-
摘要: 碳纳米点由于具有独特的发光特性、良好的生物相容性、低毒性、良好的光稳定性等特性在近年来被广泛关注。这些特性使其在光电器件、可见光通讯、肿瘤治疗、生物成像等领域拥有潜在的应用价值。受到原料和合成方法的影响,碳纳米点材料体系多种多样。本文将系统地综述本课题组近年来以柠檬酸和尿素为主要原料合成的氮掺杂碳纳米点及其物理化学性质,探讨碳纳米点能带调控的方法及原理,并介绍碳纳米点的应用研究进展。Abstract: In recent years, carbon nanodot (CDs) have been widely researched due to their unique luminescent properties, good biocompatibility, low toxicity and high photostability. These characteristics invite potential applications in optoelectronic devices, visible light communication, tumor therapy, biological imaging and other fields. There are a variety of CDs according to the different starting materials and synthesis routes. In this paper, we will systematically review nitrogen-doped CDs synthesized from citric acid and urea as the main precursor materials in our group in recent years, discuss their physicochemical properties, explore the methods and principles of CDs energy band regulation, and introduce the application progress of CDs.
-
Key words:
- carbon nanodots /
- nitrogen doping /
- photoluminescent materials
-
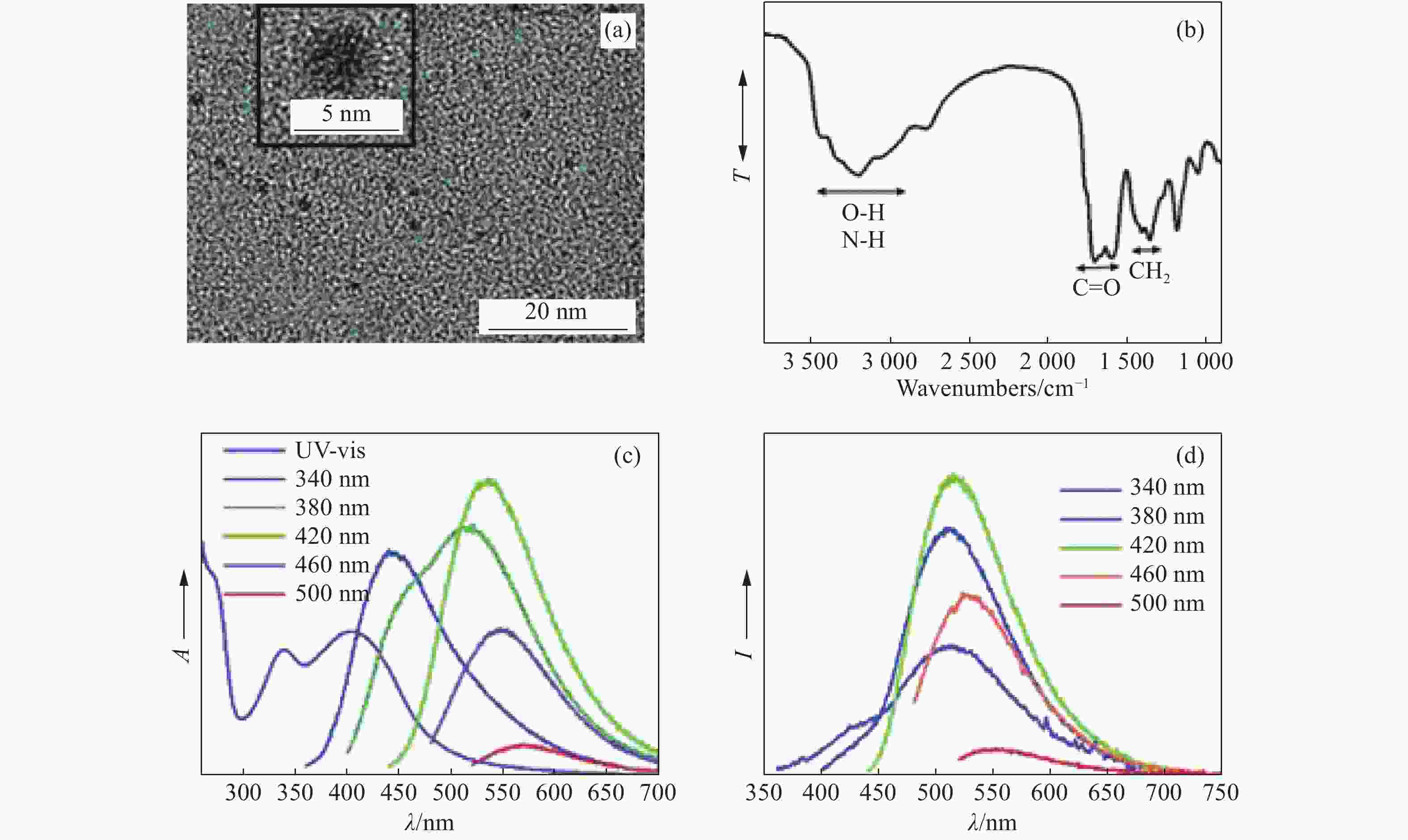
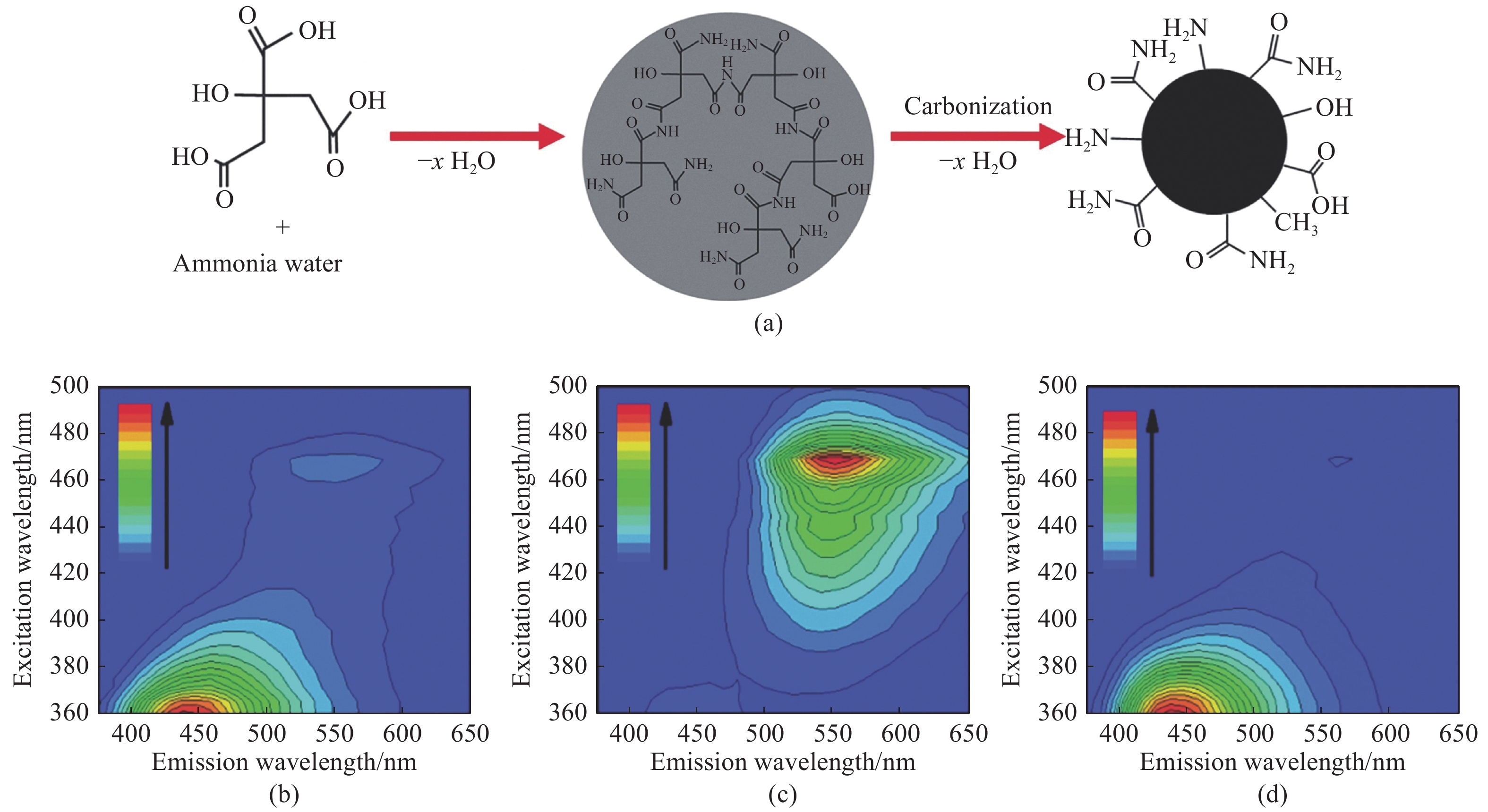
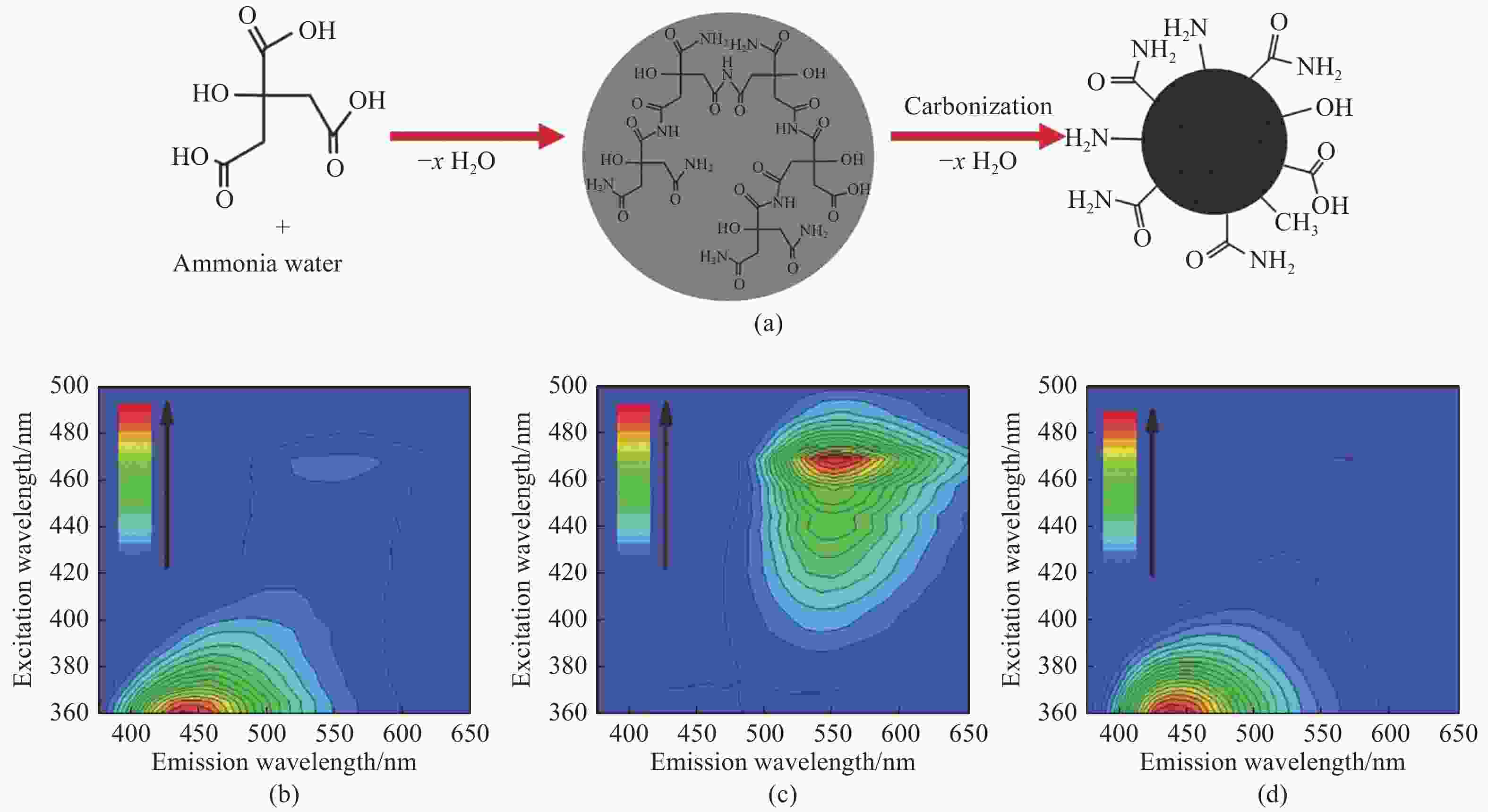
图 2 (a) g-CDs的透射电镜图;(b) g-CDs的傅立叶变换红外光谱图;(c) g-CDs溶液的吸收光谱和在不同波长激发下的发射光谱;(d) g-CDs涂在商用拭镜纸上,在不同波长激发下的发射光谱[25]
Figure 2. (a) TEM image of synthesized g-CDs; (b) Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrum of g-CDs; (c) UV/Vis absorption and PL spectra of a dilute aqueous solution of g-CDs at various excitation wavelengths; (d) PL spectra of g-CDs-coated commercially available lens paper at various excitation wavelengths[25]
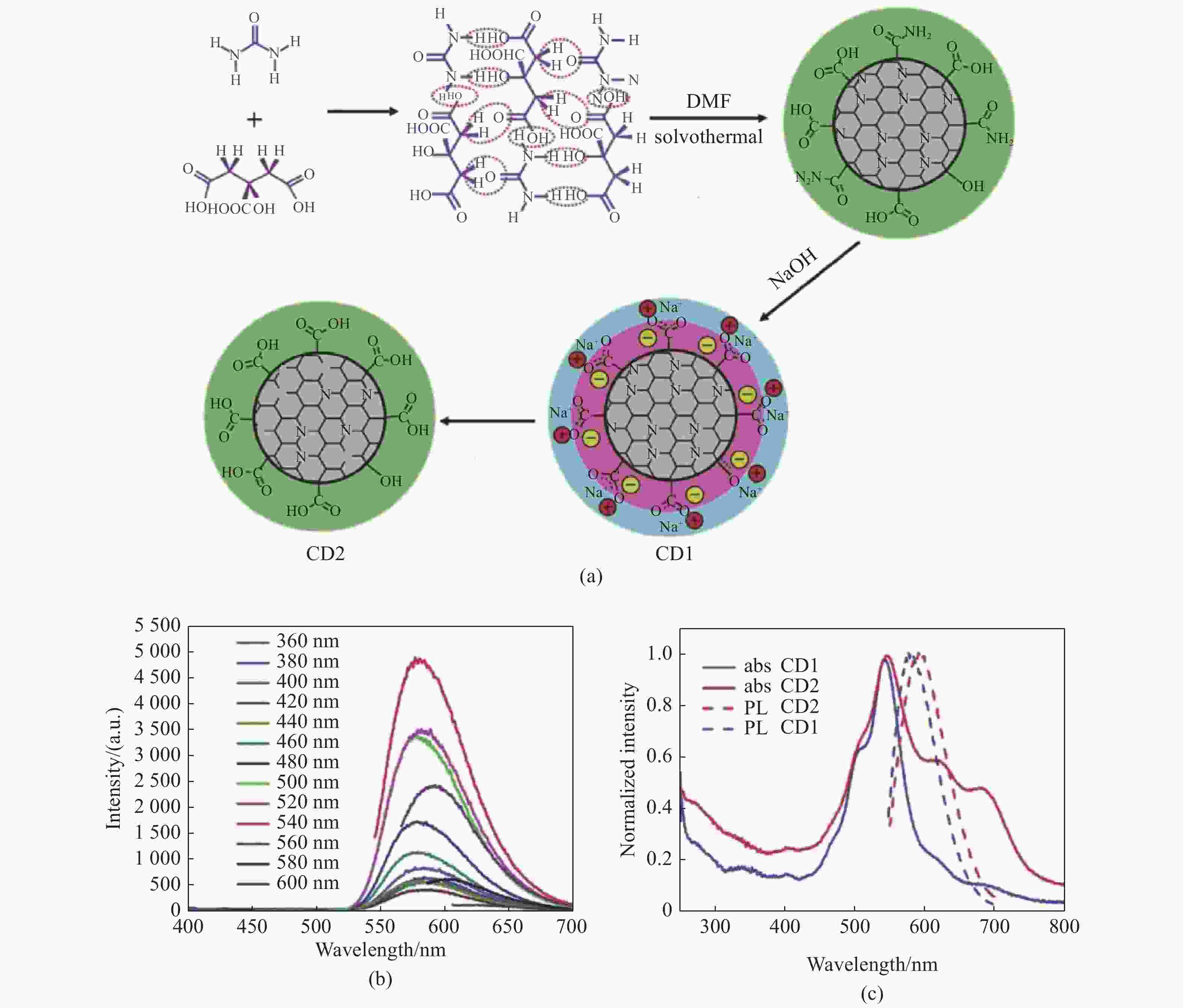
图 3 (a)一种可能的CD1和CD2形成机制示意图;(b)CD1在不同激发波长下的发射光谱;(c) CD1和CD2乙醇溶液的吸收光谱和540 nm激发下的光谱[28]
Figure 3. (a) A possible growth mechanism for CD1 and CD2; (b) PL spectra of CD1 at various excitation wavelengths; (c) UV-Vis absorption spectra and PL spectra (540 nm excitation) of CD1 and CD2 dilute ethanol solution[28]
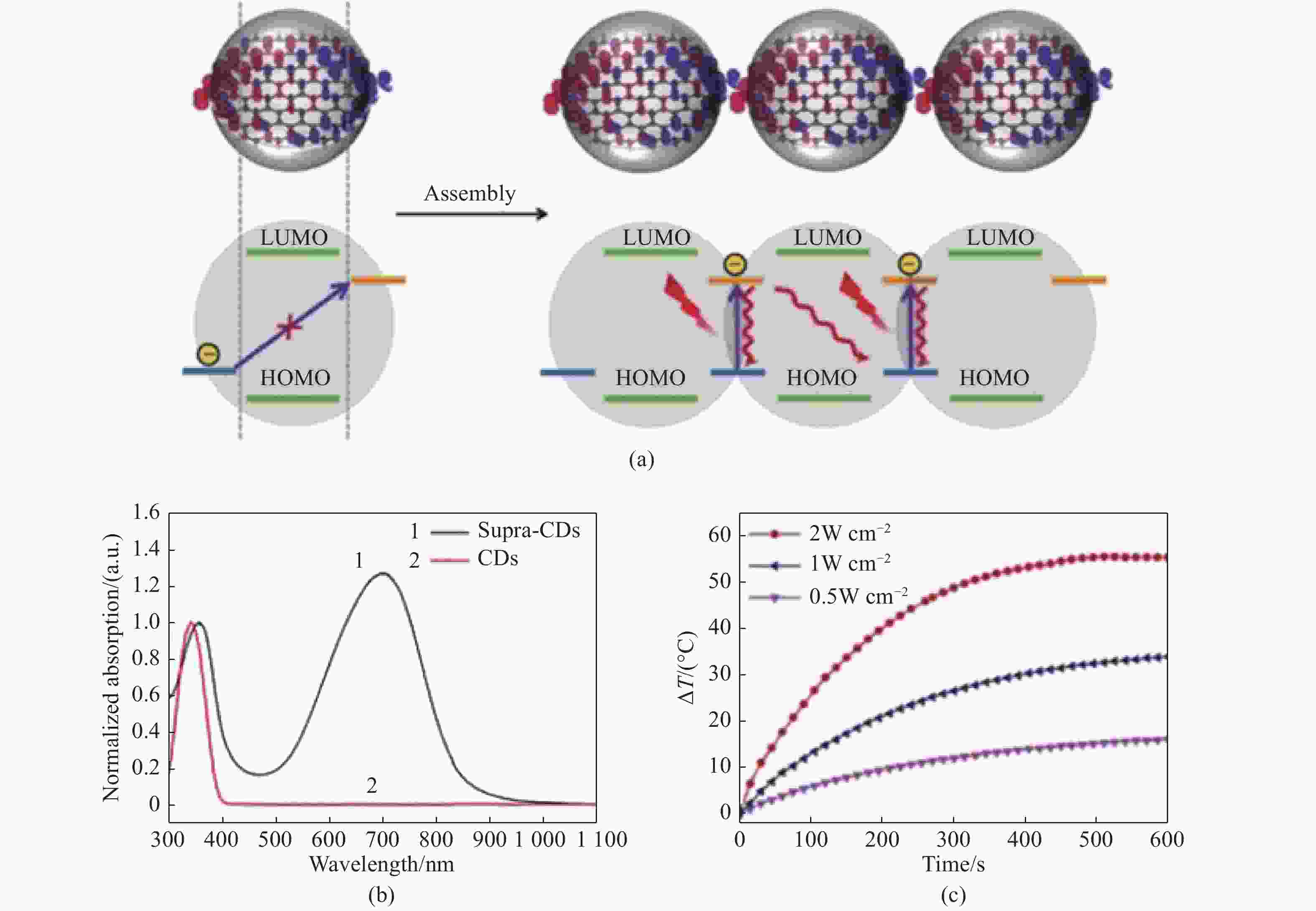
图 4 (a)Supra-CDs结构,能级,吸收原理和光热效应示意图;(b)CDs和supra-CDs的吸收光谱;(c)supra-CDs水分散体(0.1 mg/mL)在不同功率密度732 nm激光照射下的光热图像[23]
Figure 4. (a) Schematic representations of the structure, energy alignment, absorption principle and photothermal effect in surpra-CDs; (b) absorption spectra of CDs and supra-CDs; (c) photothermal profile of supra-CDs aqueous dispersions (0.1 mg/mL) irradiated by 732 nm laser with different power densities[23]
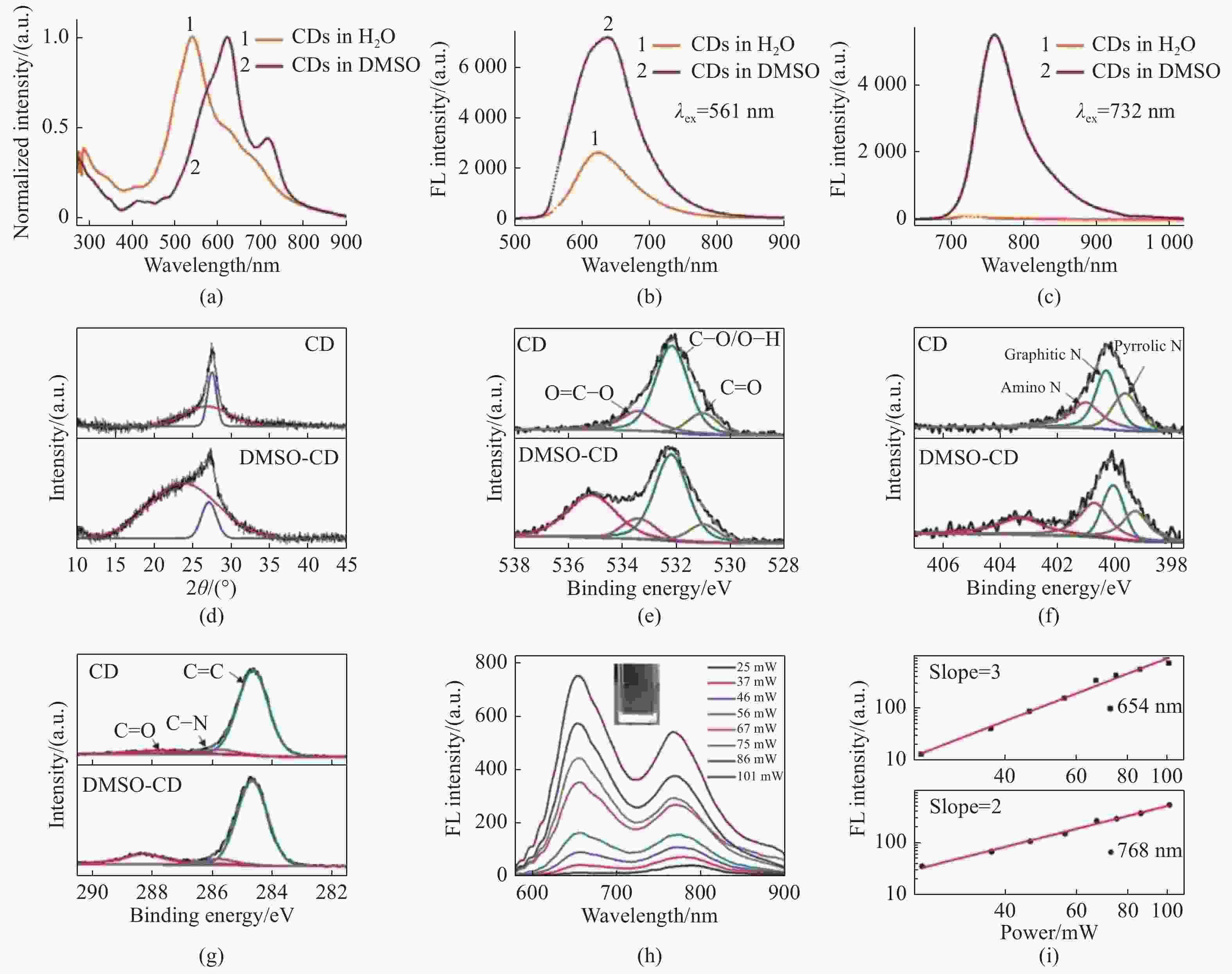
图 5 (a)CDs在水中和DMSO中的吸收光谱;CDs在水中和DMSO中在(b)561 nm和(c)732 nm波长激光激发下的荧光光谱;(d)CDs和DMSO-CDs的XRD图;高分辨XPS谱:C 1s (e), N 1s (f), O 1s (g);(h)在1400 nm激发下与入射强度相关的多光子激发的荧光光谱;(i)1400 nm激发下发射的能量依赖关系[30]
Figure 5. (a) Absorption spectra of CDs in H2O and DMSO; fluorescent spectra of CDs in H2O and DMSO under excitation of a (b) 561 nm and (c) 732 nm laser; (d) XRD profiles of bare CDs and DMSO-CDs; (e-g) high-resolution XPS spectra C 1s (e), N 1s (f), O 1s (g); (h)fluorescence spectra of multiphoton excitation associated with incident intensities at 1 400 nm excitation; (i) power dependence of emission at 1400 nm excitation[30]
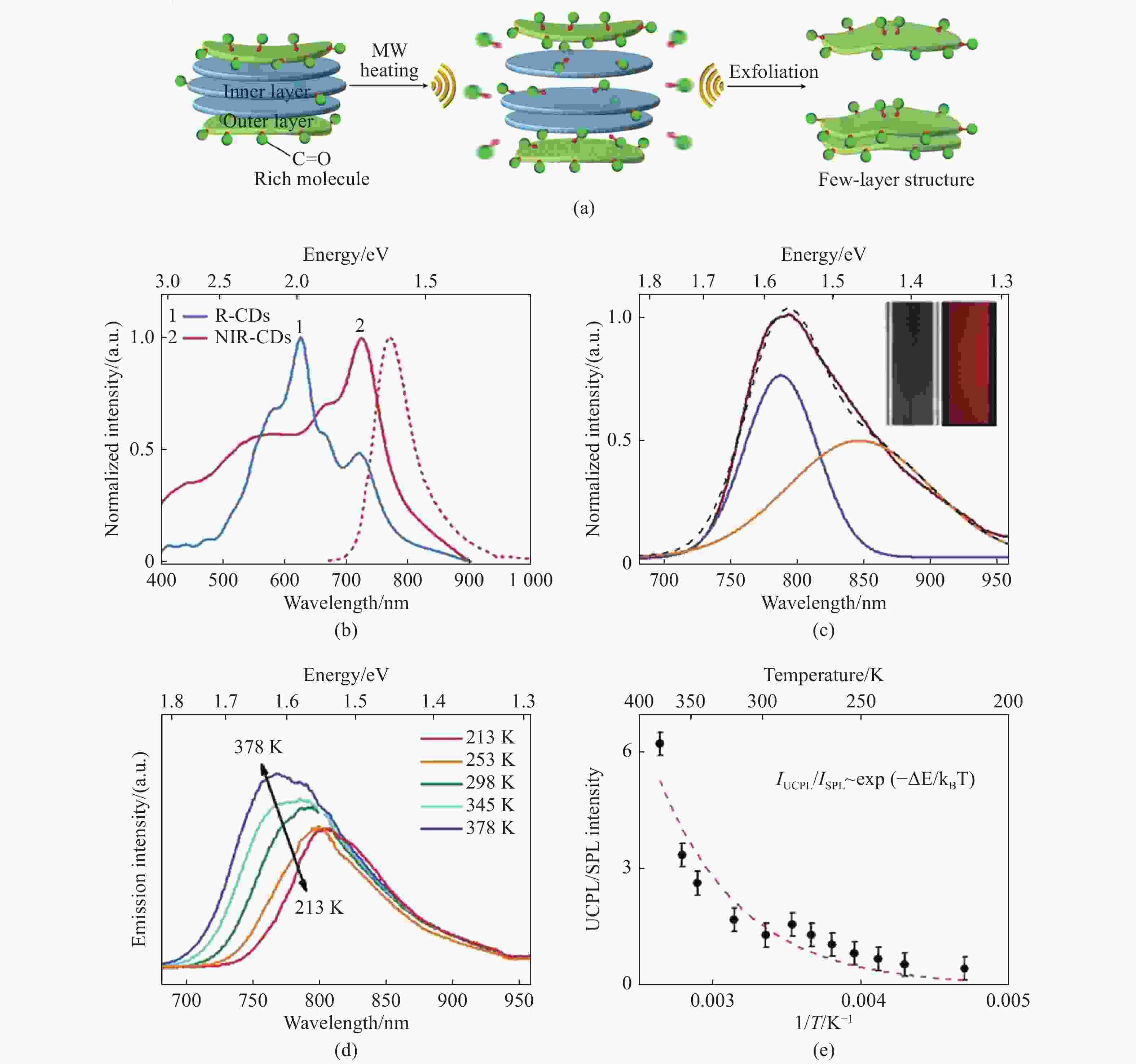
图 6 (a)R-CDs经微波辅助剥离形成 NIR-CDs示意图;(b)R-CDs和NIR-CDs的吸收光谱(实线)和NIR-COS在DMF中的发射光谱(虚线);(c)NIR-CDs在808 nm激光激发下的上转换发射光谱;(d)NIR-CDs在DMF中加热和冷却过程中的温度相关发射光谱;(e)上转换光致发光和下转换光致发光的发射强度比的温度依赖性[33]
Figure 6. (a) Schematic diagram of the formation process of NIR-CDs through the microwave-assisted exfoliation of R-CDs; (b) absorption spectra (solid lines) of R-CDs and NIR-CDs, and PL spectra of NIR-CDs (dashed line) in DMF; (c) UCPL spectrum of NIR-CDs in DMF under 808 nm laser excitation; (d) typical temperature dependent emission spectra of NIR-CDs in DMF during the heating and cooling processes; (e) temperature dependence of the integrated emission intensity ratio of UCPL and SPL bands[33]
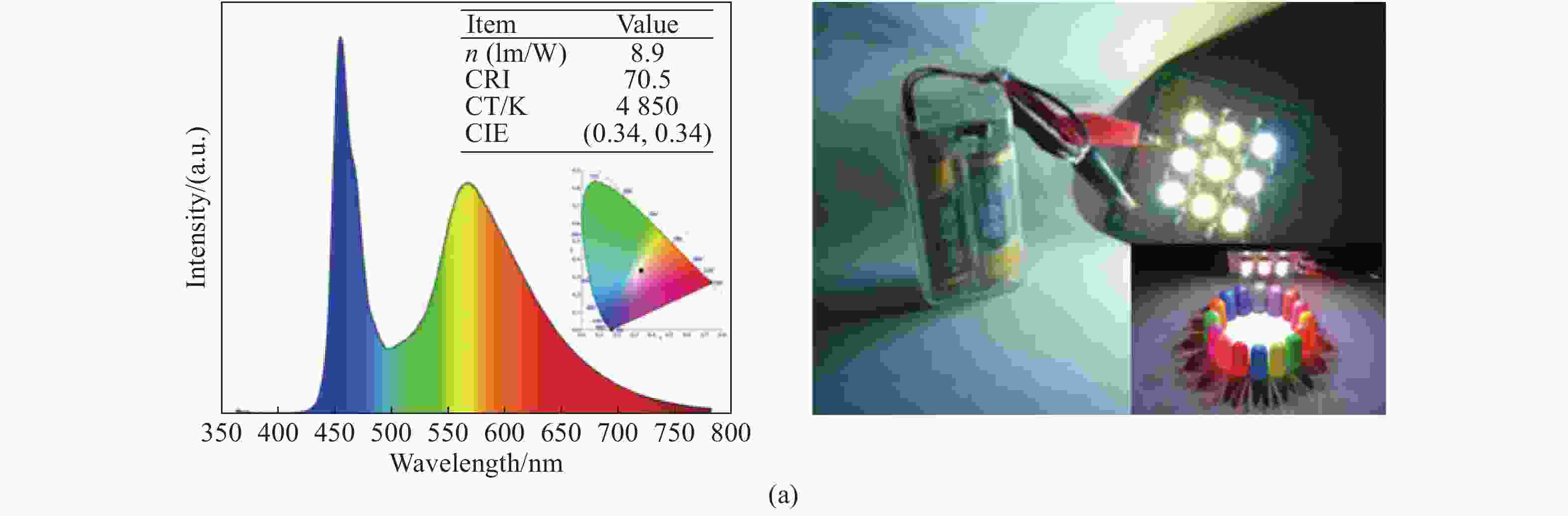
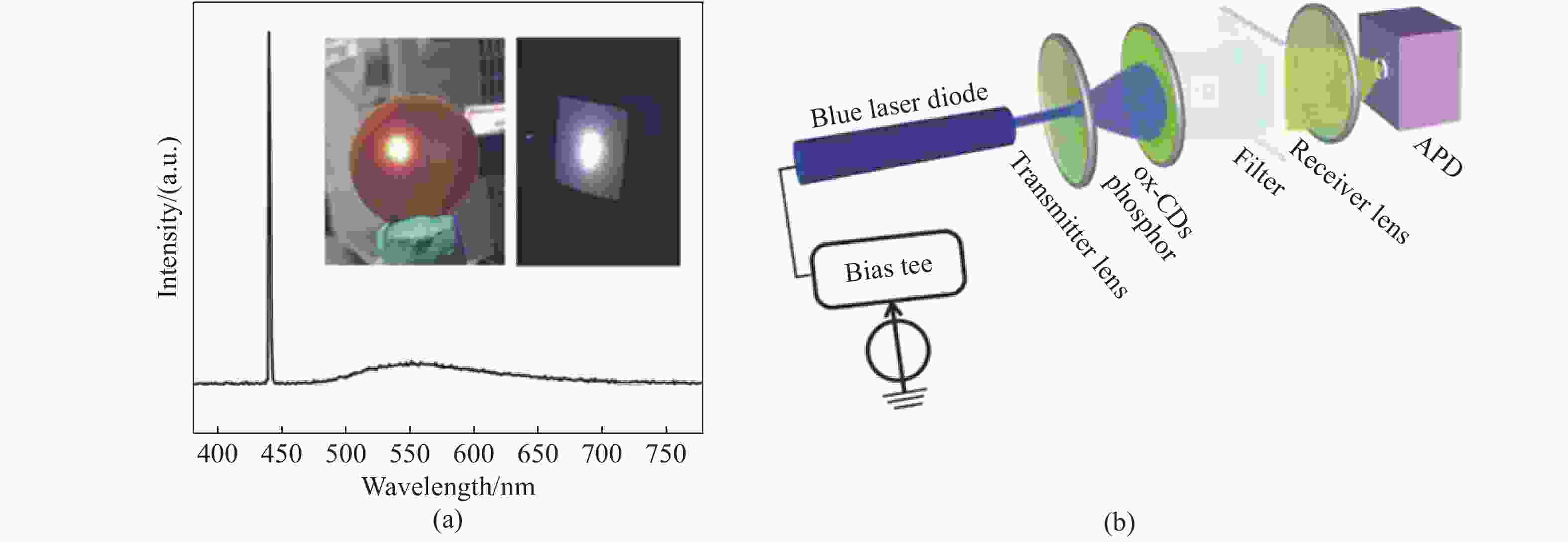
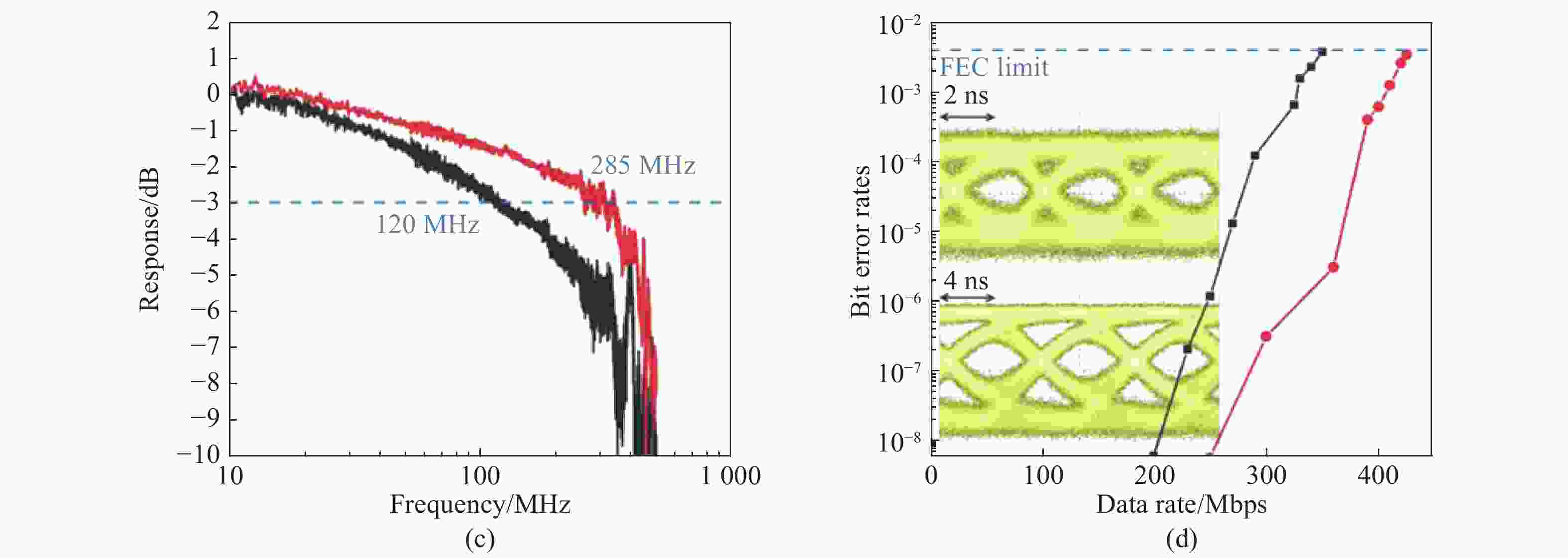
图 9 (a)使用蓝光激光二极管和ox-CDs荧光粉产生的白光光谱;(b)小信号频率响应和数据传输测量原理图;(c)ox-CDs(黑线)和蓝色激光与ox-CDs组成的白光源(红线)的频率响应;(d)ox-CDs(黑线)和白光(红线)的OOK线在不同数据速率下的误码率[10]
Figure 9. (a) White light spectrum generated by blue laser diode and ox-CDs phosphor; (b) schematic diagram of small-signal frequency response and data transmission measurements; (c) frequency responses of the ox-CDs (black line) and white-light (red line) source combining the blue laser and ox-CDs; (d) BER of OOK of ox-CDs (black line) and white-light (red line) at different data rates [10]
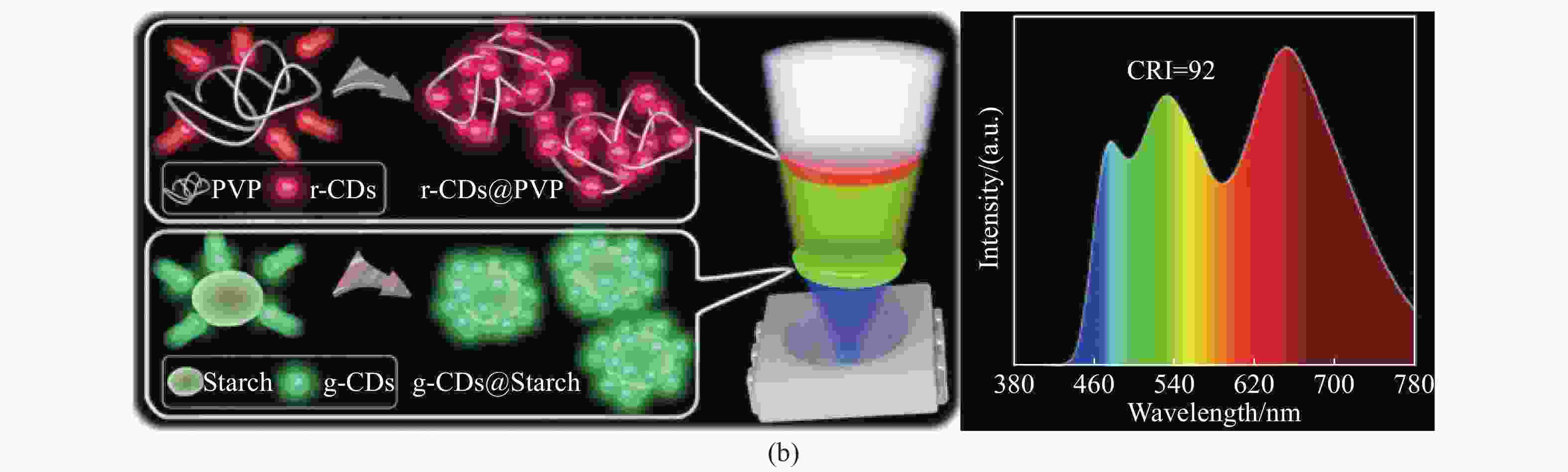
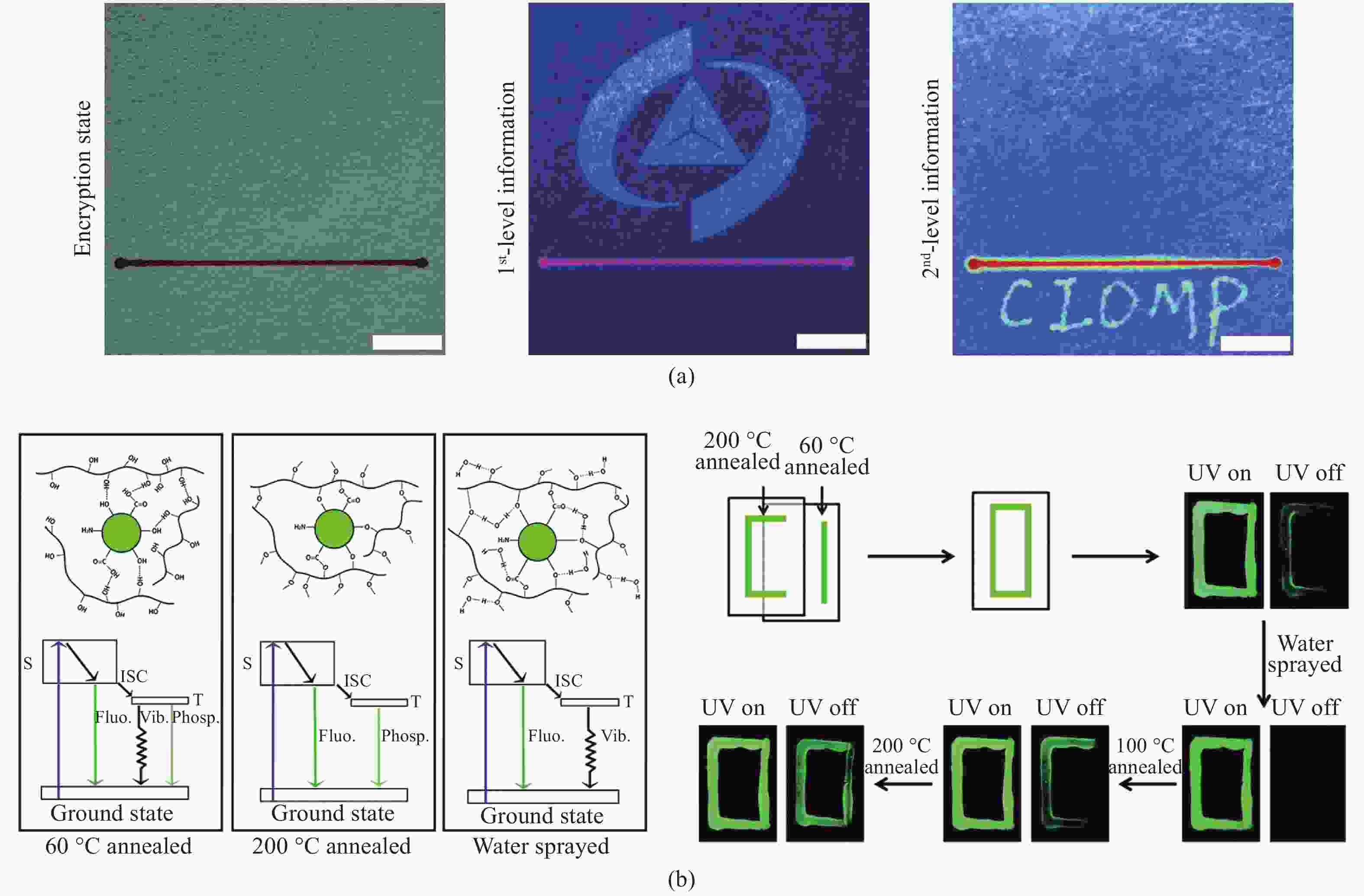
图 10 (a)使用supra-CDs喷水打印实现的数据加密照片[48];(b)CD@PVA复合材料在60 ℃退火、200 ℃退火和水雾喷涂后的发光机制示意图及经水雾喷涂、60 ℃和200 ℃退火的CD@PVA复合材料进行多重信息加密的示意图[50]
Figure 10. (a) Data encryption photograph obtained by supra-CDs water-jet printing[48]; (b) schematic diagram of luminescence mechanism of CD@PVA composites with annealing temperature of 60 ℃ and 200 ℃, and after water spraying, and corresponding multiple data encryption graph[50]
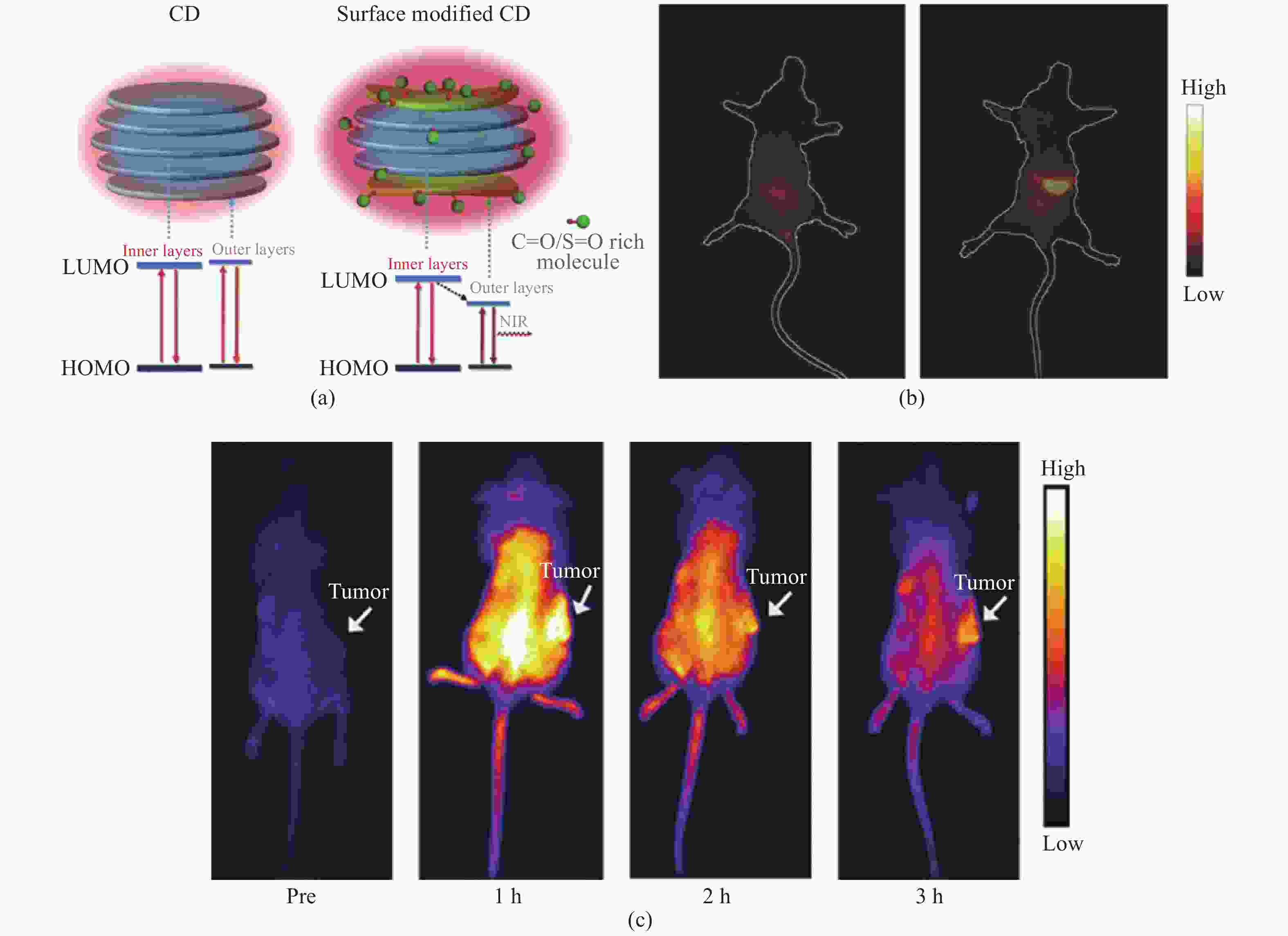
图 11 (a)未经处理的CDs和富含C=O分子修饰的CDs的结构和能级对比示意图;(b)CD/PVP水溶液灌胃前后小鼠活体荧光成像[30];(c)体内CDs的被动靶向:注射CDs后小鼠尸体在不同时间点的近红外荧光成像[29]
Figure 11. (a) Schematic of structure and energy level alignments of nontreated CDs and CDs modified with C=O-rich molecules; (b) in Vivo NIR fluorescent images of a mouse before and after gavage injection of CDs in PVP aqueous solution[30]; (c) passive targeting of CDs in vivo: NIR fluorescence images of mouse bodies after intravenous injection of CDs at various time points[29]
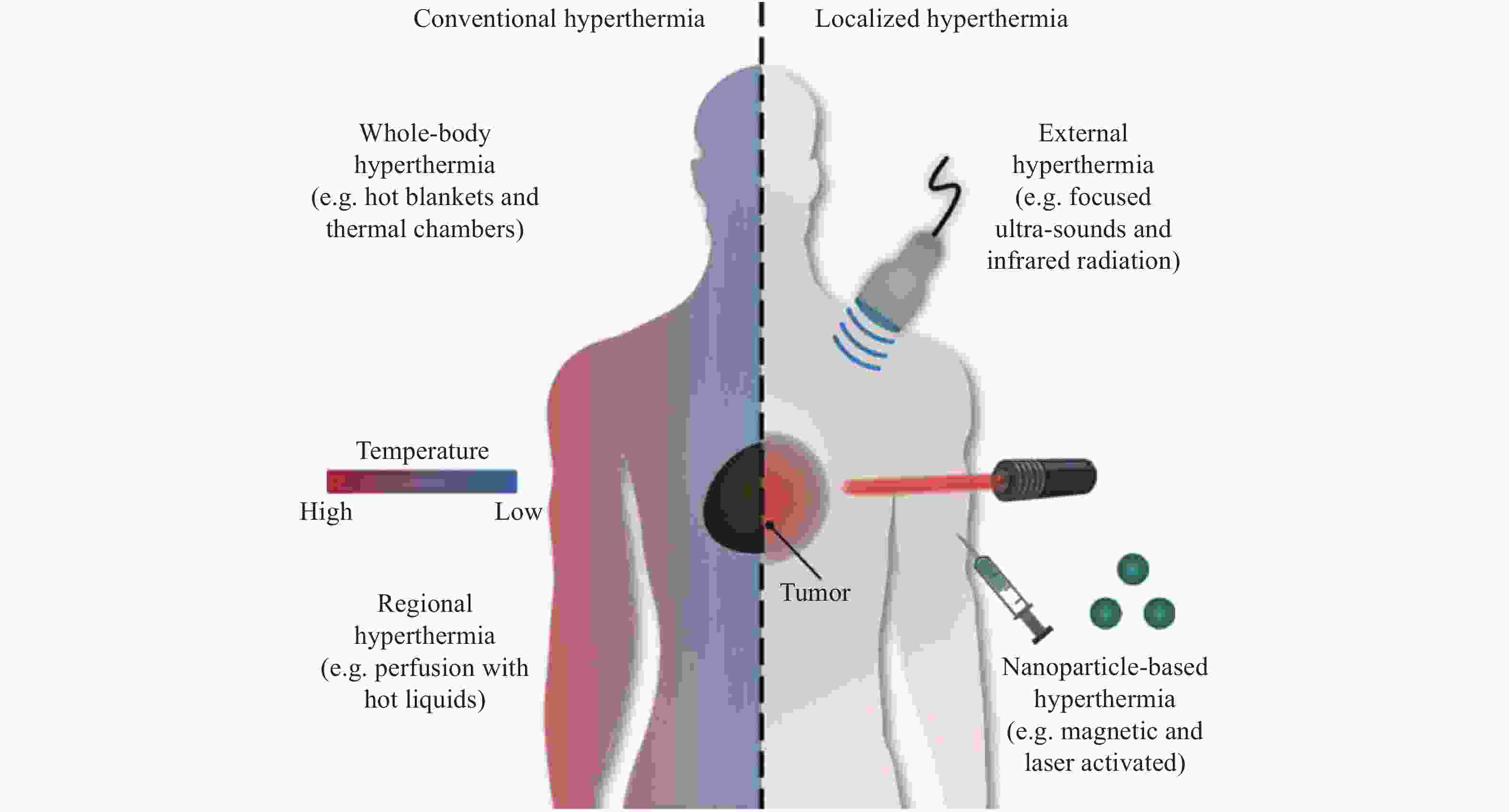
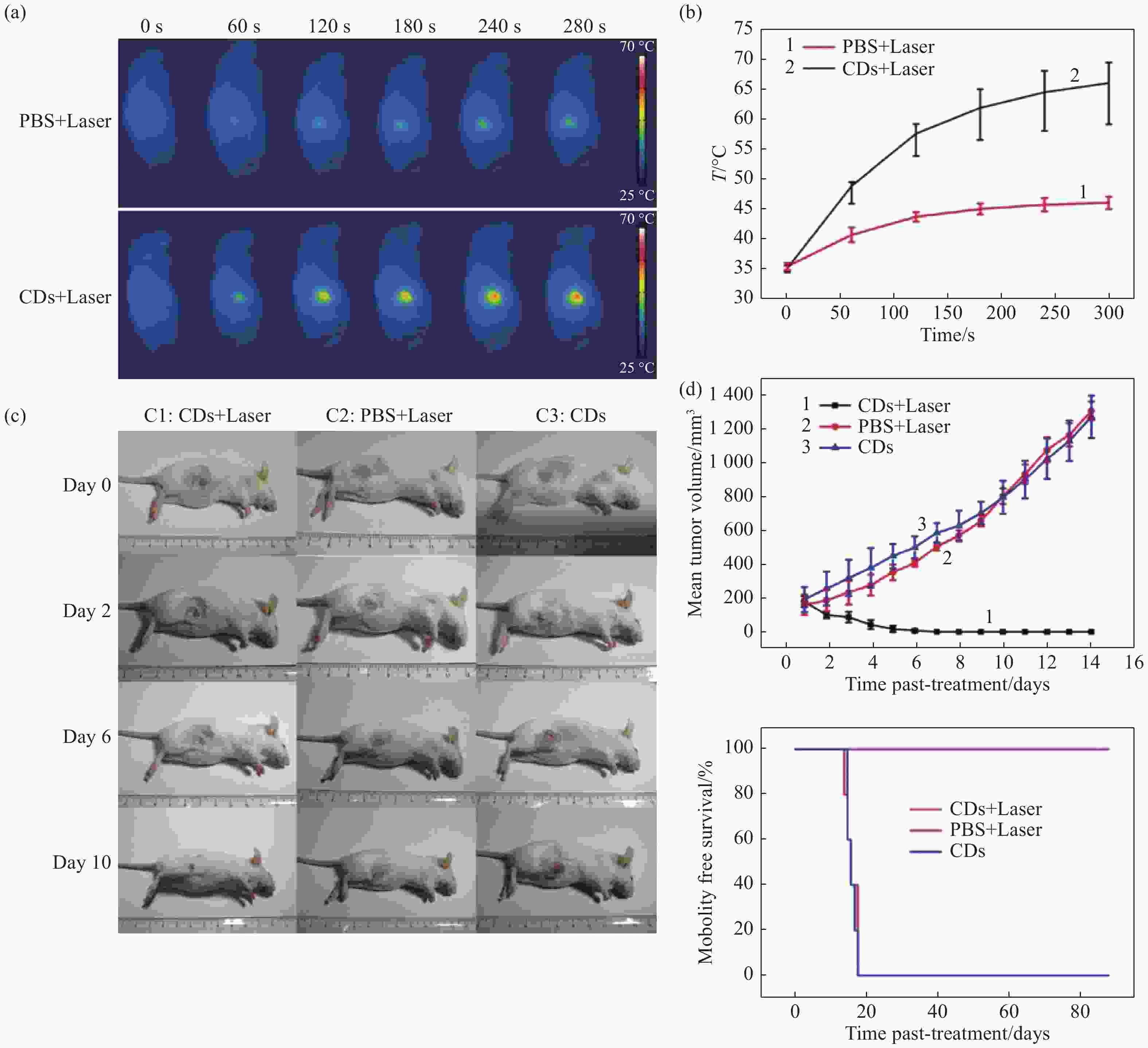
图 13 (a)静脉注射CDs的小鼠在不同时间点用1 W/cm2的655 nm激光照射下的红外热成像图;(b)小鼠肿瘤部位随照射时间变化的温度变化曲线;(c)经不同条件治疗后活鼠体内H22肿瘤发展情况图;(d)小鼠H22肿瘤生长曲线及各组治疗后的生存率[29]
Figure 13. (a) IR thermal images of mice with intravenous CDs injected at different times under irradiation at the tumor region by 655 nm laser at 1 W/cm2; (b) temperature at mouse tumor sites as a function of the irradiation duration; (c) photographs that document H22 tumor development on several days in live mice under various treatment conditions; (d) tumor growth curves of H22 tumors in mice and survival rates of the groups after therapy [29]
-
XU X Y, RAY R, GU Y L, et al. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(40): 12736-12737. doi: 10.1021/ja040082h MEHTA A, MISHRA A, BASU S, et al. Band gap tuning and surface modification of carbon dots for sustainable environmental remediation and photocatalytic hydrogen production-A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 250: 109486. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109486 康倩文, 张国, 柴瑞涛, 等. 基于碳纳米点荧光增强检测铝离子[J]. 分析化学,2019,47(12):1901-1908.KANG Q W, ZHANG G, CHAI R T, et al. Synthesis of carbon nanodots for detection of aluminum ion with fluorescence enhancement[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(12): 1901-1908. (in Chinese) XU X W, ZHANG K, ZHAO L, et al. Aspirin-based carbon dots, a good biocompatibility of material applied for bioimaging and anti-inflammation[J]. ACS Applied Materials &Interfaces, 2016, 8(48): 32706-32716. 钟青梅, 黄欣虹, 覃庆敏, 等. 以碳量子点为过氧化物模拟酶的葡萄糖测定方法[J]. 分析化学,2018,46(7):1062-1068. doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.171396ZHONG Q M, HUANG X H, QIN Q M, et al. Determination of glucose based on carbon quantum dots as peroxidase mimetic enzyme[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 46(7): 1062-1068. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.171396 CHEN A Y, LIANG W B, WANG H J, et al. Anodic electrochemiluminescence of carbon dots promoted by nitrogen doping and application to rapid cancer cell detection[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 92(1): 1379-1385. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04537 邓帅, 李雨珊, 段延芳, 等. 荧光碳点在脊椎类模式动物斑马鱼中的活体成像与毒理学研究[J]. 发光学报,2015,36(4):485-490. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20153604.0485DENG SH, LI Y SH, DUAN Y F, et al. Flourescent imaging and toxicology study of carbon dots in transparent zebrafishes[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2015, 36(4): 485-490. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20153604.0485 XIONG Y, SCHNEIDER J, RECKMEIER C J, et al. Carbonization conditions influence the emission characteristics and the stability against photobleaching of nitrogen doped carbon dots[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(32): 11730-11738. doi: 10.1039/C7NR03648E YUAN F L, LI SH H, FAN Z T, et al. Shining carbon dots: synthesis and biomedical and optoelectronic applications[J]. Nano Today, 2016, 11(5): 565-586. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2016.08.006 ZHOU ZH J, TIAN P F, LIU X Y, et al. Hydrogen peroxide-treated carbon dot phosphor with a bathochromic-shifted, aggregation-enhanced emission for light-emitting devices and visible light communication[J]. Advanced Science, 2018, 5(8): 1800369. doi: 10.1002/advs.201800369 ARDEKANI S M, DEHGHANI A, HASSAN M, et al. Two-photon excitation triggers combined chemo-photothermal therapy via doped carbon nanohybrid dots for effective breast cancer treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 330: 651-662. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.165 SHI Y P, PAN Y, ZHONG J, et al. Facile synthesis of gadolinium (III) chelates functionalized carbon quantum dots for fluorescence and magnetic resonance dual-modal bioimaging[J]. Carbon, 2015, 93: 742-750. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.05.100 姜杰, 李士浩, 严一楠, 等. 氮掺杂高量子产率荧光碳点的制备及其体外生物成像研究[J]. 发光学报,2017,38(12):1567-1574. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20173812.1567JIANG J, LI SH H, YAN Y N, et al. Preparation of N-doped fluorescent carbon dots with high quantum yield for in-vitro bioimaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2017, 38(12): 1567-1574. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20173812.1567 YAN X, CUI X, LI L SH. Synthesis of large, stable colloidal graphene quantum dots with tunable size[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(17): 5944-5945. doi: 10.1021/ja1009376 李俊芬, 王冬秀, 李鹏霞, 等. 一步水热法合成荧光碳点检测锰(Ⅶ)[J]. 分析化学,2019,47(5):731-738.LI J F, WANG D X, LI P X, et al. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of carbon dots for detection of manganese (Ⅶ)[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(5): 731-738. (in Chinese) KANG S H, MHIN S, HAN H, et al. Ultrafast method for selective design of graphene quantum dots with highly efficient blue emission[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 38423. doi: 10.1038/srep38423 DONG Y Q, PANG H CH, REN SH Y, et al. Etching single-wall carbon nanotubes into green and yellow single-layer graphene quantum dots[J]. Carbon, 2013, 64: 245-251. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2013.07.059 杜方凯, 张慧, 谭学才, 等. 基于氮掺杂石墨烯量子点/硫化镉纳米晶电化学发光传感器检测硫化氢[J]. 分析化学,2020,48(2):240-247.DU F K, ZHANG H, TAN X C, et al. Detection of hydrogen sulfide based on nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots/cadmium sulfide nanocrystals electrochemiluminescence sensor[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 48(2): 240-247. (in Chinese) 邹小波, 史永强, 郑悦, 等. 基于荧光共振能量转移的金纳米粒子/碳量子点荧光纳米探针检测精氨酸[J]. 分析化学,2018,46(6):960-968. doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.181096ZOU X B, SHI Y Q, ZHENG Y, et al. Detection of arginine by AuNPs/CQDs nanoprobes based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer effect[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 46(6): 960-968. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.181096 曲松楠, 孙铭鸿, 田震, 等. 氮掺杂碳点的合成与应用[J]. 发光学报,2019,40(5):557-580. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20194005.0557QU S N, SUN M H, TIAN ZH, et al. Synthesis and application of nitrogen-doped carbon dots[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2019, 40(5): 557-580. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20194005.0557 ZHU SH J, SONG Y B, ZHAO X H, et al. The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): current state and future perspective[J]. Nano Research, 2015, 8(2): 355-381. doi: 10.1007/s12274-014-0644-3 ZHAI X Y, ZHANG P, LIU CH J, et al. Highly luminescent carbon nanodots by microwave-assisted pyrolysis[J]. Chemical Communications, 2012, 48(64): 7955-7957. doi: 10.1039/c2cc33869f LI D, HAN D, QU S N, et al. Supra-(carbon nanodots) with a strong visible to near-infrared absorption band and efficient photothermal conversion[J]. Light:Science &Applications, 2016, 5(7): e16120. QU S N, SHEN D ZH, LIU X Y, et al. Highly luminescent carbon-nanoparticle-based materials: factors influencing photoluminescence quantum yield[J]. Particle &Particle Systems Characterization, 2014, 31(11): 1175-1182. QU S N, WANG X Y, LU Q P, et al. A biocompatible fluorescent ink based on water-soluble luminescent carbon nanodots[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(49): 12215-12218. doi: 10.1002/anie.201206791 QU S N, LIU X Y, GUO X Y, et al. Amplified spontaneous green emission and lasing emission from carbon nanoparticles[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2014, 24(18): 2689-2695. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201303352 SK M A, ANANTHANARAYANAN A, HUANG L, et al. Revealing the tunable photoluminescence properties of graphene quantum dots[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2014, 2(34): 6954-6960. doi: 10.1039/C4TC01191K QU S N, ZHOU D, LI D, et al. Toward efficient orange emissive carbon nanodots through conjugated sp2-domain controlling and surface charges engineering[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(18): 3516-3521. doi: 10.1002/adma.201504891 BAO X, YUAN Y, CHEN J Q, et al. In vivo theranostics with near-infrared-emitting carbon dots—highly efficient photothermal therapy based on passive targeting after intravenous administration[J]. Light:Science &Applications, 2018, 7(1): 91. LI D, JING P T, SUN L H, et al. Near-infrared excitation/emission and multiphoton-induced fluorescence of carbon dots[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(13): 1705913. doi: 10.1002/adma.201705913 ZHU X J, SU Q Q, FENG W, et al. Anti-Stokes shift luminescent materials for bio-applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(4): 1025-1039. doi: 10.1039/C6CS00415F CHEN G Y, QIU H L, PRASAD P N, et al. Upconversion nanoparticles: design, nanochemistry, and applications in theranostics[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(10): 5161-5214. doi: 10.1021/cr400425h LI D, LIANG CH, USHAKOVA E V, et al. Thermally activated upconversion near-infrared photoluminescence from carbon dots synthesized via microwave assisted exfoliation[J]. Small, 2019, 15(50): 1905050. doi: 10.1002/smll.201905050 CHEN Y H, ZHENG M T, XIAO Y, et al. A self-quenching-resistant carbon-dot powder with tunable solid-state fluorescence and construction of dual-fluorescence morphologies for white light-emission[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(2): 312-318. doi: 10.1002/adma.201503380 OOYAMA Y, YOSHIKAWA S, WATANABE S, et al. Molecular design of novel non-planar heteropolycyclic fluorophores with bulky substituents: convenient synthesis and solid-state fluorescence characterization[J]. Organic &Biomolecular Chemistry, 2006, 4(18): 3406-3409. SUN M Y, QU S N, HAO ZH D, et al. Towards efficient solid-state photoluminescence based on carbon-nanodots and starch composites[J]. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(21): 13076-13081. doi: 10.1039/C4NR04034A ZHAI Y CH, ZHOU D, JING P T, et al. Preparation and application of carbon-nanodot@NaCl composite phosphors with strong green emission[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2017, 497: 165-171. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2017.03.007 ZHOU D, ZHAI Y CH, QU S N, et al. Electrostatic assembly guided synthesis of highly luminescent carbon-nanodots@BaSO4 hybrid phosphors with improved stability[J]. Small, 2017, 13(6): 1602055. doi: 10.1002/smll.201602055 LIU E SH, LI D, ZHOU X J, et al. Highly emissive carbon dots in solid state and their applications in light-emitting devices and visible light communication[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry &Engineering, 2019, 7(10): 9301-9308. ZHOU D, JING P T, WANG Y, et al. Carbon dots produced via space-confined vacuum heating: maintaining efficient luminescence in both dispersed and aggregated states[J]. Nanoscale Horizons, 2019, 4(2): 388-395. doi: 10.1039/C8NH00247A SCHUBERT E F, KIM J K. Solid-state light sources getting smart[J]. Science, 2015, 308(5726): 1274-1278. LIM S H, KO Y H, RODRIGUEZ C, et al. Electrically driven, phosphor-free, white light-emitting diodes using gallium nitride-based double concentric truncated pyramid structures[J]. Light:Science &Applications, 2016, 5(2): e16030. ZHAI Y CH, WANG Y, LI D, et al. Red carbon dots-based phosphors for white light-emitting diodes with color rendering index of 92[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 528: 281-288. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.05.101 TIAN ZH, TIAN P F, ZHOU X J, et al. Ultraviolet-pumped white light emissive carbon dot based phosphors for light-emitting devices and visible light communication[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(8): 3489-3494. doi: 10.1039/C9NR00224C ELGALA H, MESLEH R, HAAS H. Indoor optical wireless communication: potential and state-of-the-art[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2011, 49(9): 56-62. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2011.6011734 CHUN H, CHIANG C J, MONKMAN A, et al. A study of illumination and communication using organic light emitting diodes[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2013, 31(22): 3511-3517. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2013.2284247 MERUGA J M, CROSS W M, MAY P S, et al. Security printing of covert quick response codes using upconverting nanoparticle inks[J]. Nanotechnology, 2012, 23(39): 395201. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/23/39/395201 ZHANG X T, LI D, ZHOU D, et al. Dual-encryption based on facilely synthesized supra-(carbon nanodots) with water-induced enhanced luminescence[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(83): 79620-79624. doi: 10.1039/C6RA11076B XU H, CHEN R F, SUN Q, et al. Recent progress in metal-organic complexes for optoelectronic applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(10): 3259-3302. doi: 10.1039/C3CS60449G BAO X, USHAKOVA E V, LIU E SH, et al. On-Off switching of the phosphorescence signal in a carbon dot/polyvinyl alcohol composite for multiple data encryption[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(30): 14250-14255. doi: 10.1039/C9NR05123F HONG G S, ANTARIS A L, DAI H J. Near-infrared fluorophores for biomedical imaging[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 1(1): 0010. doi: 10.1038/s41551-016-0010 PANSARE V J, HEJAZI S, FAENZA W J, et al. Review of long-wavelength optical and NIR imaging materials: contrast agents, fluorophores, and multifunctional nano carriers[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2012, 24(5): 812-827. doi: 10.1021/cm2028367 FERNANDES N, RODRIGUES C F, MOREIRA A F, et al. Overview of the application of inorganic nanomaterials in cancer photothermal therapy[J]. Biomaterials Science, 2020, 8(11): 2990-3020. doi: 10.1039/D0BM00222D XU G Y, BAO X, CHEN J Q, et al. In vivo tumor photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy based on supra-(carbon nanodots)[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2019, 8(2): 1800995. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201800995 ZHANG Q F, UCHAKER E, CANDELARIA S L, et al. Nanomaterials for energy conversion and storage[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2013, 42(7): 3127-3171. doi: 10.1039/c3cs00009e ZHANG X L, YANG H, GUO J L, et al. Nitrogen-doped hollow porous carbon nanospheres coated with MnO2 nanosheets as excellent sulfur hosts for Li-S batteries[J]. Nanotechnology, 2017, 28(47): 475401. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/aa8f78 WANG R H, XU CH H, SUN J, et al. Three-dimensional Fe2O3 nanocubes/nitrogen-doped graphene aerogels: nucleation mechanism and lithium storage properties[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 7171. ZHANG X T, ZHANG ZH Y, HU F, et al. Carbon-dots-derived 3D highly nitrogen-doped porous carbon framework for high-performance lithium ion storage[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry &Engineering, 2019, 7(11): 9848-9856. -





 下载:
下载: