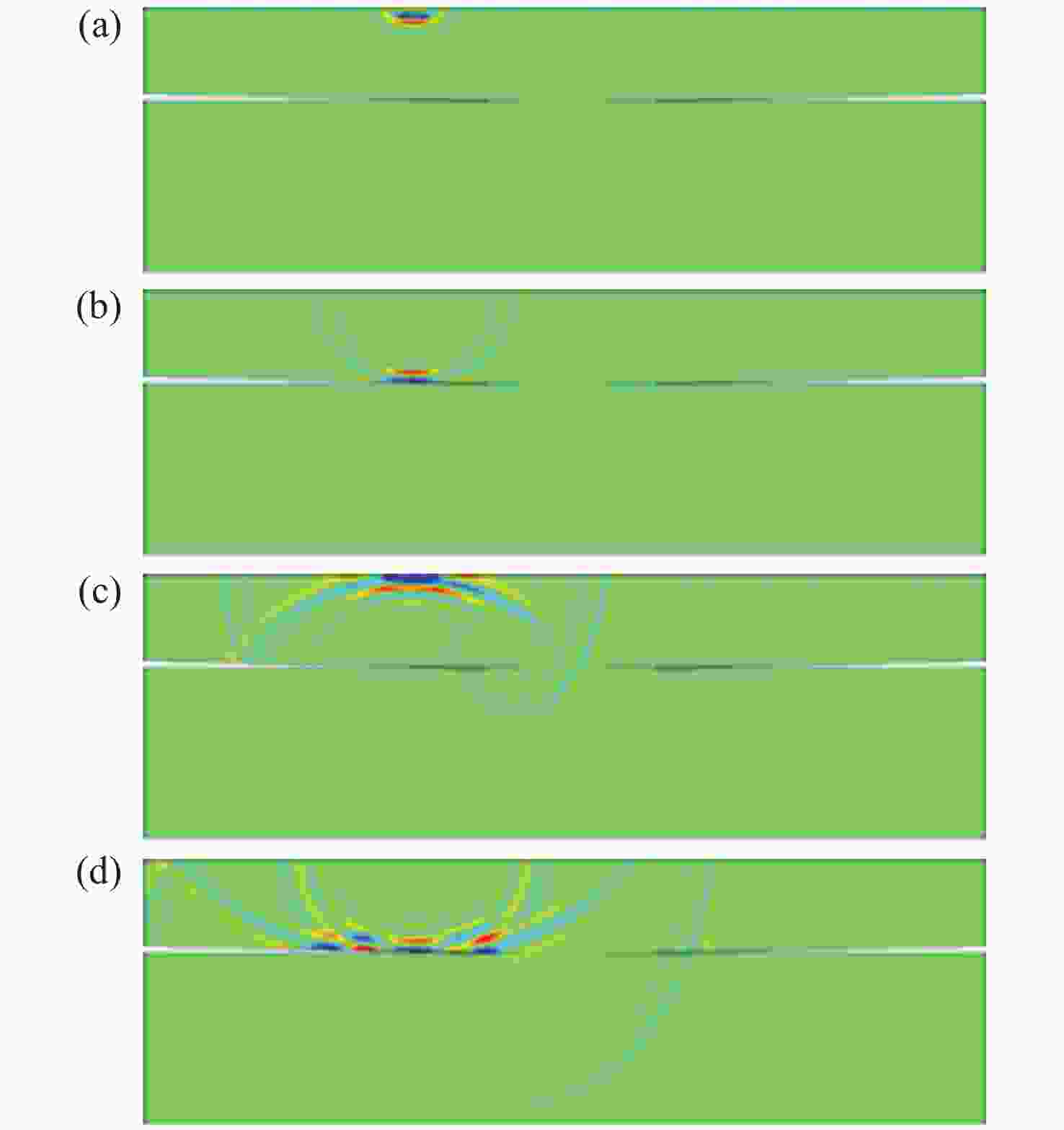
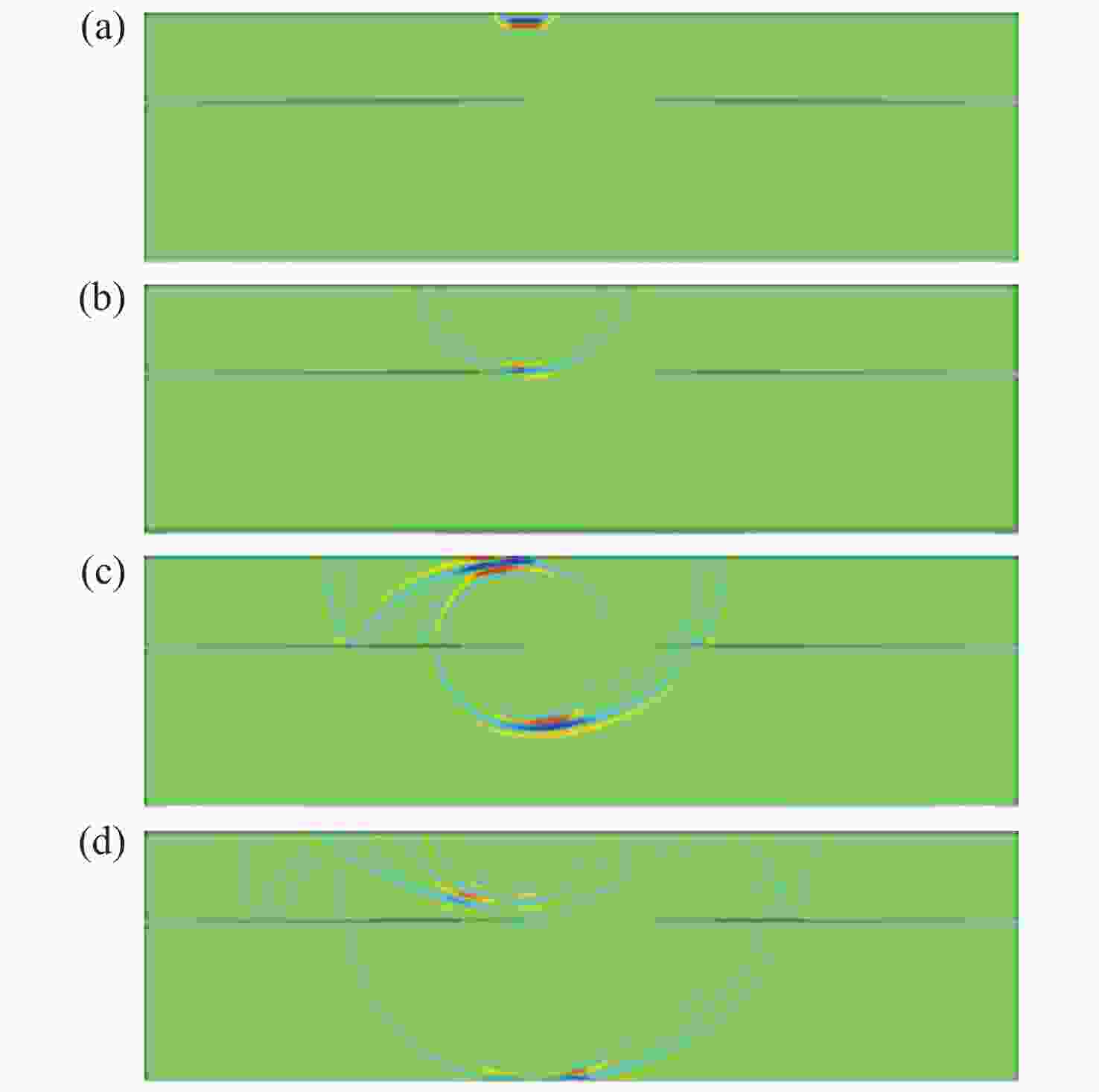
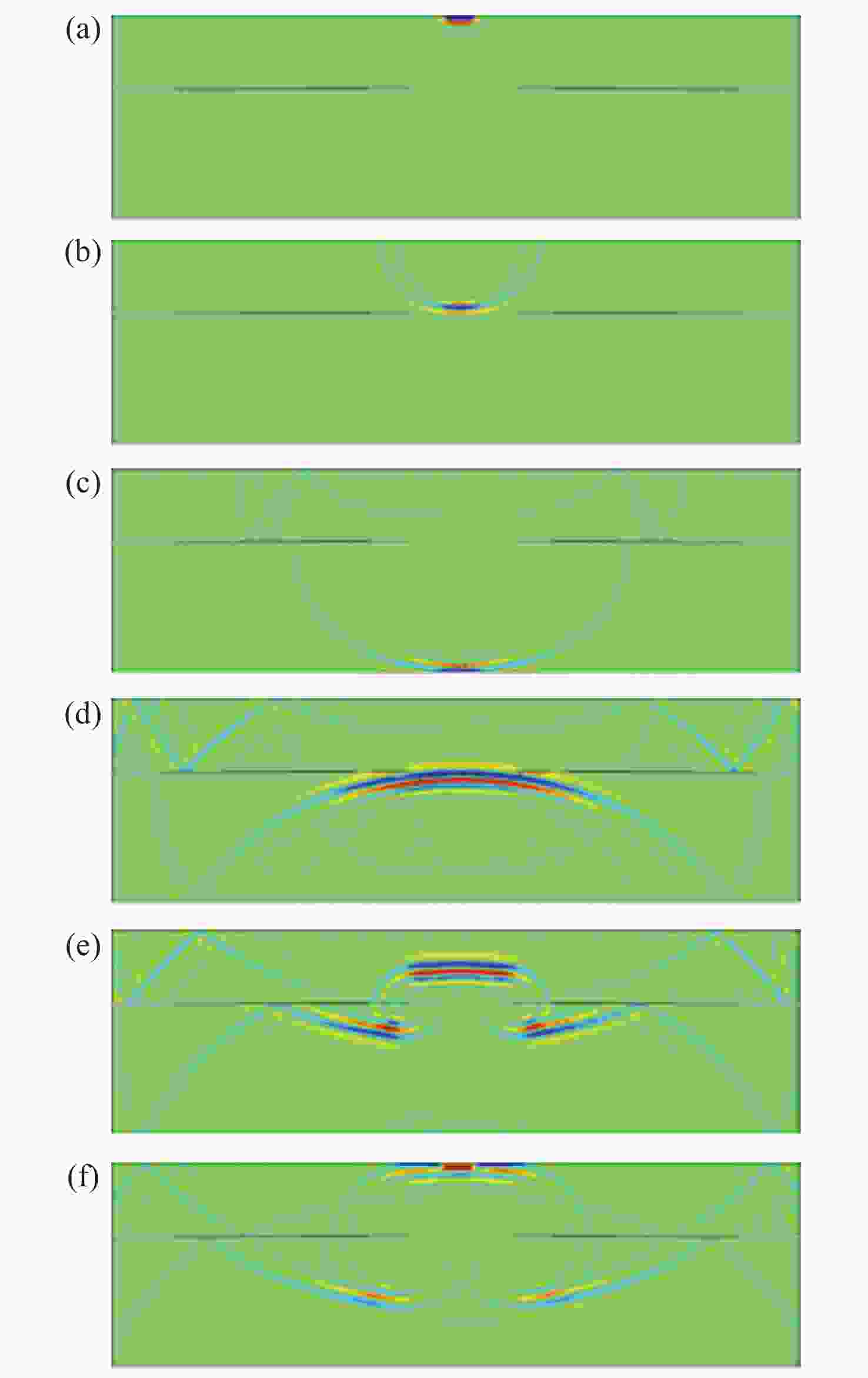
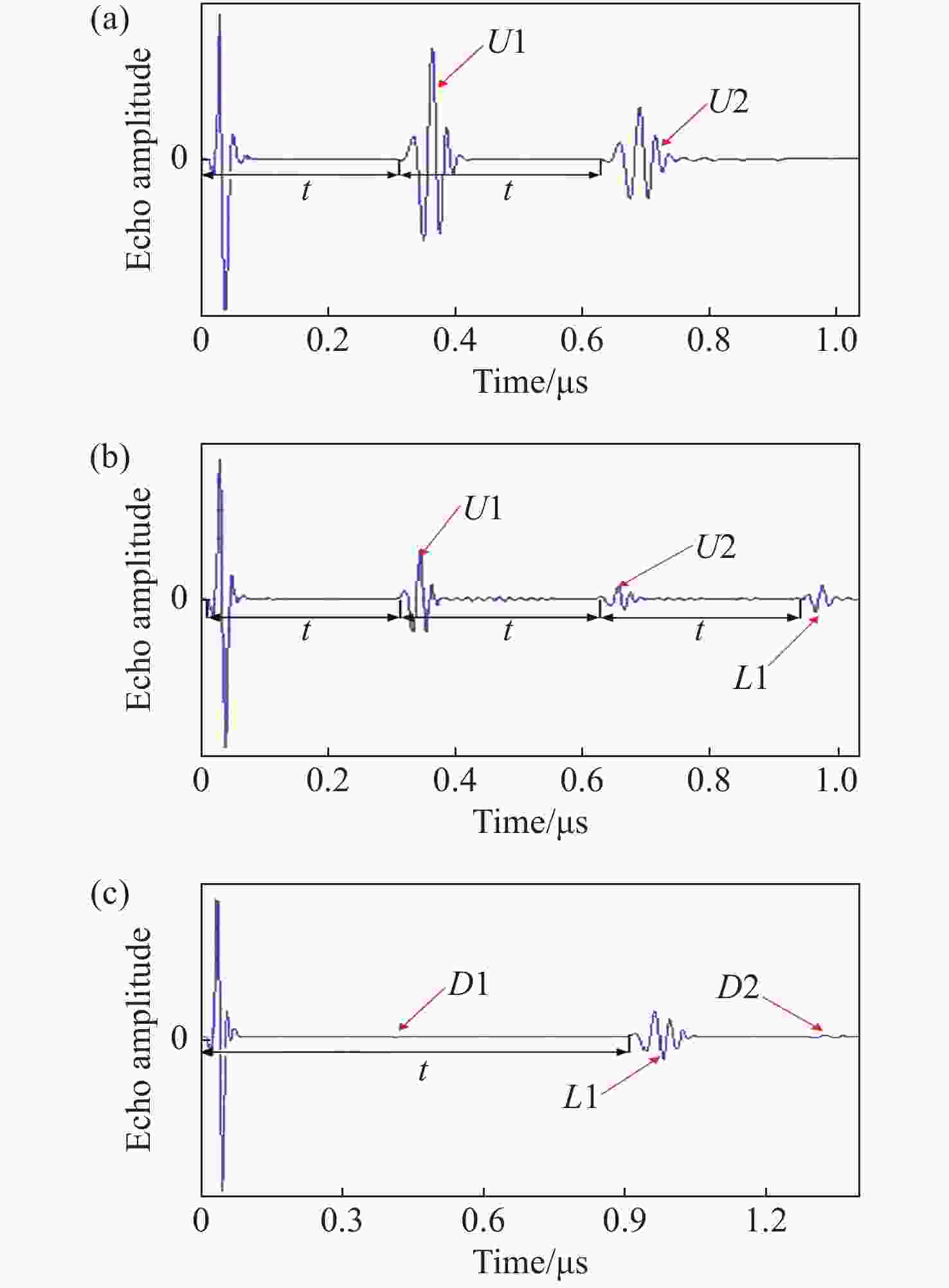
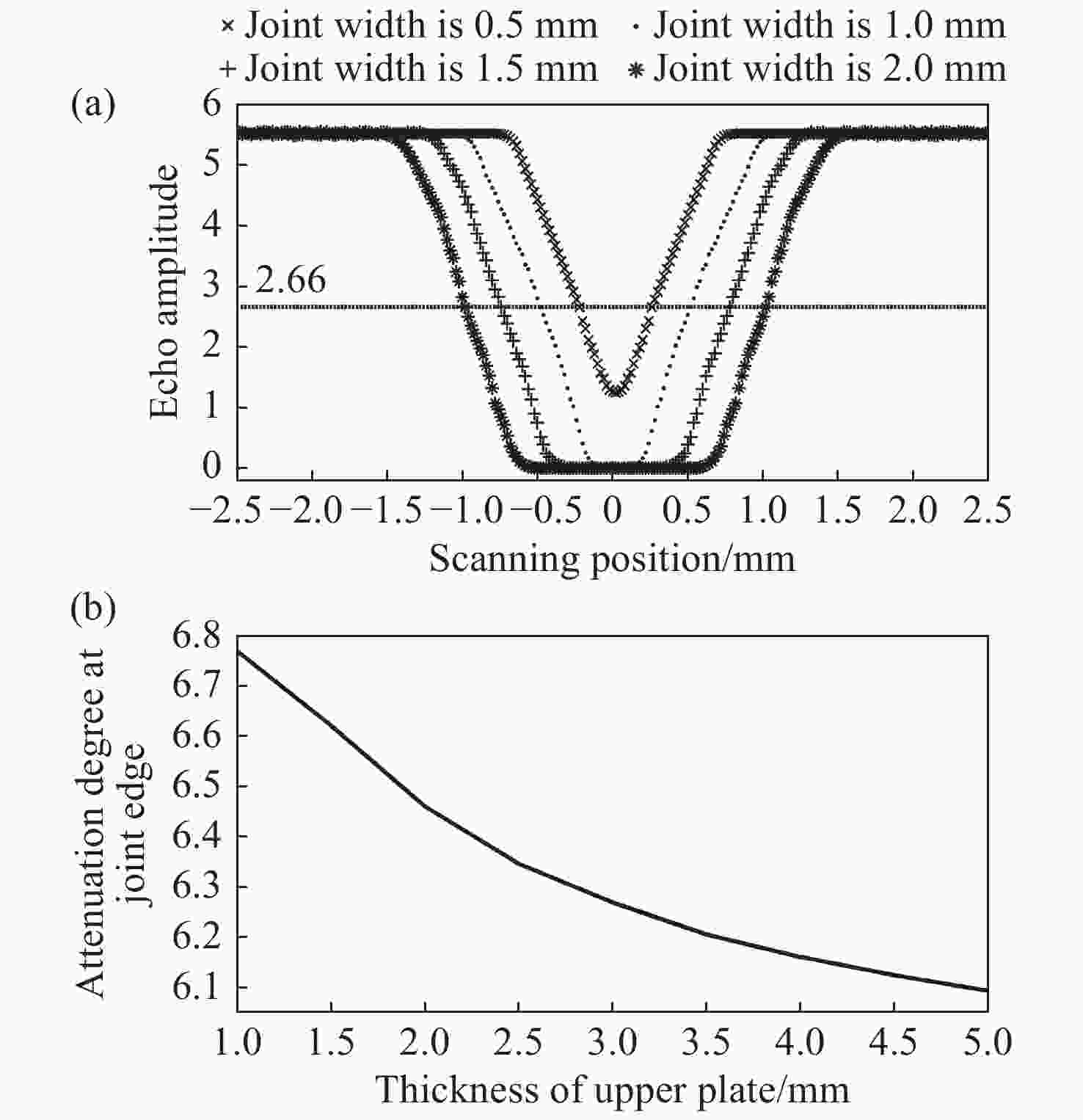
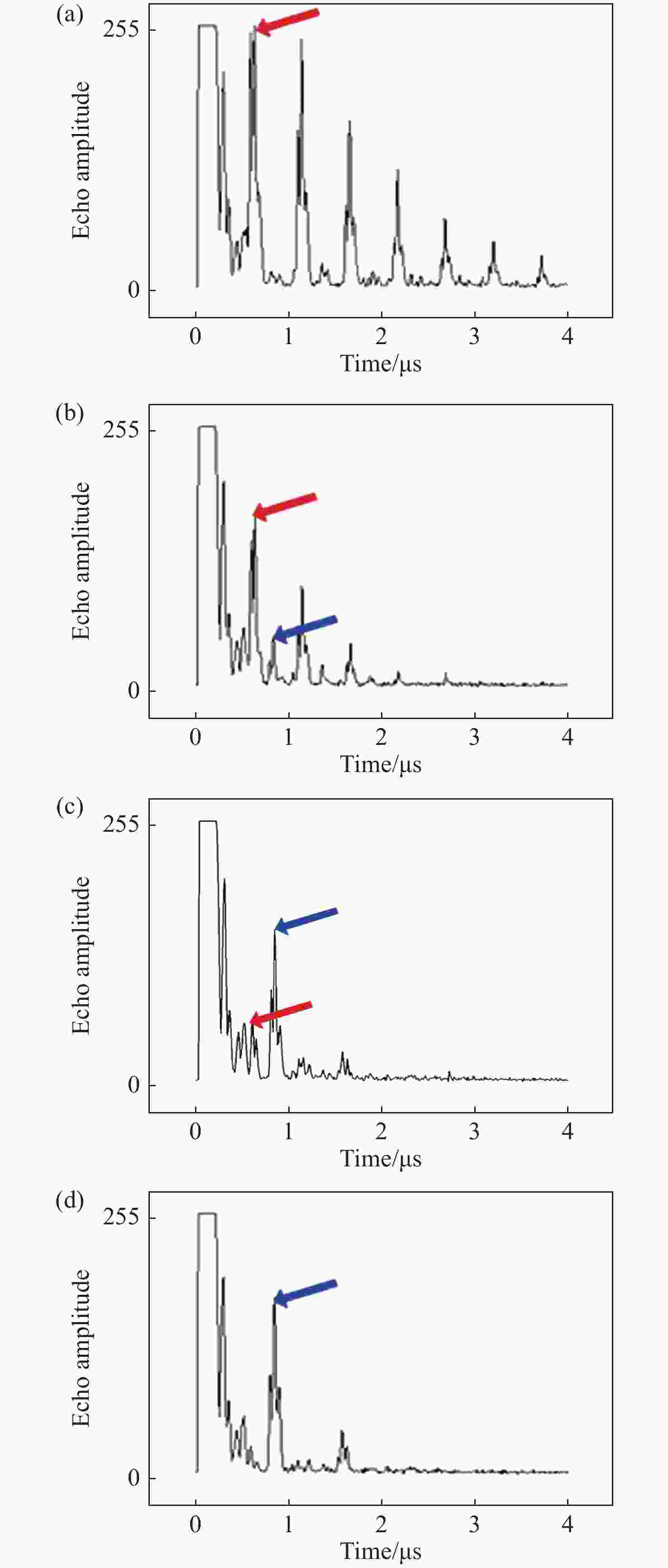
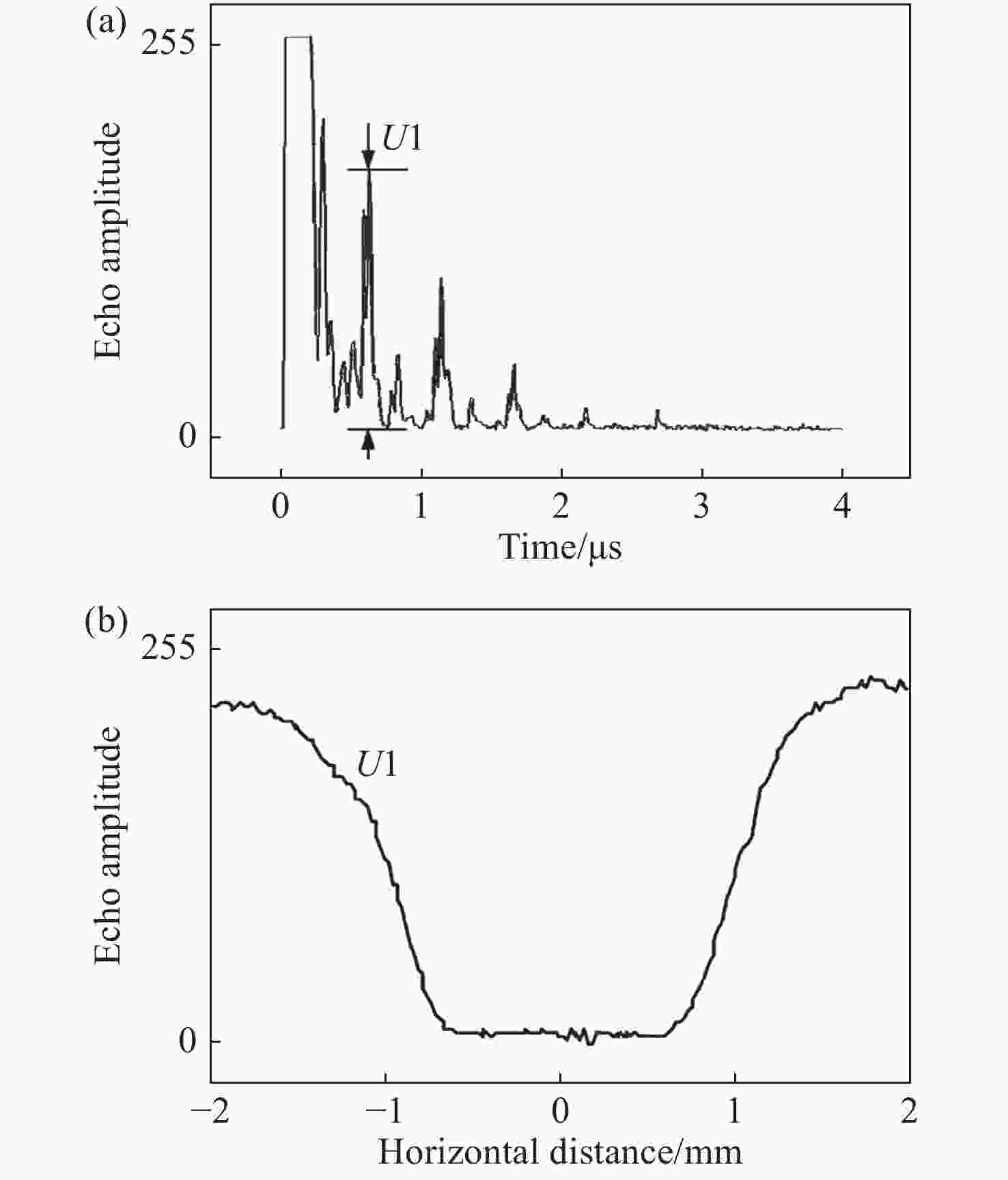
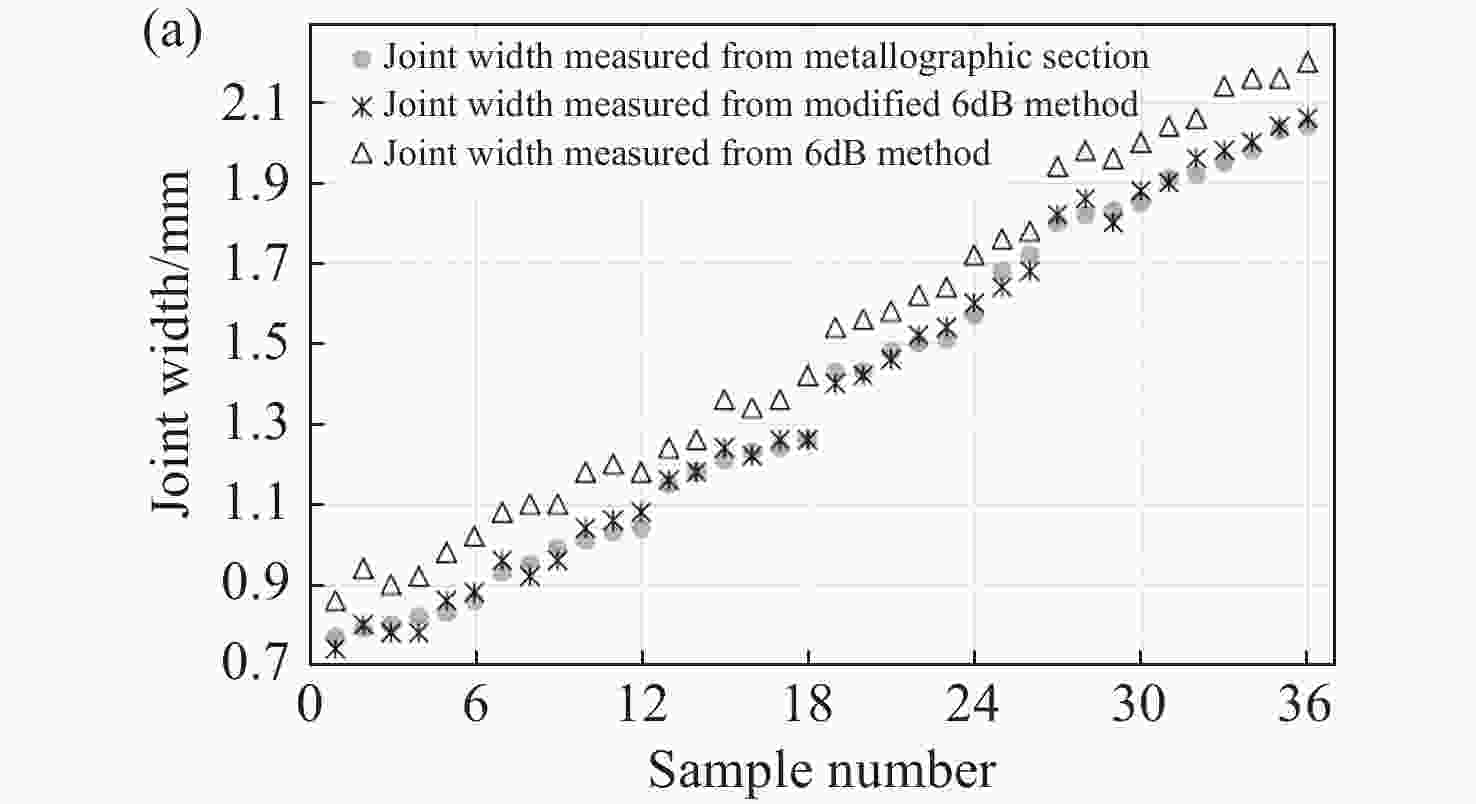
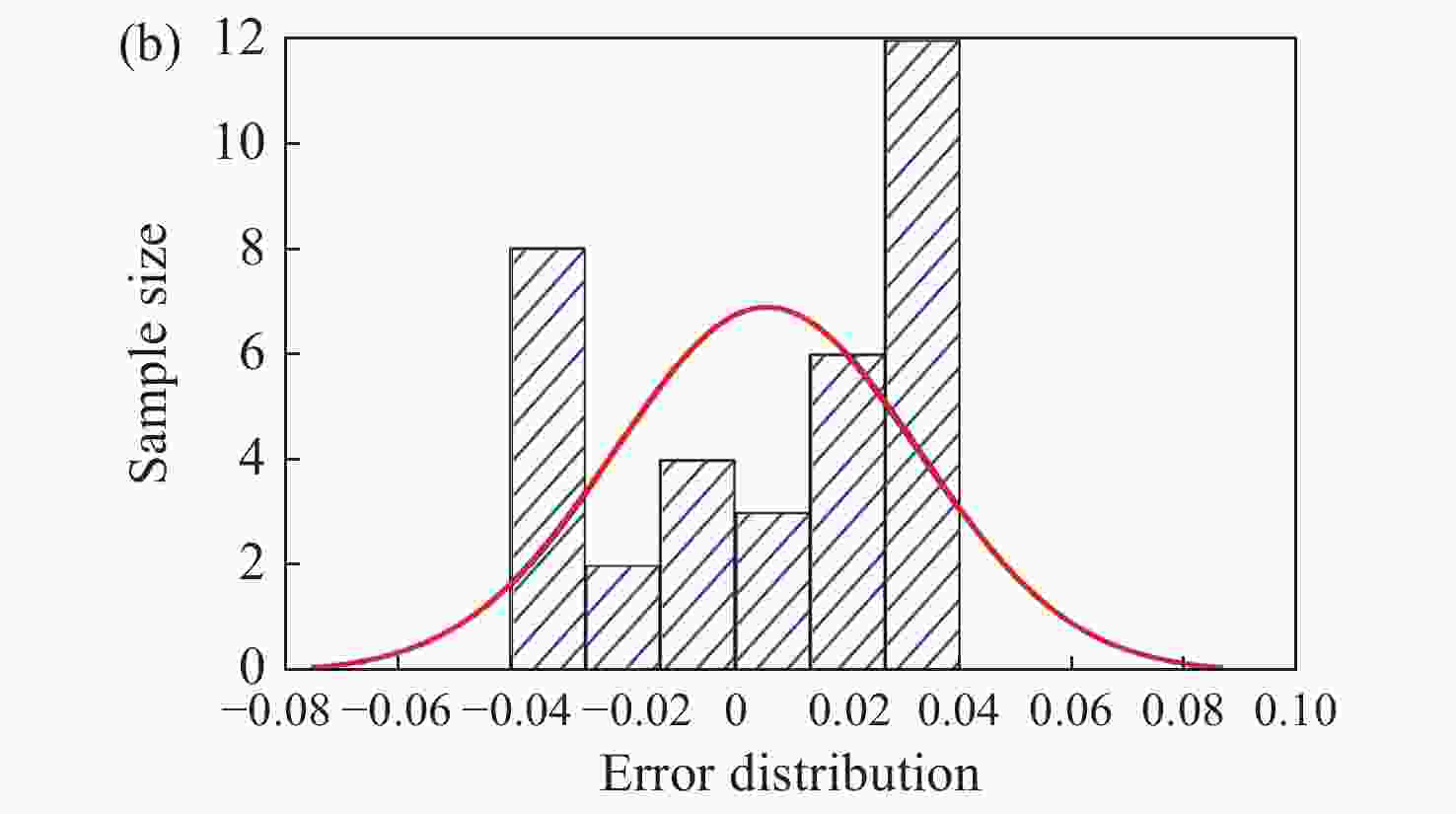
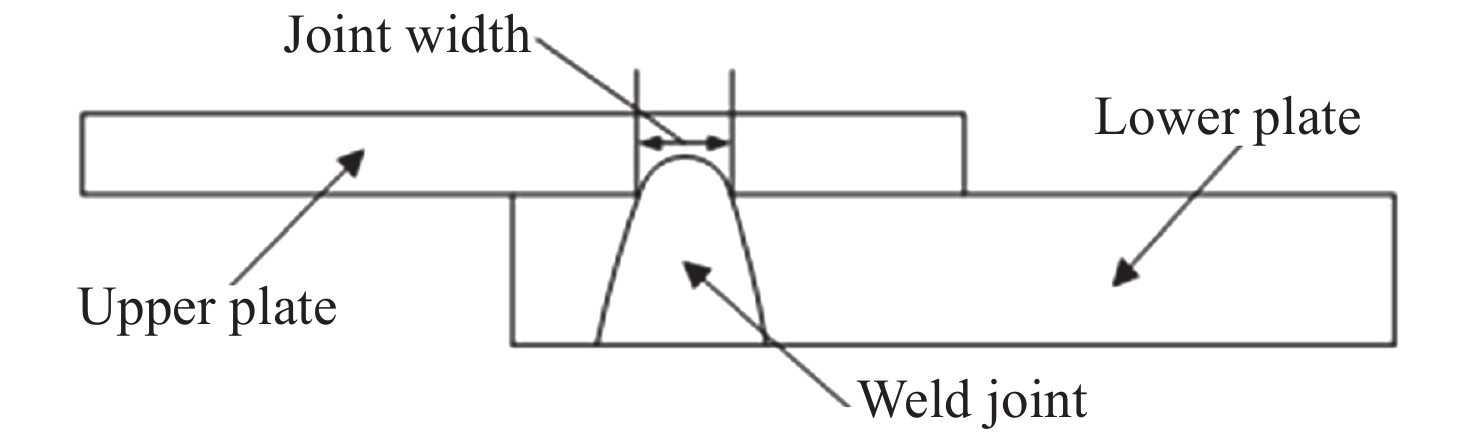
| [1] |
LI Y A, LI Y F, WANG Q L, et al. Measurement and defect detection of the weld bead based on online vision inspection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2010, 59(7): 1841-1849. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2009.2028222
|
| [2] |
韩晓辉, 陈静, 阚盈, 等. 不锈钢薄板非熔透激光搭接焊热源模型[J]. 中国激光,2017,44(5):0502002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201744.0502002HAN X H, CHEN J, KAN Y, et al. Heat source model for non-penetration laser lap welding of stainless steel sheets[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2017, 44(5): 0502002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201744.0502002
|
| [3] |
CAO X, JAHAZI M, IMMARIGEON J P, et al. A review of laser welding techniques for magnesium alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2006, 171(2): 188-204. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.06.068
|
| [4] |
LACKI P, ADAMUS K. Numerical simulation of the electron beam welding process[J]. Computers &Structures, 2011, 89(11-12): 977-985.
|
| [5] |
AI Y W, SHAO X Y, JIANG P, et al. Process modeling and parameter optimization using radial basis function neural network and genetic algorithm for laser welding of dissimilar materials[J]. Applied Physics A, 2015, 121(2): 555-569. doi: 10.1007/s00339-015-9408-5
|
| [6] |
高向东, 李竹曼, 游德勇, 等. 激光焊匙孔特征的近红外与X射线传感分析[J]. 光学 精密工程,2016,24(10):2400-2407. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162410.2400GAO X D, LI ZH M, YOU D Y, et al. Analysis of laser welding keyhole characteristics based on near-infrared high speed camera and X-ray sensing[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(10): 2400-2407. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162410.2400
|
| [7] |
陈玉华, 戈军委, 刘奋成, 等. TiNi形状记忆合金/钛合金异种材料激光焊[J]. 光学 精密工程,2014,22(8):2075-2080. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20142208.2075CHEN Y H, GE J W, LIU F CH, et al. Micro laser welding of dissimilar materials between TiNi shape memory alloy and titanium alloy[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2014, 22(8): 2075-2080. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20142208.2075
|
| [8] |
梁行, 阚盈, 姜云禄, 等. 不锈钢薄板激光搭接焊接头的力学性能[J]. 中国激光,2018,45(6):0602001. doi: 10.3788/CJL201845.0602001LIANG H, KAN Y, JIANG Y L, et al. Mechanical properties of laser overlap welded joints of stainless steel sheets[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2018, 45(6): 0602001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201845.0602001
|
| [9] |
KUO T Y, LIN H C. Effects of pulse level of Nd-YAG laser on tensile properties and formability of laser weldments in automotive aluminum alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2006, 416(1-2): 281-289. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2005.10.041
|
| [10] |
陈子琴, 高向东, 王琳. 大功率盘形激光焊焊缝背面宽度预测[J]. 光学 精密工程,2017,25(9):2524-2531. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172509.2524CHEN Z Q, GAO X D, WANG L. Weld width prediction of weldment bottom surface in high-power disk laser welding[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2017, 25(9): 2524-2531. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172509.2524
|
| [11] |
彭进, 李俐群, 张瑞珠, 等. 铝合金电弧预熔丝激光焊工艺特性研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2017,54(6):061404.PENG J, LI L Q, ZHANG R ZH, et al. Study on aluminum alloy laser welding with pre-melted liquid filler by arc[J]. Laser &Optoelectronic Progress, 2017, 54(6): 061404. (in Chinese)
|
| [12] |
黄怡洁, 高向东, 林少铎. 激光焊接参数对有机玻璃与不锈钢接头力学性能的影响[J]. 中国激光,2017,44(12):1202006. doi: 10.3788/CJL201744.1202006HUANG Y J, GAO X D, LIN SH D. Influences of laser welding parameters on mechanical properties of polymethyl methacrylate and stainless-steel joints[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2017, 44(12): 1202006. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201744.1202006
|
| [13] |
DITCHBURN R J, BURKE S K, SCALA C M. NDT of welds: state of the art[J]. NDT &E International, 1996, 29(2): 111-117.
|
| [14] |
MANSOUR T M. Ultrasonic inspection of spot welds in thin-gage steel[J]. Materials Evaluation, 1988, 46(5): 650-658.
|
| [15] |
LIU J, XU G CH, GU X P, et al. Ultrasonic C-scan detection for stainless steel spot welds based on signal analysis in frequency domain[J]. ISIJ International, 2014, 54(8): 1876-1882. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.54.1876
|
| [16] |
CHERTOV A M, MAEV R G, SEVERIN F M. Acoustic microscopy of internal structure of resistance spot welds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics,Ferroelectrics,and Frequency Control, 2007, 54(8): 1521-1529. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2007.422
|
| [17] |
ZHOU G H, XU G CH, GU X P, et al. Research on evaluating laser welding quality based on two-dimensional array ultrasonic probe[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 84(5): 1717-1723.
|
| [18] |
CHEN ZH H, SHI Y W, JIAO B Q, et al. Ultrasonic nondestructive evaluation of spot welds for zinc-coated high strength steel sheet based on wavelet packet analysis[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209(5): 2329-2337. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.05.030
|
| [19] |
SONG Y K, HUA L, WANG X K, et al. Research on the detection model and method for evaluating spot welding quality based on ultrasonic A-scan analysis[J]. Journal of Nondestructive Evaluation, 2016, 35(1): 4. doi: 10.1007/s10921-015-0319-3
|
| [20] |
NAKAHATA K, CHANG J J, TAKAHASHI M, et al. Finite integration technique for coupled acoustic and elastic wave simulation and its application to noncontact ultrasonic testing[J]. Acoustical Science and Technology, 2014, 35(5): 260-268. doi: 10.1250/ast.35.260
|
| [21] |
DELRUE S, VAN DEN ABEELE K, BLOMME E, et al. Two-dimensional simulation of the single-sided air-coupled ultrasonic pitch-catch technique for non-destructive testing[J]. Ultrasonics, 2010, 50(2): 188-196. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2009.08.005
|
| [22] |
BAEK E, YIM H. Numerical modeling and simulation for ultrasonic inspection of anisotropic austenitic welds using the mass-spring lattice model[J]. NDT &E International, 2011, 44(7): 571-582.
|





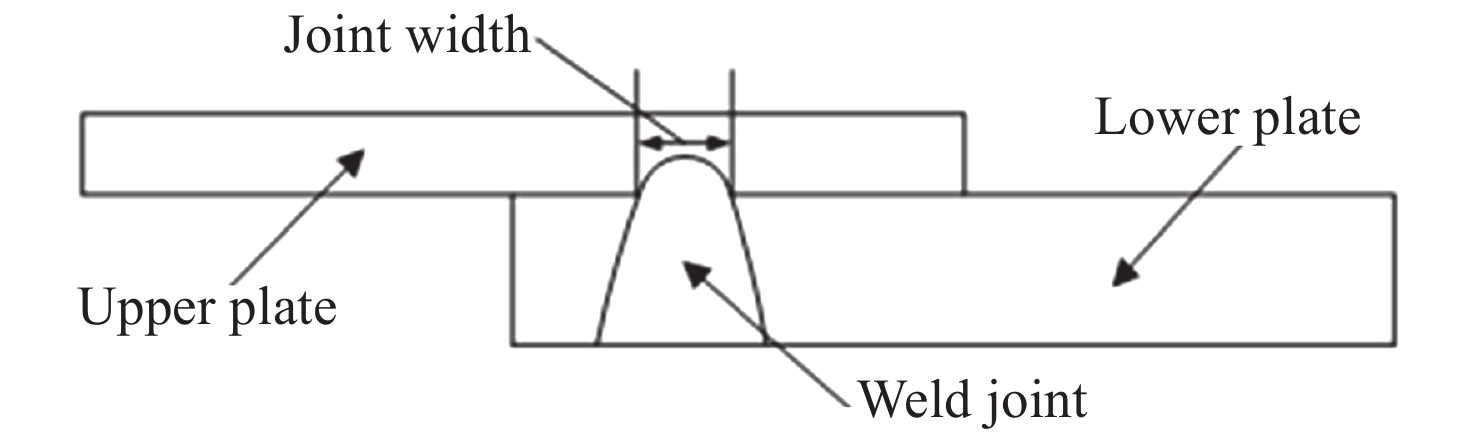
 下载:
下载: