-
摘要:
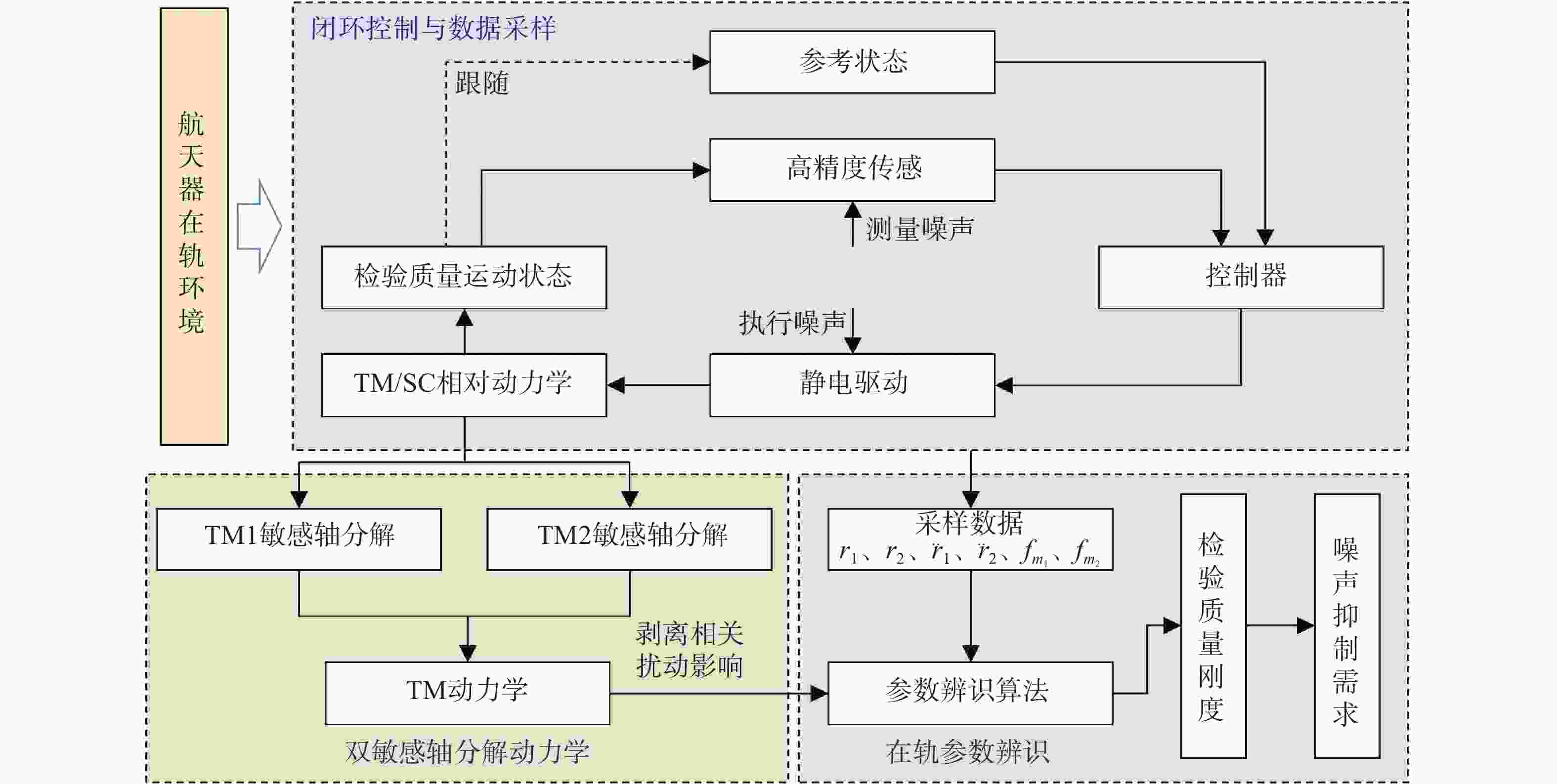
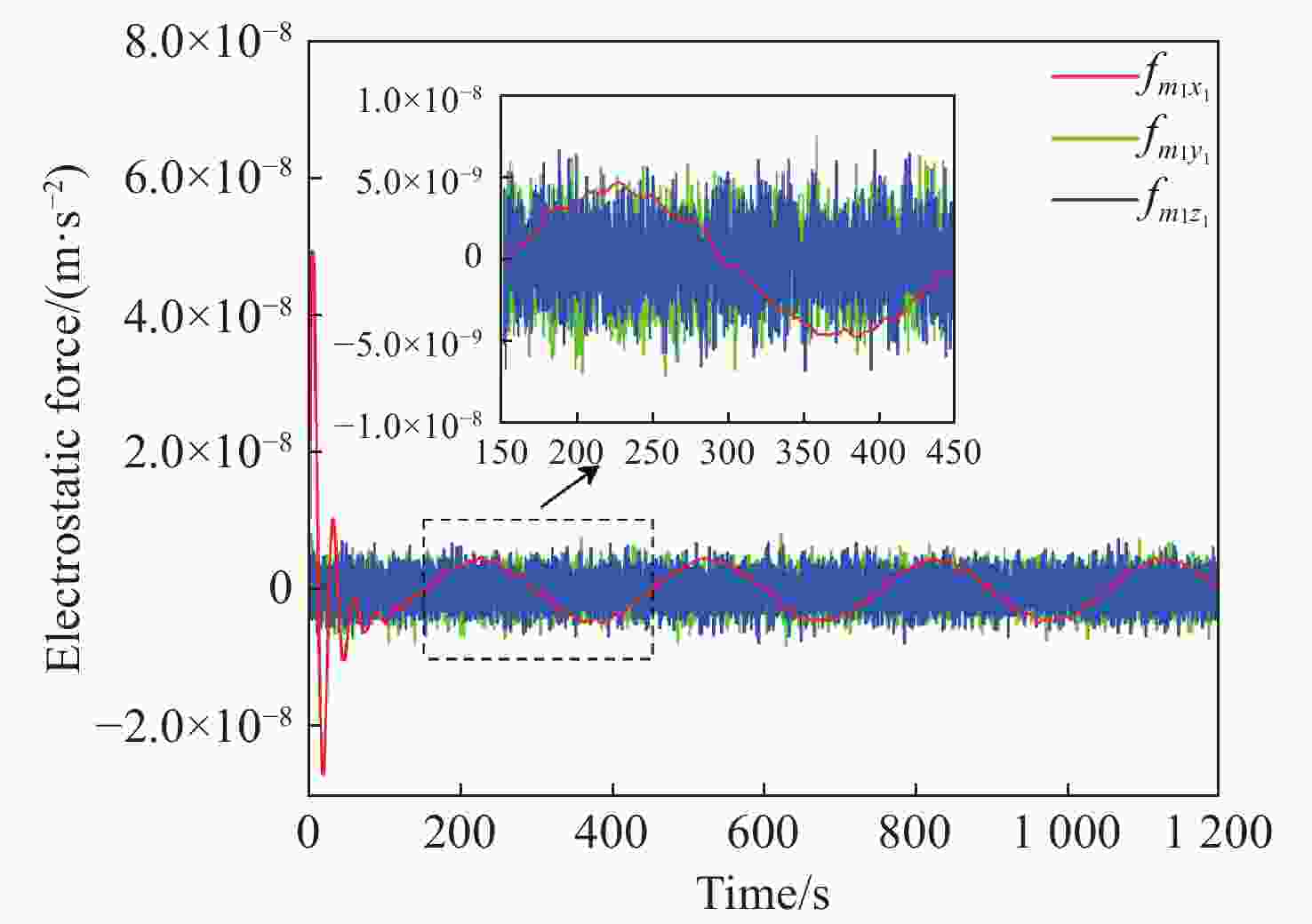
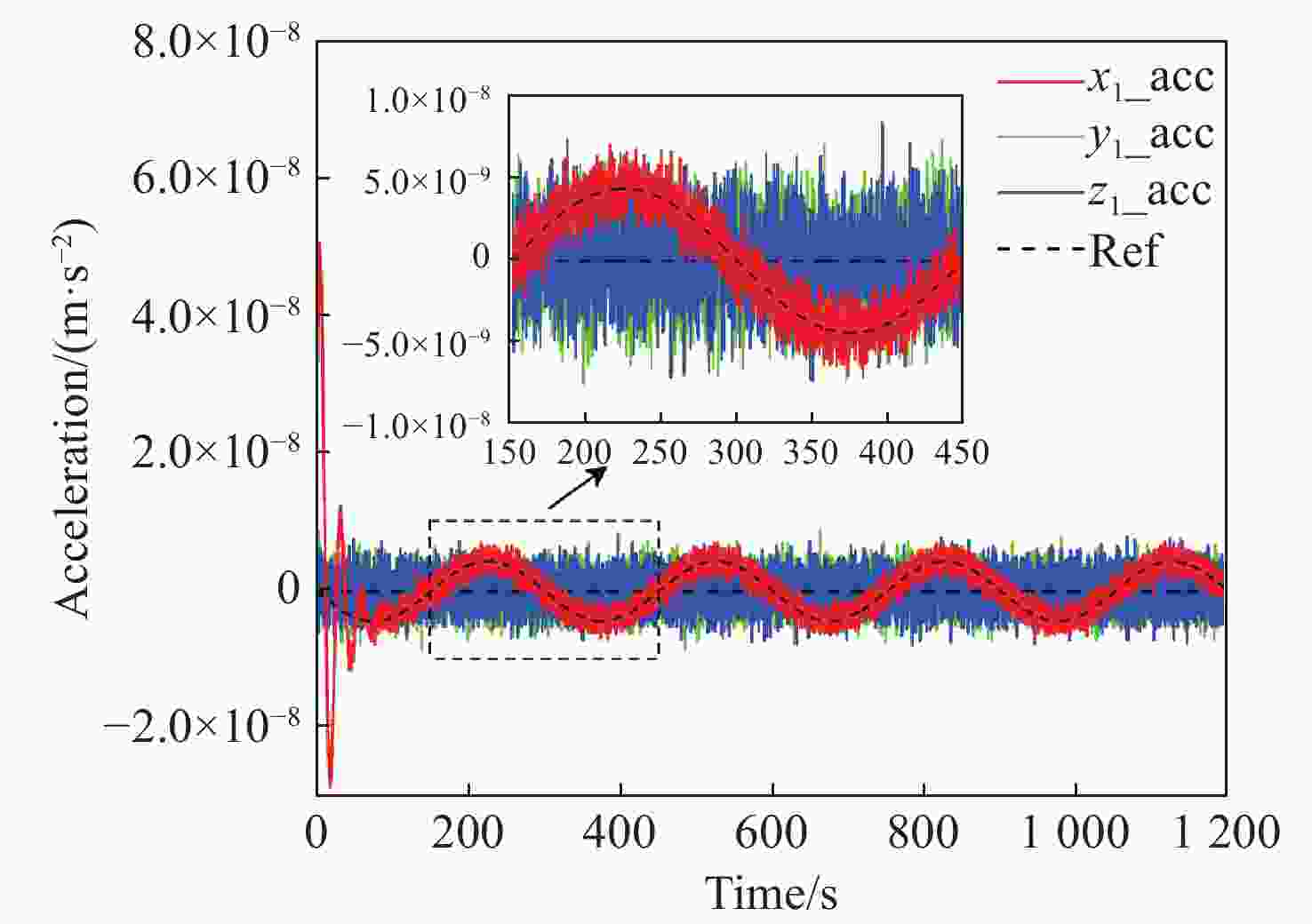
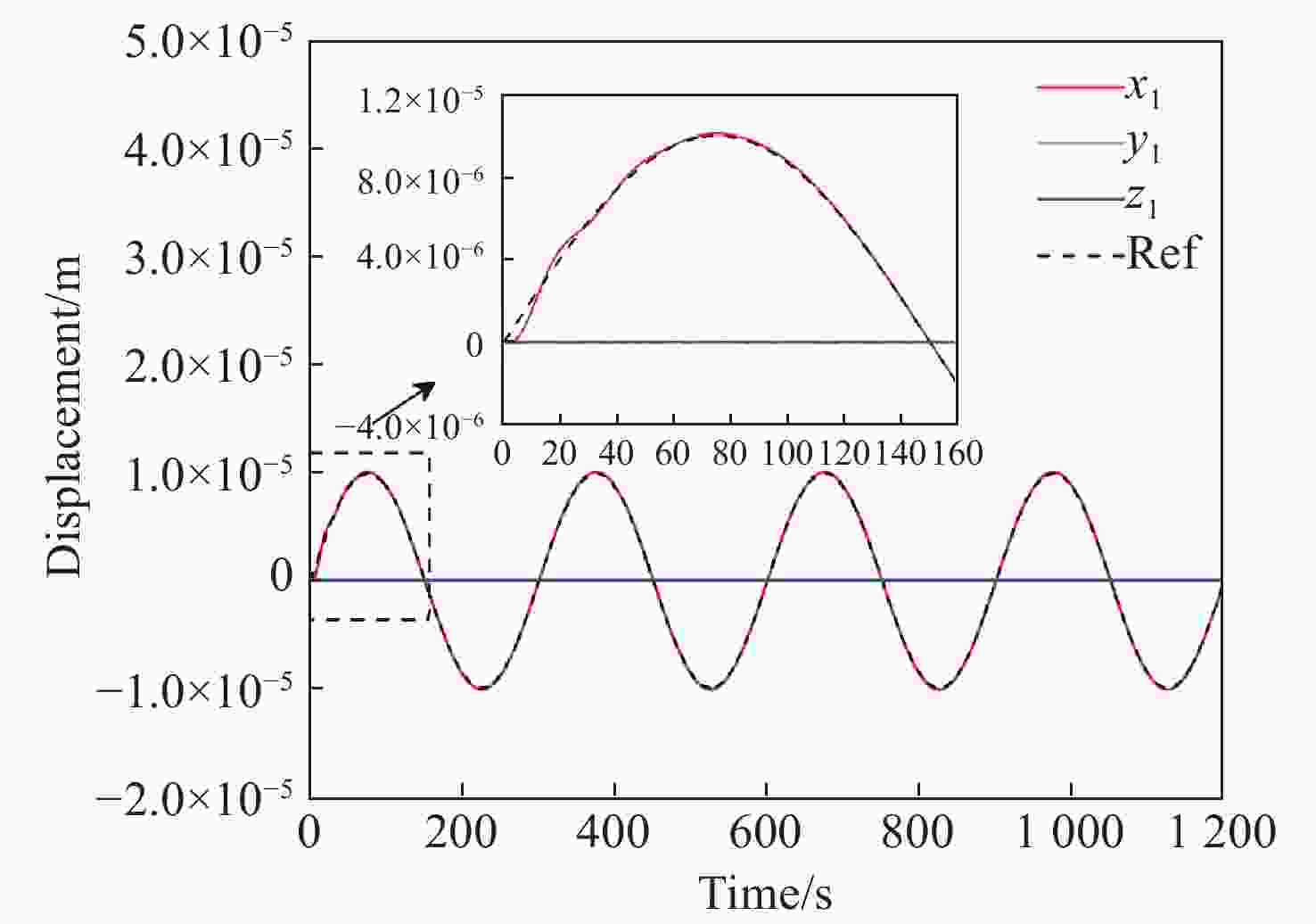
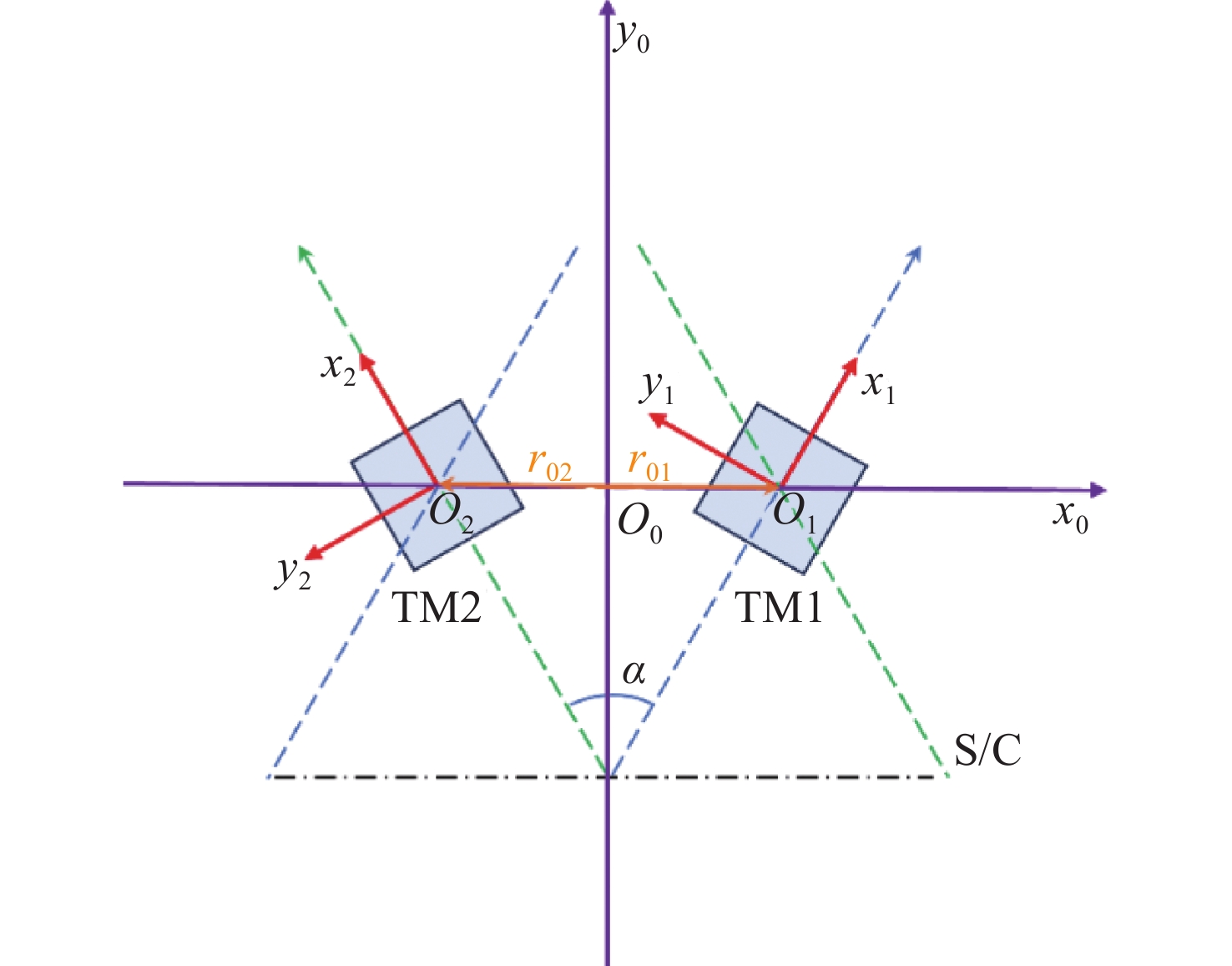
检验质量刚度与位移耦合噪声作为残余加速度噪声的重要组成部分,极大影响空间引力波探测性能,需要辨识刚度以验证、优化控制效果,满足噪声抑制需求。针对非同轴检验质量布局,本文提出了一种基于双敏感轴分解的刚度辨识方法。首先,构建检验质量与航天器间的相对动力学模型,并将模型参数沿双敏感轴分解从而剥离航天器加速度扰动和主要的角加速度扰动对在轨辨识的影响。其次,结合星内激光干涉仪、惯性传感器和相关控制环路,设计在轨辨识方案并提出采用递归最小二乘辨识刚度的方法。最后,开展数值仿真实验以验证方法性能。实验结果表明:本文提出的刚度辨识方法可有效辨识检验质量敏感轴刚度,在给定仿真条件下平均绝对误差小于5×10−9 s−2,均方根误差小于1.5×10−8 s−2,最大稳态误差小于2×10−9 s−2,可应用于后续引力波科学探测任务中。
Abstract:The coupling noise between test mass stiffness and displacement, as a significant component of the residual acceleration noise, critically impacts the performance of space gravitational wave detection, making stiffness identification essential for validating and optimizing control strategies and meeting the noise suppression requirements. For non-coaxial test mass configurations, this paper proposes a novel identification method based on dual sensitive axis decomposition. First, a relative dynamic model between the test mass and the spacecraft is constructed, and the model parameters are decomposed along the dual sensitive axis to isolate the influence of spacecraft acceleration disturbances and predominant angular acceleration disturbances on the on-orbit identification. Second, utilizing on-board laser interferometers, inertial sensors, and associated control loops, an on-orbit identification scheme is designed and a stiffness identification method using recursive least squares is proposed. Finally, numerical simulations are performed to verify the performance of the method. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed stiffness identification method can effectively identify the stiffness of the test mass on the sensitive axis. Under the given simulation conditions, the mean absolute error is less than 5×10−9 s−2, the root mean square error is less than 1.5×10−8 s−2, and the maximum steady-state error is less than 2×10−9 s−2. These findings suggest that the method can be applied to future gravitational wave science missions.
-
表 1 数值仿真实验参数设置
Table 1. Numerical simulation experiment parameter settings
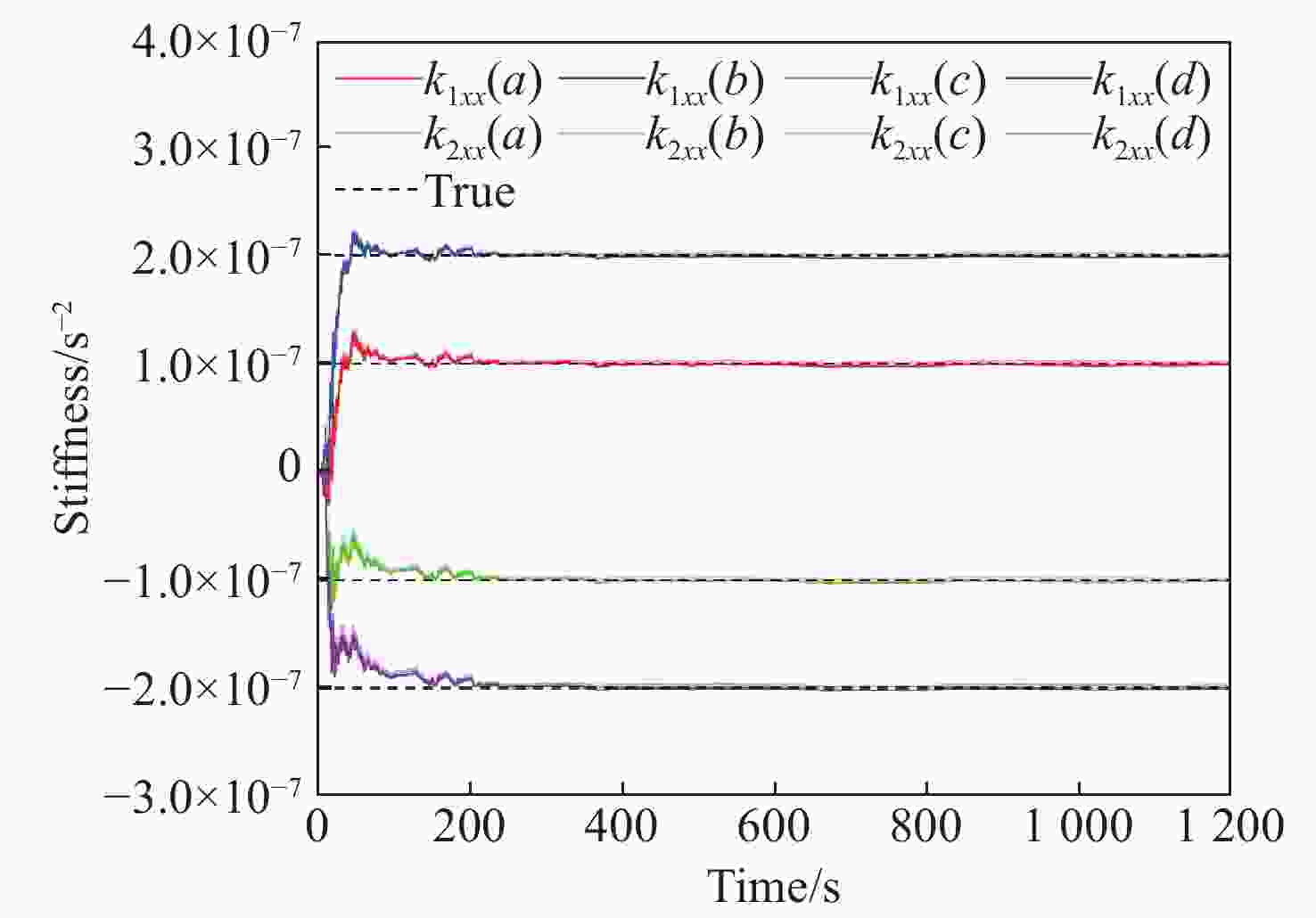
参数 数值 航天器转动惯量/(kg·m2) diag(450,450,450) TM1刚度/s−2 [1,1,1]×10−7 TM2刚度/s−2 [1,1,1]×10−7 r1参考状态/m [10sin(2πt/300),0,0]×10−6 r2参考状态/m [10sin(2πt/300),0,0]×10−6 fd1/(m·s−2) [1,1,1]×10−10 fd2/(m·s−2) [1,1,1]×10−10 表 2 测量噪声与执行噪声设置
Table 2. Parameter settings for measurement noise and execution noise
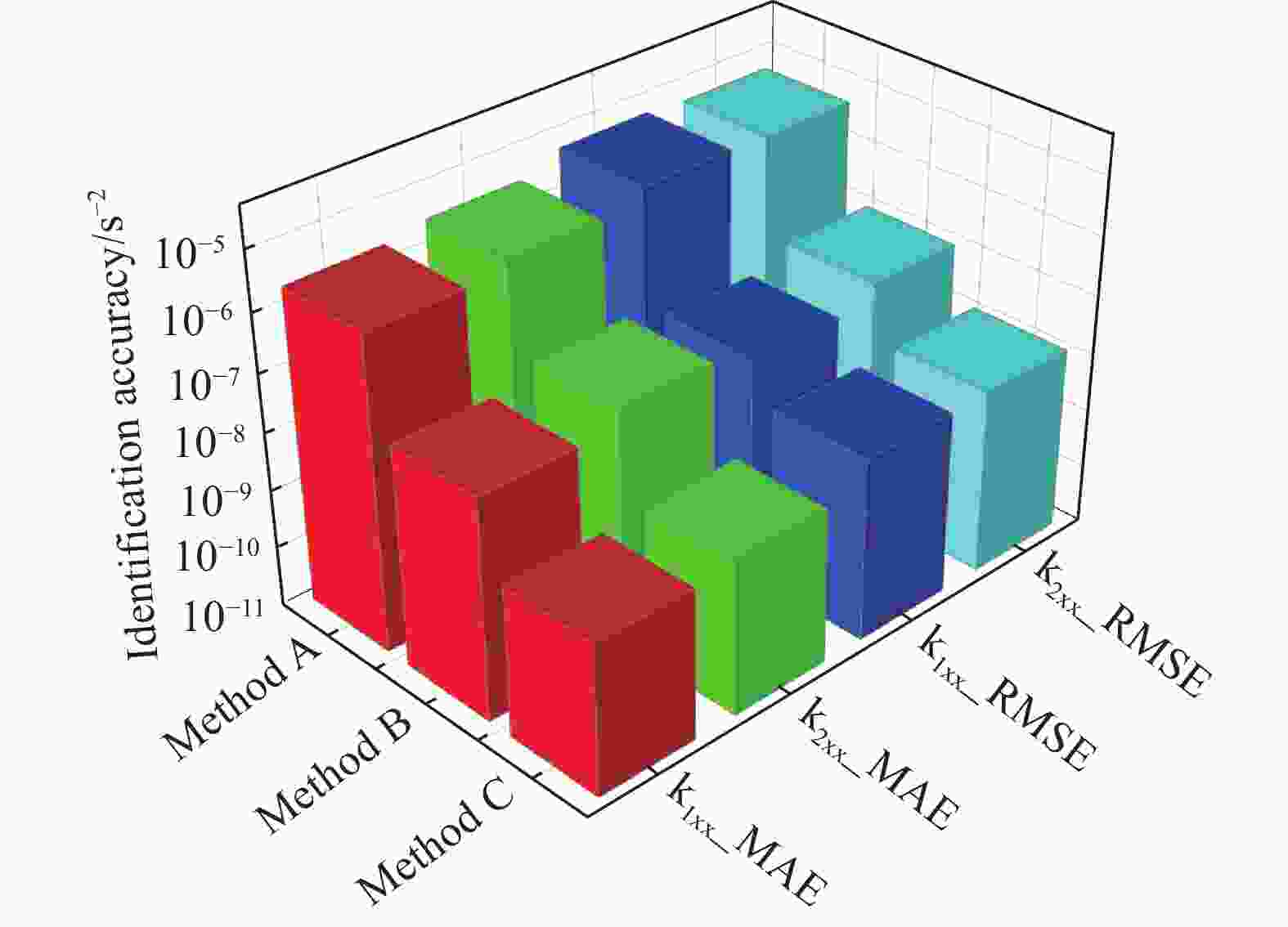
参数 获得途径 高斯白噪声均方差 敏感轴位移/m 星内激光干涉仪 1×10−11 非敏感轴位移/m 惯性传感器 1×10−8 加速度/(m·s−2) 惯性传感器 1×10−12 静电力/(m·s−2) 静电控制回路 1×10−12 表 3 参数辨识精度
Table 3. Parameter identification accuracy
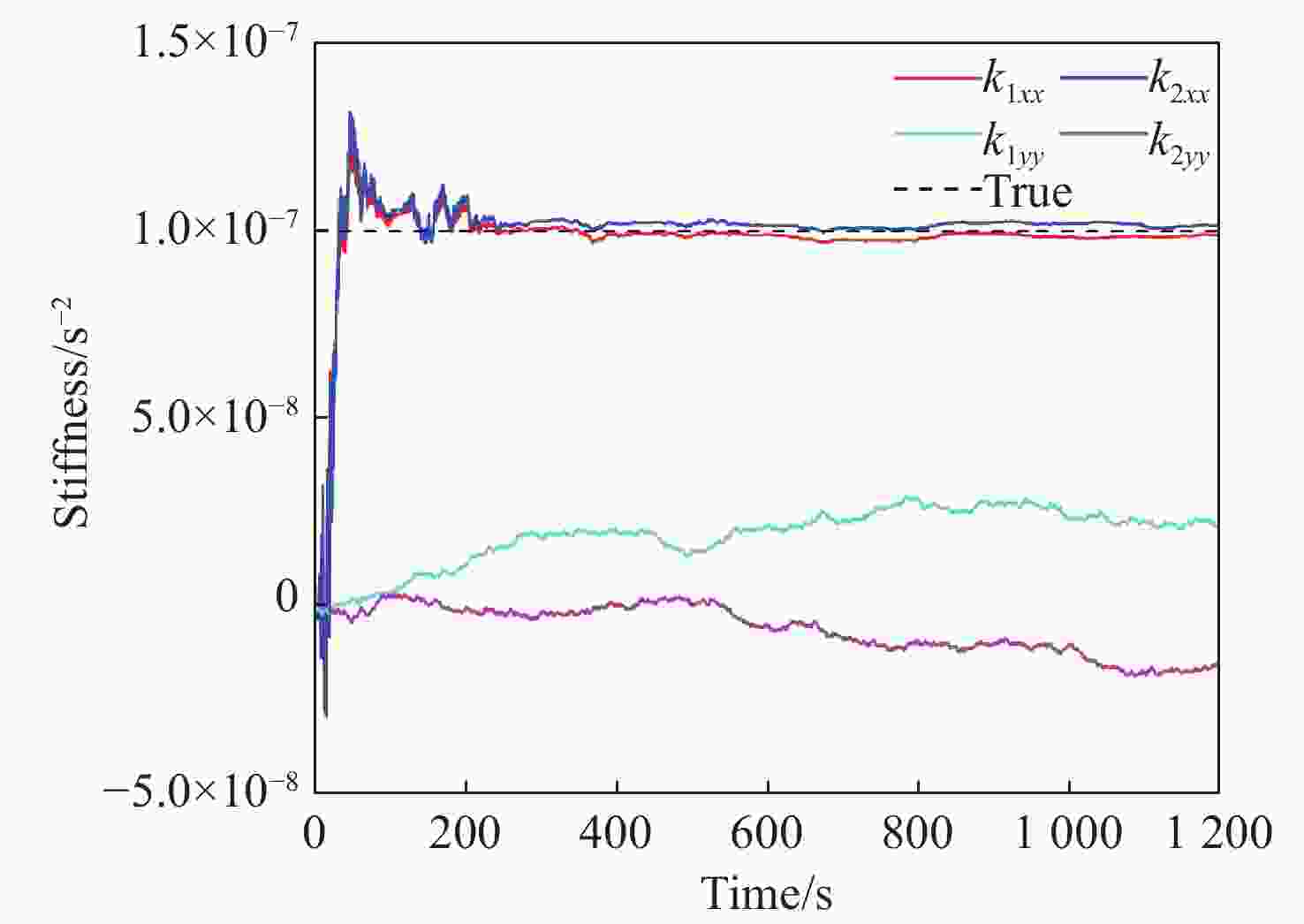
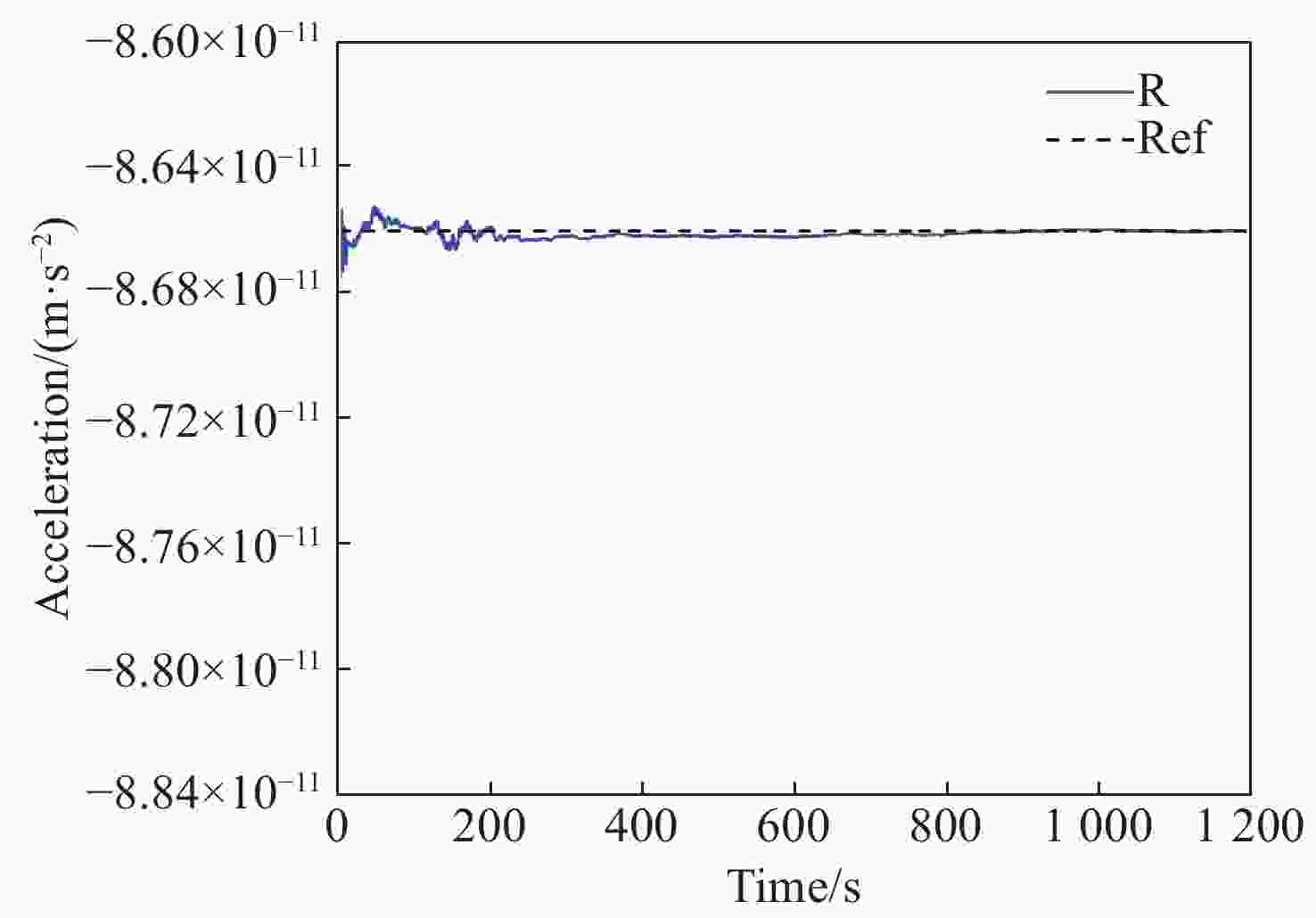
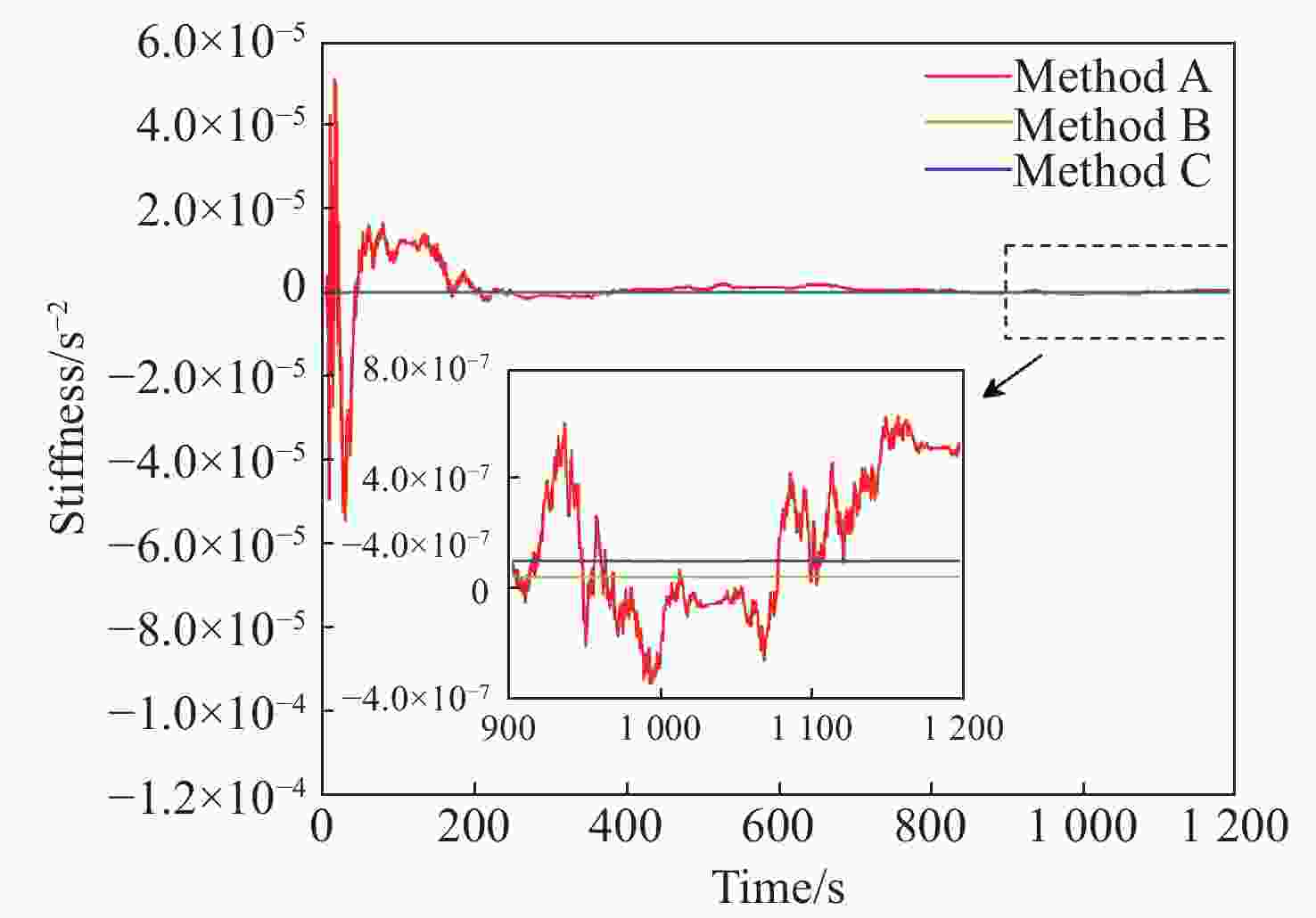
参数 MAE RMSE Emax k1xx/s−2 3.8726 ×10−91.3753 ×10−81.6792 ×10−9k2xx/s−2 4.5863 ×10−91.4114 ×10−81.7344 ×10−9k1yy/s−2 8.1416 ×10−88.1765 ×10−8未收敛 k2yy/s−2 1.0652 ×10−71.0671 ×10−7未收敛 R/(m·s−2) 1.4004 ×10−142.7194 ×10−141.9547 ×10−13 -
[1] GIAMMARCHI M, RICCI F. Gravitational waves, event horizons and black hole observation: a new frontier in fundamental physics[J]. Symmetry, 2022, 14(11): 2276. [2] MASTROGIOVANNI S, KARATHANASIS C, GAIR J, et al. Cosmology with gravitational waves: a review[J]. Annalen der Physik, 2024, 536(2): 2200180. doi: 10.1002/andp.202200180 [3] 吴岳良, 胡文瑞, 王建宇, 等. 空间引力波探测综述与拟解决的科学问题[J]. 空间科学学报,2023,43(4):589-599.WU Y L, HU W R, WANG J Y, et al. Review and scientific objectives of spaceborne gravitational wave detection missions[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2023, 43(4): 589-599. (in Chinese). [4] BAYLE J B, BONGA B, CAPRINI C, et al. Overview and progress on the laser interferometer space antenna mission[J]. Nature Astronomy, 2022, 6(12): 1334-1338. [5] LUO Z R, WANG Y, WU Y L, et al. The Taiji program: a concise overview[J]. Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics, 2021, 2021(5): 05A108. doi: 10.1093/ptep/ptaa083 [6] MEI J W, BAI Y ZH, BAO J H, et al. The TianQin project: current progress on science and technology[J]. Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics, 2021, 2021(5): 05A107. doi: 10.1093/ptep/ptaa114 [7] 罗子人, 白姗, 边星, 等. 空间激光干涉引力波探测[J]. 力学进展,2013,43(4):415-447. doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-13-044LUO Z R, BAI SH, BIAN X, et al. Space laser interferometry gravitational wave detection[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2013, 43(4): 415-447. (in Chinese). doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-13-044 [8] 范一迪, 王鹏程, 卢苇, 等. 双检验质量无拖曳卫星鲁棒控制[J]. 深空探测学报(中英文),2023,10(3):310-321.FAN Y D, WANG P CH, LU W, et al. Robust controller design for drag-free satellites with two test masses[J]. Journal of Deep Space Exploration, 2023, 10(3): 310-321. (in Chinese). [9] 苟兴宇, 王丽娇, 许现民, 等. 位移无拖曳控制的动力学协调条件研究[J]. 宇航学报,2024,45(4):540-549. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2024.04.006GOU X Y, WANG L J, XU X M, et al. Study on dynamic coordination condition of displacement drag-free control[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2024, 45(4): 540-549. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2024.04.006 [10] YUE CH L, JIAO B H, DANG ZH H, et al. A review on DFACS (II): modeling and analysis of disturbances and noises[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2024, 37(5): 120-147. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2024.02.013 [11] HAO L W, ZHANG Y C. Design and analysis of the integrated drag-free and attitude control system for TianQin mission: a preliminary result[J]. Aerospace, 2024, 11(6): 416. [12] WANG J H, GUO X, MA ZH J, et al. A low fuel-consumption drag-free tracking approach for space-based gravitational wave detection satellite[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(2): 1545-1555. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3336827 [13] VIDANO S, NOVARA C, COLANGELO L, et al. The LISA DFACS: a nonlinear model for the spacecraft dynamics[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 107: 106313. [14] ARMANO M, AUDLEY H, BAIRD J, et al. Beyond the required LISA free-fall performance: new LISA pathfinder results down to 20 μHz[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 120(6): 061101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.061101 [15] ZIEGLER T, FICHTER W. Test mass stiffness estimation for the LISA Pathfinder drag-free system[C]. Proceedings of AIAA Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference and Exhibit, AIAA, 2007: 6669. [16] NOFRARIAS M, RÖVER C, HEWITSON M, et al. Bayesian parameter estimation in the second LISA Pathfinder mock data challenge[J]. Physical Review D, 2010, 82(12): 122002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.82.122002 [17] CONGEDO G, FERRAIOLI L, HUELLER M, et al. Time domain maximum likelihood parameter estimation in LISA Pathfinder data analysis[J]. Physical Review D, 2012, 85(12): 122004. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.85.122004 [18] ARMANO M, AUDLEY H, BAIRD J, et al. Calibrating the system dynamics of LISA Pathfinder[J]. Physical Review D, 2018, 97(12): 122002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.97.122002 [19] WEBER W J, BORTOLUZZI D, CAVALLERI A, et al. Position sensors for flight testing of LISA drag-free control[J]. Gravitational-Wave Detection, 2003, 4856: 31-42. doi: 10.1117/12.458564 [20] ARMANO M, AUDLEY H, AUGER G, et al. Constraints on LISA Pathfinder’s self-gravity: design requirements, estimates and testing procedures[J]. Classical and Quantum gravity, 2016, 33(23): 235015. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/33/23/235015 [21] JIAO B H, LIU Q F, DANG ZH H, et al. A review on DFACS (I): system design and dynamics modeling[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2024, 37(5): 92-119. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2024.01.031 [22] 王娟, 齐克奇, 王少鑫, 等. 面向空间引力波探测的激光干涉技术研究进展及展望[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学,2024,54(7):109-127.WANG J, QI K Q, WANG SH X, et al. Advance and prospect in the study of laser interferometry technology for space gravitational wave detection[J]. Scientia Sinica (Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica), 2024, 54(7): 109-127. (in Chinese) [23] 王少鑫, 郭纬川, 赵平安, 等. 空间引力波探测惯性传感器及其关键技术[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学,2024,54(7):91-108.WANG SH X, GUO W CH, ZHAO P A, et al. Inertial sensor for space gravitational wave detection and its key technologies[J]. Scientia Sinica (Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica), 2024, 54(7): 91-108. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: