Methods for processing renal tissue samples for single-slice dual-mode optical correlation imaging
-
摘要:
明场成像能够提供细胞或组织的形态学信息,荧光成像可以获取关键蛋白的表达信息,基于二者的双模态关联成像是目前医学和科研中常用的组织样本检查方式。然而,在临床检查时通常利用基于邻近切片之间的关联成像进行观察。此时,组织结构和细胞层次均会有或多或少的改变,这在样本量不足、切片上的细胞有限或需要获得点对点精准形态学信息的情景下显得十分不利。本研究提出了一种在单张组织切片中实现苏木素-伊红染色和免疫荧光染色的样本处理方法,用于双模态成像技术。重点优化了褪色处理和免疫荧光复染方案,比较了三种褪色方案(盐酸乙醇、冰醋酸-草酸和高锰酸钾-草酸)以及三种抗原修复方案(EDTA、Tris-EDTA和柠檬酸)。通过对不同条件下获取的图像信噪比进行对比分析,发现经冰醋酸-草酸褪色结合EDTA抗原修复的免疫荧光图像质量最佳。此外,还实现了明场与荧光图像的融合,从而在单张切片上展示更完整的组织形态和免疫信息。
Abstract:Bright-field imaging can provide cellular and histological morphological information, while fluorescence imaging can provide expression information of key proteins. Dual-mode correlation imaging that combines both techniques is used for examining tissue samples in medical and scientific research. However, in clinical, correlation imaging often relies on adjacent tissue sections for observation. This can result in inconsistencies at both the tissue structure and the cellular level, which is problematic when the sample volume is limited, the number of cells on the slices is sparse, or precise point-to-point morphological information is required. In this study, we present a sample preparation method that enables both Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining and immunofluorescence staining on a single tissue section, enabling dual-mode imaging. We focused on optimizing the decolorizing process and the immunofluorescence restaining protocol, comparing three decolorization methods (hydrochloric acid ethanol, acetic acid-oxalic acid, and potassium permanganate-oxalic acid) and three antigen retrieval methods (EDTA, Tris-EDTA, and citric acid). By analyzing the signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) of images obtained under different conditions, we found that the combination of acetic acid-oxalic acid decolorization with EDTA antigen retrieval produced the best quality immunofluorescence images. Additionally, we successfully fused brightfield and fluorescence images, providing more comprehensive tissue morphology and immunological information on a single section.
-
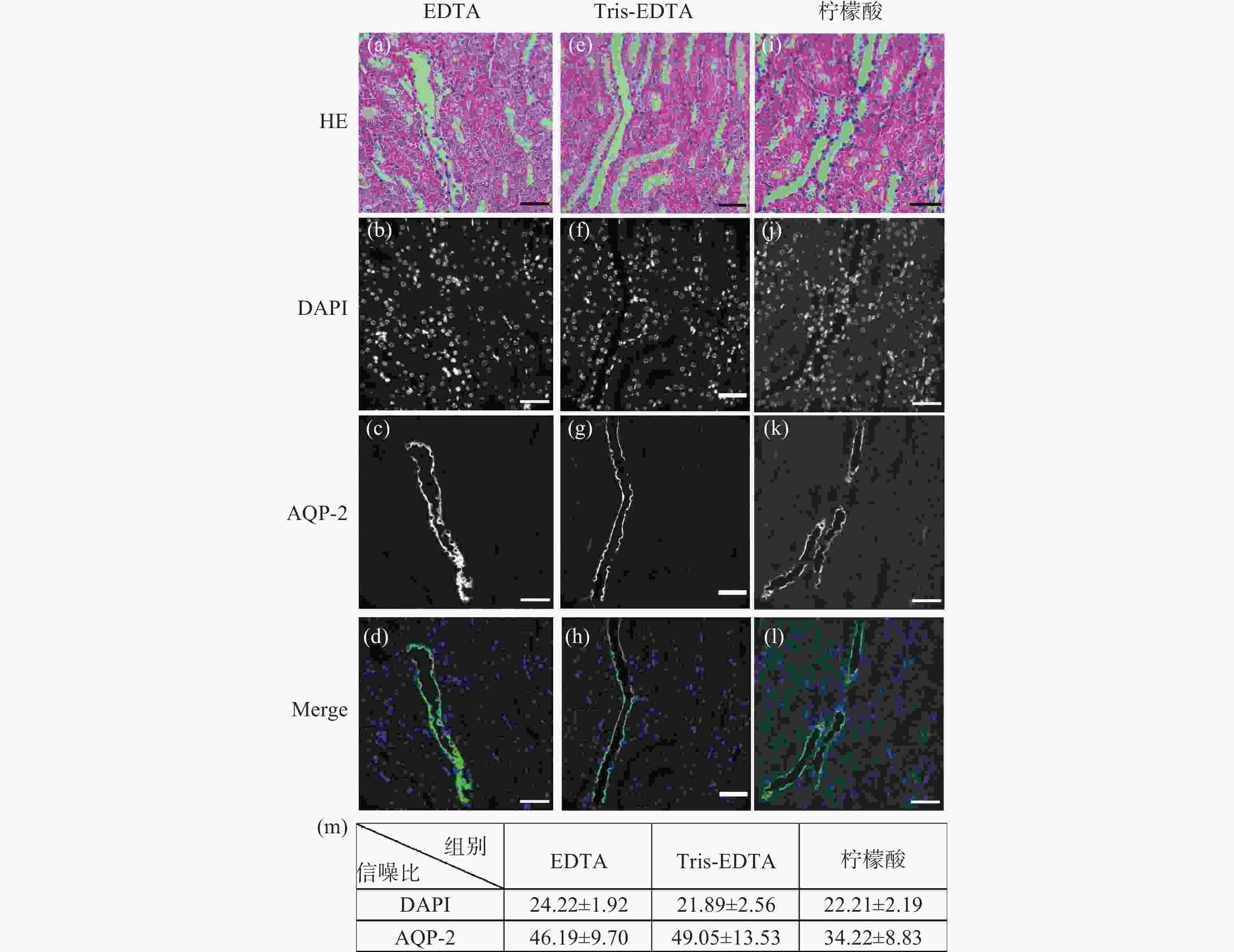
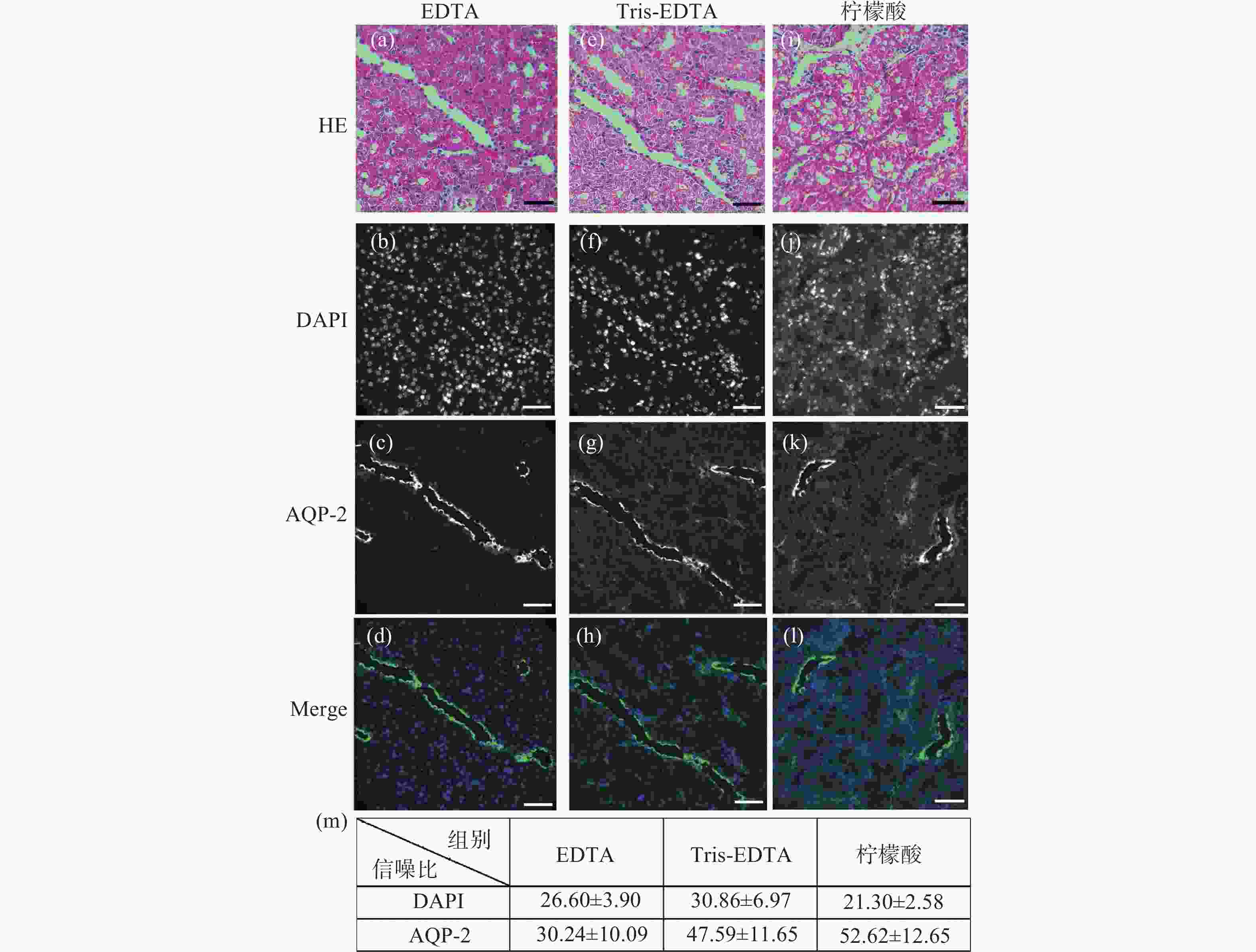
图 1 小鼠肾脏组织石蜡切片HE染色后盐酸乙醇褪色的单切片双模态图。(a)、(e)、(i)为HE染色图;(b)~(d)是图(a)褪色后EDTA抗原修复的同一视野免疫荧光图;(f)~(h)是图(b)褪色后Tris-EDTA抗原修复的同一视野的免疫荧光图;(j)~(l)是图(i)褪色后柠檬酸抗原修复的同一视野免疫荧光图;(m)为盐酸乙醇褪色后不同抗原修复条件下的免疫荧光图像信噪比统计分析。标尺为50 μm
Figure 1. The single slice bimodal images of the decolorization of hydrochloric acid ethanol after HE staining of paraffin slices of mouse renal tissue. (a), (e) and (i) are HE staining images. (b)~(d) are the same field of view immunofluorescence images of EDTA antigen retrieval after de-colorizing in Fig.(a). (f)~(h) are the immunofluorescence images of the same field of view of Tris-EDTA antigen retrieval after the decolorization of Fig.(b). (j)~(l) are the same field of view immunofluorescence images of citric acid antigen retrieval after de-colorizing in Fig.(i). (m) is the statistical analysis of the signal-to-noise ratio of immunofluorescence images under different antigen retrieval conditions after hydrochloric acid ethanol decolorization. Scale: 50 μm
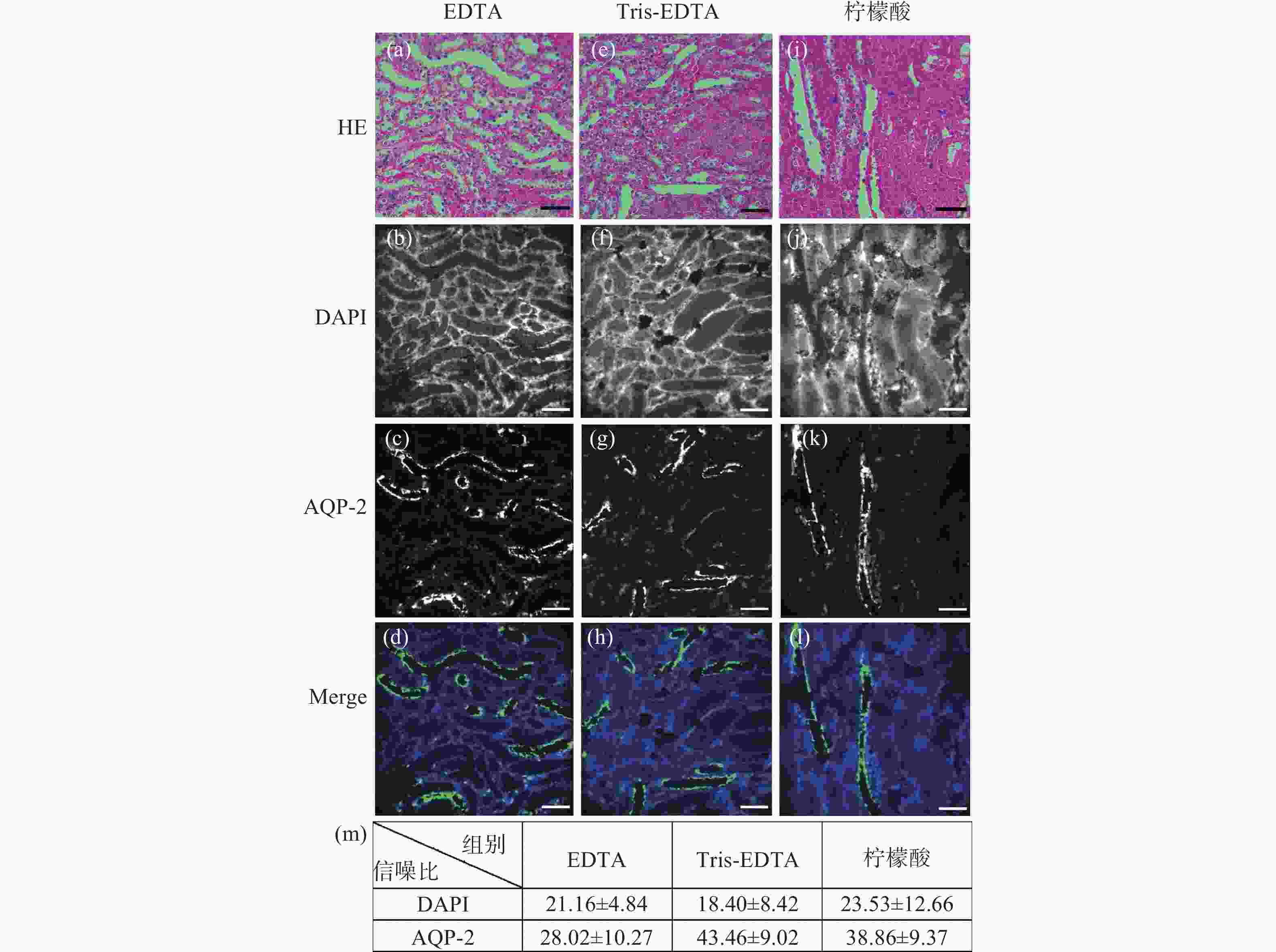
图 2 小鼠肾脏组织石蜡切片HE染色后冰醋酸-草酸褪色的单切片双模态图。(a)、(e)、(i)为HE染色图;(b)~(d)是图(a)褪色后EDTA抗原修复的同一视野免疫荧光图;(f)~(h)是图(b)褪色后Tris-EDTA抗原修复的同一视野的免疫荧光图;(j)~(l)是图(i)褪色后柠檬酸抗原修复的同一视野免疫荧光图;(m)为冰醋酸-草酸褪色后不同抗原修复条件下的免疫荧光图像信噪比统计分析。标尺为50 μm
Figure 2. The single-slice bimodal images of glacial acetic acid and oxalic acid decolorization after HE staining of paraffin slices of mouse renal tissue. (a), (e) and (i) are HE staining images, and (b)~(d) are the same field of view immunofluorescence images of EDTA antigen retrieval after de-colorizing in Fig.(a). (f)~(h) are the immunofluorescence images of the same field of view of Tris-EDTA antigen retrieval after the decolorization of Fig.(b). (j)~(l) are the same field of view immunofluorescence images of citric acid antigen retrieval after de-colorizing in Fig.(i). (m) is the statistical analysis of the signal-to-noise ratio of immunofluorescence images under different antigen retrieval conditions after glacial acetic acid-oxalic acid decolorization. Scale: 50 μm
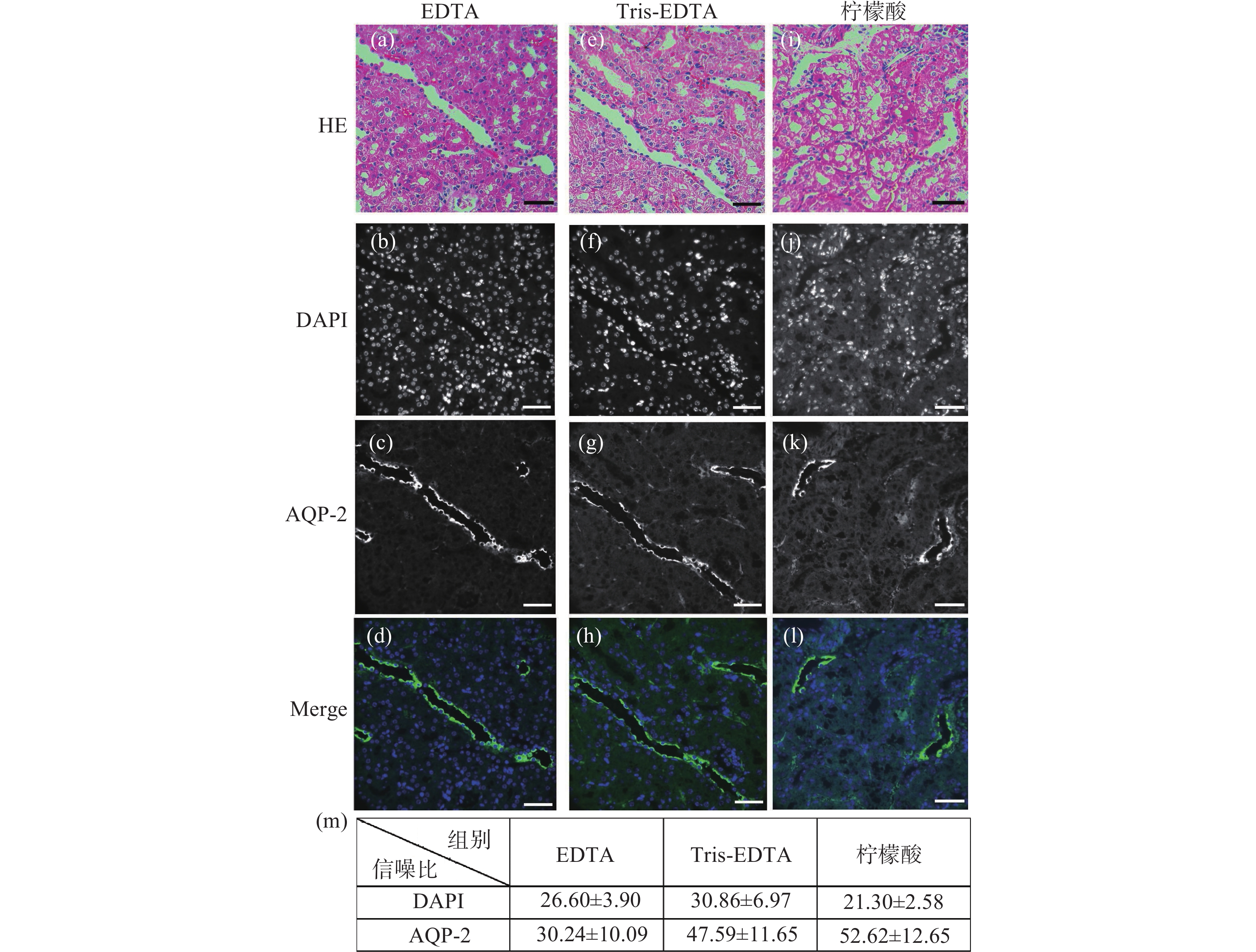
图 3 小鼠肾脏组织石蜡切片HE染色后高锰酸钾-草酸褪色的单切片双模态图。(a)、(e)、(i)为HE染色图;(b)~(d)是图(a)褪色后EDTA抗原修复的同一视野免疫荧光图;(f)~(h)是图(b)褪色后Tris-EDTA抗原修复的同一视野的免疫荧光图;(j)~(l)是图(i)褪色后柠檬酸抗原修复的同一视野免疫荧光图;(m)为高锰酸钾-草酸褪色后不同抗原修复条件下的免疫荧光图像信噪比统计分析。标尺为50 μm
Figure 3. The single-slice bimodal images of potassium permanganate-oxalic acid decolorization after HE staining of paraffin slices of mouse renal tissue. (a), (e), (i) are HE staining. (b)~(d) are the same field of view immunofluorescence images of EDTA antigen retrieval after de-colorizing in Fig.(a). (f)~(h) are the immunofluorescence images of the same field of view of Tris-EDTA antigen retrieval after de-colorizing in Fig.(b). (j)~(l) are the same field of view immunofluorescence images of citric acid antigen retrieval after de-colorizing in Fig.(i). (m) is the statistical analysis of the signal-to-noise ratio of immunofluorescence images under different antigen repair conditions after potassium permanganate-oxalic acid decolorization. Scale: 50 μm
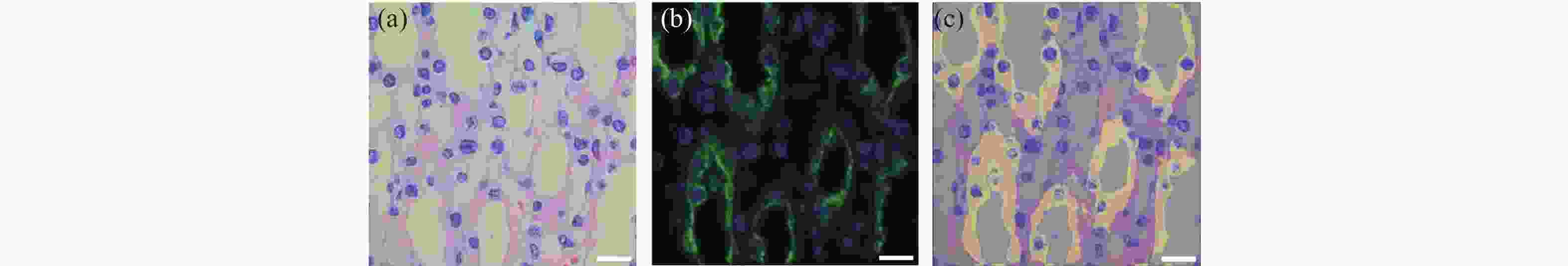
图 4 小鼠肾脏组织HE染色后,使用冰醋酸和草酸褪色后并用EDTA修复所获得的单切片双模态图。(a)为60 ×镜下所采的HE染色;(b)为同视野下AQP-2和DAPI双标记的肾集合管免疫荧光图像;(c)为HE和免疫荧光融合图。
Figure 4. The single-slice bimodal images of the mouse renal tissue de-colorized with glacial acetic acid and oxalic acid and repaired with EDTA, after HE staining. (a) is HE staining image obtained under a 60 × microscope. (b) is an immunofluorescence image of the renal collecting duct labeled with AQP-2 and DAPI in the same field of view. (c) is the fusion image of HE and immunofluorescence
-
[1] MASOOD S. The changing role of pathologists from morphologists to molecular pathologists in the era of precision medicine[J]. The Breast Journal, 2020, 26(1): 27-34. doi: 10.1111/tbj.13728 [2] 王义强, 林方睿, 胡睿, 等. 大视场光学显微成像技术[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(6):1194-1210. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0098WANG Y Q, LIN F R, HU R, et al. Large field-of-view optical microscopic imaging technology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(6): 1194-1210. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0098 [3] 王鹏, 周瑶, 赵宇轩, 等. 用于多尺度高分辨率三维成像的双环光片荧光显微技术[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(6):1321-1331.WANG P, ZHOU Y, ZHAO Y X, et al. Double-ring-modulated light sheet fluorescence microscopic technique for multi-scale high-resolution 3D imaging[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(6): 1321-1331. (in Chinese) [4] 耿佳美, 马素芳, 刘文, 等. 肝靶向荧光探针用于HepG2细胞中ONOO−的特异性检测[J]. 应用化学,2023,40(3):441-448.GENG J M, MA S F, LIU W, et al. Liver-targeted fluorescent probes for specific detection of ONOO− in HepG2 cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry,2023,40(3):441-448. [5] LIM H G, LIU H C, YOON C W, et al. Investigation of cell mechanics using single-beam acoustic tweezers as a versatile tool for the diagnosis and treatment of highly invasive breast cancer cell lines: an in vitro study[J]. Microsystems & Nanoengineering, 2020, 6: 39. [6] 于绍楠, 任玲玲, 任立群, 等. 基于上转换纳米粒子-金纳米棒的荧光共振能量转移免疫分析法用于癌胚抗原检测[J]. 分析化学, 2022, 50(9): 1299-1307.YU S N, REN L L, REN L Q, et al. Upconversion nanoparticles/gold nanorods-based fluorescence resonance energy transfer immunoassay for detection of carcinoembryonic antigen[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 50(9): 1299-1307. [7] LÜTGERATH C, WEIß C, BÖER-AUER A. Clinicopathological features and histological tumor residues in re-excision specimens of incompletely resected basal cell carcinomas[J]. JDDG:Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft, 2022, 20(11): 1476-1483. [8] MORRISON L E, LEFEVER M R, LEWIS H N, et al. Conventional histological and cytological staining with simultaneous immunohistochemistry enabled by invisible chromogens[J]. Laboratory Investigation, 2022, 102(5): 545-553. doi: 10.1038/s41374-021-00714-2 [9] 田野, 高丽丽, 张巍, 等. 糖尿病肾病生物标志物电化学检测方法研究进展[J]. 分析化学, 2023, 51(5): 744-756.TIAN Y, GAO L L, ZHANG W, et al. Recent advances in electrochemistry assays of diabetic kidney disease biomarkers[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 51(5): 744-756. [10] WALKER P D, CAVALLO T, BONSIB S M. Practice guidelines for the renal biopsy[J]. Modern Pathology, 2004, 17(12): 1555-1563. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800239 [11] OZAWA A, SAKAUE M. New decolorization method produces more information from tissue sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin stain and masson-trichrome stain[J]. Annals of Anatomy-Anatomischer Anzeiger, 2020, 227: 151431. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2019.151431 [12] 王超宇, 赵璐, 王科伟, 等. 共价有机框架的构筑策略及其在肿瘤治疗中应用的研究进展[J]. 应用化学, 2023, 40(7): 976-994.WANG CH Y, ZHAO L, WANG K W, et al. Research progress in preparation strategy of covalent organic frameworks and its application in tumor therapy[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2023, 40(7): 976-994. (in chinese [13] 李丽, 杨桂芳. HE染色切片褪色后再进行免疫组化染色方法的比较[J]. 数理医药学杂志,2015,28(11):1618-1619. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4337.2015.11.015LI L, YANG G F. Comparison of immunohistochemical staining methods for HE stained sections after de-colorizing[J]. Journal of Mathematical Medicine and Pharmacy, 2015, 28(11): 1618-1619. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4337.2015.11.015 [14] 王兴波, 陈怀敏, 王秀珍, 等. HE染色褪色后免疫染色的病理观察[J]. 中国医药导报,2007,4(22):124, 157.WANG X B, CHEN H M, WANG X ZH, et al. Pathological observation of immunostaining after HE staining de-colorizing[J]. Chinese Medical Bulletin, 2007, 4(22): 124, 157. (in Chinese) [15] 梁龄尹, 朱小兰, 骆新兰. 小标本切片HE染色褪色后再进行4种特殊染色方法的探讨[J]. 诊断病理学杂志,2020,27(6):443-444. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8096.2020.06.020LIANG L Y, ZHU X L, LUO X L. Discussion on four special staining methods after HE staining de-colorizing of small specimen sections[J]. Chinese Journal of Diagnostic Pathology, 2020, 27(6): 443-444. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8096.2020.06.020 [16] 刘海芳. HE染色切片褪色后免疫组化染色方法研究[J]. 中国现代医生,2011,49(17):81-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9701.2011.17.039LIU H F. Explore the method of immunohistochemiscal staining for HE slides after decoloration[J]. China Modern Doctor, 2011, 49(17): 81-82. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9701.2011.17.039 [17] 李钦丽, 张继伟. HE切片经不同方法褪色后行EGFR基因突变检测的对比分析[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志,2021,37(8):1004-1006.LI Q L, ZHANG J W. Comparative analysis of EGFR gene mutation detection after different Methods of de-colorizing HE slices[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, 2021, 37(8): 1004-1006. (in Chinese) [18] 章克萍, 龙飞. 组织苏木精-伊红染色的石蜡切片褪色后还原对比染色[J]. 实用临床医学,2008,9(1):16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8194.2008.01.005ZHANG K P, LONG F. Reduction contrast staining after de-colorizing of paraffin slices stained with hematoxylin eosin in tissue[J]. Practical Clinical Medicine, 2008, 9(1): 16. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8194.2008.01.005 [19] 高洪彬, 梁十, 郭扬清, 等. HE切片褪色后进行免疫荧光染色的方法探讨[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志,2020,36(10):1241-1242. doi: 10.13315/j.cnki.cjcep.2020.10.027GAO H B, LIANG SH, GUO Y Q, et al. Discussion on the method of immunofluorescence staining after HE section de-colorizing[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, 2020, 36(10): 1241-1242. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13315/j.cnki.cjcep.2020.10.027 [20] KOMURA D, ONOYAMA T, SHINBO K, et al. Restaining-based annotation for cancer histology segmentation to overcome annotation-related limitations among pathologists[J]. Patterns, 2023, 4(2): 100688. doi: 10.1016/j.patter.2023.100688 [21] LI ZH M, MUENCH G, GOEBEL S, et al. Flow chamber staining modality for real-time inspection of dynamic phenotypes in multiple histological stains[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18(5): e0284444. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0284444 [22] JOHANN D J, SHIN I J, ROBERGE A, et al. Effect of antigen retrieval on genomic DNA from immunodissected samples[J]. Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry, 2022, 70(9): 643-658. [23] GEORGE B, HAQUE A, SAHU V, et al. Enhancing antigen retrieval to unmask signaling phosphoproteins in formalin-fixed archival tissues[J]. Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology, 2022, 30(5): 333-339. [24] DUNKENBERGER L, DEL VALLE L. Antigen retrieval and signal amplification[M]//DEL VALLE L. Immunohistochemistry and Immunocytochemistry: Methods and Protocols. New York: Humana, 2022: 65-74. -





 下载:
下载: