Polarization sensitive luminescence properties of europium ions in ZnO microrod matrix
-
摘要:
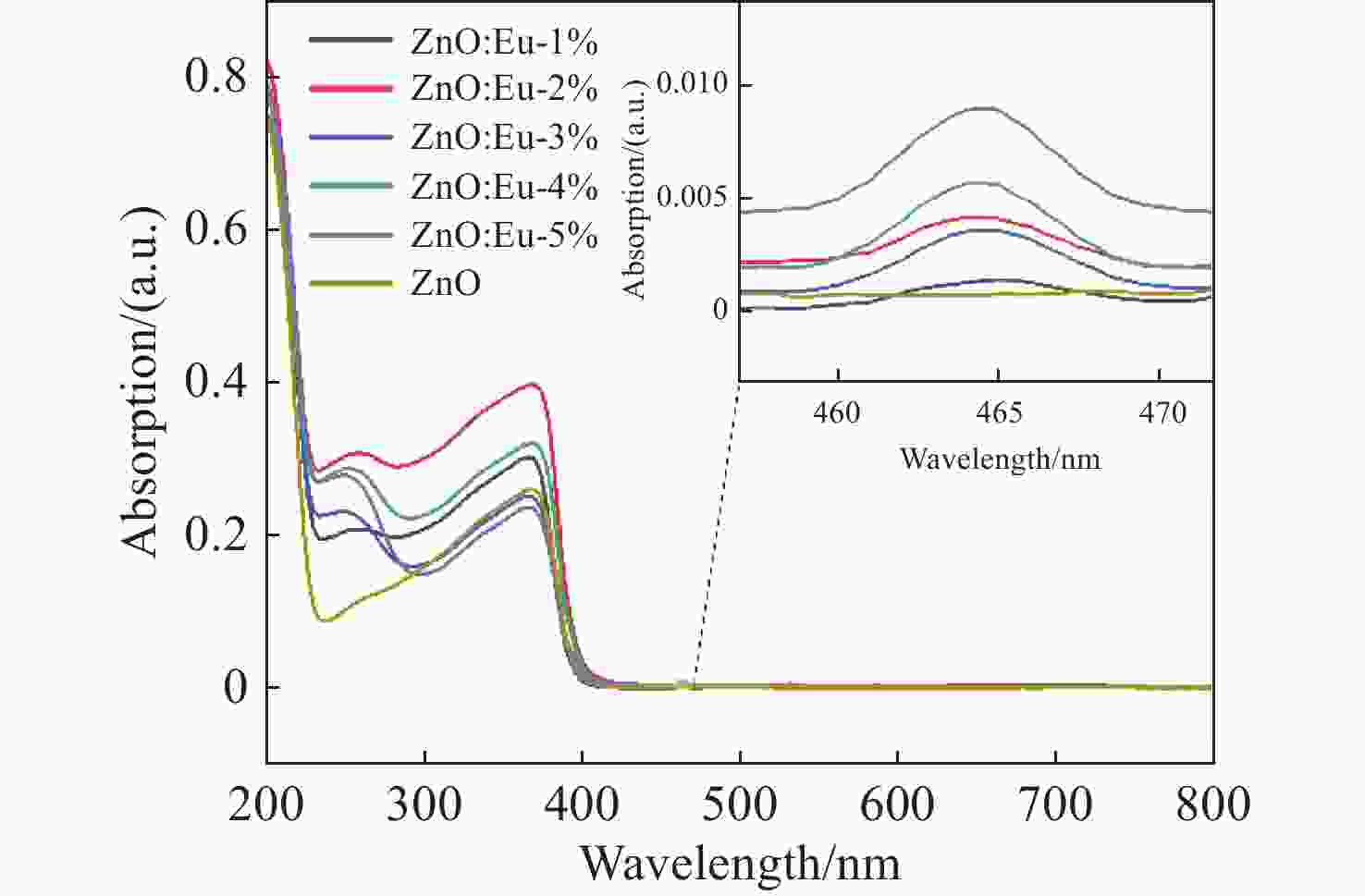
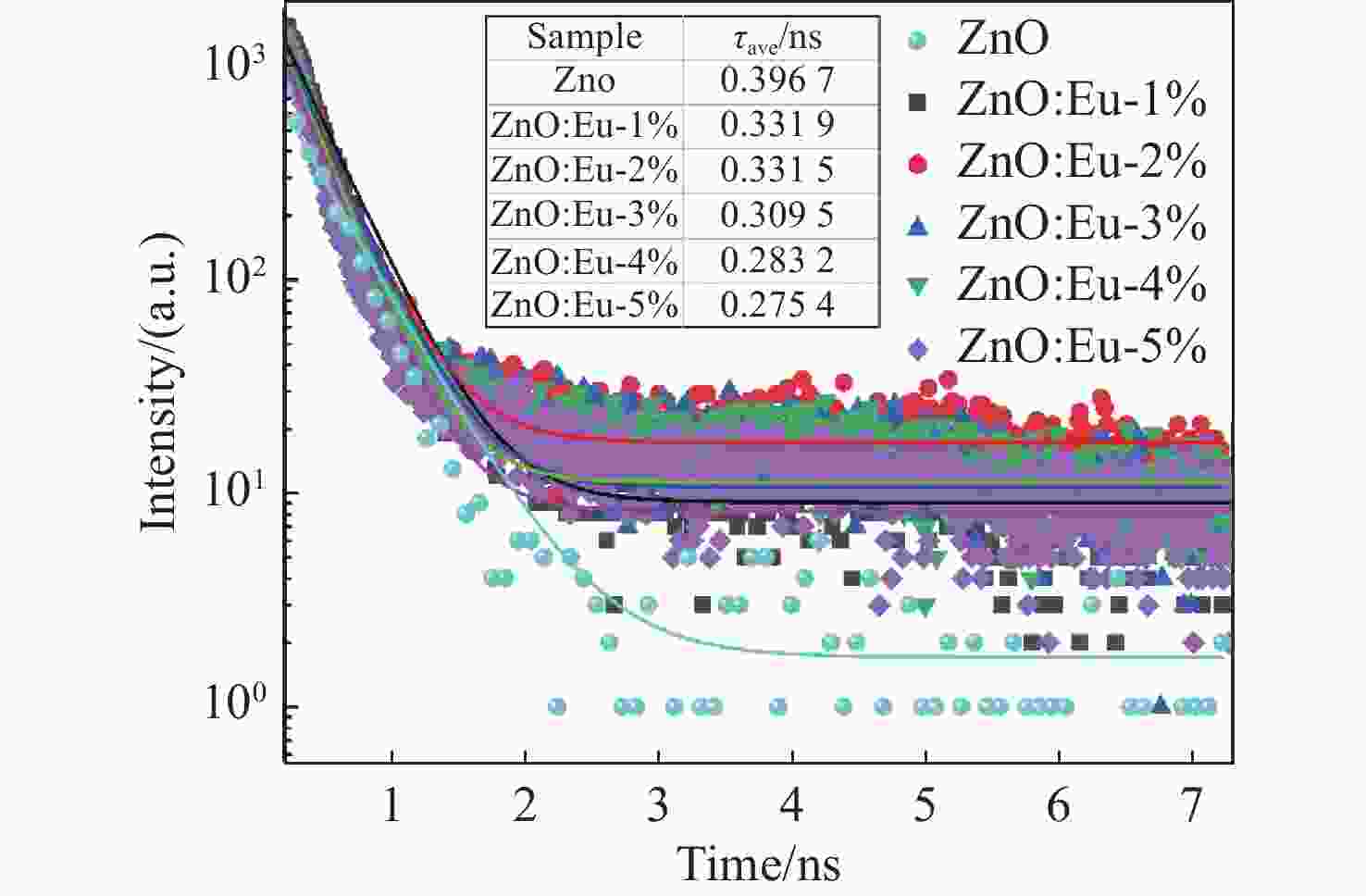
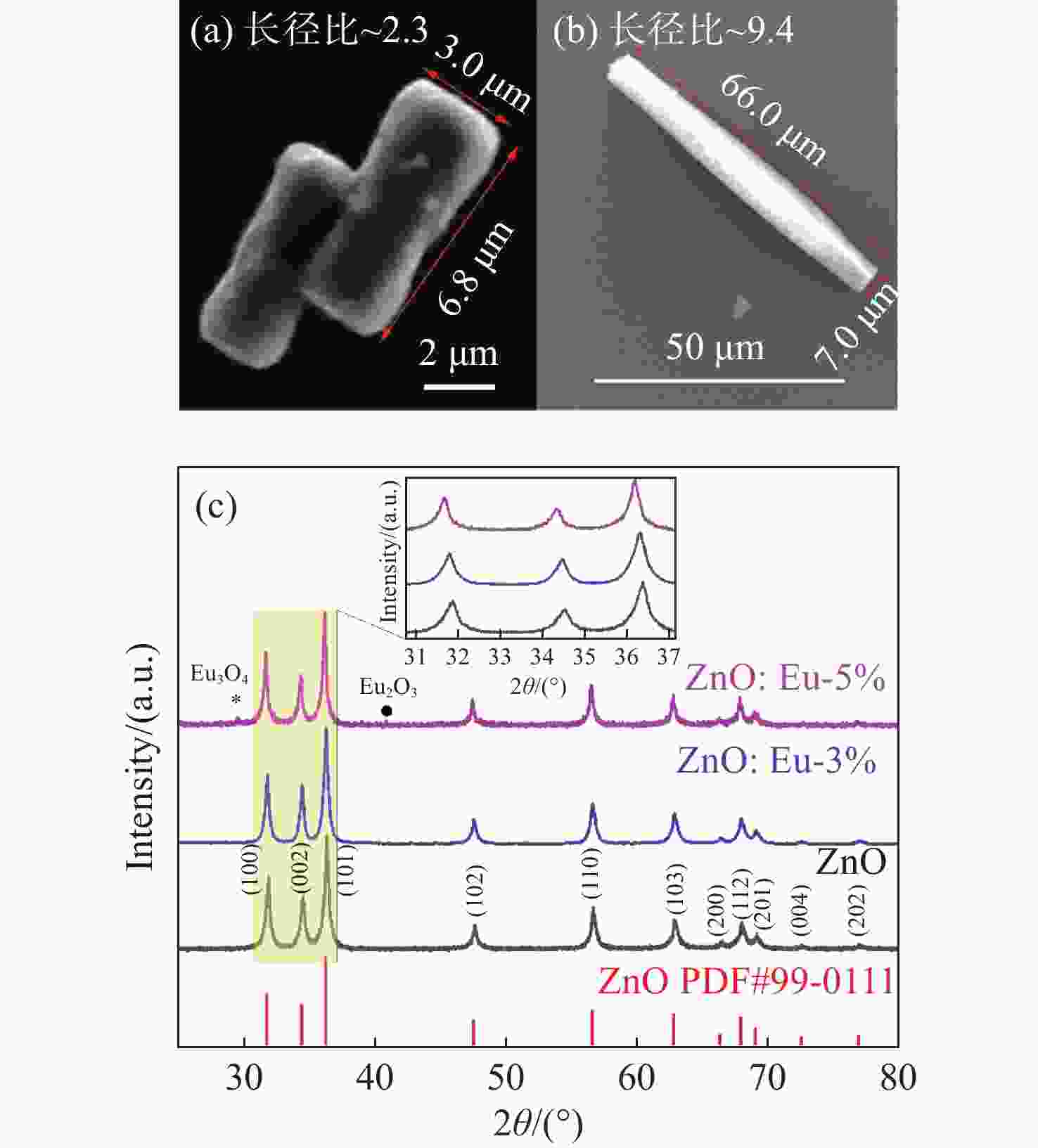
针对基质晶格各向异性对稀土离子偏振发光特性的影响,采用水热法制备了ZnO微米棒及铕掺杂ZnO微米棒。对照研究发现,掺杂后的样品长径比增加,形貌由哑铃型转变为直微米棒。光学性质分析表明,385 nm处的束缚激子发光使得ZnO微米棒的紫外发光呈明显不对称线形,550 nm处观测到一个较弱的可见区发光。掺杂铕离子后,可见区域发光明显增强。对于Eu3+离子掺杂ZnO微米棒,532 nm激发下可观测到窄半峰宽的Eu3+离子特征发光峰。调节入射激发光的偏振方向时,Eu3+离子发光峰强度随偏振光角度呈周期性变化,且发光偏振度随掺杂浓度的增加而增大。结果表明,借助ZnO微米棒基质晶格可获得对激发光偏振敏感的铕离子发光。掺杂ZnO微米棒能够将低维ZnO材料的紫外光吸收性能与稀土离子优异的可见发光特性进行整合,使其在偏振光谱探测等领域具有重要的应用价值。
Abstract:Focusing on the influence of the matrix lattice anisotropy on the polarization luminescence of rare earth ions, ZnO microrods and europium-doped ZnO microrods were prepared using a hydrothermal method. Comparative studies have found that the length-to-diameter ratio of doped samples increases, and the morphology of the microrod changes from dumbbell-like to straight. Analysis of the optical properties shows that the bound exciton luminescence at 385-nm makes the UV luminescence of ZnO microrods appear asymmetrical, and a weak luminescence in visible region is observed at 550 nm. After europium ion doping, the luminescence in the visible region is enhanced. For Eu3+ doped ZnO microrods, Eu3+ ion characteristic luminescence peaks with narrow half width can be observed under 532-nm excitation. When the polarization direction of the incident excitation light is adjusted, the emission of Eu3+ ions changes periodically with the angle of the polarized light. The polarization degree increases as the doping concentration increases. These results show that the luminescence of the europium ions in the ZnO microrod matrix lattice is sensitive to the polarization of excited light. Doped ZnO microrods can integrate the ultraviolet absorption properties of low-dimensional ZnO materials with the excellent visible luminescence properties of rare earth ions, meaning they have significant application value in fields such as polarization detection.
-
Key words:
- ZnO microrods /
- rare earth doped /
- polarization sensitive
-
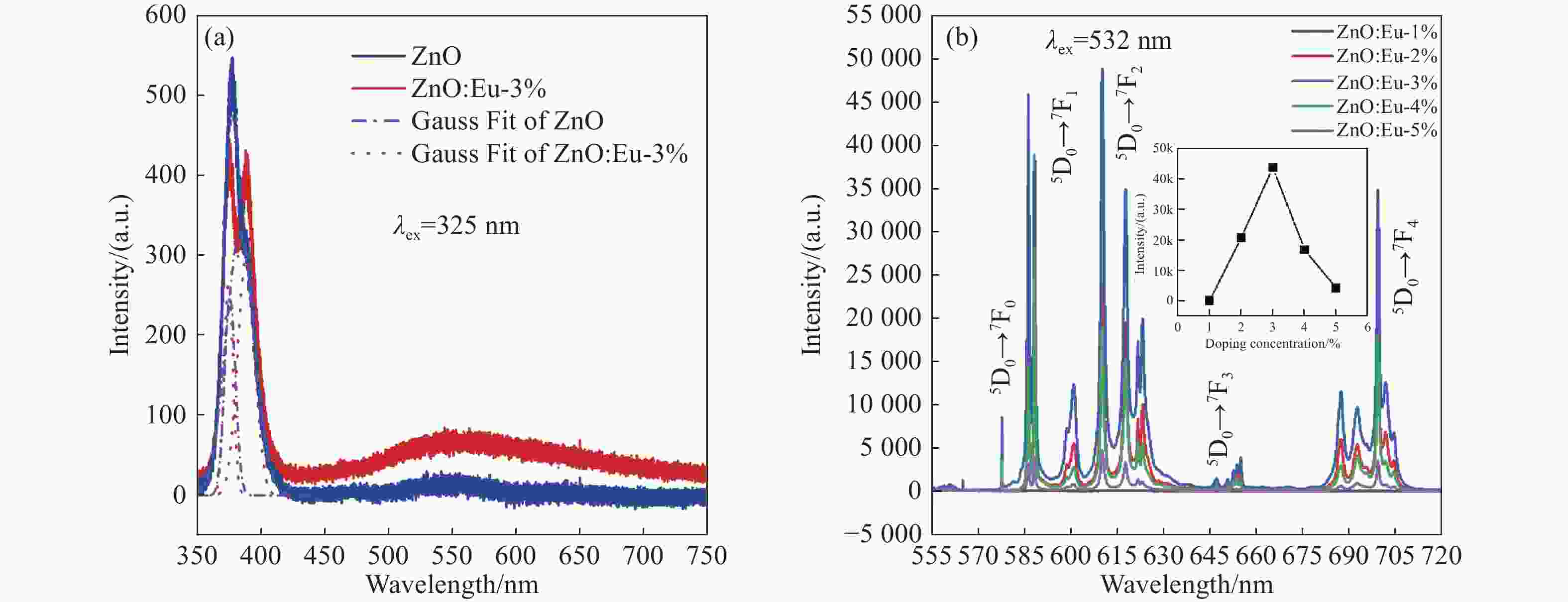
图 2 (a) 325 nm激发下掺杂前后单个ZnO微米棒PL光谱图(蓝色点划线是ZnO拟合后的分峰,红色点线是ZnO:Eu-3%拟合后的分峰);(b) 532 nm激发下不同掺杂浓度的单个ZnO:Eu微米棒PL光谱图(插图是浓度猝灭曲线)
Figure 2. (a) PL spectra of a single ZnO microrod before and after doping under 325-nm excitation (the blue dot line is the peak fitting for ZnO, and the red dot line is the peak fitting for ZnO:Eu-3%); (b) PL spectra of a single ZnO:Eu microrod with different doping concentrations at 532-nm excitation (Inset is the concentration quenching curve)
图 5 (a) 偏振敏感的发光特性测试光路图;(b)、(c)和(d) 532 nm激发下不同掺杂浓度ZnO:Eu微米棒发光峰值随偏振光角度变化图像
Figure 5. (a) Experimental setup for measuring the polarization-sensitive luminescence; (b), (c) and (d) The luminescence intensities of ZnO:Eu microrods with different doping concentrations vary with the angle of polarized light under of 532-nm excitation
-
[1] ZHENG B ZH, FAN J Y, CHEN B, et al. Rare-earth doping in nanostructured inorganic materials[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2022, 122(6): 5519-5603. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00644 [2] 卜芃, 李宏亮. 稀土Yb3+/Tm3+掺杂NaGd (MO4)2荧光粉的制备及其光致发光[J]. 应用化学,2023,40(3):374-379.BU P, LI H L. Preparation and upconversion luminescence study of rare earth Yb3+/Tm3+ doped NaGd (MO4)2 phosphors[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2023, 40(3): 374-379. (in Chinese). [3] 安正策, 王丽萍, 周博. Er3+/Tm3+共掺镱基纳米晶上转换白光调控及应用[J]. 应用化学,2023,40(12):1623-1629.AN ZH C, WANG L P, ZHOU B. White-light upconversion and application of Er3+/Tm3+ Co-doped ytterbium-based nanoparticles[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2023, 40(12): 1623-1629. (in Chinese). [4] 张松涛, 王樱蕙, 张洪杰. Nd3+离子敏化的荧光纳米探针用于近红外二区血管成像[J]. 应用化学,2022,39(4):685-693.ZHANG S T, WANG Y H, ZHANG H J. Nd3+ sensitized fluorescent nanoprobes for vascular imaging in the second near infrared window[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2022, 39(4): 685-693. (in Chinese). [5] 文飞, 涂大涛, 廉纬, 等. 稀土掺杂无序结构晶体的局域位置对称性与发光调控[J]. 发光学报,2023,44(7):1202-1219. doi: 10.37188/CJL.20230040WEN F, TU D T, LIAN W, et al. Local site symmetry and luminescence manipulation of lanthanide doped disordered crystals[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2023, 44(7): 1202-1219. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CJL.20230040 [6] 宋宏伟, 周东磊, 白雪, 等. 稀土掺杂铅卤钙钛矿发光、光电材料与器件研究进展[J]. 发光学报,2023,44(3):387-412. doi: 10.37188/CJL.20220391SONG H W, ZHOU D L, BAI X, et al. Advances in rare earth doped lead halide perovskite luminescence, optoelectronic materials and devices[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2023, 44(3): 387-412. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CJL.20220391 [7] SATPATHY S K, PANIGRAHI U K, BISWAL R, et al. Investigation on the microstructural, optical and magnetic properties of Ce doped ZnO nanorods[J]. Materialia, 2022, 25: 101536. doi: 10.1016/j.mtla.2022.101536 [8] SENAPATI S, NANDA K K. Ultrahigh-sensitive optical temperature sensing based on quasi-thermalized green emissions from Er: ZnO[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2017, 19(3): 2346-2352. doi: 10.1039/C6CP06608A [9] 夏冬林, 郭锦华, 秦可. 钇掺杂多孔结构氧化锌纳米棒的制备与性能研究[J]. 人工晶体学报,2020,49(2):264-269,275.XIA D L, GUO J H, QIN K. Preparation and properties of yttrium-doped porous zinc oxide nanorods[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2020, 49(2): 264-269,275. (in Chinese). [10] LI P, ZHANG H Y, LI ZH J, et al. Effect of surfactants on morphology, structure and photoluminescence properties of Eu-doped ZnO microsphere[J]. Optoelectronics Letters, 2020, 16(4): 293-297. doi: 10.1007/s11801-020-9126-x [11] ZHOU J J, CHEN G X, WU E, et al. Ultrasensitive polarized up-conversion of Tm3+–Yb3+ doped β-NaYF4 single nanorod[J]. Nano Letters, 2013, 13(5): 2241-2246. doi: 10.1021/nl400807m [12] KIM J, CHACÓN R, WANG Z J, et al. Measuring 3D orientation of nanocrystals via polarized luminescence of rare-earth dopants[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1943. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22158-4 [13] 彭友元, 邱雨琴, 叶新滔, 等. 纳米氧化锌分子印迹电聚合光电化学传感器检测双酚A[J]. 分析化学,2023,51(7):1154-1162.PENG Y Y , QIU Y Q, YE X T, et al. Photoelectrochemical sensor for determination of bisphenol A based on zinc oxide and electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polypyrrole film[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 51(7): 1154-1162. (in Chinese). [14] 王闯, 覃露媛, 李冬梅, 等. 纳米材料在激光解吸电离质谱技术中的应用进展[J]. 分析化学,2023,51(2):172-183.WANG CH, QIN L Y, LI D M, et al. Application advance of nanomaterials in laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 51(2): 172-183. (in Chinese). [15] 王弘, 苏星松, 周飞, 等. 氧化锌单层空心球阵列薄膜的制备及其紫外光驱动下对二氧化氮的超快气敏响应[J]. 分析化学,2022,50(7):1112-1121.WANG H, SU X S, ZHOU F, et al. Preparation of zinc oxide monolayer porous hollow sphere array and its ultra-fast response to NO2 at room temperature under ultraviolet irradiation[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 50(7): 1112-1121. (in Chinese). [16] GUO R Q, MATSUMOTO M, MATSUMOTO T, et al. Aligned growth of ZnO nanowires by NAPLD and their optical characterizations[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2009, 255(24): 9671-9675. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.04.049 [17] VALENTE P, SERÉ A, PEREYRA C J, et al. Depolarizing optical effect by ZnO nanowire arrays[J]. Physica E: Low-Dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 2019, 114: 113600. doi: 10.1016/j.physe.2019.113600 [18] WETZEL C, ZHU M, SENAWIRATNE J, et al. Light-emitting diode development on polar and non-polar GaN substrates[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2008, 310(17): 3987-3991. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2008.06.028 [19] LI H Y, RüHLE S, KHEDOE R, et al. Polarization, microscopic origin, and mode structure of luminescence and lasing from single ZnO nanowires[J]. Nano Letters, 2009, 9(10): 3515-3520. doi: 10.1021/nl9017012 [20] DUAN Y Y, HAN L, ZHANG J L, et al. Optically active nanostructured ZnO films[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(50): 15170-15175. doi: 10.1002/anie.201507502 [21] VEZZOLI S, MANCEAU M, LEMÉNAGER G, et al. Exciton fine structure of CdSe/CdS nanocrystals determined by polarization microscopy at room temperature[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(8): 7992-8003. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b01354 [22] JING CH J, PAN Z Y, ZOU H Y, et al. ZnO micron rods as single dielectric resonator for optical sensing[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2020, 1109: 107-113. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2020.03.009 [23] CHU X Y, HONG X, LI X H, et al. Microphotoluminescence investigation on single ZnO microrods with different morphologies[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2009, 105(12): 123109. doi: 10.1063/1.3153120 [24] SAMUEL J, RAJESH T S F, BIJU C S, et al. Synthesis, structural, photoluminescence, ultraviolet blocking and antibacterial performances of Ba-doped ZnO nanostructures[J]. Results in Optics, 2023, 12: 100482. doi: 10.1016/j.rio.2023.100482 [25] 高伟, 杨平. 基于第一性原理的Ga-Eu共掺ZnO光电性质的研究[J]. 半导体光电,2019,40(3):380-384,419.GAO. W, YANG P. Investigation on electronic and optical properties of Ga-Eu codoped ZnO based on the first principle[J]. Semiconductor Optoelectronics, 2019, 40(3): 380-384,419. (in Chinese) [26] WEI Y, YANG H, GAO ZH Y, et al. Strategies for designing antithermal-quenching red phosphors[J]. Advanced Science, 2020, 7(8): 1903060. doi: 10.1002/advs.201903060 [27] SENAPATI S, NANDA K K. Designing dual emissions via co-doping or physical mixing of individually doped ZnO and their implications in optical thermometry[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(19): 16305-16312. [28] GUPTA A K, HSU C H, PURWIDYANTRI A, et al. ZnO-Nanorod processed PC-SET as the light-harvesting model for plasmontronic fluorescence Sensor[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2020, 307: 127597. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2019.127597 [29] ZOU T, XING X X, YANG Y, et al. Water-soluble ZnO quantum dots modified by (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane: the promising fluorescent probe for the selective detection of Cu2+ ion in drinking water[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 825: 153904. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.153904 [30] NTWAEABORWA O M, MOFOKENG S J, KUMAR V, et al. Structural, optical and photoluminescence properties of Eu3+ doped ZnO nanoparticles[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2017, 182: 42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2017.03.067 [31] LÜ W, HAO ZH D, ZHANG X, et al. Tunable full-color emitting BaMg2Al6Si9O30: Eu2+, Tb3+, Mn2+ phosphors based on energy transfer[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2011, 50(16): 7846-7851. doi: 10.1021/ic201033e [32] 覃辉军. Tm3+/Eu3+掺杂ZnO微晶玻璃的制备及发光性能研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2015.QIN H J. Preparation and photoluminescence properties of Tm3+/Eu3+ doped glass ceramics containing ZnO nanocrystals[D] Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2015. (in Chinese). [33] WANG X B, WANG Y, GAO W Y, et al. Polarization-sensitive halide perovskites for polarized luminescence and detection: recent advances and perspectives[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(12): 2003615. doi: 10.1002/adma.202003615 [34] MCDONALD M P, VIETMEYER F, KUNO M. Direct measurement of single CdSe nanowire extinction polarization anisotropies[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2012, 3(16): 2215-2220. doi: 10.1021/jz3008112 [35] HENDRICKSON O D, TARANOVA N A, ZHERDEV A V, et al. Fluorescence polarization-based bioassays: new horizons[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(24): 7132. doi: 10.3390/s20247132 [36] CUNNINGHAM P D, SOUZA JR J B, FEDIN I, et al. Assessment of anisotropic semiconductor nanorod and nanoplatelet heterostructures with polarized emission for liquid crystal display technology[J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(6): 5769-5781. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b07949 -





 下载:
下载: