-
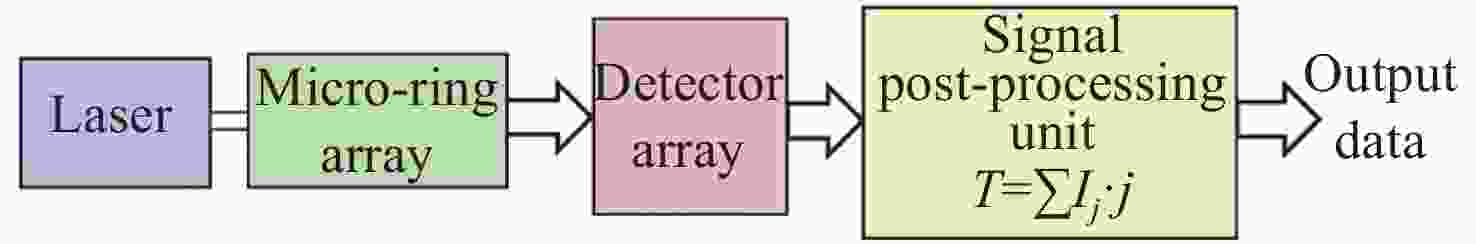
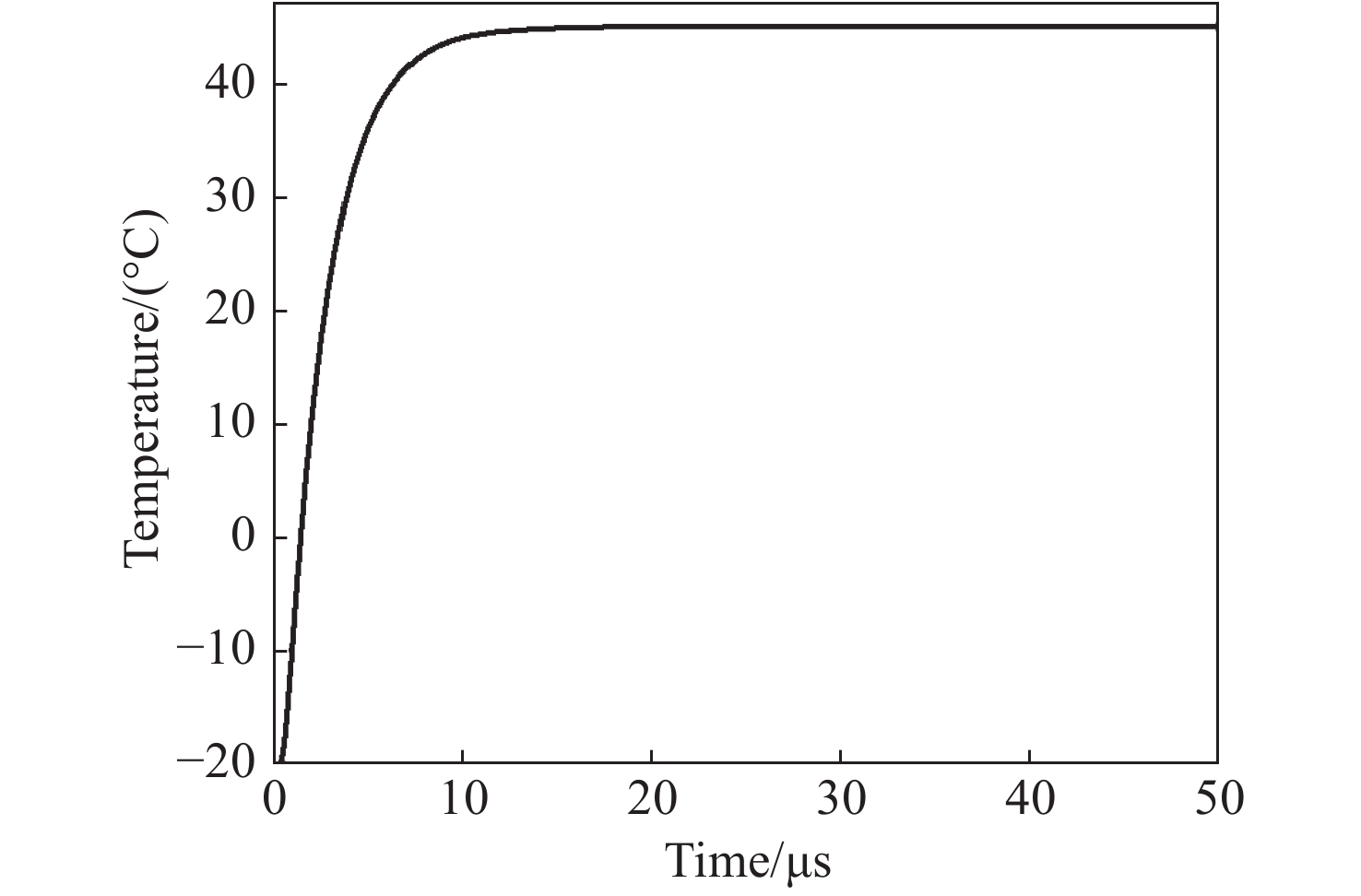
摘要: 传统温度检测在传感精度和响应时间等方面存在一定局限性,而基于热光效应的芯片级光电传感器不仅能够提升测量灵敏度和速度,也有利于降低系统复杂度和制造成本,近年来引起了人们广泛的关注。目前的集成温度传感器大多通过测量光学谐振腔对宽谱光源或可调谐光源的光谱响应来提供精准快速的测量解决方案,但这种基于宽光谱检测的方案无法实现实时处理,且成本较高,信号后处理较复杂,难以实现系统的整体集成。本文针对以上问题,采用硅基集成微环阵列技术设计了快速高精度的温度测量方法,通过对不同温度下级联微环阵列对单频激光的不同响应,构建光电二极管输出响应与温度变化的单调关系,从而实现实时高精度温度测量。为了提升单频光下的温度传感范围,使用多微环级联结构,并基于该结构设计了一种包括光源、微环阵列、探测器阵列、信号后处理单元和输出数据单元的硅基集成温度传感系统。根据实际用途的不同,在保证低功耗低成本的同时,该系统可以通过分别对级联微环数量、中心谐振波长以及谐振峰半高宽的设计改变温度测量范围以及温度测量分辨率,拥有比较大的设计自由度以及灵活的测量范围。通过对微环阵列的优化设计,实现了响应范围覆盖−20~105 ℃、精度优于60 mK、响应时间优于20 μs的精准快速测量的温度传感。Abstract: Traditional temperature detection has certain limitations in terms of sensing accuracy and response time. Chip-level photoelectric sensors based on the thermo-optic effect recently aroused widespread interest not only because they can improve measurement sensitivity and speed, but also because they can help reduce system complexity and cost. State-of-art integrated optical temperature sensors mostly measure the optical interference of broadband light sources or tunable light sources in the micro-resonators to provide accurate and fast measurement solutions. However, these solutions based on wide-spectrum detection cannot achieve real-time processing, are costly with complicated signal post-processing, and are difficult to implement in highly integrated systems. To solve the above problems, we show a fast and high-precision temperature measurement method using a silicon-based integrated micro-ring array. The different responses of the cascaded micro-ring array are measured by a single-frequency laser at different temperatures. The results are utilized to model the relationship between the electrical response of the detector array and the real temperature, thereby realizing real-time high-precision temperature measurement. In addition, to enlarge the temperature detection range under a fixed-wavelength light source, a cascaded micro-ring structure is adopted. Based on the proposed structure, a silicon-based integrated temperature sensing system including a light source, a micro-ring array, a detector array, a signal post-processing unit and an output data unit is designed. Depending on the requirement of actual applications, the system can change the temperature measurement range and resolution by separately designing the number of cascaded micro-rings, the center resonance wavelength, and the half-width of the resonance peak while ensuring low system power consumption and cost. Through the optimized design of the micro-ring array, a temperature sensor with a response range covering −20~105°C, accuracy better than 60 mK, and a response time as quick as 20 μs is demonstrated.
-
Key words:
- integrated optics /
- temperature measurement /
- micro-ring array /
- integrated sensor
-
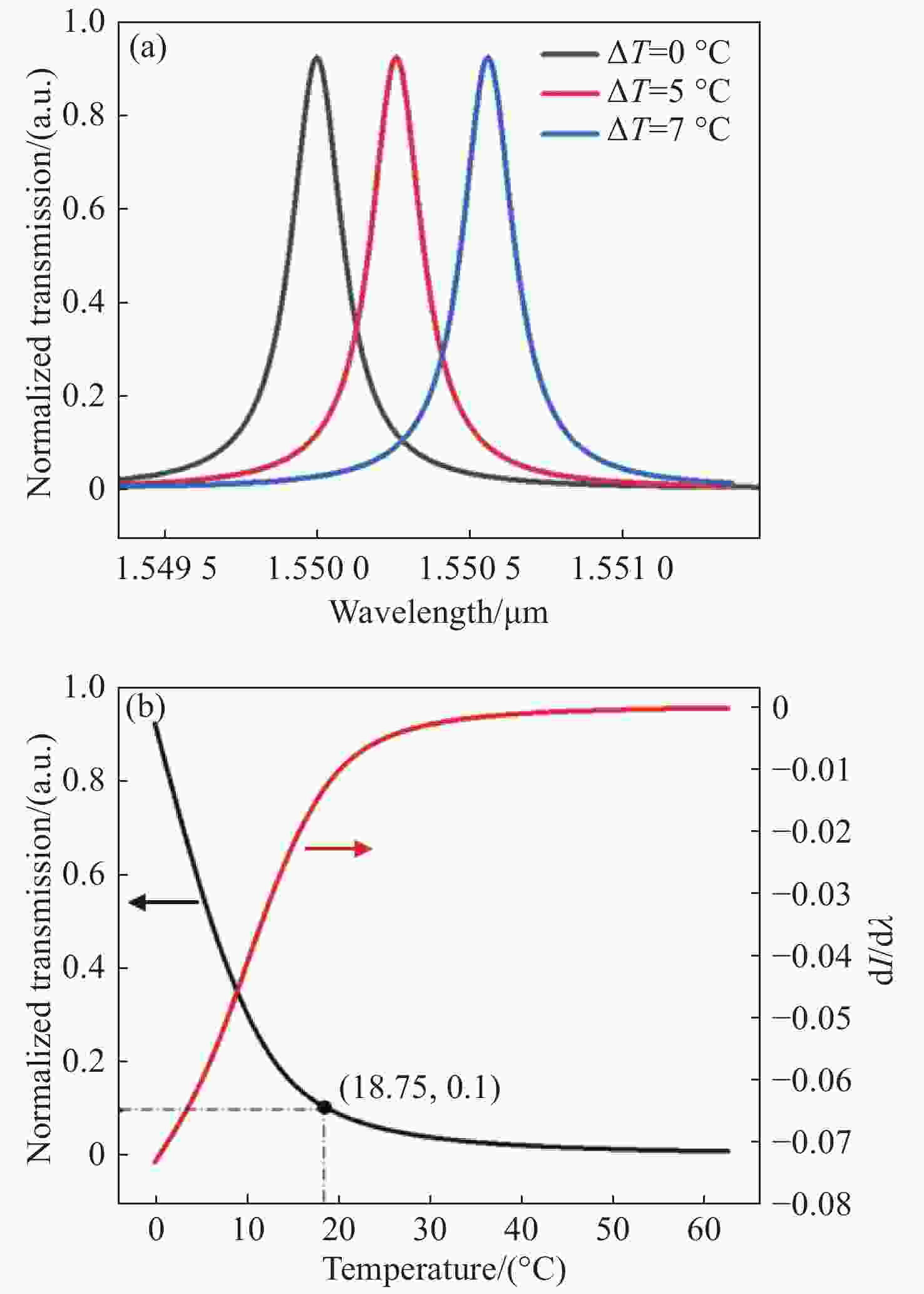
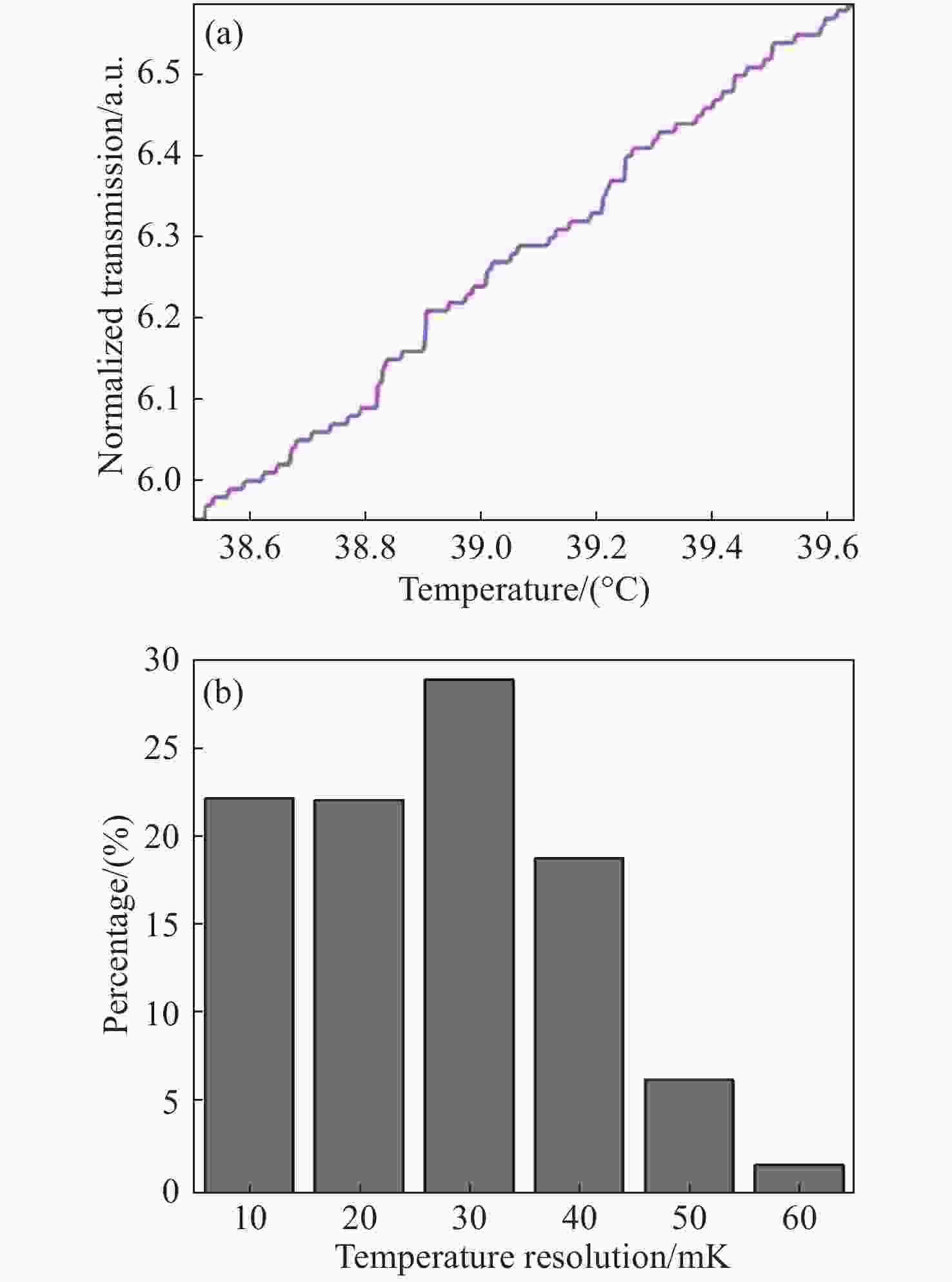
图 2 (a)单个微环在不同温度下的波长响应结果;(b)左轴为输入波长固定时在不同温度下输出光强的变化;右轴为输入波长固定时输出光强对波长求导结果随温度的变化情况
Figure 2. (a) Wavelength response results of a single micro-ring at different temperatures; (b) normalized transmission is the change in output light intensity at different temperatures when the input wavelength is fixed;
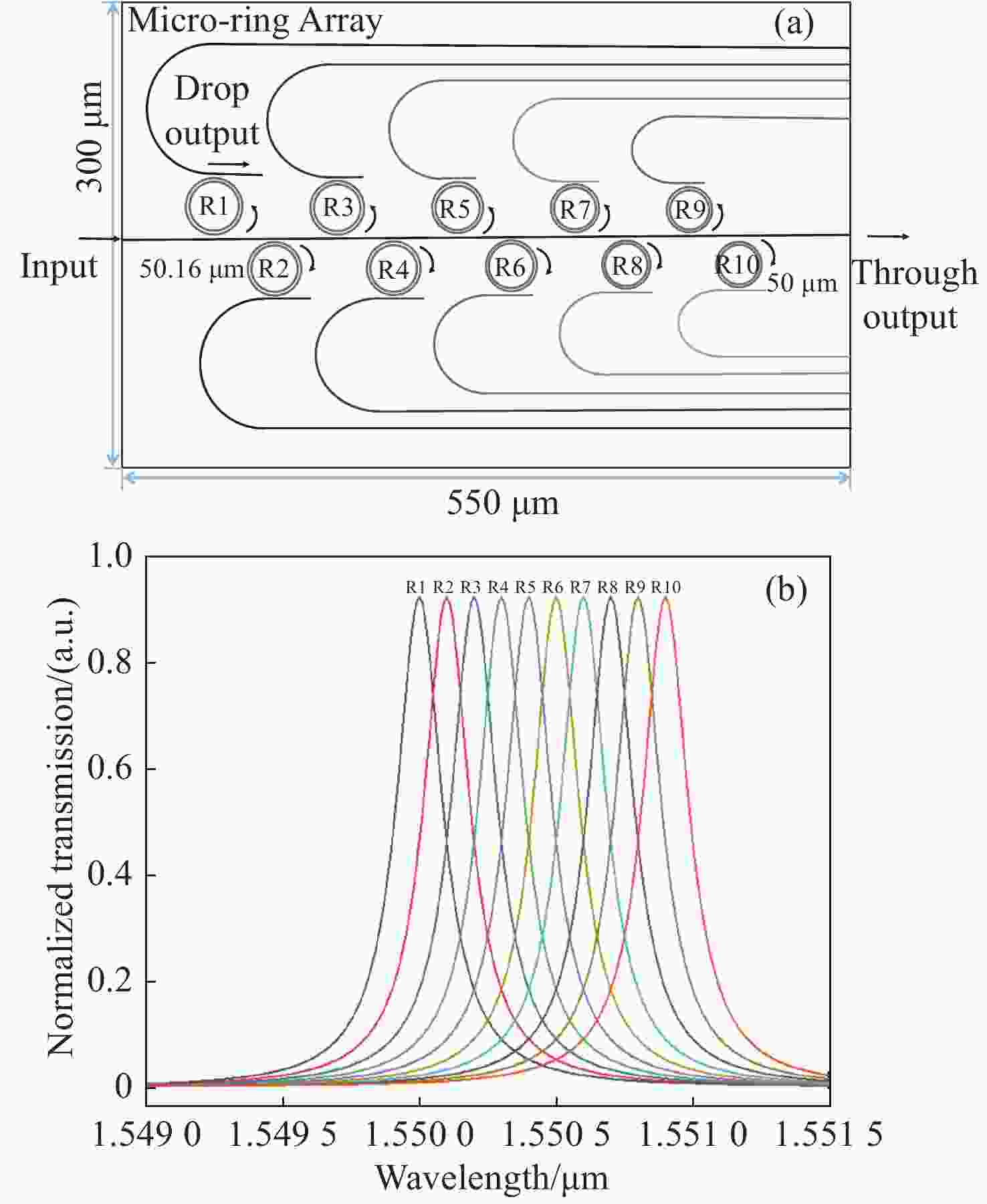
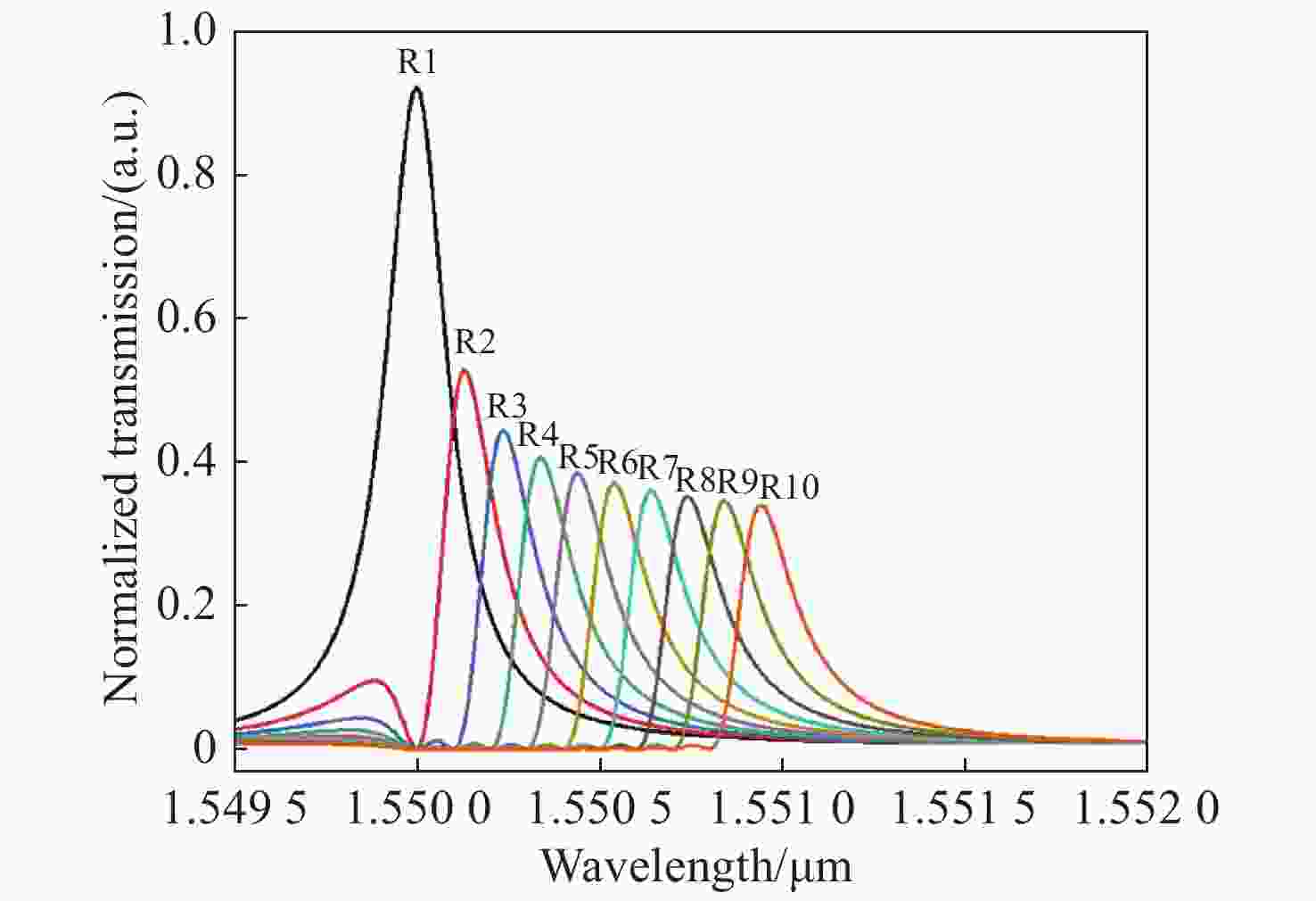
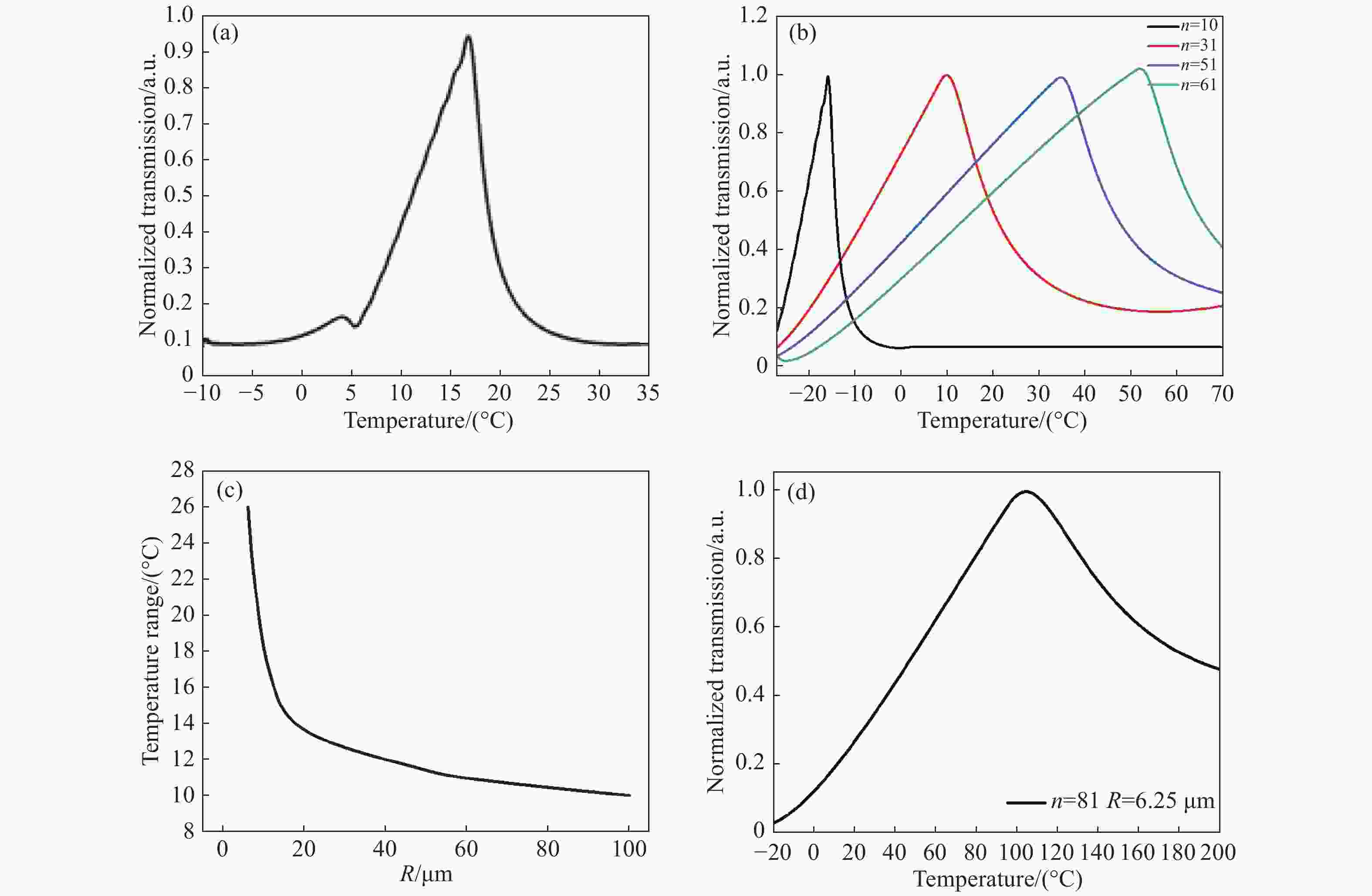
$\dfrac{{\rm{d}}I}{{\rm{d}}\lambda }$ is the derivation for output light intensity versus wavelength varying with temperature when the input wavelength is fixed图 6 (a)输出信号进行加权求和之后的相对输出电信号强度与实际温度的关系;(b)不同微环数量的微环阵列输出信号加权求和后相对输出电信号强度对应实际温度的关系;(c)微环阵列温度测量范围对应半径的关系;(d)灵活配置级联阵列参数得到最大温度测量范围时输出信号与实际温度的关系
Figure 6. (a) Relationship between the relative output signal intensity and the actual temperature after the weighted summation of the output signal; (b) relationship between the relative output signal intensity and the actual temperature after the weighted summation of the output signals of the micro-ring array with different numbers of micro-rings; (c) relationship between the micro-ring array temperature measurement range and the corresponding radius; (d) relationship between the output signal and the actual temperature when the cascade array parameters are configured flexibly to obtain the maximum temperature measurement range
-
[1] XU H T, HAFEZI M, FAN J, et al. Ultra-sensitive chip-based photonic temperature sensor using ring resonator structures[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(3): 3098-3104. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.003098 [2] KLIMOV N N, MITTAL S, BERGER M, et al. On-chip silicon waveguide Bragg grating photonic temperature sensor[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(17): 3934-3936. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.003934 [3] ZHANG H, SHANG J Y, LIU X J, et al. High-sensitivity fiber liquid crystals temperature sensor with tiny size and simple tapered structure[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2020, 18(10): 101202. doi: 10.3788/COL202018.101202 [4] RAO Y J, WEBB D J, JACKSON D A, et al. In-fiber Bragg-grating temperature sensor system for medical applications[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 1997, 15(5): 779-785. doi: 10.1109/50.580812 [5] IRACE A, BREGLIO G. All-silicon optical temperature sensor based on Multi-Mode Interference[J]. Optics Express, 2003, 11(22): 2807-2812. doi: 10.1364/OE.11.002807 [6] 史振江, 李志全, 陆飞. 硅基波导微环谐振腔光学传输特性研究[J]. 传感器世界,2020,26(8):7-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-883X.2020.08.001SHI ZH J, LI ZH Q, LU F. Research on optical transmission characteristics of microring resonator with silicon waveguide[J]. Sensor World, 2020, 26(8): 7-11. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-883X.2020.08.001 [7] QU ZH Y, LU P, LI Y J, et al. Low-frequency acoustic Fabry–Pérot fiber sensor based on a micromachined silicon nitride membrane[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2020, 18(10): 101201. doi: 10.3788/COL202018.101201 [8] 吴妮珊, 夏历. 基于微波光子学的准分布式光纤传感解调技术[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(2):245-263. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0121WU N SH, XIA L. Interrogation technology for quasi-distributed optical fiber sensing systems based on microwave photonics[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(2): 245-263. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0121 [9] GUAN X W, WANG X Y, FRANDSEN L H. Silicon photonic thermometer operating on multiple polarizations[C]. Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, Optical Society of America, 2016: JW2A. 131. [10] KLIMOV N N, PURDY T, AHMED Z. Chip-packaged silicon photonic nanoscale thermometers[C]. Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, Optical Society of America, 2016: AW1J. 6. [11] KLIMOV N, PURDY T, AHMED Z. Towards replacing resistance thermometry with photonic thermometry[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2018, 269: 308-312. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2017.11.055 [12] KLIMOV N N, PURDY T, AHMED Z. On-chip integrated silicon photonic thermometers[J]. Sensors &Transducers, 2015, 191(8): 67-71. [13] BOGAERTS W, DE HEYN P, VAN VAERENBERGH T, et al. Silicon microring resonators[J]. Laser &Photonics Reviews, 2012, 6(1): 47-73. [14] AHMED Z, FILLA J, GUTHRIE W, et al. Fiber Bragg grating based thermometry[J]. NCSLI Measure, 2015, 10(4): 28-31. doi: 10.1080/19315775.2015.11721744 [15] LEUTHOLD J, KOOS C, FREUDE W, et al. Silicon-organic hybrid electro-optical devices[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2013, 19(6): 3401413. [16] 张家一, 罗莉君, 刘晓红, 等. 电化学发光传感器在农业传感领域中的研究进展[J]. 应用化学,2019,34(6):379-391.ZHANG J Y, LUO L J, LIU X H, et al. Research progress of electrochemistry sensors in the field of agricultural sensing[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2019, 34(6): 379-391. (in Chinese) -





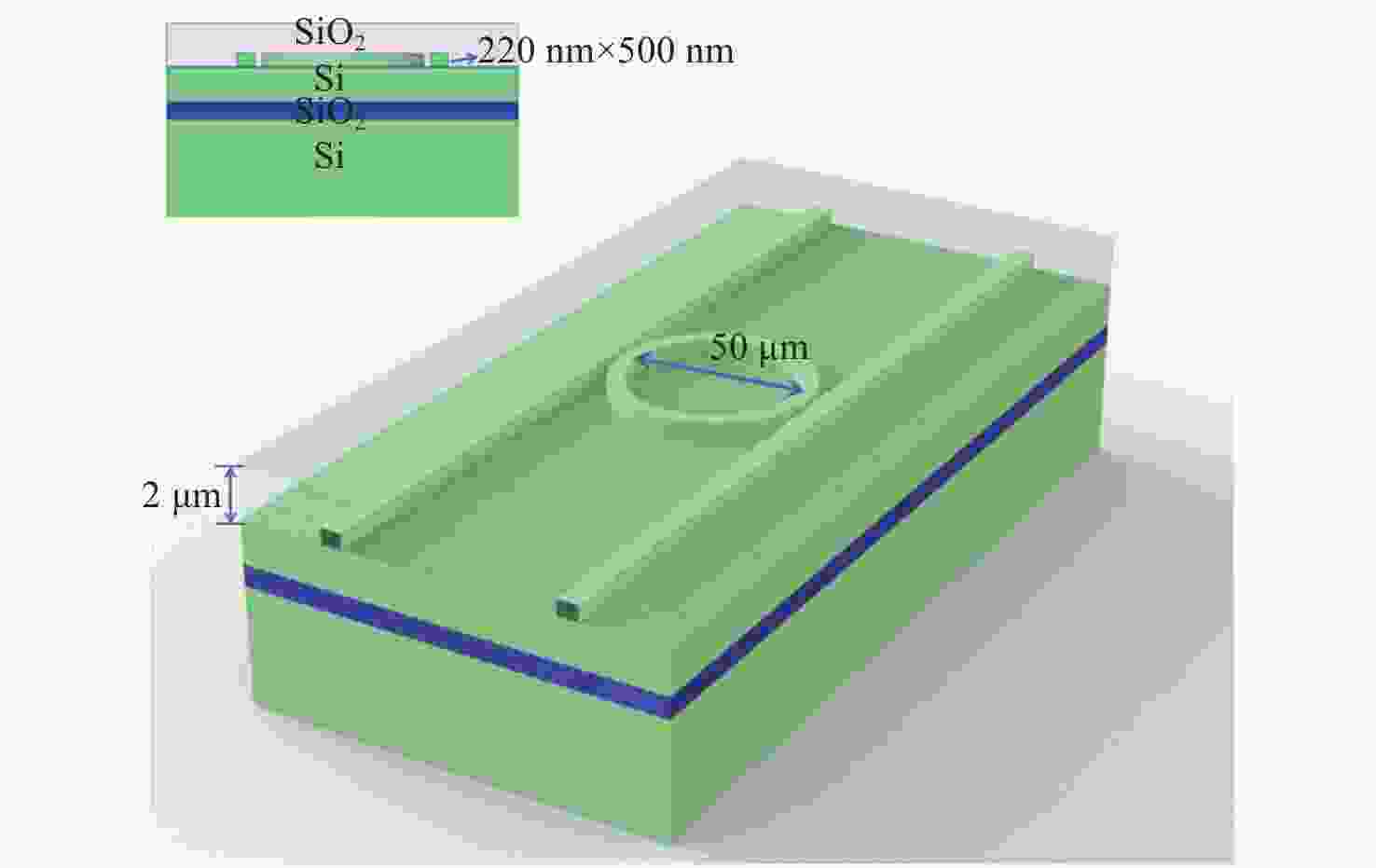
 下载:
下载: