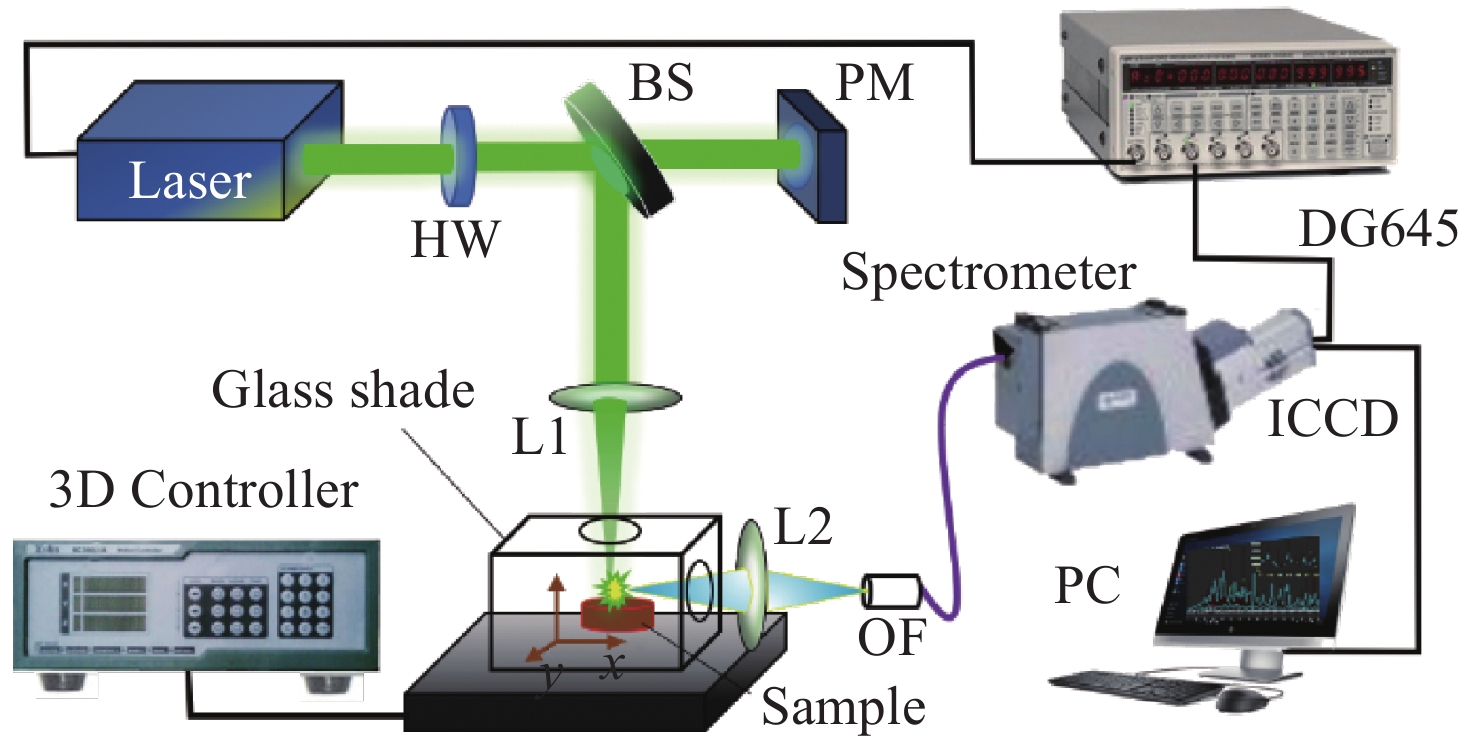
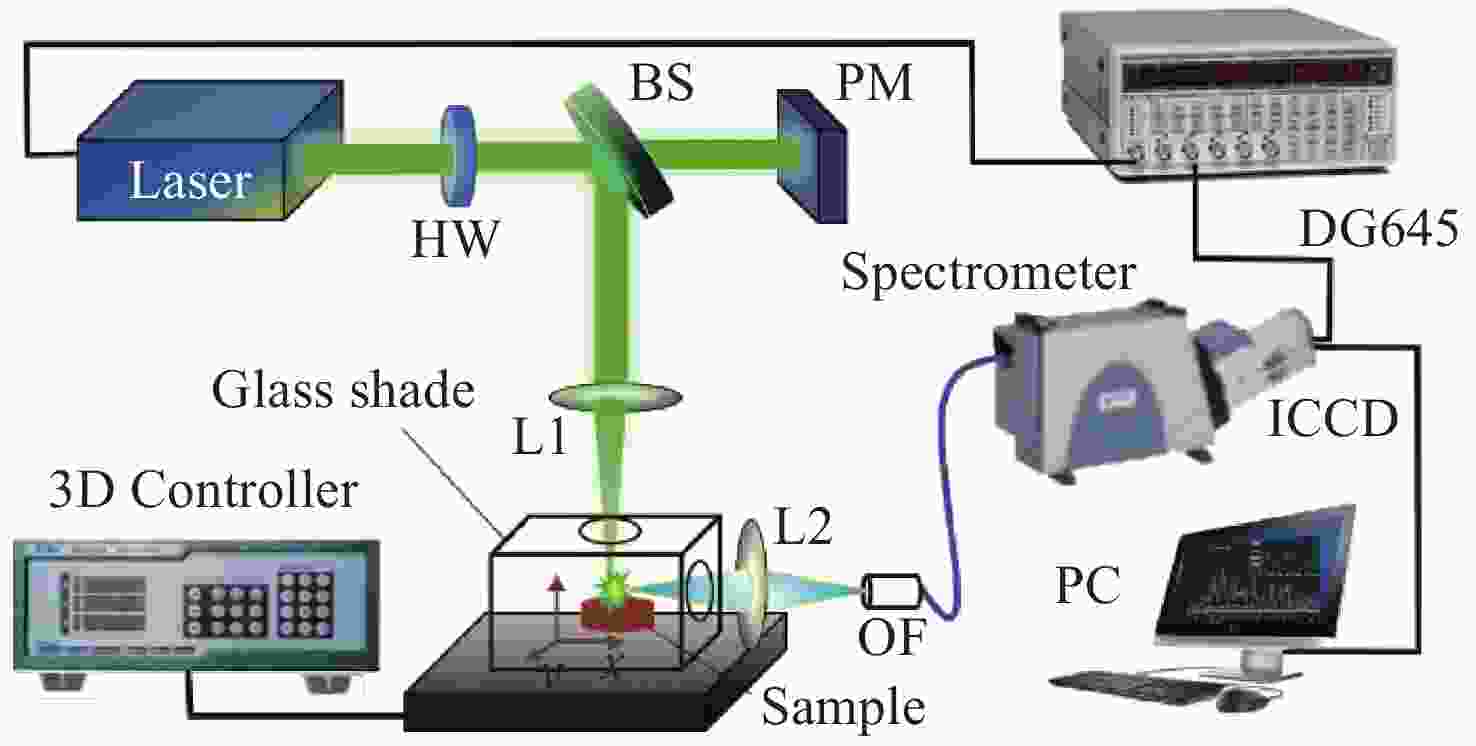
Measurement of Sm in rare earth mineral soil using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
-
摘要:
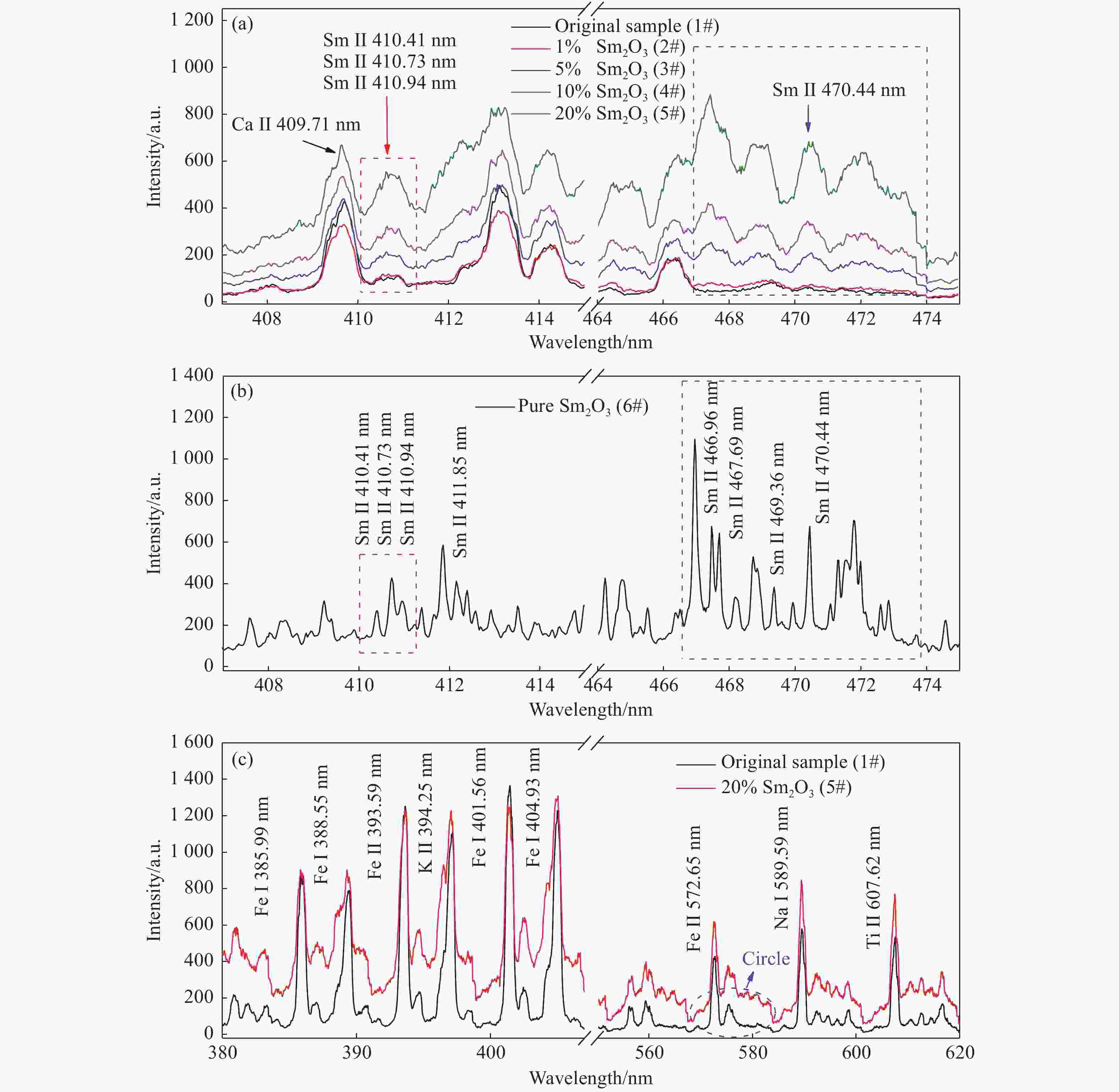
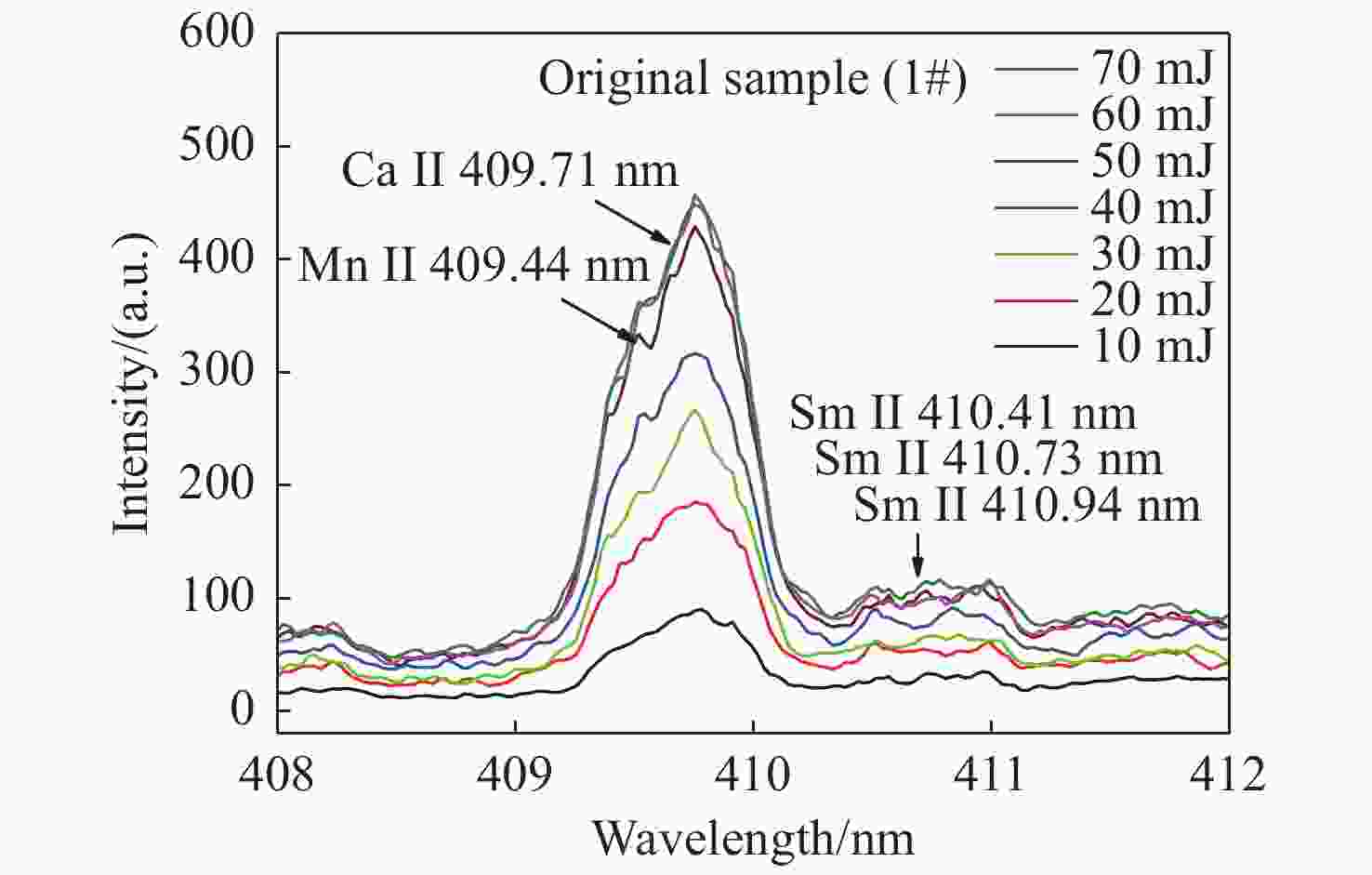
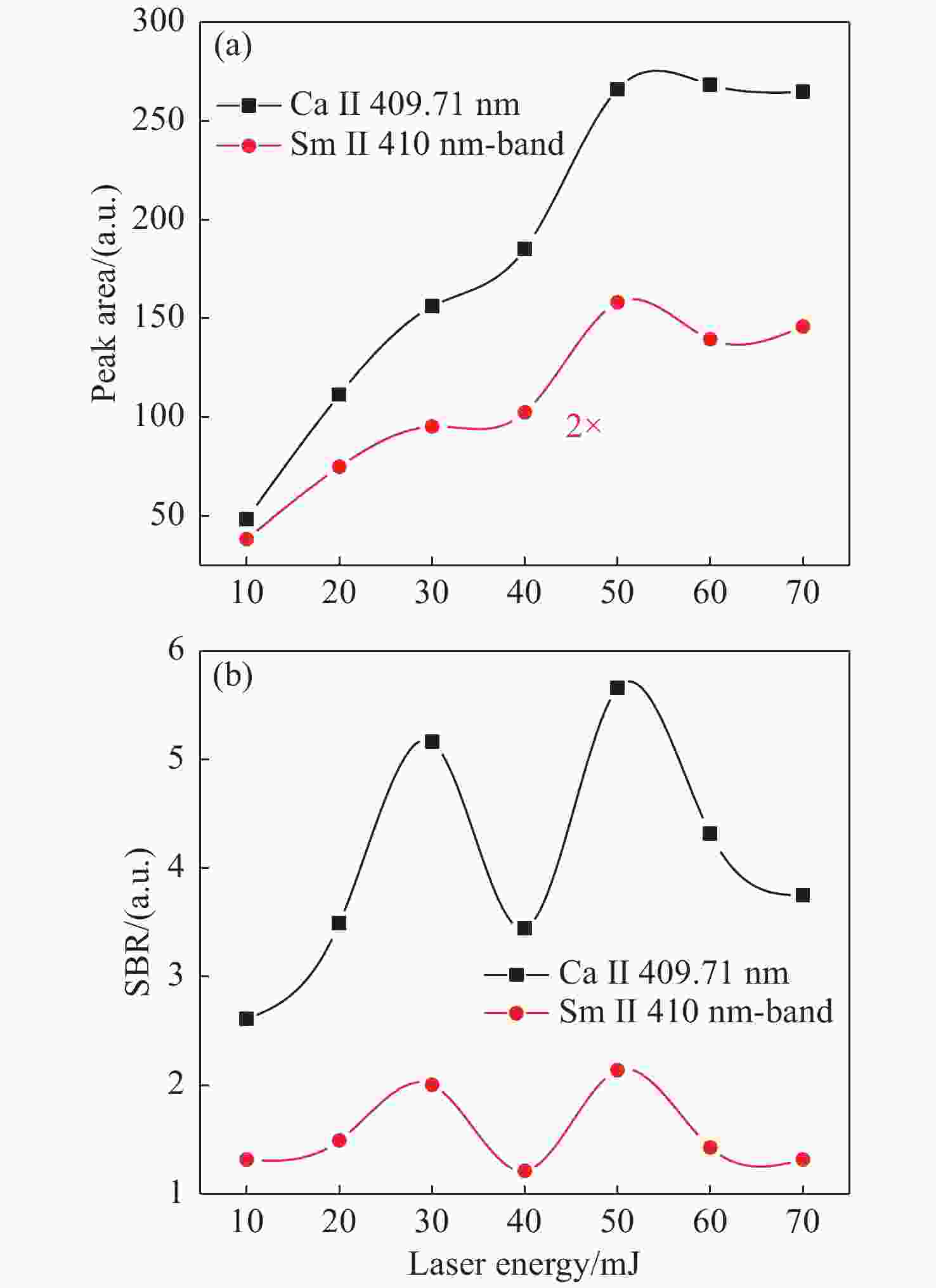
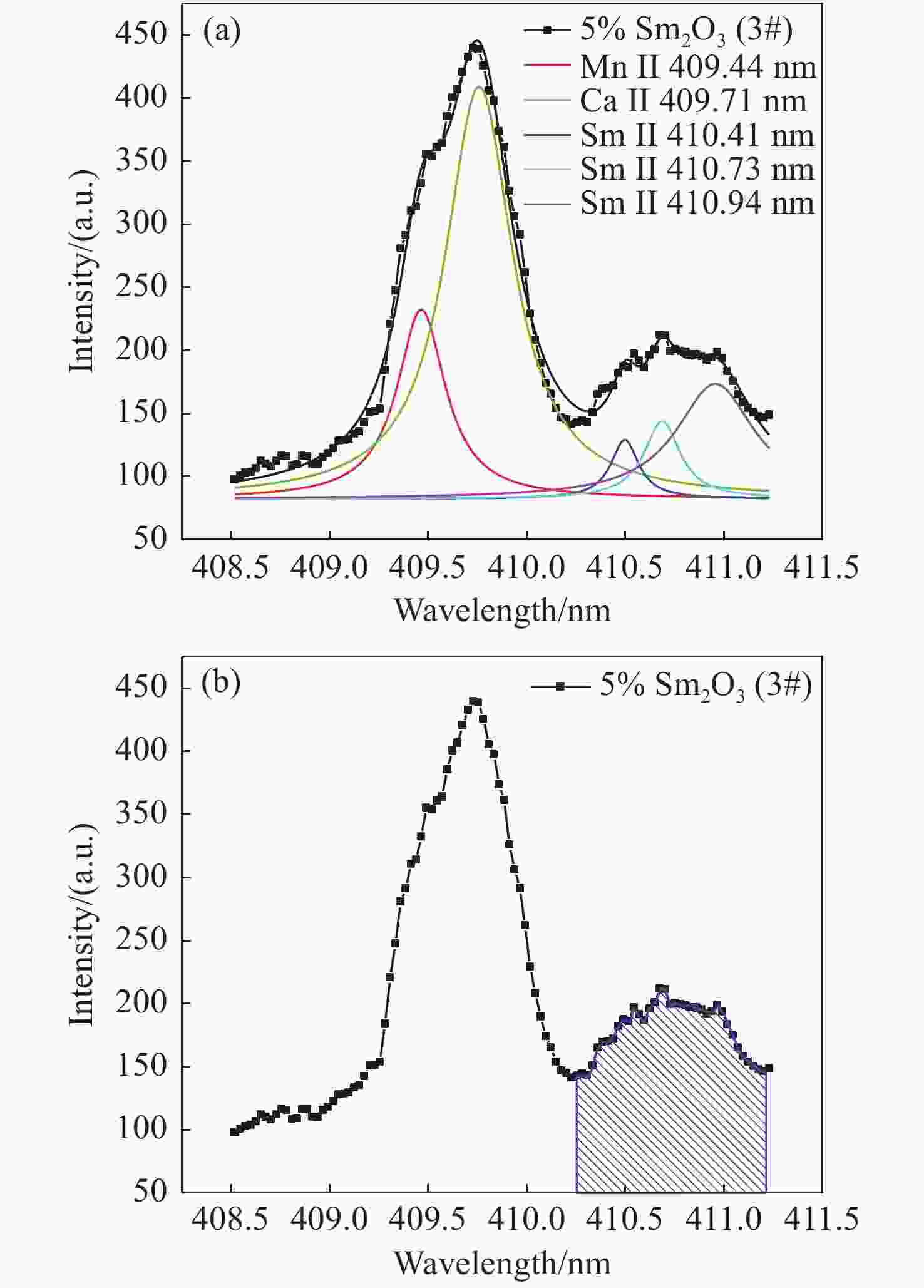
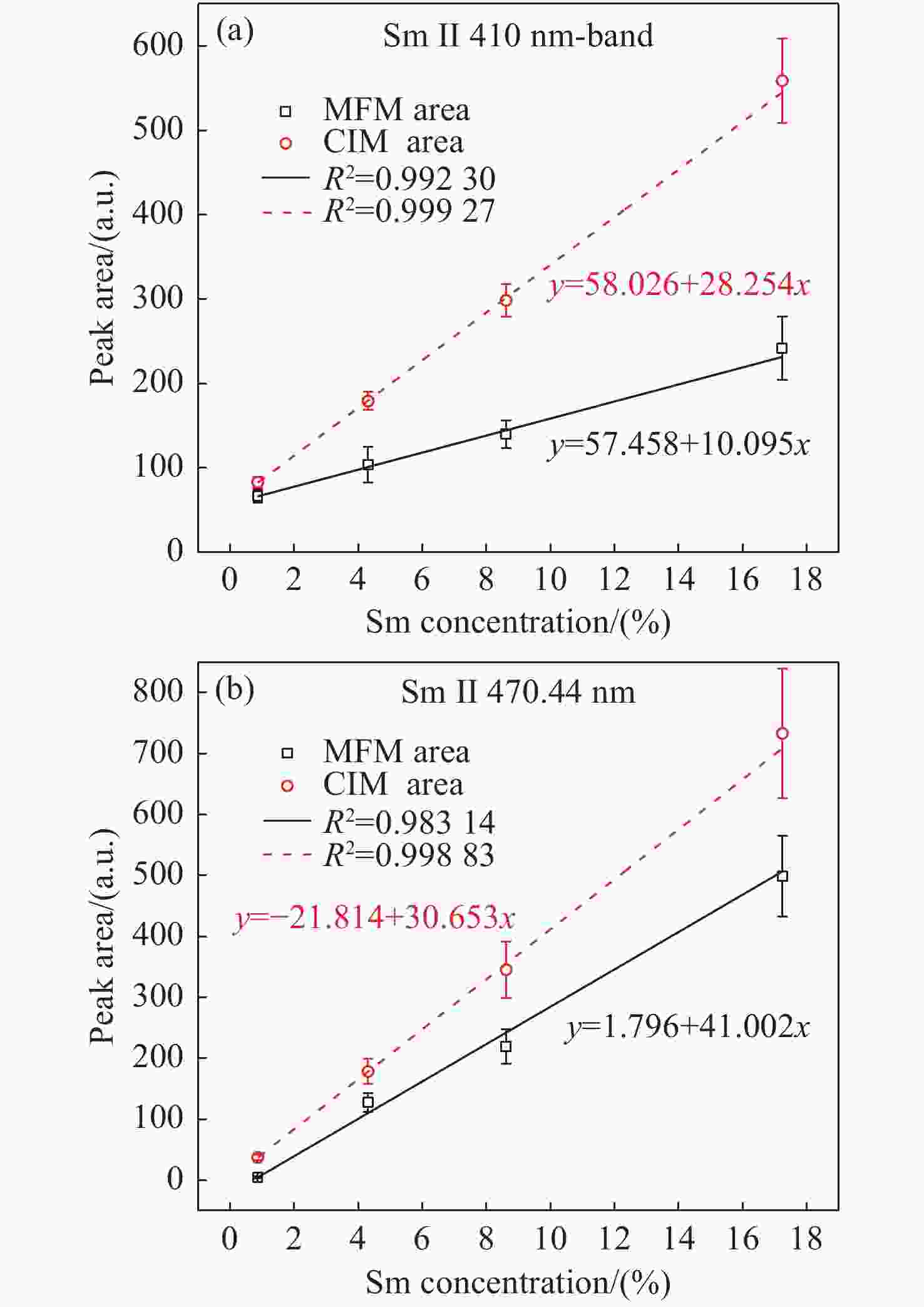
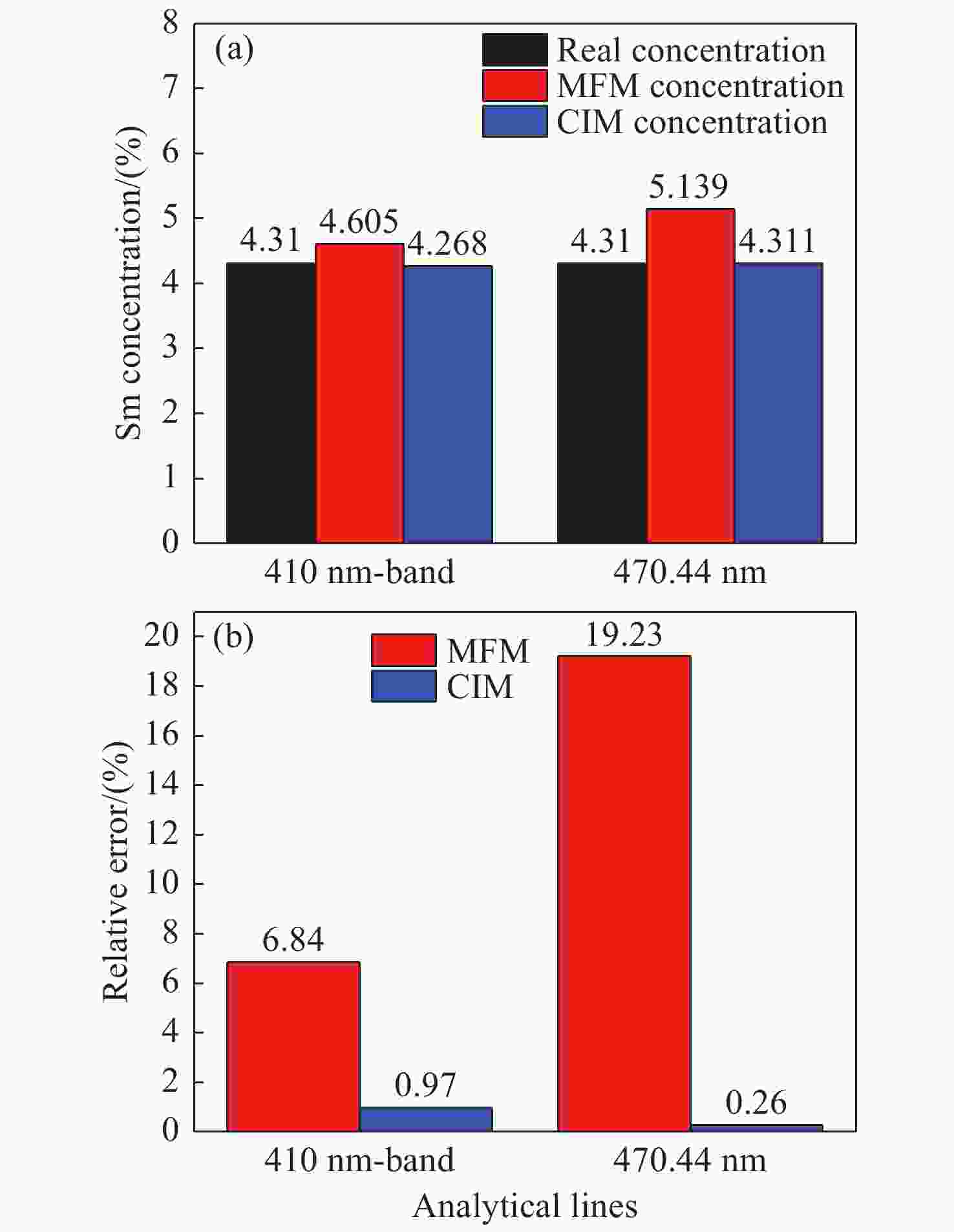
为了满足现代分析检测技术发展的新要求,促进激光诱导击穿光谱技术(LIBS)在元素分析中的应用,本文利用LIBS结合定标曲线法对内蒙古白云鄂博稀土矿区土壤中的稀土元素钐(Sm)进行了定量分析,初步检验了LIBS对稀土矿样元素成分的检测能力。首先,以编号为GBW07402a国家标准物质土壤为基底,采用标准加样法制备了Sm2O3含量分别为1%、5%、10%和20%的待分析样品。其次,通过调节激光脉冲能量参数对基底样品进行激发,探究了激光能量参数对谱线强度和信背比的影响,得出最优化的实验条件后,对所有待分析样品进行激发以获取等离子体光谱信息。接着,分别采用多峰Lorentz拟合扣除背底法(MFM)和级联积分保留背底法(CIM)对光谱信息进行处理,构建以谱线积分强度与元素含量为关联量的定标曲线。最后,根据定标曲线进行含量预测,初步评估了LIBS用于稀土矿区土壤样品中Sm元素的检测性能。研究结果表明:受稀土矿区土壤基体效应的影响,Sm元素的谱线出现了强烈的展宽而导致无法进行有效分辨,而钠(Na)、钾(K)、钛(Ti)和铁(Fe)等元素的谱线没有呈现出明显的展宽。通过对比不同含量下的光谱信息,选取410 nm-band和470.44 nm为Sm元素分析谱线用于定量分析。基于积分强度和元素含量构建的定标曲线都有着较好的线性相关度,拟合系数(
R 2)值大都在0.99以上;相比而言,采用CIM处理光谱信息,可以获取更好的线性相关度,最大值为0.99927。以Sm含量为4.310%的3#样品为未知待测样品,采用留一法构建定标曲线对其含量进行预测分析,结果显示CIM法使得分析线具有极佳的预测性能,两条分析线对3#样品含量的预测相对误差均在1%以内。实验结果说明LIBS能够实现稀土矿区土壤中稀土元素Sm含量的检测分析,满足现代分析技术的新要求,为开发便携式稀土元素检测仪提供了实验依据。Abstract:This paper aims to meet the new requirements of modern analytical and testing technology development, and to promote the application of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) in the field of element analysis, especially for the measurement of rare earth element in soil. A LIBS system combined with calibration curve method was used to quantitatively analyze samarium (Sm) in the soil of Bayan Obo rare earth mining region. Firstly, the samples containing 1%, 5%, 10% and 20% Sm2O3 were prepared by Standard Addition Method (SAM) with the soil of national standard material GBW07402a as the base. Secondly, through analyzing the substrate excited by different laser pulse energy parameters, the influence of laser pulse energy parameters on the spectral line intensity and Signal to Back Ratio (SBR) was researched, an optimum laser pulse energy parameter was finally selected for the next measurement. Thirdly, in order to get and study the linearity of the calibration curve constructed between the peak area and the Sm concentration, the original spectra data were processed with multiple peak Lorentz fitting method without background subtraction (MFM) and Concatenation-based Integration Method (CIM) with background retention, respectively. Finally, according to the calibration curve, the concentration prediction was carried out, and the detection performance of LIBS for Sm in soil samples of rare earth mining area was preliminarily evaluated. The results show that the matrix effect of the soil can significantly broaden the emission lines of Sm element, which makes it impossible to distinguish them from each other. However, the effect of the soil matrix on sodium (Na), potassium (K), Titanium (Ti) and iron (Fe) is much weaker than that on Sm. By comparing the spectral region of interest, the 410 nm-band and 470.44 nm emission lines were identified and selected as the analysis lines, and subsequently used for quantitatively analysis. Results show that calibration curves for Sm element constructed by the peak area and concentration have good linear correlations and most of the linear relationships of the regression coefficients (
R 2) for the Sm emission lines are better than 0.99. Compared with the results by using MFM, CIM could obtain better linear correlation, and the maximum of was 0.99927 for the 410 nm-band. The better analytical predictive skill of LIBS measurement by using the leave-one-out method with CIM data was found as well, the relative errors of the prediction for both the analysis lines were all within 1% for the 3# sample with the Sm concentration of 4.310%. The achievements of this study demonstrate that the LIBS spectral analysis is capable of monitoring special elements in the rare earth mineral sample, which meets new requirements of modern analysis technology, and provides an experimental basis for the development of portable rare earth element detector as well.-
Key words:
- laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) /
- soil /
- Sm /
- rare earth element /
- quantitative analysis
-
表 1 采用留一法构建的定标曲线参数及R2值
Table 1. The value of R2 and fitting parameters from the calibration curves constructed by leave-one-out method
410 nm-band 470.44 nm MFM CIM MFM CIM a 57.260 58.137 -20.286 1.798 b 10.067 28.323 28.785 40.999 R2 0.9905 0.9989 0.9962 0.9976 -
[1] 石勇. 我国富有的战略资源—稀土材料研究综述[J]. 机械管理开发,2010,25(1):44-45,47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-773X.2010.01.023SHI Y. Research on the summarization of rare-earth material-full of China strategic resources[J]. Mechanical Management and Development, 2010, 25(1): 44-45,47. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-773X.2010.01.023 [2] 张琦, 张乾, 师晓梦, 等. 稀土溴化物固态电解质材料在全固态电池中的应用研究进展[J]. 应用化学,2022,39(4):585-598.ZHANG Q, ZAHNG Q, SHI X M, et al. Research progress of rare earth bromides based solid electrolytes for all-solid-state batteries[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2022, 39(4): 585-598. (in Chinese) [3] 胡家乐, 薛冬峰. 稀土离子特性与稀土功能材料研究进展[J]. 应用化学,2020,37(3):245-255. doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2020.03.190350HU J L, XUE D F. Research progress on the characteristics of rare earth ions and rare earth functional materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2020, 37(3): 245-255. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2020.03.190350 [4] 刘江, 赵颖如, 徐文贵. 放射性核素钐153的应用进展[J]. 国际医学放射学杂志,2014,37(4):366-370. doi: 10.3874/j.issn.1674-1897.2014.04.Z0412LIU J, ZHAO Y R, XU W G. Application progress of radionuclide Samarium 153[J]. International Journal of Medical Radiology, 2014, 37(4): 366-370. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3874/j.issn.1674-1897.2014.04.Z0412 [5] 石向东, 董广成, 张旭明, 等. 利用中子吸收材料进行乏燃料贮存的研究进展[J]. 辽宁工业大学学报(自然科学版),2020,40(6):376-380.SHI X D, DONG G CH, ZHANG X M, et al. Research progress on neutron absorber materials of spent fule storage[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Technology (Natural Science Edition) , 2020, 40(6): 376-380. (in Chinese) [6] 罗明标, 杨枝, 郭国林, 等. 白云鄂博铁矿石中稀土的赋存状态研究[J]. 中国稀土学报,2007,25(S1):57-61.LUO M B, YANG ZH, GUO G L, et al. Research on occurrence state of REE in Bayan obo iron ore[J]. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 2007, 25(S1): 57-61. (in Chinese) [7] 高娟琴, 于扬, 李以科, 等. 内蒙白云鄂博稀土矿土壤-植物稀土元素及重金属分布特征[J]. 岩矿测试,2021,40(6):871-882.GAO J Q, YU Y, LI Y K, et al. Distribution characteristics of rare earth elements and heavy metals in a soil-plant system at Bayan Obo Rare Earth Mine, Inner Mongolia[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(6): 871-882. (in Chinese) [8] 王哲, 赵莹晨, 骆逸飞, 等. 内蒙古白云鄂博矿区土壤稀土元素污染特征及评价[J]. 环境科学,2021,42(3):1503-1513.WANG ZH, ZHAO Y CH, LUO Y F, et al. Characteristics and evaluation of soil rare earth element pollution in the Bayan Obo mining region of Inner Mongolia[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(3): 1503-1513. (in Chinese) [9] PAGANO G, GUIDA M, TOMMASI F, et al. Health effects and toxicity mechanisms of rare earth elements-Knowledge gaps and research prospects[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2015, 115: 40-48. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.01.030 [10] RIM K T, KOO K H, PARK J S. Toxicological evaluations of rare earths and their health impacts to workers: a literature review[J]. Safety and Health at Work, 2013, 4(1): 12-26. doi: 10.5491/SHAW.2013.4.1.12 [11] VEERASAMY N, SAHOO S K, MURUGAN R, et al. ICP-MS measurement of trace and rare earth elements in beach placer-deposit soils of Odisha, East Coast of India, to estimate natural enhancement of elements in the environment[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(24): 7510. doi: 10.3390/molecules26247510 [12] WU W Q, XU T, HAO Q, et al. Applications of X-ray fluorescence analysis of rare earths in China[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2010, 28(S1): 30-36. [13] MONDAL S, GHAR A, SATPATI A K, et al. Recovery of rare earth elements from coal fly ash using TEHDGA impregnated resin[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2019, 185: 93-101. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.02.005 [14] 黄尧, 赵南京, 孟德硕, 等. 土壤多组分PAHs激光诱导二维荧光光谱定量方法研究[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(6):1401-1410.HUANG Y, ZHAO N J, MENG D SH, et al. Study on quantitative methods of laser-induced two-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy of multicomponent PAHs in soils[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(6): 1401-1410. (in Chinese) [15] CREMERS D A, RADZIEMSKI L J. Handbook of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy[M]. 2nd ed. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2013. [16] 李晨毓, 曲亮, 高飞, 等. 激光诱导击穿光谱对金属、陶瓷文物成分的表面及深度分布分析[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(6):1239-1248. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0112LI CH Y, QU L, GAO F, et al. Composition analysis of the surface and depth distribution of metal and ceramic cultural relics by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(6): 1239-1248. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0112 [17] 侯冠宇, 王平, 佟存柱. 激光诱导击穿光谱技术及应用研究进展[J]. 中国光学,2013,6(4):490-500.HOU G Y, WANG P, TONG C ZH. Progress in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and its applications[J]. Chinese Optics, 2013, 6(4): 490-500. (in Chinese) [18] GUDMUNDSSON S H, MATTHIASSON J, LEOSSON K. Accurate Real-Time Elemental (LIBS) analysis of molten aluminum and aluminum alloys[M]//TOMSETT A. Light Metals 2020. Cham: Springer, 2020: 860-864. [19] SEZER B, BILGE G, BOYACI I H. Capabilities and limitations of LIBS in food analysis[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 97: 345-353. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2017.10.003 [20] KAUTZ E J, DEVARAJ A, SENOR D J, et al. Hydrogen isotopic analysis of nuclear reactor materials using ultrafast laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(4): 4936-4946. doi: 10.1364/OE.412351 [21] TAVARES T R, MOUAZEN A M, NUNES L C, et al. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) for tropical soil fertility analysis[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2022, 216: 105250. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2021.105250 [22] MARTIN M, MARTIN R C, ALLMAN S, et al. Quantification of rare earth elements using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2015, 114: 65-73. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2015.10.005 [23] RETHFELDT N, BRINKMANN P, RIEBE D, et al. Detection of rare earth elements in minerals and soils by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) using interval PLS[J]. Minerals, 2021, 11(12): 1379. doi: 10.3390/min11121379 [24] NIST atomic spectra database lines[EB/OL]. https://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/ASD/lines_form.html. [25] CHINNI R C, CREMERS D A, RADZIEMSKI L J, et al. Detection of uranium using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2009, 63(11): 1238-1250. doi: 10.1366/000370209789806867 [26] RUSSO R E, MAO X L, LIU H C, et al. Time-resolved plasma diagnostics and mass removal during single-pulse laser ablation[J]. Applied Physics A, 1999, 69(S1): S887-S894. [27] YI R X, GUO L B, ZOU X H, et al. Background removal in soil analysis using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with standard addition method[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(3): 2607-2618. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.002607 [28] DEVANGAD P, UNNIKRISHNAN V K, NAYAK R, et al. Performance evaluation of Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) for quantitative analysis of rare earth elements in phosphate glasses[J]. Optical Materials, 2016, 52: 32-37. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2015.12.001 -





 下载:
下载: