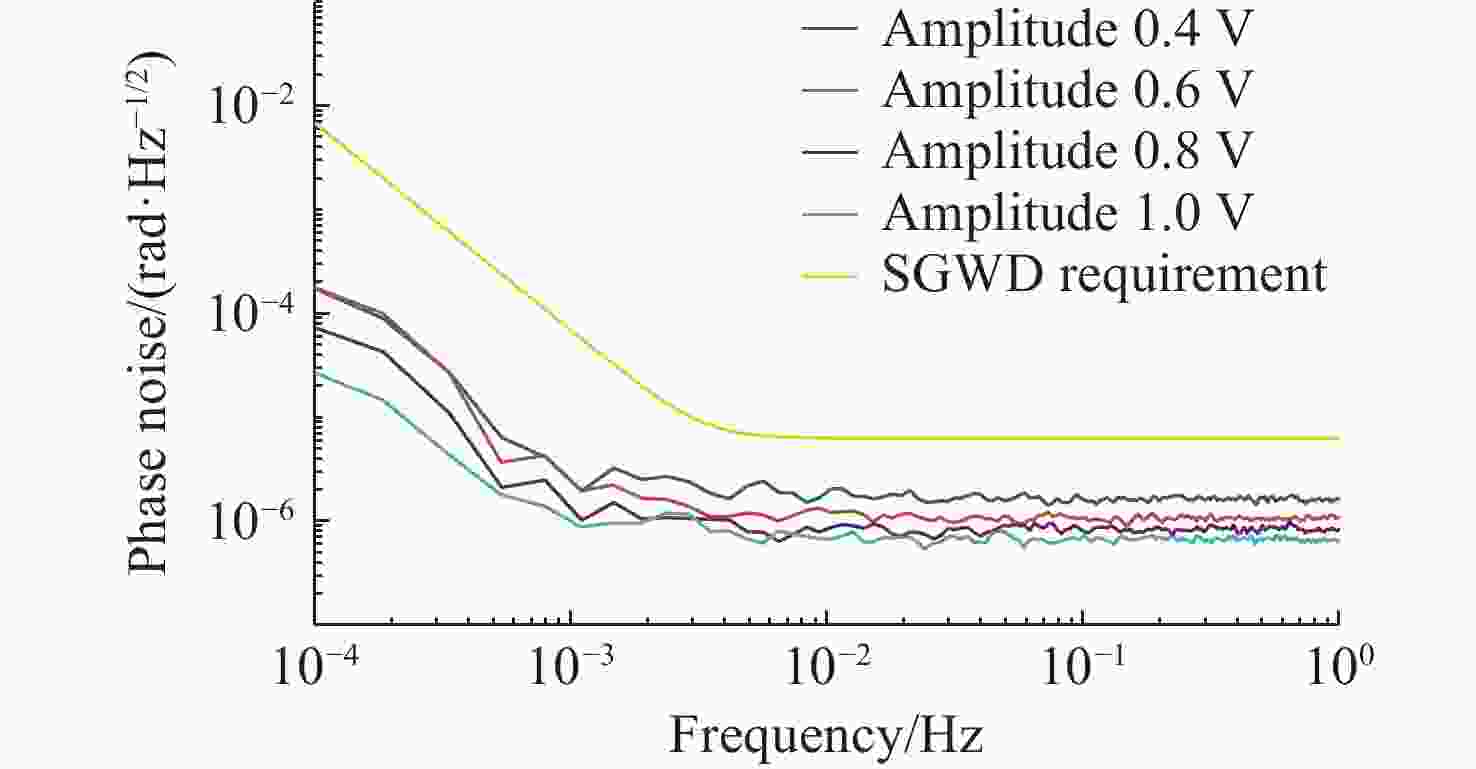
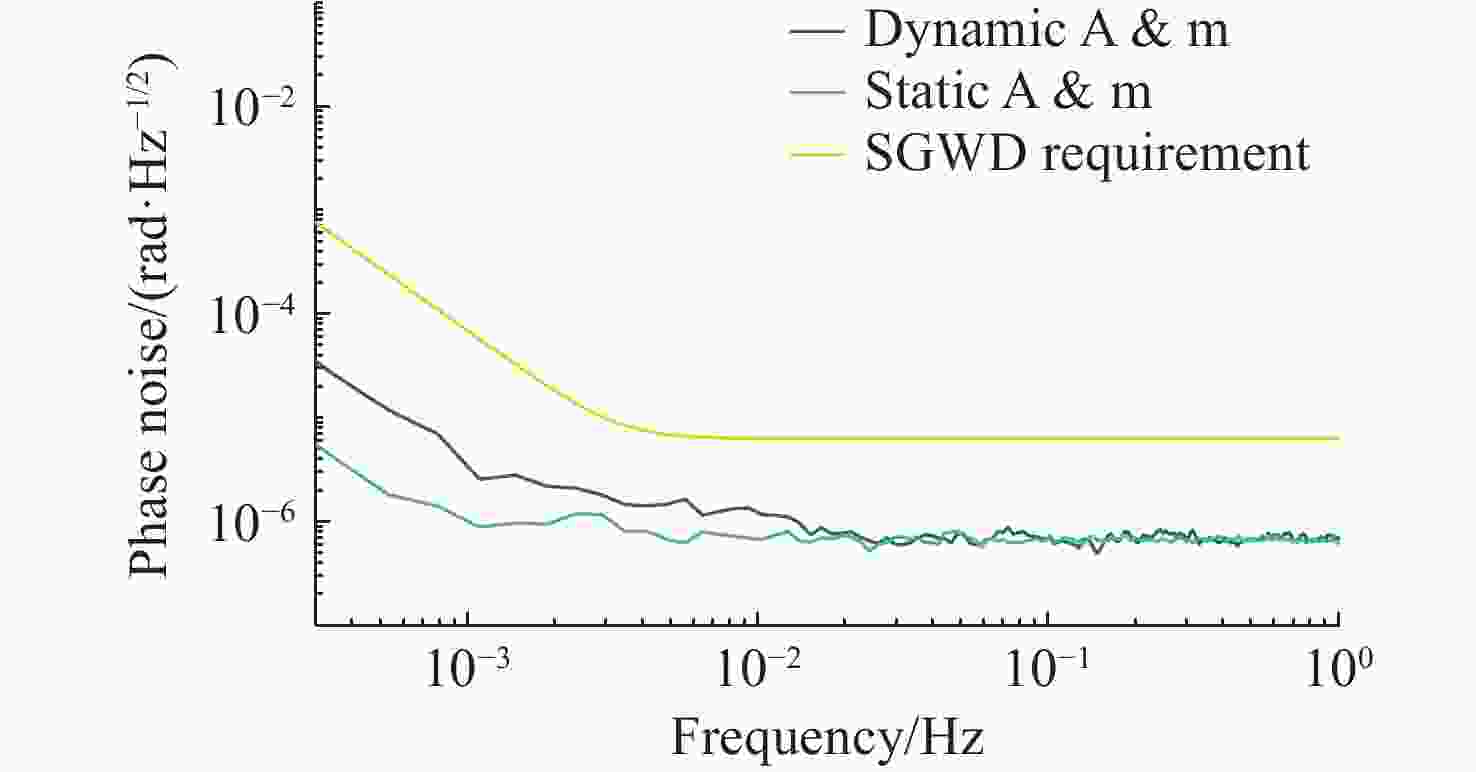
深度频率调制(DFM)干涉技术是实现空间引力波探测激光干涉测量系统简化的有效方案。当前DFM干涉技术普遍使用kHz级调制,导致激光功率噪声会耦合进入系统,从而增加本底噪声,难以满足高精度空间测量的要求。本文提出将DFM的调制频率提升至MHz量级以减少激光功率噪声的影响。通过深入分析DFM技术原理,采用贝塞尔函数展开、正交解调和推广J1···J4方法设计了DFM干涉相位信号提取方法。基于MHz级信号处理需求,完成了相位测量系统的软硬件构建,并对系统在多种工况下的性能进行测试与评估。测试结果表明:相位测量系统具有良好的线性度和准确度,且在不同工况下,2 mHz ~ 1 Hz频段内的相位噪声均优于 2π µrad/
$\sqrt{{\mathrm{Hz}}} $ ,能够满足空间引力波探测的相位测量需求。Abstract:Deep Frequency Modulation (DFM) interferometry is an effective approach for simplifying laser interferometry systems in space gravitational wave detection. However, the conventional use of kHz-level modulation frequencies in current DFM techniques introduces coupling of laser power noise into the system, which increases background noise and limits the ability to meet the stringent requirements of high-precision space measurements. This paper proposes to increase the DFM modulation frequency to the MHz range to mitigate the effects of laser power noise. Through an in-depth analysis of the DFM technique, we developed a phase signal extraction method for DFM interferometry using Bessel function expansion, orthogonal demodulation, and promotion of J1···J4 method. Based on the signal processing requirements at the MHz-level, the hardware and software architecture of a phase measurement system was developed, followed by extensive testing and evaluation under various operating conditions. The results demonstrate that the phase measurement system exhibits excellent linearity and accuracy, with phase noise in the frequency band from 2 mHz to 1 Hz consistently below 2π µrad/
$\sqrt{{\mathrm{Hz}}} $ , thus meeting the phase measurement requirements for space-based gravitational wave detection.-
Key words:
- laser interference /
- deep frequency modulation /
- phase measurement
-
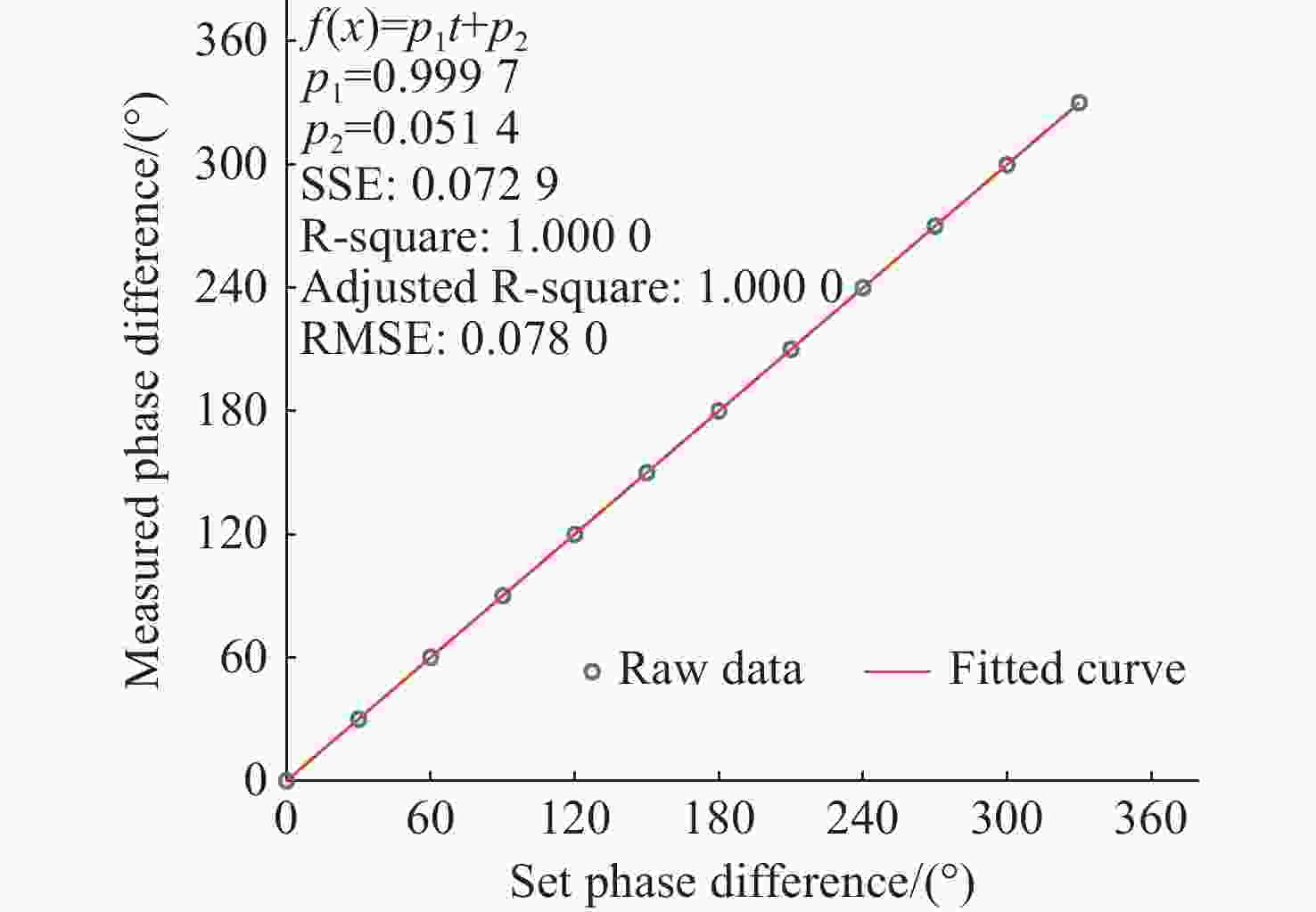
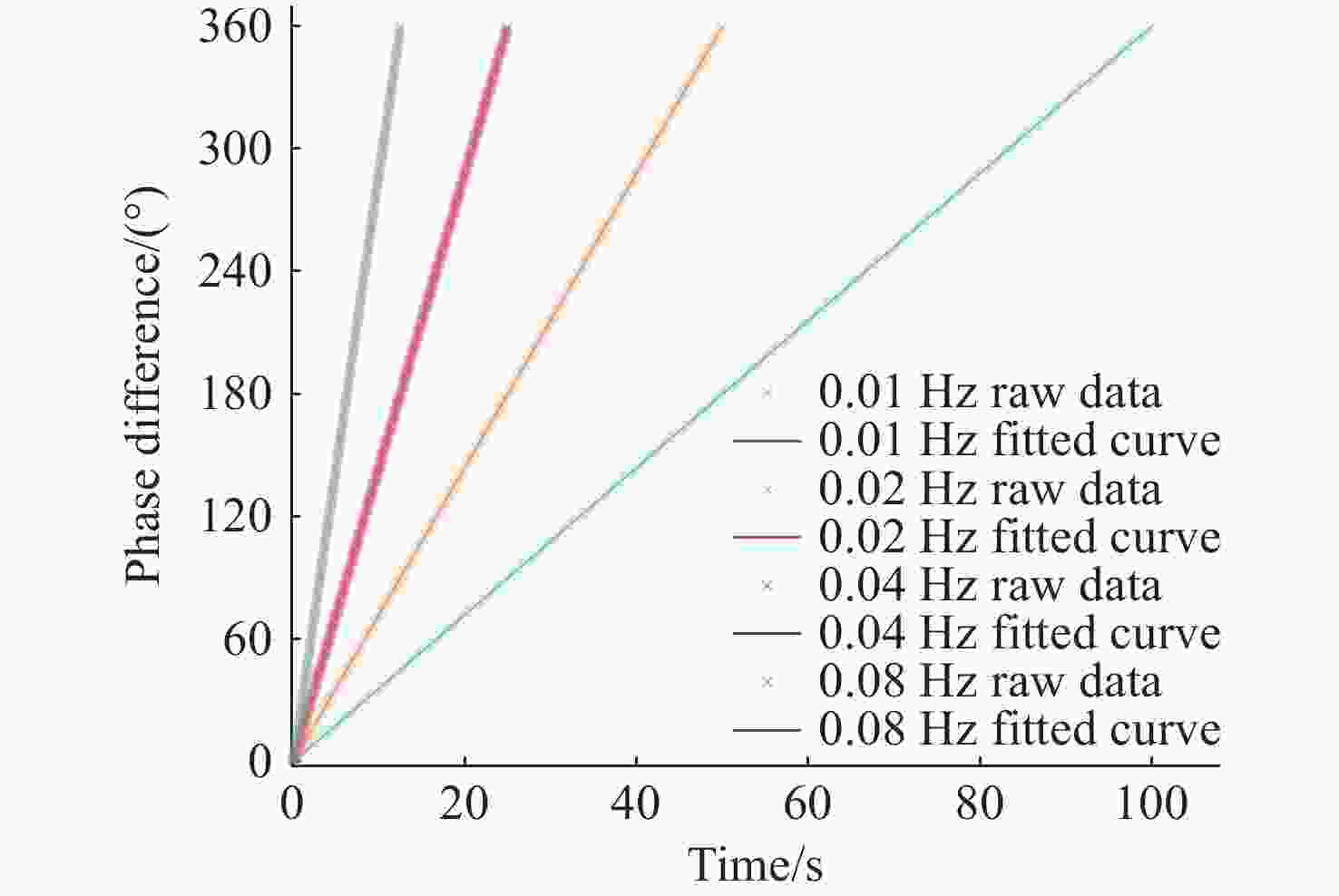
表 1 动态测试下拟合曲线评价参数
Table 1. Evaluation parameters of fitted curves in dynamic test
相位变化频率(Hz) $ f(x) = {p_1}t + {p_2} $ SSE R-square Adjusted R-square RMSE $ {p_1} $ $ {p_2} $ 0.01 3.6001 - 0.0896 46.5577 1.0000 1.0000 0.0682 0.02 7.2002 0.0045 6.7390 1.0000 1.0000 0.0367 0.04 14.4001 0.0109 3.2861 1.0000 1.0000 0.0363 0.08 28.8006 - 0.0727 1.6601 1.0000 1.0000 0.0364 -
[1] 徐欣, 谈宜东, 穆衡霖, 等. 空间引力波探测中的激光干涉多自由度测量技术[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2023,60(3):0312006.XU X, TAN Y D, MU H L, et al. Laser interferometric multi-degree-of-freedom measurement technology in space gravitational-wave detection[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(3): 0312006. (in Chinese). [2] WATCHI J, COOPER S, DING B L, et al. Contributed review: a review of compact interferometers[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2018, 89(12): 121501. doi: 10.1063/1.5052042 [3] SUTTON A J, GERBERDING O, HEINZEL G, et al. Digitally enhanced homodyne interferometry[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(20): 22195-22207. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.022195 [4] SHADDOCK D A. Digitally enhanced heterodyne interferometry[J]. Optics Letters, 2007, 32(22): 3355-3357. doi: 10.1364/OL.32.003355 [5] VINE G, RABELING D S, SLAGMOLEN B J J, et al. Picometer level displacement metrology with digitally enhanced heterodyne interferometry[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(2): 828-837. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.000828 [6] LIU H SH, WANG J, GAO R H, et al. Constant amplitude modulation heterodyne interferometry[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 61(28): 8493-8499. doi: 10.1364/AO.456944 [7] LAI L X, DONG P, LIU H SH, et al. Experimental demonstration of constant amplitude modulation heterodyne interferometry[J]. Optics Letters, 2024, 49(11): 2873-2876. doi: 10.1364/OL.524447 [8] HEINZEL G, CERVANTES F G, MARÍN A F G, et al. Deep phase modulation interferometry[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(18): 19076-19086. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.019076 [9] SCHWARZE T S, GERBERDING O, CERVANTES F G, et al. Advanced phasemeter for deep phase modulation interferometry[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(15): 18214-18223. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.018214 [10] TERÁN M, MARTÍN V, GESA L, et al. Towards a FPGA-controlled deep phase modulation interferometer[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2015, 610: 012042. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/610/1/012042 [11] GERBERDING O. Deep frequency modulation interferometry[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(11): 14753-14762. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.014753 [12] SCHWARZE T S. Phase extraction for laser interferometry in space: phase readout schemes and optical testing[D]. Hannover: Leibniz University, 2018. [13] ISLEIF K S. Laser interferometry for LISA and satellite geodesy missions[D]. Hannover: Leibniz Universität Hannover, 2018. [14] ISLEIF K S, GERBERDING O, SCHWARZE T S, et al. Experimental demonstration of deep frequency modulation interferometry[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(2): 1676-1684. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.001676 [15] ISLEIF K S, HEINZEL G, MEHMET M, et al. Compact multifringe interferometry with subpicometer precision[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2019, 12(3): 034025. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.12.034025 [16] GERBERDING O, ISLEIF K S. Ghost beam suppression in deep frequency modulation interferometry for compact on-axis optical heads[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(5): 1708. doi: 10.3390/s21051708 [17] SMETANA J, WALTERS R, BAUCHINGER S, et al. Compact Michelson interferometers with subpicometer sensitivity[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2022, 18(3): 034040. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.18.034040 [18] WISSEL L, WITTCHEN A, SCHWARZE T S, et al. Relative-intensity-noise coupling in heterodyne interferometers[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2022, 17(2): 024025. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.17.024025 [19] SUDARSHANAM V S, SRINIVASAN K. Linear readout of dynamic phase change in a fiber-optic homodyne interferometer[J]. Optics Letters, 1989, 14(2): 140-142. doi: 10.1364/OL.14.000140 [20] JIN W, ZHANG L M, UTTAMCHANDANI D, et al. Modified J1 … J4 method for linear readout of dynamic phase changes in a fiber-optic homodyne interferometer[J]. Applied Optics, 1991, 30(31): 4496-4499. doi: 10.1364/AO.30.004496 [21] SUDARSHANAM V S, CLAUS R O. Generic J1…J4 method of optical phase detection: accuracy and range enhancement[J]. Journal of Modern Optics, 1993, 40(3): 483-492. doi: 10.1080/09500349314550481 [22] 张强涛, 刘河山, 罗子人. 面向空间激光干涉的多通道相位测量系统[J]. 中国光学 (中英文),2023,16(5):1089-1099. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0258ZHANG Q T, LIU H SH, LUO Z R. Multi-channel phase measurement system for the space laser interferometry[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(5): 1089-1099. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0258 [23] ZHANG Q T, LIU H SH, DONG P, et al. Multi-frequency signal acquisition and phase measurement in space gravitational wave detection[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2024, 95(5): 054501. doi: 10.1063/5.0198104 [24] 刘河山. 面向空间引力波探测的激光差分干涉相位计研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2015.LIU H SH. The research on phasemeter of heterodyne laser interferometry for the space gravitational wave detection[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015. (in Chinese) [25] HEWITSON M, ARMANO M, BENEDETTI M, et al. Data analysis for the LISA technology package[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2009, 26(9): 094003. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/26/9/094003 -







 下载:
下载: